Deck 17: High-Risk Neonatal Nursing Care
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: High-Risk Neonatal Nursing Care
1
A nurse is assessing a preterm baby with a gestational age of 32 weeks and birth weight of 1,389 grams. Which of the following signs if present would be a possible indication of RDS?
A) Expiratory grunting and intercostal retractions
B) Respiratory rate of 46 breaths per minute and presence of acrocyanosis
C) Mild nasal flaring and heart rate of 140 beats perminute
D) Bradycardia and bounding pulse
A) Expiratory grunting and intercostal retractions
B) Respiratory rate of 46 breaths per minute and presence of acrocyanosis
C) Mild nasal flaring and heart rate of 140 beats perminute
D) Bradycardia and bounding pulse
Signs of respiratory distress syndrome are:
• Tachypnea
• Intercostal retractions; seesaw breathing patterns occur
• Expiratory grunting
• Nasal flaring
• Skin color is grey or dusky
Tachypnea and presence of acrocyanosis are possible indications of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the correct option is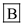 .
.
Expiratory grunting and intercostal retractions are present in respiratory distress syndrome. But these are not possible indications of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the option "A" is incorrect.
Mild nasal flaring and heart rate of 140 beats per minute are not indication of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the option "C" is incorrect.
Tachycardia and bounding pulse are seen in patent ductus arteriosus.
Hence, option "D" is incorrect.
• Tachypnea
• Intercostal retractions; seesaw breathing patterns occur
• Expiratory grunting
• Nasal flaring
• Skin color is grey or dusky
Tachypnea and presence of acrocyanosis are possible indications of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the correct option is
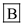 .
.Expiratory grunting and intercostal retractions are present in respiratory distress syndrome. But these are not possible indications of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the option "A" is incorrect.
Mild nasal flaring and heart rate of 140 beats per minute are not indication of respiratory distress syndrome.
Hence, the option "C" is incorrect.
Tachycardia and bounding pulse are seen in patent ductus arteriosus.
Hence, option "D" is incorrect.
2
The primary risk factor for necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is:
A) Early oral feedings with formula
B) Passage of meconium during labor
C) Prematurity
D) Low birth weight
A) Early oral feedings with formula
B) Passage of meconium during labor
C) Prematurity
D) Low birth weight
Risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis:
• Prematurity is the most common risk factor.
• Bacterial colonization can occur from contaminated nasogastric feeding tubes among premature neonates receiving formula.
• Umbilical catheter placement.
Hence, the correct option is .
.
• Prematurity is the most common risk factor.
• Bacterial colonization can occur from contaminated nasogastric feeding tubes among premature neonates receiving formula.
• Umbilical catheter placement.
Hence, the correct option is
 .
. 3
A common characteristic of a premature infant is:
A) Absence of lanugo
B) Dry skin
C) Increased flexion of arms and legs
D) Transparent and red skin
A) Absence of lanugo
B) Dry skin
C) Increased flexion of arms and legs
D) Transparent and red skin
In premature infant the skin is translucent, transparent and red.
Hence, the correct option is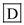 .
.
Lanugo is present between 20 and 28 weeks of gestation. At 28 weeks of gestation, lanugo begins to disappear on the face and the front of the trunk.
Hence, option "A" is incorrect.
Skin is moist in premature infant.
Hence, option "A" is incorrect.
Tone and flexion increase with greater age. Early in gestation, resting tone and posture are hypotonic and extended.
Hence, option "C" is incorrect.
Hence, the correct option is
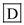 .
.Lanugo is present between 20 and 28 weeks of gestation. At 28 weeks of gestation, lanugo begins to disappear on the face and the front of the trunk.
Hence, option "A" is incorrect.
Skin is moist in premature infant.
Hence, option "A" is incorrect.
Tone and flexion increase with greater age. Early in gestation, resting tone and posture are hypotonic and extended.
Hence, option "C" is incorrect.
4
When gavage feeding a preterm neonate, the nurse should:
A) Measure the tube before insertion from the mouth to the sternum.
B) Check for placement by injecting a small amount of sterile water into the feeding tube and listen for a gurgling noise.
C) Instill formula over a 20-minute period of time.
D) Flush the tube at the end of feeding with dextrose water.
A) Measure the tube before insertion from the mouth to the sternum.
B) Check for placement by injecting a small amount of sterile water into the feeding tube and listen for a gurgling noise.
C) Instill formula over a 20-minute period of time.
D) Flush the tube at the end of feeding with dextrose water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is true regarding hyperbilirubinemia?
A) Jaundice covers the entire body in pathological jaundice versus only the face in physiological jaundice.
B) Jaundice occurs within the first 24 hours post-birth in pathological jaundice versus after 24 hours in physiological jaundice.
C) Kernicterus only occurs in pathological jaundice.
D) Jaundice begins to appear in term neonates when the bilirubin level is 3 mg/dL.
A) Jaundice covers the entire body in pathological jaundice versus only the face in physiological jaundice.
B) Jaundice occurs within the first 24 hours post-birth in pathological jaundice versus after 24 hours in physiological jaundice.
C) Kernicterus only occurs in pathological jaundice.
D) Jaundice begins to appear in term neonates when the bilirubin level is 3 mg/dL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Clinical management strategies for prevention of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) focus on targeting appropriate _____________ ranges for infants at risk.
A) Arterial pH
B) Oxygen saturation
C) Heart rate
D) Core temperature
A) Arterial pH
B) Oxygen saturation
C) Heart rate
D) Core temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A neonate born at 37 weeks' gestation is determined to be small for gestational age (SGA). The most common immediate problem for this infant would be:
A) Anemia
B) Hypovolemia
C) Hypoglycemia
D) Hypocalcemia
A) Anemia
B) Hypovolemia
C) Hypoglycemia
D) Hypocalcemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following treatments is recommended for the infant experiencing drug withdrawal symptoms?
A) Morphine
B) Diluted formula
C) Frequent awakening
D) Well-lit room
A) Morphine
B) Diluted formula
C) Frequent awakening
D) Well-lit room

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which is not a risk to the infant of a diabetic mother?
A) Hyperglycemia
B) Poor feeding
C) Macrosomia
D) Respiratory distress
A) Hyperglycemia
B) Poor feeding
C) Macrosomia
D) Respiratory distress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a pregnant woman is group beta strep (GBS) positive, prophylactic antibiotics should be administered if:
A) She is a planned cesarean section
B) The gestational age of her baby is less than 37 weeks
C) She has vomiting and diarrhea during labor
D) Her baby has a known congenital anomaly
A) She is a planned cesarean section
B) The gestational age of her baby is less than 37 weeks
C) She has vomiting and diarrhea during labor
D) Her baby has a known congenital anomaly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



