Deck 2: Cellular Homeostasis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Cellular Homeostasis
1
What does the phrase lipid asymmetry mean when describing cell membranes?
The cell membrane is a semipermeable membrane, which allows the passage of selected particles inside the cell. The reason for the selective nature of the cell membrane is its composition. It mainly contains proteins and lipids. The cell membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it.
The proteins and lipids are distributed asymmetrically in the membrane. There are four types of phospholipids in the membrane; namely, SM (sphingomyelin), PC (phosphatidylcholine), PE (phosphatidylethanolamine), as well as PS (phosphatidylserine).
Lipid asymmetry refers to the uneven distribution of the different phospholipids in the two lipid layers. The distribution of these four phospholipids is asymmetric in the inner and outer lipid layers. The PE and PS components are found within the inner lipid layer, while the PC and SM components are found within the outer lipid layer.
The proteins and lipids are distributed asymmetrically in the membrane. There are four types of phospholipids in the membrane; namely, SM (sphingomyelin), PC (phosphatidylcholine), PE (phosphatidylethanolamine), as well as PS (phosphatidylserine).
Lipid asymmetry refers to the uneven distribution of the different phospholipids in the two lipid layers. The distribution of these four phospholipids is asymmetric in the inner and outer lipid layers. The PE and PS components are found within the inner lipid layer, while the PC and SM components are found within the outer lipid layer.
2
The protein responsible for binding the transcription factors E2F and blocking cell-cycle progression beyond the restriction point (R) is: (Objective 6)
A) p53
B) p15
C) p21
D) Rb
A) p53
B) p15
C) p21
D) Rb
The phosphorylating enzymes, kinase complexes with the regulatory protein cyclin control the transition between different stages of the cell cycle. Therefore, this kinase protein is named as Cdk (cyclin dependent kinase). This kinase activity is regulated by major mechanisms, which includes Cdk activating kinase (CAK) and Cdk inhibitors.
The p 21 is the first Cdk inhibitor, which was identified. It binds to a majority of complexes, namely, cyclin D/Cdk4/6 complex and cyclin A/Cdk2 complex and inhibits the cell cycle progression.
Another inhibitor group comprises p 15 , which inhibits particularly Cdk6 and Cdk4 and arrest the cell cycle in the G 1 phase. P53 is protein, essential for the regulating the cell cycle. It is a transcription factor, which can inhibit as well as activate expression of genes. It is one of the tumor suppressor gene and plays a crucial role in the G 1 (growth phase) and G 2 (growth phase/M (mitosis) checkpoints.
Hence, the options A, B and C are incorrect.
Rb is an essential protein in regulating the cell cycle. It binds to the transcription factor, E2F, which is essential for the transcription of genes related to cell proliferation. Thus, it blocks the cell cycle progression beyond the restriction point.
Hence, the correct answer is option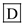 .
.
The p 21 is the first Cdk inhibitor, which was identified. It binds to a majority of complexes, namely, cyclin D/Cdk4/6 complex and cyclin A/Cdk2 complex and inhibits the cell cycle progression.
Another inhibitor group comprises p 15 , which inhibits particularly Cdk6 and Cdk4 and arrest the cell cycle in the G 1 phase. P53 is protein, essential for the regulating the cell cycle. It is a transcription factor, which can inhibit as well as activate expression of genes. It is one of the tumor suppressor gene and plays a crucial role in the G 1 (growth phase) and G 2 (growth phase/M (mitosis) checkpoints.
Hence, the options A, B and C are incorrect.
Rb is an essential protein in regulating the cell cycle. It binds to the transcription factor, E2F, which is essential for the transcription of genes related to cell proliferation. Thus, it blocks the cell cycle progression beyond the restriction point.
Hence, the correct answer is option
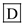 .
. 3
Selective cellular permeability and structural stability are provided by: (Objective 1)
A) membrane lipids
B) membrane proteins
C) ribosomes
D) the nucleus
A) membrane lipids
B) membrane proteins
C) ribosomes
D) the nucleus
Lipids are organic compounds containing hydrocarbons and occur naturally. They are insoluble in water. Lipids are non-polar and are soluble in nonpolar environments, for example, acetone, ether, benzene and chloroform, and water. They are found in eukaryotes and bacteria. Membrane lipids are all closed bodies separating the substitute parts of a cell.
The nucleus is the central component of all living cells. It occupies nearly 10% of the total cell space. It carries almost all the genetic material and is responsible for processes like replication and transcription.
Ribosomes are one of the important cell constituents, first observed by Palade (1955), essentially involved in protein synthesis. If iodoacetate treatment is given, then thiolate of cysteine is modified.
Hence, the options A, C and D are incorrect.
Membrane proteins are anchored in the phospholipid bilayer. Selective cellular permeability as well as structural ability is provided by the membrane proteins. Proteins with extracellular domains are involved with cell-to-cell communications. Proteins with cytosolic domains (inside the cell) have the widest range of functions.
Hence, the correct answer is option .
.
The nucleus is the central component of all living cells. It occupies nearly 10% of the total cell space. It carries almost all the genetic material and is responsible for processes like replication and transcription.
Ribosomes are one of the important cell constituents, first observed by Palade (1955), essentially involved in protein synthesis. If iodoacetate treatment is given, then thiolate of cysteine is modified.
Hence, the options A, C and D are incorrect.
Membrane proteins are anchored in the phospholipid bilayer. Selective cellular permeability as well as structural ability is provided by the membrane proteins. Proteins with extracellular domains are involved with cell-to-cell communications. Proteins with cytosolic domains (inside the cell) have the widest range of functions.
Hence, the correct answer is option
 .
. 4
The point in the cell cycle at which cell proliferation (cycling) no longer depends on extracellular signals is: (Objective 4)
A) G 1
B) R
C) G 2
D) M
A) G 1
B) R
C) G 2
D) M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
UTRs are regions of mRNA that: (Objective 1)
A) represent variations of the genetic sequence of a gene in different individuals
B) represent the regions of the gene that are transcribed
C) contain the splice sites for mRNA processing
D) influence the stability of mRNA and translation of protein
A) represent variations of the genetic sequence of a gene in different individuals
B) represent the regions of the gene that are transcribed
C) contain the splice sites for mRNA processing
D) influence the stability of mRNA and translation of protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Apoptotic cell death is characterized by all of the following except: (Objective 14)
A) triggering an inflammatory response
B) condensation of the nucleus
C) cleavage of chromatin into discrete fragments ( multiples of 185 base pairs)
D) condensation of the cytoplasm and cell shrinkage
A) triggering an inflammatory response
B) condensation of the nucleus
C) cleavage of chromatin into discrete fragments ( multiples of 185 base pairs)
D) condensation of the cytoplasm and cell shrinkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Explain the difference between densely staining chromatin and lighter staining chromatin when viewing blood cells under a microscope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Programmed cell death (cell suicide) is also known as: (Objective 5)
A) Necrosis
B) senescence
C) apoptosis
D) terminal differentiation
A) Necrosis
B) senescence
C) apoptosis
D) terminal differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Rough endoplasmic reticulum is important in: (Objective 1)
A) synthesizing lipid
B) synthesizing hormones
C) synthesizing and assembling proteins
D) phagocytosis
A) synthesizing lipid
B) synthesizing hormones
C) synthesizing and assembling proteins
D) phagocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The components of apoptosis directly responsible for dismantling the cell during the programmed cell death process are: (Objective 8)
A) Bcl-2 family members
B) IAPs
C) initiator caspases
D) effector caspases
A) Bcl-2 family members
B) IAPs
C) initiator caspases
D) effector caspases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The main function of the ubiquitin-proteosome system is to: (Objective 2)
A) assist in the three-dimensional folding of polypeptides into their tertiary structure
B) degrade unwanted or damaged polypeptides
C) facilitate transfer of polypeptides from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi
D) direct post-translational modifications of proteins
A) assist in the three-dimensional folding of polypeptides into their tertiary structure
B) degrade unwanted or damaged polypeptides
C) facilitate transfer of polypeptides from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi
D) direct post-translational modifications of proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following are considered initiators of apoptosis except: (Objective 6)
A) estrogens
B) death cytokines
C) loss of matrix attachment
D) cell-damaging stress
A) estrogens
B) death cytokines
C) loss of matrix attachment
D) cell-damaging stress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the difference between a polymorphism and a mutation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A predominance of Bax-Bax homodimers has what effect on apoptosis? (Objective 11)
A) inhibits initiator caspases
B) promotes activation of effector caspases
C) activates death receptors on the cell surface
D) neutralizes IAPs
A) inhibits initiator caspases
B) promotes activation of effector caspases
C) activates death receptors on the cell surface
D) neutralizes IAPs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The fundamental subunit of chromatin composed of ·180 base pairs of DNA wrapped around a histone protein is called: (Objective 1)
A) nucleolus
B) genome
C) heterochromatin
D) nucleosome
A) nucleolus
B) genome
C) heterochromatin
D) nucleosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following events in hematopoiesis is regulated by apoptosis? (Objective 7)
A) removal of excess neutrophils following cessation of bacterial challenge
B) removal of excess B lymphocytes following immune stimulation
C) removal of excess platelets following hemostatic challenge
D) A and B
A) removal of excess neutrophils following cessation of bacterial challenge
B) removal of excess B lymphocytes following immune stimulation
C) removal of excess platelets following hemostatic challenge
D) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The kinase complex responsible for passage through and exit from mitosis is composed of: (Objective 3)
A) cyclin A/Cdk2
B) cyclin D/Cdk4
C) cyclin B/Cdk1
D) cyclin E/Cdk2
A) cyclin A/Cdk2
B) cyclin D/Cdk4
C) cyclin B/Cdk1
D) cyclin E/Cdk2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following are associated with gene silencing? (Objective 13)
A) DNA (CpG) methylation and histone acetylation
B) DNA (CpG) methylation and histone deacetylation
C) unmethylated CpG and histone acetylation
D) unmethylated CpG and histone deacetylation
A) DNA (CpG) methylation and histone acetylation
B) DNA (CpG) methylation and histone deacetylation
C) unmethylated CpG and histone acetylation
D) unmethylated CpG and histone deacetylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A cell undergoing mitosis fails to attach one of its duplicated chromosomes to the microtubules of the spindle apparatus during metaphase. The cell's metaphase checkpoint malfunctions and does not detect the error. What is the effect (if any) on the daughter cells produced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Condensation of chromosomes occurs during which phase of mitosis? (Objective 3)
A) anaphase
B) telophase
C) prophase
D) metaphase
A) anaphase
B) telophase
C) prophase
D) metaphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
CAK, the kinase activity responsible for the activating phosphorylations of Cdks, consists of: (Objective 4)
A) cyclin A/Cdk1
B) cyclin H/Cdk7
C) cyclin F/Cdk6
D) cyclin C/Cdk2
A) cyclin A/Cdk1
B) cyclin H/Cdk7
C) cyclin F/Cdk6
D) cyclin C/Cdk2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What would be the effect on the hematopoietic system homeostasis if the expanded clone of antigen-activated B lymphocytes failed to undergo apoptosis after the antigenic challenge was removed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Cells that have exited the cell cycle and entered a nonproliferative phase are said to be in: (Objective 3)
A) quiescence
B) interphase
C) G 1
D) G 2
A) quiescence
B) interphase
C) G 1
D) G 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Overexpression of the p21 protein would have what effect on the cell cycle of proliferating cells? (Objective 4)
A) decrease cell-cycle progression
B) increase cell-cycle progression
C) trigger apoptosis
D) none
A) decrease cell-cycle progression
B) increase cell-cycle progression
C) trigger apoptosis
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The regulatory subunit of the active enzyme complex responsible for regulating passage through the various phases of the cell cycle is: (Objective 3)
A) cyclin
B) Cdk
C) Cdk inhibitor
D) p21
A) cyclin
B) Cdk
C) Cdk inhibitor
D) p21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



