Deck 8: Management of Transaction Exposure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Management of Transaction Exposure
1
Discuss and compare hedging transaction exposure using the forward contract vs. money market instruments. When do the alternative hedging approaches produce the same result
Management of transaction exposure
Fluctuating exchange rates is the risk associated with internal business. Changes in the foreign currency rates affects the cash flows, valuations and finalization of contracts. It important for management of the company manage the foreign currency exposure and cash flows.
Hedging transaction exposure using forward contract and money market instrument
Under forward contract, a company sells its foreign currency receivables forward to mitigate the transaction exposure. A fixed exchange rate is decided for maturity date and that rate is used to convert the foreign currency receivable. For example, a company is expecting to receive GBP 1000 after one year and its takes forward contract with a bank to convert GBP 1000 into dollar with cross rate $/£ as 1.48. The forward rate mitigates the risk of exchange fluctuations in future. On the maturity date i.e. after one year, company shall receive $1460 i.e. GBP 1000 multiplied with cross rate i.e. 1.46. It does not matter what the spot rate on the maturity date is.
Under money market instruments, a company borrows an amount at the discounted rate and the amount payable on maturity is equal to the value of FX receivables. In the above case, company may borrow GBP 917 at discounted rate of 9% that need to be paid after 1 year as GBP 1000. Company can use its FX receivable i.e. GBP 1000 after one year to pay off this loan of GBP 1000. The amount received in advance i.e. GBP 917 is converted into US dollars at prevailing cross rate $/£ i.e. 1.5 which is $1,375 and proceeds may be invested in US market. The maturity value of amount invested i.e. $1375 in US market, will be more after one year i.e. $1460. Company has hedged the risk of transaction exposure by investing in money market instruments.
The maturity value of investment under forward contract and money market instrument are same when interest rate parity condition prevails. Proceeds from money market instrument is not same as forward contract proceeds if interest rate parity condition is not holding.
Fluctuating exchange rates is the risk associated with internal business. Changes in the foreign currency rates affects the cash flows, valuations and finalization of contracts. It important for management of the company manage the foreign currency exposure and cash flows.
Hedging transaction exposure using forward contract and money market instrument
Under forward contract, a company sells its foreign currency receivables forward to mitigate the transaction exposure. A fixed exchange rate is decided for maturity date and that rate is used to convert the foreign currency receivable. For example, a company is expecting to receive GBP 1000 after one year and its takes forward contract with a bank to convert GBP 1000 into dollar with cross rate $/£ as 1.48. The forward rate mitigates the risk of exchange fluctuations in future. On the maturity date i.e. after one year, company shall receive $1460 i.e. GBP 1000 multiplied with cross rate i.e. 1.46. It does not matter what the spot rate on the maturity date is.
Under money market instruments, a company borrows an amount at the discounted rate and the amount payable on maturity is equal to the value of FX receivables. In the above case, company may borrow GBP 917 at discounted rate of 9% that need to be paid after 1 year as GBP 1000. Company can use its FX receivable i.e. GBP 1000 after one year to pay off this loan of GBP 1000. The amount received in advance i.e. GBP 917 is converted into US dollars at prevailing cross rate $/£ i.e. 1.5 which is $1,375 and proceeds may be invested in US market. The maturity value of amount invested i.e. $1375 in US market, will be more after one year i.e. $1460. Company has hedged the risk of transaction exposure by investing in money market instruments.
The maturity value of investment under forward contract and money market instrument are same when interest rate parity condition prevails. Proceeds from money market instrument is not same as forward contract proceeds if interest rate parity condition is not holding.
2
Using an example, discuss the possible effect of hedging on a firm's tax obligations.
Hedge funds are the funds in which an investor invests with the basic purpose of covering risk. Hedging is a practice of reducing or eliminating risks.
Recently, the purpose of hedge funds has changed and they are primarily used for maximizing the return on investment.
Hedging and tax obligation
Hedging helps the small and medium firm to cover risk and reduces their tax obligations.
For example :if a firms hedges their fund by purchasing debts in money market instruments, they will get tax benefit on paying of interest as the interest is tax-deductible. Moreover, they will be benefited in case foreign exchanges, whenever the prices are inflated and investors are suffering losses.
Recently, the purpose of hedge funds has changed and they are primarily used for maximizing the return on investment.
Hedging and tax obligation
Hedging helps the small and medium firm to cover risk and reduces their tax obligations.
For example :if a firms hedges their fund by purchasing debts in money market instruments, they will get tax benefit on paying of interest as the interest is tax-deductible. Moreover, they will be benefited in case foreign exchanges, whenever the prices are inflated and investors are suffering losses.
3
Suppose that Diva chooses to hedge its exposure in yen using the forward contract or the currency option. Assume that you lock in these contracts at the forward price implied by interest rate parity for September 1995. Draw the payoffs to the position at maturity for each alternative with the exchange rate defined in $/¥ × 10,000 units (i.e., the same units as the currency option is quoted). What do you see as the trade-offs between the alternatives
Many companies which transact with other global institutes face the risk of currency appreciation and depreciation. To minimize this risk, companies can hedge using derivative instruments like the forward contract, options, swaps and other money market techniques. This risk is called as a transaction exposure and hedging the exposure with the derivatives are termed as forward market hedging, money market hedging, Option market hedging and Swap market hedging. The companies can also cross hedge by hedging on some underlying asset to meet the requirement in other assets or obligations. They can also use other techniques like the lead and lag strategies for paying or collecting early/late to meet an obligation or can use exposure netting to minimize this risk, in which the company only hedge for the net requirement, rather than the complete obligation amount.
Given that the Diva wants to hedge its currency exchange exposure using forward contracts. Using the information from exhibit 8.15, let us assume the interest rates in the U.S and Japan as on 1th April 1995 for the next six months is assume to be r $ = 6.12% , r ¥ = 1.69% and given the spot rate on 1 st April 1995 is S 0 = ¥89.6/$. Therefore, the spot rate on 1 st September 1995 is estimated using the interest rate parity as: Therefore, from the interest rate parity the expected future contract rate is ¥87.71/$ (approximately). So, for ¥10,000 the payoff for forward hedging will be
Therefore, from the interest rate parity the expected future contract rate is ¥87.71/$ (approximately). So, for ¥10,000 the payoff for forward hedging will be 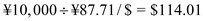 .
.
Alternatively, we can also use options for hedging, but the company would have to pay some premium for the options. Assuming that the premium is ¥0.02/$, then the cost of each contract would be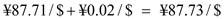 . Moreover, this contract has to be exercised on or before a given date but does not have an obligation to exercise. If it is exercised, the payoff for option hedging will be
. Moreover, this contract has to be exercised on or before a given date but does not have an obligation to exercise. If it is exercised, the payoff for option hedging will be 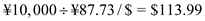 .
.
If the money market hedging is to be used, the company needs to borrow an amount that along with its interest will be equivalent to ¥10,000 and to be paid in 6 months. Assuming an interest rate of r ¥ = 1.69% per annum = 0.85% per semi-annum. Therefore, amount to be borrowed is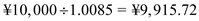 . With this amount buy dollars at spot rate of ¥89.6/$, thus you get $110.67. This when invested in U.S. six month bonds at an interest rate of r $ = 6.12% per annum = 3.06% per semi-annum, the amount we receive after six months is
. With this amount buy dollars at spot rate of ¥89.6/$, thus you get $110.67. This when invested in U.S. six month bonds at an interest rate of r $ = 6.12% per annum = 3.06% per semi-annum, the amount we receive after six months is 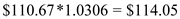 and the
and the 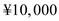 , we receive from the client can be used to repay the loan we borrowed.
, we receive from the client can be used to repay the loan we borrowed. 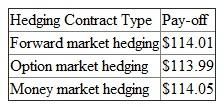 From the above, the key trade-off is that in for Diva Inc., the pay-off is comparatively high in money market hedging followed by forward market hedging and least for option market hedging, if executed.
From the above, the key trade-off is that in for Diva Inc., the pay-off is comparatively high in money market hedging followed by forward market hedging and least for option market hedging, if executed.
Given that the Diva wants to hedge its currency exchange exposure using forward contracts. Using the information from exhibit 8.15, let us assume the interest rates in the U.S and Japan as on 1th April 1995 for the next six months is assume to be r $ = 6.12% , r ¥ = 1.69% and given the spot rate on 1 st April 1995 is S 0 = ¥89.6/$. Therefore, the spot rate on 1 st September 1995 is estimated using the interest rate parity as:
 Therefore, from the interest rate parity the expected future contract rate is ¥87.71/$ (approximately). So, for ¥10,000 the payoff for forward hedging will be
Therefore, from the interest rate parity the expected future contract rate is ¥87.71/$ (approximately). So, for ¥10,000 the payoff for forward hedging will be 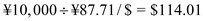 .
. Alternatively, we can also use options for hedging, but the company would have to pay some premium for the options. Assuming that the premium is ¥0.02/$, then the cost of each contract would be
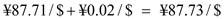 . Moreover, this contract has to be exercised on or before a given date but does not have an obligation to exercise. If it is exercised, the payoff for option hedging will be
. Moreover, this contract has to be exercised on or before a given date but does not have an obligation to exercise. If it is exercised, the payoff for option hedging will be 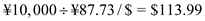 .
. If the money market hedging is to be used, the company needs to borrow an amount that along with its interest will be equivalent to ¥10,000 and to be paid in 6 months. Assuming an interest rate of r ¥ = 1.69% per annum = 0.85% per semi-annum. Therefore, amount to be borrowed is
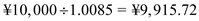 . With this amount buy dollars at spot rate of ¥89.6/$, thus you get $110.67. This when invested in U.S. six month bonds at an interest rate of r $ = 6.12% per annum = 3.06% per semi-annum, the amount we receive after six months is
. With this amount buy dollars at spot rate of ¥89.6/$, thus you get $110.67. This when invested in U.S. six month bonds at an interest rate of r $ = 6.12% per annum = 3.06% per semi-annum, the amount we receive after six months is 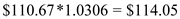 and the
and the 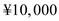 , we receive from the client can be used to repay the loan we borrowed.
, we receive from the client can be used to repay the loan we borrowed.  From the above, the key trade-off is that in for Diva Inc., the pay-off is comparatively high in money market hedging followed by forward market hedging and least for option market hedging, if executed.
From the above, the key trade-off is that in for Diva Inc., the pay-off is comparatively high in money market hedging followed by forward market hedging and least for option market hedging, if executed. 4
Explain contingent exposure and discuss the advantages of using currency options to manage this type of currency exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Airbus sold an A400 aircraft to Delta Airlines, a U.S. company, and billed $30 million payable in six months. Airbus is concerned about the euro proceeds from international sales and would like to control exchange risk. The current spot exchange rate is $1.05/€ and the six-month forward exchange rate is $1.10/€. Airbus can buy a six-month put option on U.S. dollars with a strike price of €0.95/$ for a premium of €0.02 per U.S. dollar. Currently, six-month interest rate is 2.5 percent in the euro zone and 3.0 percent in the United States.
If Airbus decides to hedge using put options on U.S. dollars, what would be the "expected" euro proceeds from the American sale Assume that Airbus regards the current forward exchange rate as an unbiased predictor of the future spot exchange rate.
If Airbus decides to hedge using put options on U.S. dollars, what would be the "expected" euro proceeds from the American sale Assume that Airbus regards the current forward exchange rate as an unbiased predictor of the future spot exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain cross-hedging and discuss the factors determining its effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You plan to visit Geneva, Switzerland in three months to attend an international business conference. You expect to incur the total cost of SF 5,000 for lodging, meals and transportation during your stay. As of today, the spot exchange rate is $0.60/SF and the three-month forward rate is $0.63/SF. You can buy the three-month call option on SF with the exercise rate of $0.64/SF for the premium of $0.05 per SF. Assume that your expected future spot exchange rate is the same as the forward rate. The three-month interest rate is 6 percent per annum in the United States and 4 percent per annum in Switzerland.
(a) Calculate your expected dollar cost of buying SF5,000 if you choose to hedge via call option on SF.
(b) Calculate the future dollar cost of meeting this SF obligation if you decide to hedge using a forward contract.
(c) At what future spot exchange rate will you be indifferent between the forward and option market hedges
(d) Illustrate the future dollar costs of meeting the SF payable against the future spot exchange rate under both the options and forward market hedges.
(a) Calculate your expected dollar cost of buying SF5,000 if you choose to hedge via call option on SF.
(b) Calculate the future dollar cost of meeting this SF obligation if you decide to hedge using a forward contract.
(c) At what future spot exchange rate will you be indifferent between the forward and option market hedges
(d) Illustrate the future dollar costs of meeting the SF payable against the future spot exchange rate under both the options and forward market hedges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Discuss and compare the costs of hedging via the forward contract and the options contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Do you think Bisno should remain strictly a shoe salesman or do you favor hedging his exposure If you favor hedging, which alternative would you recommend to him Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Airbus sold an A400 aircraft to Delta Airlines, a U.S. company, and billed $30 million payable in six months. Airbus is concerned about the euro proceeds from international sales and would like to control exchange risk. The current spot exchange rate is $1.05/€ and the six-month forward exchange rate is $1.10/€. Airbus can buy a six-month put option on U.S. dollars with a strike price of €0.95/$ for a premium of €0.02 per U.S. dollar. Currently, six-month interest rate is 2.5 percent in the euro zone and 3.0 percent in the United States.
At what future spot exchange do you think Airbus will be indifferent between the option and money market hedge
At what future spot exchange do you think Airbus will be indifferent between the option and money market hedge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Boeing just signed a contract to sell a Boeing 737 aircraft to Air France. Air France will be billed €20 million which is payable in one year. The current spot exchange rate is $1.05/€ and the one-year forward rate is $1.10/€. The annual interest rate is 6.0% in the U.S. and 5.0% in France. Boeing is concerned with the volatile exchange rate between the dollar and the euro and would like to hedge exchange exposure.
(a) It is considering two hedging alternatives: sell the euro proceeds from the sale forward or borrow euros from Credit Lyonnaise against the euro receivable. Which alternative would you recommend Why
(b) Other things being equal, at what forward exchange rate would Boeing be indifferent between the two hedging methods
(a) It is considering two hedging alternatives: sell the euro proceeds from the sale forward or borrow euros from Credit Lyonnaise against the euro receivable. Which alternative would you recommend Why
(b) Other things being equal, at what forward exchange rate would Boeing be indifferent between the two hedging methods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are the advantages of a currency options contract as a hedging tool compared with the forward contract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What are Diva's projected profits for the fiscal year ending September 1995

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose that Baltimore Machinery sold a drilling machine to a Swiss firm and gave the Swiss client a choice of paying either $10,000 or SF 15,000 in three months.
(a) In the above example, Baltimore Machinery effectively gave the Swiss client a free option to buy up to $10,000 dollars using Swiss franc. What is the 'implied' exercise exchange rate
(b) If the spot exchange rate turns out to be $0.62/SF, which currency do you think the Swiss client will choose to use for payment What is the value of this free option for the Swiss client
(c) What is the best way for Baltimore Machinery to deal with the exchange exposure
(a) In the above example, Baltimore Machinery effectively gave the Swiss client a free option to buy up to $10,000 dollars using Swiss franc. What is the 'implied' exercise exchange rate
(b) If the spot exchange rate turns out to be $0.62/SF, which currency do you think the Swiss client will choose to use for payment What is the value of this free option for the Swiss client
(c) What is the best way for Baltimore Machinery to deal with the exchange exposure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Airbus sold an A400 aircraft to Delta Airlines, a U.S. company, and billed $30 million payable in six months. Airbus is concerned about the euro proceeds from international sales and would like to control exchange risk. The current spot exchange rate is $1.05/€ and the six-month forward exchange rate is $1.10/€. Airbus can buy a six-month put option on U.S. dollars with a strike price of €0.95/$ for a premium of €0.02 per U.S. dollar. Currently, six-month interest rate is 2.5 percent in the euro zone and 3.0 percent in the United States.
Compute the guaranteed euro proceeds from the American sale if Airbus decides to hedge using a forward contract.
Compute the guaranteed euro proceeds from the American sale if Airbus decides to hedge using a forward contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose your company has purchased a put option on the euro to manage exchange exposure associated with an account receivable denominated in that currency. In this case, your company can be said to have an 'insurance' policy on its receivable. Explain in what sense this is so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Cray Research sold a super computer to the Max Planck Institute in Germany on credit and invoiced €10 million payable in six months. Currently, the six-month forward exchange rate is $1.10/€ and the foreign exchange advisor for Cray Research predicts that the spot rate is likely to be $1.05/€ in six months.
(a) What is the expected gain/loss from the forward hedging
(b) If you were the financial manager of Cray Research, would you recommend hedging this euro receivable Why or why not
(c) Suppose the foreign exchange advisor predicts that the future spot rate will be the same as the forward exchange rate quoted today. Would you recommend hedging in this case Why or why not
(a) What is the expected gain/loss from the forward hedging
(b) If you were the financial manager of Cray Research, would you recommend hedging this euro receivable Why or why not
(c) Suppose the foreign exchange advisor predicts that the future spot rate will be the same as the forward exchange rate quoted today. Would you recommend hedging in this case Why or why not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Princess Cruise Company (PCC) purchased a ship from Mitsubishi Heavy Industry. PCC owes Mitsubishi Heavy Industry 500 million yen in one year. The current spot rate is 124 yen per dollar and the one-year forward rate is 110 yen per dollar. The annual interest rate is 5% in Japan and 8% in the U.S. PCC can also buy a one-year call option on yen at the strike price of $.0081 per yen for a premium of.014 cents per yen.
(a) Compute the future dollar costs of meeting this obligation using the money market hedge and the forward hedges.
(b) Assuming that the forward exchange rate is the best predictor of the future spot rate, compute the expected future dollar cost of meeting this obligation when the option hedge is used.
(c) At what future spot rate do you think PCC may be indifferent between the option and forward hedge
(a) Compute the future dollar costs of meeting this obligation using the money market hedge and the forward hedges.
(b) Assuming that the forward exchange rate is the best predictor of the future spot rate, compute the expected future dollar cost of meeting this obligation when the option hedge is used.
(c) At what future spot rate do you think PCC may be indifferent between the option and forward hedge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How would you define transaction exposure How is it different from economic exposure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Recent surveys of corporate exchange risk management practices indicate that many U.S. firms simply do not hedge. How would you explain this result

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What factors affect a firm's exposure to exchange risk How much exposure to exchange risk does Diva shoes have in April 1995

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider a U.S.-based company that exports goods to Switzerland. The U.S. Company expects to receive payment on a shipment of goods in three months. Because the payment will be in Swiss francs, the U.S. Company wants to hedge against a decline in the value of the Swiss franc over the next three months. The U.S. risk-free rate is 2 percent, and the Swiss risk-free rate is 5 percent. Assume that interest rates are expected to remain fixed over the next six months. The current spot rate is $0.5974
a. Indicate whether the U.S. Company should use a long or short forward contract to hedge currency risk.
b. Calculate the no-arbitrage price at which the U.S. Company could enter into a forward contract that expires in three months.
c. It is now 30 days since the U.S. Company entered into the forward contract. The spot rate is $0.55. Interest rates are the same as before. Calculate the value of the U.S. Company's forward position.
a. Indicate whether the U.S. Company should use a long or short forward contract to hedge currency risk.
b. Calculate the no-arbitrage price at which the U.S. Company could enter into a forward contract that expires in three months.
c. It is now 30 days since the U.S. Company entered into the forward contract. The spot rate is $0.55. Interest rates are the same as before. Calculate the value of the U.S. Company's forward position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Airbus sold an A400 aircraft to Delta Airlines, a U.S. company, and billed $30 million payable in six months. Airbus is concerned about the euro proceeds from international sales and would like to control exchange risk. The current spot exchange rate is $1.05/€ and the six-month forward exchange rate is $1.10/€. Airbus can buy a six-month put option on U.S. dollars with a strike price of €0.95/$ for a premium of €0.02 per U.S. dollar. Currently, six-month interest rate is 2.5 percent in the euro zone and 3.0 percent in the United States.
If Airbus decides to hedge using money market instruments, what action does Airbus need to take What would be the guaranteed euro proceeds from the American sale in this case
If Airbus decides to hedge using money market instruments, what action does Airbus need to take What would be the guaranteed euro proceeds from the American sale in this case

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Should a firm hedge Why or why not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
IBM purchased computer chips from NEC, a Japanese electronics concern, and was billed ¥250 million payable in three months. Currently, the spot exchange rate is ¥105/$ and the three-month forward rate is ¥100/$. The three-month money market interest rate is 8 percent per annum in the U.S. and 7 percent per annum in Japan. The management of IBM decided to use the money market hedge to deal with this yen account payable.
(a) Explain the process of a money market hedge and compute the dollar cost of meeting the yen obligation.
(b) Conduct the cash flow analysis of the money market hedge.
(a) Explain the process of a money market hedge and compute the dollar cost of meeting the yen obligation.
(b) Conduct the cash flow analysis of the money market hedge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that you are a U.S.-based importer of goods from the United Kingdom. You expect the value of the pound to increase against the U.S. dollar over the next 30 days. You will be making payment on a shipment of imported goods in 30 days and want to hedge your currency exposure. The U.S. risk-free rate is 5.5 percent, and the U.K. risk-free rate is 4.5 percent. These rates are expected to remain unchanged over the next month. The current spot rate is $1.50.
a. Indicate whether you should use a long or short forward contract to hedge currency risk.
b. Calculate the no-arbitrage price at which you could enter into a forward contract that expires in three months.
c. Move forward 10 days. The spot rate is $1.53. Interest rates are unchanged. Calculate the value of your forward position.
a. Indicate whether you should use a long or short forward contract to hedge currency risk.
b. Calculate the no-arbitrage price at which you could enter into a forward contract that expires in three months.
c. Move forward 10 days. The spot rate is $1.53. Interest rates are unchanged. Calculate the value of your forward position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



