Deck 41: Personal Income Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 41: Personal Income Taxes
1
When there is only one employer in a city, the model that economists use is one for
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) perfect competition.
D) monopolistic competition.
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) perfect competition.
D) monopolistic competition.
The objective is to understand the situation where there is only one employer in a city.
Note that a monopoly is where there is only one seller while monopsony is a case where there is only one buyer in the market. The perfect competition on the other hand is a situation of larger number of buyers and sellers with the identical product being traded in the market. However when the products are differentiated, then that market structure is called monopolistic competition.
Thus, a case where there is only one employer which means that there is only one buyer of labour in the market, then this model will be called a case of monopsony and hence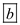 is the correct answer.
is the correct answer.
Note that a monopoly is where there is only one seller while monopsony is a case where there is only one buyer in the market. The perfect competition on the other hand is a situation of larger number of buyers and sellers with the identical product being traded in the market. However when the products are differentiated, then that market structure is called monopolistic competition.
Thus, a case where there is only one employer which means that there is only one buyer of labour in the market, then this model will be called a case of monopsony and hence
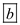 is the correct answer.
is the correct answer. 2
Explain why the marginal resource cost rises faster than the supply curve for labor.
When the firm hires more labor, it needs to pay more to all the workers and not only to the new workers. Thus its cost do not rise along the supply curve, it rises faster than the increase in the supply in the labor market.
The cost of increasing the hiring of labor is thus not the supply curve but another curve which is steeper than the supply curve: the marginal resource curve. This shows the increase in total labor cost to the firm of buying increasing amounts of labor. Henceforth, the marginal resource cost rises faster than the supply curve for labor.
The cost of increasing the hiring of labor is thus not the supply curve but another curve which is steeper than the supply curve: the marginal resource curve. This shows the increase in total labor cost to the firm of buying increasing amounts of labor. Henceforth, the marginal resource cost rises faster than the supply curve for labor.
3
When there are many employers in a city and one union, the model that economists use is one for
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) perfect competition.
D) monopolistic competition.
A) monopoly.
B) monopsony.
C) perfect competition.
D) monopolistic competition.
The objective is to understand the situation where there is only one union and many employers in a city.
Note that a monopoly is where there is only one seller while monopsony is a case where there is only one buyer in the market. The perfect competition on the other hand is a situation of larger number of buyers and sellers with the identical product being traded in the market. However when the products are differentiated, then that market structure is called monopolistic competition.
Thus, a case where there is only one union which basically is a seller of labour to number of employers in the city will be called a case of monopoly and hence is the correct answer.
is the correct answer.
Note that a monopoly is where there is only one seller while monopsony is a case where there is only one buyer in the market. The perfect competition on the other hand is a situation of larger number of buyers and sellers with the identical product being traded in the market. However when the products are differentiated, then that market structure is called monopolistic competition.
Thus, a case where there is only one union which basically is a seller of labour to number of employers in the city will be called a case of monopoly and hence
 is the correct answer.
is the correct answer. 4
Explain why, in a negotiation between a monopolistic union and a monopsonistic company in a town, there would not be a single outcome of wage and quantity like there is if only one of those two conditions hold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under perfect competition marginal resource cost _____ supply; under monopsony marginal resource cost _____ supply.
A) equals; equals
B) equals; is greater than
C) equals; is less than
D) is greater than; is less than
A) equals; equals
B) equals; is greater than
C) equals; is less than
D) is greater than; is less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain why there has been such a reduction in the number of work stoppages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A union that trains and restricts supply has an effect on the supply curve that moves it to the _____ and, at a point, makes it _____.
A) left; vertical
B) left; horizontal
C) right; vertical
D) right; horizontal
A) left; vertical
B) left; horizontal
C) right; vertical
D) right; horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the context of the monopoly-monopsony tension to explain why public employees are so heavily unionized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Labor unions have greater representation in _____ employees.
A) public
B) service
C) manufacturing
D) retail
A) public
B) service
C) manufacturing
D) retail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the past 30 years work stoppages have
A) plummeted.
B) remained constant.
C) increased slowly.
D) increased rapidly.
A) plummeted.
B) remained constant.
C) increased slowly.
D) increased rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



