Deck 4: Hematopoiesis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/24
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Hematopoiesis
1
Hematopoietic stem cells are characterized by all of the following markers except : (Objective 1) 

In humans the phenotype of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) is characterized by a number of surface markers. These markers are used for separating rare HSC from blood cells that surround them.
CD34 (cluster of differentiation), a glycoprotein with molecular weight of 110kDa is expressed not only by HSC but also by early progenitor and vascular endothelial cells also. At maturation the expression of CD34 is lost
Lin refers to lineage specific markers e.g. Glycophorin A present on erythrocytes, CD13 present on Neutrophils. Lin - refers to absence of lineage specific markers on lineage restricted progenitors.
Rhodamine 123 is a florescent dye, which is taken up by majority of living cells. The pumps present in HSC remove this dye out of the cell because of which HSC shows low intensity staining for Rhodamine123 (Rho123 Lo ).
Hence, the options A, B and D are incorrect.
HLA-DR is present on the MHC class II (Major histocompatibility complex) antigen. It is encoded by the HLA (Human Leukocyte antigen) complex. It is not a phenotype of HSC.
Hence, the correct answer is option .
.
CD34 (cluster of differentiation), a glycoprotein with molecular weight of 110kDa is expressed not only by HSC but also by early progenitor and vascular endothelial cells also. At maturation the expression of CD34 is lost
Lin refers to lineage specific markers e.g. Glycophorin A present on erythrocytes, CD13 present on Neutrophils. Lin - refers to absence of lineage specific markers on lineage restricted progenitors.
Rhodamine 123 is a florescent dye, which is taken up by majority of living cells. The pumps present in HSC remove this dye out of the cell because of which HSC shows low intensity staining for Rhodamine123 (Rho123 Lo ).
Hence, the options A, B and D are incorrect.
HLA-DR is present on the MHC class II (Major histocompatibility complex) antigen. It is encoded by the HLA (Human Leukocyte antigen) complex. It is not a phenotype of HSC.
Hence, the correct answer is option
 .
. 2
Cytokine regulation in which the cytokine is not secreted by the producing cell but remains membrane bound, necessitating direct cell-cell contact to achieve the desired effect is: (Objective 5)
A) paracrine
B) endocrine
C) juxtacrine
D) autocrine
A) paracrine
B) endocrine
C) juxtacrine
D) autocrine
Cell signaling involves binding of signal molecule to the receptor present on the target cell. This further activates the cascading molecules, in order to generate the desired biochemical reaction.
These signaling molecules can be hormones, growth factors and different proteins. They bind to the signal molecule in four different ways, namely, autocrine, paracrine, endocrine and juxtacrine.
The autocrine signaling molecules act on the same cell from, which they are produced. The paracrine signaling molecules act on the immediate adjacent cell to the cell, from which they are synthesized. They can travel only over short distances.
The endocrine signaling molecules are produced from one cell and act on another cell present at the different site or different organ. These signaling molecules travel long distances through blood circulation.
Hence, options A, B and D are incorrect.
The juxtacrine signaling molecule is not secreted out from the parent cell but, it remains membrane bound to the cell, from which it is produced. Therefore, the cell signaling via this mode requires a direct cell to cell contact of producer cell and the target cell.
Hence, the correct answer is option .
.
These signaling molecules can be hormones, growth factors and different proteins. They bind to the signal molecule in four different ways, namely, autocrine, paracrine, endocrine and juxtacrine.
The autocrine signaling molecules act on the same cell from, which they are produced. The paracrine signaling molecules act on the immediate adjacent cell to the cell, from which they are synthesized. They can travel only over short distances.
The endocrine signaling molecules are produced from one cell and act on another cell present at the different site or different organ. These signaling molecules travel long distances through blood circulation.
Hence, options A, B and D are incorrect.
The juxtacrine signaling molecule is not secreted out from the parent cell but, it remains membrane bound to the cell, from which it is produced. Therefore, the cell signaling via this mode requires a direct cell to cell contact of producer cell and the target cell.
Hence, the correct answer is option
 .
. 3
Explain the difference in the nomenclature used to label progenitor cells from that used to label maturing cells within the hematopoietic hierarchy of cells.
A progenitor cell is a cell that has the tendency to differentiate into other specialized cells. These cells can divide for a limited number of times only. They are responsible for replacing the cells that are lost by normal attrition.
Maturing cells constitute a majority of the precursor haemopoetic cells. Most of these cells lose their ability to proliferate, before full maturation. They can be easily recognized and classified based on their lineages. This is because; they exhibit recognizable nuclear and cytoplasmic morphological characteristics.
The progenitor cells are named after the cell lineage , to which they are committed. For example, CFU-E (colony forming unit) is derived from erythrocytes (E), CFU-Ba from basophils, CFU-Mk from megakaryocytes. Each progenitor cell differentiates into morphologically identifiable precursors of its lineage.
The maturing cells are generally named using the earliest morphologically recognized cell line along with the suffix blast ( lymphoblast, myoblast). Qualifying adjectives and prefixes are also added to describe additional stages of differentiation, for example, proerythroblast.
Maturing cells constitute a majority of the precursor haemopoetic cells. Most of these cells lose their ability to proliferate, before full maturation. They can be easily recognized and classified based on their lineages. This is because; they exhibit recognizable nuclear and cytoplasmic morphological characteristics.
The progenitor cells are named after the cell lineage , to which they are committed. For example, CFU-E (colony forming unit) is derived from erythrocytes (E), CFU-Ba from basophils, CFU-Mk from megakaryocytes. Each progenitor cell differentiates into morphologically identifiable precursors of its lineage.
The maturing cells are generally named using the earliest morphologically recognized cell line along with the suffix blast ( lymphoblast, myoblast). Qualifying adjectives and prefixes are also added to describe additional stages of differentiation, for example, proerythroblast.
4
The stromal elements of the hematopoietic microenvironment include all of the following except : (Objective 7)
A) B lymphocytes
B) adipocytes
C) fibroblasts
D) osteoblasts
A) B lymphocytes
B) adipocytes
C) fibroblasts
D) osteoblasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Precursor cells that are morphologically recognizable are found in the: (Objective 2)
A) stem cell compartment
B) progenitor cell compartment
C) maturing cell compartment
D) differentiating cell compartment
A) stem cell compartment
B) progenitor cell compartment
C) maturing cell compartment
D) differentiating cell compartment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following are thought to be negative regulators of hematopoiesis except : (Objective 6) 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The major molecular marker that differentiates CLP from CMP is: (Objective 1) 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following cytoadhesion molecules plays an important role in retaining erythroid-developing cells in the bone marrow microenvironment? (Objective 7)
A) hemonectin
B) fibronectin
C) thrombospondin
D) glycosaminoglycans
A) hemonectin
B) fibronectin
C) thrombospondin
D) glycosaminoglycans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cytokine control of hematopoiesis is said to be characterized by redundancy and pleiotrophy. What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The hematopoietic microenvironment is composed of: (Objective 7)
A) hepatocytes and extrahepatic matrix
B) osteoblasts and osteoclasts
C) marrow stromal cells and extracellular matrix
D) hepatocytes and splenic macrophages
A) hepatocytes and extrahepatic matrix
B) osteoblasts and osteoclasts
C) marrow stromal cells and extracellular matrix
D) hepatocytes and splenic macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The MEP gives rise to: (Objective 3)
A) eosinophils and megakaryocytes
B) erythrocytes and monocytes
C) eosinophils and megakaryocytes
D) erythrocytes and megakaryocytes
A) eosinophils and megakaryocytes
B) erythrocytes and monocytes
C) eosinophils and megakaryocytes
D) erythrocytes and megakaryocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The role of the osteoblastic stem cell "niche" in the bone marrow is thought to be to: (Objective 7)
A) protect hematopoietic precursor cells from the lytic action of osteoclasts
B) provide nourishment (oxygen, nutrients) to developing precursor cells
C) regulate the quiescent state of stem cells blocking differentiation-inducing signals
D) produce cytoadhesion molecules important for homing to the marrow
A) protect hematopoietic precursor cells from the lytic action of osteoclasts
B) provide nourishment (oxygen, nutrients) to developing precursor cells
C) regulate the quiescent state of stem cells blocking differentiation-inducing signals
D) produce cytoadhesion molecules important for homing to the marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are important regulators of granulopoiesis except : (Objective 2)
A) GM-CSF
B) FL
C) IL-2
D) IL-3
A) GM-CSF
B) FL
C) IL-2
D) IL-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Individuals with congenital defects of the 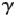
chain of the IL-2 receptor suffer from profound defects of lymphopoiesis far greater than individuals with congenital defects of the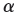
chain of the IL-2 receptor. Why?
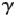
chain of the IL-2 receptor suffer from profound defects of lymphopoiesis far greater than individuals with congenital defects of the
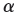
chain of the IL-2 receptor. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All hematopoietic cells are derived from the CFU-GEMM except : (Objective 3)
A) lymphocytes
B) platelets
C) eosinophils
D) erythrocytes
A) lymphocytes
B) platelets
C) eosinophils
D) erythrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The major cytokine important for eosinophil differentiation is: (Objective 2)
A) IL-3
B) IL-5
C) IL-7
D) IL-11
A) IL-3
B) IL-5
C) IL-7
D) IL-11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following cell that is most sensitive to erythropoietin is: (Objective 4)
A) reticulocyte
B) CFU-GEMM
C) BFU-E
D) CFU-E
A) reticulocyte
B) CFU-GEMM
C) BFU-E
D) CFU-E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following growth factor receptors share a common ? chain? (Objective 3)
A) IL-3 and GM-CSF
B) TPO and EPO
C) IL-2 and IL-3
D) G-CSF and GM-CSF
A) IL-3 and GM-CSF
B) TPO and EPO
C) IL-2 and IL-3
D) G-CSF and GM-CSF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All of the following are considered "early acting, multilineage" cytokines except: (Objective 4)
A) IL-5
B) GM-CSF
C) SCF
D) IL-3
A) IL-5
B) GM-CSF
C) SCF
D) IL-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Cytokine receptors that lack an intrinsic kinase domain generally signal: (Objective 4)
A) through an intrinsic phosphatase domain
B) by recruiting membrane-embedded kinases
C) through an intrinsic protease domain
D) by recruiting cytoplasmic kinases
A) through an intrinsic phosphatase domain
B) by recruiting membrane-embedded kinases
C) through an intrinsic protease domain
D) by recruiting cytoplasmic kinases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Hematopoietic stem cells that have initiated a differentiation program are sometimes described as undergoing death by differentiation. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Pleiotrophy refers to: (Objective 4)
A) multiple different cells that can produce the same cytokine
B) a cytokine with multiple biologic activities
C) multiple cytokines that can induce the same cellular effect
D) a cytokine that can be produced by multiple different tissues
A) multiple different cells that can produce the same cytokine
B) a cytokine with multiple biologic activities
C) multiple cytokines that can induce the same cellular effect
D) a cytokine that can be produced by multiple different tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Self-renewal and pluripotential differentiation potential are characteristics of: (Objective 2)
A) mature cells
B) stem cells
C) progenitor cells
D) maturing cells
A) mature cells
B) stem cells
C) progenitor cells
D) maturing cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The function of the JAK-STAT pathway in hematopoiesis is to: (Objective 4)
A) localize cytokines in the hematopoietic microenvironment
B) generate homing receptors for stem and progenitor cells
C) produce cytoadhesion molecules to retain precursor cells in the marrow
D) function as a signal transduction pathway for cytokineactivated receptors
A) localize cytokines in the hematopoietic microenvironment
B) generate homing receptors for stem and progenitor cells
C) produce cytoadhesion molecules to retain precursor cells in the marrow
D) function as a signal transduction pathway for cytokineactivated receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 24 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



