Deck 5: Capacity Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Capacity Management
1
A work center consists of 3 machines each working a 16-hour day for 5 days a week. What is the weekly available time?
Available time: It can be defined as the number of hours that could be used in a workstation. It depends upon the number of working machines, allocated workforce, and hours of operation in a week.
Consider the following information in the workstation:
Number of machines = 3 machines
Each machine works (hours per day) =16 hours a day
Number of working days in a week = 5 working days in a week.
Calculate the weekly available time taken by all three machines using the following formula: …… (1)
…… (1)
Substitute the values in the equation (1) Therefore, the weekly available time for a work center, consisting 3 machines, 16 daily hours and 5 working days a week is 240 hours per week.
Therefore, the weekly available time for a work center, consisting 3 machines, 16 daily hours and 5 working days a week is 240 hours per week.
Consider the following information in the workstation:
Number of machines = 3 machines
Each machine works (hours per day) =16 hours a day
Number of working days in a week = 5 working days in a week.
Calculate the weekly available time taken by all three machines using the following formula:
 …… (1)
…… (1)Substitute the values in the equation (1)
 Therefore, the weekly available time for a work center, consisting 3 machines, 16 daily hours and 5 working days a week is 240 hours per week.
Therefore, the weekly available time for a work center, consisting 3 machines, 16 daily hours and 5 working days a week is 240 hours per week. 2
What are the responsibilities of capacity management?
Capacity is the rate of work that can be carried out in a particular time period. Capacity is the ability of an employee or labor, appliance, work center, plant, or business to produce output for a particular time period.
Capacity management is the authority for deciding the ability required to accomplish the preference plans along with providing, examining and controlling the ability so the preference plan can be fulfilled.
Responsibilities of capacity management :
(1) Capacity management is responsible for confirming the capacity management tools and procedures for efficient automation work.
(2) Capacity management has drawn up capacity plans related to every stage of service decided.
(3) Capacity management is responsible for managing and justifying demand for products and services.
(4) Capacity management should act as a proficient and consultant on all capacity and performance issues and requirements.
Capacity management is the authority for deciding the ability required to accomplish the preference plans along with providing, examining and controlling the ability so the preference plan can be fulfilled.
Responsibilities of capacity management :
(1) Capacity management is responsible for confirming the capacity management tools and procedures for efficient automation work.
(2) Capacity management has drawn up capacity plans related to every stage of service decided.
(3) Capacity management is responsible for managing and justifying demand for products and services.
(4) Capacity management should act as a proficient and consultant on all capacity and performance issues and requirements.
3
The work center in problem is utilized 75% of the time. What are the hours per week actually worked?
Calculate hours per week actually worked:
Utilization is the percentage of time that work place is active and matched up to the available time. Utilization is a scale of how exclusively a resource is being used to manufacture goods and services.
Analysis:
In a work station there are 4 machines. Each machine works for 16 hours a day. There are 5 working days in a week. The utilization of time is 75 percent. Using formula of utilization, estimate hours per week actually worked.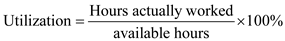 From problem 1:
From problem 1:
In a work station, there are 4 machines. Each machine works 16 hours per day. There are 5 working days in a week. Calculate the weekly hours taken by all four machines. Following formula is used to calculate available time.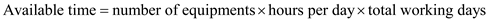 By substituting the values,
By substituting the values, 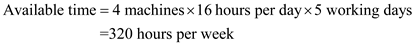 Substitute, 75 percent as utilization and 320 as hours available per week. We have to calculate hours per week actually worked.
Substitute, 75 percent as utilization and 320 as hours available per week. We have to calculate hours per week actually worked. 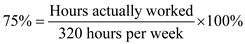
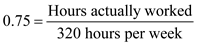 …… (Divided by 100 both side)
…… (Divided by 100 both side) 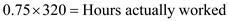 …… (Cross multiplication)
…… (Cross multiplication) 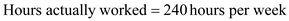 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
If the utilization capacity of 4 machines is 75 percent and total hours available is 320 hours per week, then actual worked hours per week is 240 hours per week.
Utilization is the percentage of time that work place is active and matched up to the available time. Utilization is a scale of how exclusively a resource is being used to manufacture goods and services.
Analysis:
In a work station there are 4 machines. Each machine works for 16 hours a day. There are 5 working days in a week. The utilization of time is 75 percent. Using formula of utilization, estimate hours per week actually worked.
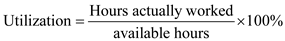 From problem 1:
From problem 1: In a work station, there are 4 machines. Each machine works 16 hours per day. There are 5 working days in a week. Calculate the weekly hours taken by all four machines. Following formula is used to calculate available time.
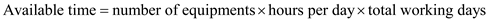 By substituting the values,
By substituting the values, 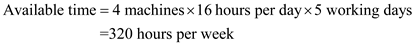 Substitute, 75 percent as utilization and 320 as hours available per week. We have to calculate hours per week actually worked.
Substitute, 75 percent as utilization and 320 as hours available per week. We have to calculate hours per week actually worked. 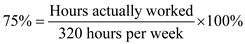
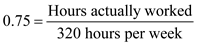 …… (Divided by 100 both side)
…… (Divided by 100 both side) 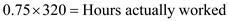 …… (Cross multiplication)
…… (Cross multiplication) 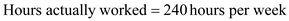 Conclusion:
Conclusion: If the utilization capacity of 4 machines is 75 percent and total hours available is 320 hours per week, then actual worked hours per week is 240 hours per week.
4
What is capacity planning?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the efficiency of the work center in problem 5.1 is 120%, what is the rated capacity of the work center?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe the three steps of capacity planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A work center consisting of 7 machines is operated 16 hours a day for a 5-day week. Utilization is 80%, and efficiency is 110%. What is the rated weekly capacity in standard hours?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Relate the three levels of priority planning to capacity planning. Describe each level in terms of the detail and the time horizons used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A work center consists of 4 machines working 8 hours a day for a 5-day week. If the utilization is 80% and the efficiency is 90%, what is the rated capacity of the work center?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is capacity requirements planning? At what level of the priority planning process does it occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Over a period of 4 weeks, a work center produced 50, 45, 42, and 52 standard hours of work. What is the demonstrated capacity of the work center?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are the inputs to the CRP process? Where is this information obtained?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In an 11-week period, a work center produces 1050 standard hours of work. What is the measured capacity of the work center?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe each of the following and the information they contain.
a. Open order.
b. Routing.
c. Work center.
a. Open order.
b. Routing.
c. Work center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In 1 week, a work center produces 75 standard hours of work. The hours scheduled are 80, and 72 hours are actually worked. Calculate the utilization and efficiency of the work center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is a shop calendar? Why is it needed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A work center consisting of 3 machines operates 40 hours a week. In a 4-week period, it actually worked 355 hours and produced 475 standard hours of work. Calculate the utilization and efficiency of the work center. What is the demonstrated weekly capacity of the work center?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which file would you find the following information?
a. A scheduled receipt.
b. A planned receipt.
c. Efficiency and utilization.
d. Sequence of operations on a part.
a. A scheduled receipt.
b. A planned receipt.
c. Efficiency and utilization.
d. Sequence of operations on a part.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A firm wishes to determine the efficiency and utilization of a work center composed of 5 machines each working 16 hours per day for 5 days a week. A study undertaken by the materials management department found that over the past 50 weeks the work center was actually working for 16,000 hours, and work performed was 15,200 standard hours. Calculate the utilization, efficiency, and demonstrated weekly capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Define capacity available.What are the four factors that affect it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How many standard hours are needed to run an order of 200 pieces if the setup time is 1.3 hours and the run time 0.3 hours per piece? How many actual hours are needed at the work center if the efficiency is 130% and the utilization is 70%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why is standard time usually used to measure capacity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How many standard hours are needed to run an order of 500 pieces if the setup time is 2.0 hours and the run time 0.3 hours per piece? How many actual hours are needed at the work center if the efficiency is 110% and the utilization is 85%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are rated capacity, utilization, and efficiency? How are they related?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A work center has the following open and planned orders for week 4. Calculate the total standard time required (load). 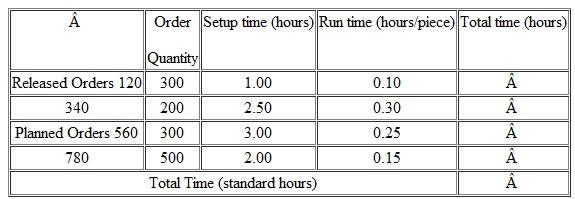


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is measured or demonstrated capacity? How is it different from rated capacity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A work center has the following open and planned orders for week 4. Calculate the total standard time required (load). 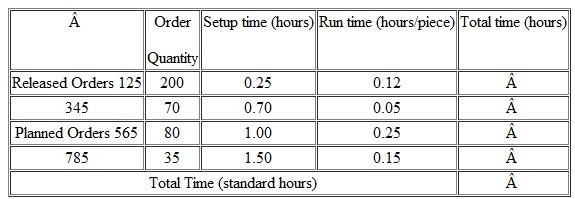


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is load?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using the information in the following route file, open order file, and MRP planned orders, calculate the load on the work center. 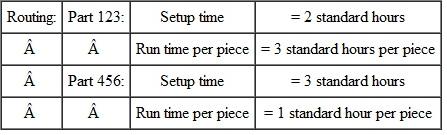 Open Orders for parts
Open Orders for parts 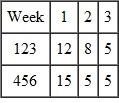 Planned Orders for parts
Planned Orders for parts 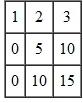 Load report
Load report 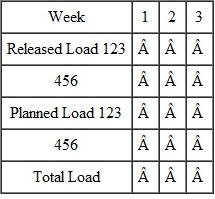
 Open Orders for parts
Open Orders for parts  Planned Orders for parts
Planned Orders for parts  Load report
Load report 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is a work center load report? What information does it contain?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Complete the following load report and suggest possible courses of action. 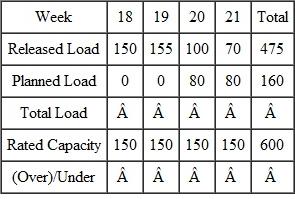


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is a schedule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Back schedule the following shop order. All times are given in days. Move time between operations is 1 day, and wait time is 1 day. Due date is day 150. Assume orders start at the beginning of a day and finish at the end of a day. 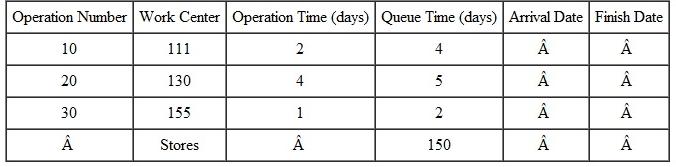


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Describe the process of back scheduling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Back schedule the following shop order. All times are given in days. Move time between operations is 1 day, and wait time is 1 day. Due date is day 200. Assume orders start at the beginning of a day and finish at the end of a day. 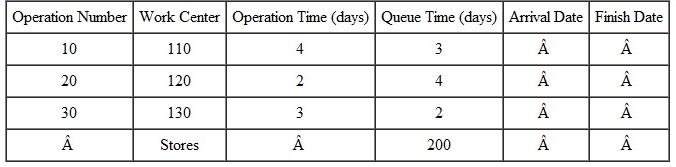


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What are the two ways of balancing capacity available and load? Which is preferred? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What are some of the ways capacity available can be altered in the short run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why is feedback necessary in a control system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What might be some of the problems in scheduling rated capacity too closely to the load?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How is safety capacity used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Discuss the nature and probable sources of the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Examine the rough-cut capacity situation using the data Jason gathered. Discuss the results and how they are linked to the problems identified in question 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the information and your knowledge of the situation to develop a complete plan for Jason to use in the future. Part of this plan should be to build and demonstrate the approach to master scheduling for the data given in the case

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



