Deck 8: Regional Trading Arrangements
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/6
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Regional Trading Arrangements
1
What is meant by the term economic integration? What are the various stages that economic integration can take?
Economic integration defines the removal of restrictions on international trade, payments, and the mobility of factors among countries. One of the stages that economic integration can take is having a free-trade area in which a group of trading nations agrees to remove all tariff and non-tariff barriers for all of the participating members. Integration can also take the form of a customs union , which is an agreement among at least two trading countries to remove all trade barriers among themselves.
Another more complete stage of economic integration is the creation of a common market , which is a group of trading nations come together to allow the free movement of factors of production, goods, and services across national borders among member nations and put up common external trade restrictions against the nonmembers. Past these stages of economic integration as mentioned above, integration could develop to the stage of economic union , in which participating nations agree to transfer economic sovereignty to a global authority and adopt a common currency for the convenience of free trade between the nations in the economic union.
Another more complete stage of economic integration is the creation of a common market , which is a group of trading nations come together to allow the free movement of factors of production, goods, and services across national borders among member nations and put up common external trade restrictions against the nonmembers. Past these stages of economic integration as mentioned above, integration could develop to the stage of economic union , in which participating nations agree to transfer economic sovereignty to a global authority and adopt a common currency for the convenience of free trade between the nations in the economic union.
2
How do the static welfare effects of trade creation and trade diversion relate to a nation's decision to form a customs union? Of what importance to this decision are the dynamic welfare effects?
A customs union is an agreement among two or more nations to remove all forms of trade barriers between themselves. The static effects of economic integration for a nation result from two opposing forces: a trade-creation effect which increases a nation's welfare and a trade-diversion effect which decreases welfare. Trade creation occurs when some domestic production of one customs union member is replaced by another member's imports with lower costs. This increases welfare in the domestic economy because it is able to have access to lower-cost goods and the resulting gain in consumer surplus exceeds the loss in producer surplus. Trade diversion occurs when the opposite happens: a customs union member is replaced by another member's imports with higher costs. This results in a decrease in welfare in the domestic economy because the loss in consumer surplus exceeds the gain in producer surplus. Together, these static welfare effects affect a nation's decision to form a customs union because when the nation sees that the trade creation effect is greater than the trade diversion effect, it will choose to form a customs union in order to increase its welfare. Conversely, when the trade diversion effect is greater than the trade creation effect, the nation will choose not to form a customs union in order to avoid the decrease in welfare.
The dynamic effects of economic integration relate to a customs-union member's long-term rates of growth. Dynamic gains in an economy include greater competition, a stimulus of investment, and economies of scale. If the creation of a customs union enlarges the market hence increasing competition for the domestic nation, then more efficient production would occur that would contribute to the nation's long-term economic growth. It is positive dynamic effects like this that contribute to a nation's decision to form a customs union.
The dynamic effects of economic integration relate to a customs-union member's long-term rates of growth. Dynamic gains in an economy include greater competition, a stimulus of investment, and economies of scale. If the creation of a customs union enlarges the market hence increasing competition for the domestic nation, then more efficient production would occur that would contribute to the nation's long-term economic growth. It is positive dynamic effects like this that contribute to a nation's decision to form a customs union.
3
Why has the so-called common agricultural policy been a controversial issue for the European Union?
The common agricultural policy provided price supports for agricultural goods so that farmers are able to receive fair and higher prices for their produce. This policy has been a controversial issue for the European Union (EU) because it encouraged inefficient farm production by EU members since farmers took advantage of the high price supports. It also restricted food imports from non-EU members and decreased the welfare of the EU by decreasing efficiency in production.
4
What are the welfare effects of trade creation and trade diversion for the European Union, as determined by empirical studies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 8.8 depicts the supply and demand schedules of gloves for Portugal, a small nation that is unable to affect the world price. On graph paper, draw the supply and demand schedules of gloves for Portugal.
a. Assume that Germany and France can supply gloves to Portugal at a price of $2 and $3, respectively. With free trade, which nation exports gloves to Portugal? How many gloves does Portugal produce, consume, and import?
b. Suppose Portugal levies a 100 percent nondiscriminatory tariff on its glove imports. Which nation exports gloves to Portugal? How many gloves will Portugal produce, consume, and import?
c. Suppose Portugal forms a customs union with France. Determine the trade-creation effect and the trade-diversion effect of the customs union. What is the customs union's overall effect on the welfare of Portugal?
d. Suppose instead that Portugal forms a customs union with Germany. Is this a trade-diverting or trade-creating customs union? By how much does the customs union increase or decrease the welfare of Portugal?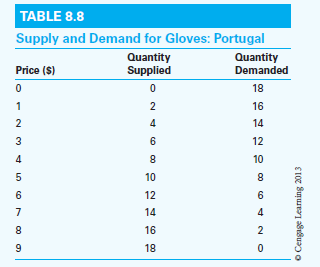
a. Assume that Germany and France can supply gloves to Portugal at a price of $2 and $3, respectively. With free trade, which nation exports gloves to Portugal? How many gloves does Portugal produce, consume, and import?
b. Suppose Portugal levies a 100 percent nondiscriminatory tariff on its glove imports. Which nation exports gloves to Portugal? How many gloves will Portugal produce, consume, and import?
c. Suppose Portugal forms a customs union with France. Determine the trade-creation effect and the trade-diversion effect of the customs union. What is the customs union's overall effect on the welfare of Portugal?
d. Suppose instead that Portugal forms a customs union with Germany. Is this a trade-diverting or trade-creating customs union? By how much does the customs union increase or decrease the welfare of Portugal?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How can trade liberalization exist on a nondiscriminatory basis versus a discriminatory basis? What are some actual examples of each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 6 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



