Deck 19: Economic Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/6
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Economic Development
1
Besides income, identify ways that low-income economies differ from high-income economies
(Worlds Apart) Per capita income most recently was about 160 times greater in the United States than in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Suppose per capita income grows an average of 3 percent per year in the richer country and 6 percent per year in the poorer country. Assuming such growth rates continue indefinitely into the future, how many years would it take before per capita income in the Congo exceeds that of the United States? (To simplify the math, suppose at the outset per capita income is $160,000 in the richer country and $1,000 in the poorer country.)
(Worlds Apart) Per capita income most recently was about 160 times greater in the United States than in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Suppose per capita income grows an average of 3 percent per year in the richer country and 6 percent per year in the poorer country. Assuming such growth rates continue indefinitely into the future, how many years would it take before per capita income in the Congo exceeds that of the United States? (To simplify the math, suppose at the outset per capita income is $160,000 in the richer country and $1,000 in the poorer country.)
Required number of years to surpass the GDP of another country:
Per capita income of country US is 160 times greater than that of country C. country US 's per capita income grows 3 percent per year, whereas country C 's per capita income grows at 6 percent. Thus, Per capita income of country C grows 3 percent faster than country US.
The following formula is used to calculate the number of years required for country C to surpass: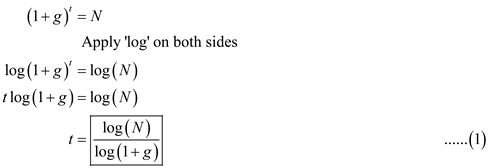 Where,
Where,
Growth rate is represented by G ,
Required number of years is represented by t ,
Per capita income is represented by N.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to obtain the required number of years.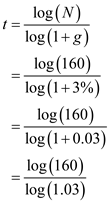
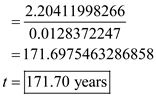 Hence, if both the countries grow in present rate, then after
Hence, if both the countries grow in present rate, then after 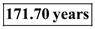 , per capita income of country C will surpass country US.
, per capita income of country C will surpass country US.
Per capita income of country US is 160 times greater than that of country C. country US 's per capita income grows 3 percent per year, whereas country C 's per capita income grows at 6 percent. Thus, Per capita income of country C grows 3 percent faster than country US.
The following formula is used to calculate the number of years required for country C to surpass:
 Where,
Where, Growth rate is represented by G ,
Required number of years is represented by t ,
Per capita income is represented by N.
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to obtain the required number of years.
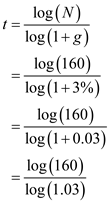
 Hence, if both the countries grow in present rate, then after
Hence, if both the countries grow in present rate, then after 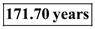 , per capita income of country C will surpass country US.
, per capita income of country C will surpass country US. 2
Describe the factors that make workers in high-income economies more productive than workers in other economies
(Why Incomes Differ) What factors help workers in high-income economies become more productive than those in other economies?
(Why Incomes Differ) What factors help workers in high-income economies become more productive than those in other economies?
Following factors help workers in high income economies to become more productive than those in other economies -
1. Investment in human and physical capital - Due to availability of abundant capital, investment in human and physical capital is considerable in high-income economies.
On the other hand, deficiency of capital in other economies results in lesser investment in human and physical capital.
Higher the capital per worker, higher is the productivity and vice-versa.
Hence, workers in high-income economies are more productive than workers in other economies.
2. High-income economies utilize their labor more efficiently. Instances of underemployment and disguised unemployment are too few or altogether absent in high-income economies.
On the other hand, other economies utilize their labor in less-efficient manner. These economies are plagued by high instances of underemployment and disguised unemployment.
This efficient utilization of labor in high-income economies results in high labor productivity relative to other economies.
3. In high-income economies, level of technical know-how is considerably vast and widespread resulting in higher labor productivity as worker work in technologically advanced settings directly impacting their productivity in positive manner.
On the other hand, level of technical know-how is considerably low and restricted resulting in low labor productivity as worker work in technologically handicapped setting invoking negative impact on their productivity.
1. Investment in human and physical capital - Due to availability of abundant capital, investment in human and physical capital is considerable in high-income economies.
On the other hand, deficiency of capital in other economies results in lesser investment in human and physical capital.
Higher the capital per worker, higher is the productivity and vice-versa.
Hence, workers in high-income economies are more productive than workers in other economies.
2. High-income economies utilize their labor more efficiently. Instances of underemployment and disguised unemployment are too few or altogether absent in high-income economies.
On the other hand, other economies utilize their labor in less-efficient manner. These economies are plagued by high instances of underemployment and disguised unemployment.
This efficient utilization of labor in high-income economies results in high labor productivity relative to other economies.
3. In high-income economies, level of technical know-how is considerably vast and widespread resulting in higher labor productivity as worker work in technologically advanced settings directly impacting their productivity in positive manner.
On the other hand, level of technical know-how is considerably low and restricted resulting in low labor productivity as worker work in technologically handicapped setting invoking negative impact on their productivity.
3
IMPORT SUBSTITUTION VERSUS EXPORT PROMOTION Explain why domestic producers who supply a good that competes with imports would prefer an import-substitution approach to trade policy rather than an export-promotion approach. Which policy would domestic consumers prefer and why?
Import substitution policy:
Import substitution policy refers to the government policy which discourages the imports of goods and service and encourages production of those goods within the country.
Export promotion policy:
Export promotion policy refers to the government policy which encourages the domestic firm to export more goods and services.
Producer prefers import substitution policy:
The import goods prices are lower than the domestic price. This creates more competition, which reduces the price of goods consequently and in turn reduces the profit of the domestic firm. Therefore, to protect the firm from the competition and avoid reduction in the price and profit, domestic firms prefer import substitution policy over export promotion.
Consumer prefers imports:
Import goods create competition in the domestic market, which in turn causes price reduction and offers best-quality products. Hence, consumer prefers foreign imports over the import substitution policy.
Import substitution policy refers to the government policy which discourages the imports of goods and service and encourages production of those goods within the country.
Export promotion policy:
Export promotion policy refers to the government policy which encourages the domestic firm to export more goods and services.
Producer prefers import substitution policy:
The import goods prices are lower than the domestic price. This creates more competition, which reduces the price of goods consequently and in turn reduces the profit of the domestic firm. Therefore, to protect the firm from the competition and avoid reduction in the price and profit, domestic firms prefer import substitution policy over export promotion.
Consumer prefers imports:
Import goods create competition in the domestic market, which in turn causes price reduction and offers best-quality products. Hence, consumer prefers foreign imports over the import substitution policy.
4
INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND DEVELOPMENT From the perspective of citizens in a developing country, what are some of the benefits and drawbacks of international trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
FOREIGN AID AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Foreign aid, if it is to be successful in enhancing economic development, must lead to a more productive economy. Describe some of the problems in achieving such an objective through foreign aid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Outline some unintended consequences of foreign aid on economic development
(In-Kind Aid) What has been an unintended consequences of richer countries giving food and clothing to poorer countries?
(In-Kind Aid) What has been an unintended consequences of richer countries giving food and clothing to poorer countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



