Deck 21: Economics, Ethics, and Public Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Economics, Ethics, and Public Policy
1
The usual argument against government bureaucracy is that:
A) with budget constraints public bureaucracies won't have an incentive to maintain sufficient quality.
B) with budget constraints public bureaucracies will have to cut costs at the expense of quality.
C) without the profit incentive public bureaucracies will have to increase costs to maintain the quality.
D) without the profit incentive public bureaucracies won't have an incentive to cut costs.
A) with budget constraints public bureaucracies won't have an incentive to maintain sufficient quality.
B) with budget constraints public bureaucracies will have to cut costs at the expense of quality.
C) without the profit incentive public bureaucracies will have to increase costs to maintain the quality.
D) without the profit incentive public bureaucracies won't have an incentive to cut costs.
D
2
Careful design of an incentive scheme can narrow the gap between:
A) what you pay for and what you want.
B) what you want and what you do not want.
C) what you pay for and what you do not pay for.
D) what you want and what you do not pay for.
A) what you pay for and what you want.
B) what you want and what you do not want.
C) what you pay for and what you do not pay for.
D) what you want and what you do not pay for.
A
3
Paying car salespeople by commission may lead to:
A) overly aggressive car salespeople and unethical sales pitches.
B) salespeople willing to work unpleasant hours.
C) fewer repeat customers for the car dealership.
D) All of these possibilities are correct.
A) overly aggressive car salespeople and unethical sales pitches.
B) salespeople willing to work unpleasant hours.
C) fewer repeat customers for the car dealership.
D) All of these possibilities are correct.
D
4
Piece rate pay works better when:
A) output is harder to measure.
B) output is easier to measure.
C) quality matters a great deal.
D) no monitoring is required.
A) output is harder to measure.
B) output is easier to measure.
C) quality matters a great deal.
D) no monitoring is required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose that a car dealer in California advertises that its sales staff is not paid on commission. Which of the following is correct with regards to the strategy of this advertising?
A) Car dealers who rely on repeat business prefer a low- pressure, informative sales staff.
B) Car dealers who rely on selling cars to first-time buyers prefer a lower-pressure, informative sales staff.
C) Car dealers who rely on repeat business prefer high- pressure sales tactics.
D) Car dealers who rely on selling cars to first-time buyers prefer high-pressure sales tactics.
A) Car dealers who rely on repeat business prefer a low- pressure, informative sales staff.
B) Car dealers who rely on selling cars to first-time buyers prefer a lower-pressure, informative sales staff.
C) Car dealers who rely on repeat business prefer high- pressure sales tactics.
D) Car dealers who rely on selling cars to first-time buyers prefer high-pressure sales tactics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What evidence was put forth for teachers cheating on standardized tests?
A) groups of students who had the same exact right and wrong answers
B) students who missed easy questions but got the hard questions right
C) students with high test scores in one year but who earned low test scores the next year
D) All of these things were found to have occurred.
A) groups of students who had the same exact right and wrong answers
B) students who missed easy questions but got the hard questions right
C) students with high test scores in one year but who earned low test scores the next year
D) All of these things were found to have occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Piece rates do not work well when:
A) workers use tools in production.
B) quality is not important.
C) quality control is important and simple to perform.
D) quality is important but quality control is expensive.
A) workers use tools in production.
B) quality is not important.
C) quality control is important and simple to perform.
D) quality is important but quality control is expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the concern with private prisons?
A) Private prisons may cut costs to increase profit at the expense of prisoner rehabilitation programs, civil rights, and safety.
B) The increased efficiency of private prisons may put public prisons out of business.
C) Private prisons will cost taxpayers too much money to operate because they will cut costs in the short run increasing recidivism rates.
D) Private prisons are likely to overemphasize quality and cost taxpayers too much money in the long run.
A) Private prisons may cut costs to increase profit at the expense of prisoner rehabilitation programs, civil rights, and safety.
B) The increased efficiency of private prisons may put public prisons out of business.
C) Private prisons will cost taxpayers too much money to operate because they will cut costs in the short run increasing recidivism rates.
D) Private prisons are likely to overemphasize quality and cost taxpayers too much money in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cheap cars are sometimes lemons. The lesson here is that:
A) used car dealers must never be trusted.
B) incentives must be tied to effort.
C) what you pay for is not always what you want.
D) money is not everything.
A) used car dealers must never be trusted.
B) incentives must be tied to effort.
C) what you pay for is not always what you want.
D) money is not everything.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Schools are rewarded for how well their students perform on standardized test scores but allowed to exclude test scores for learning disabled students when submitting results to the state. What incentive does this policy provide?
A) work with low-performing students to increase their test scores
B) channel low-performing students into learning disability programs
C) increase vigilance in testing for learning disabilities
D) hire more special needs educators for the public school system
A) work with low-performing students to increase their test scores
B) channel low-performing students into learning disability programs
C) increase vigilance in testing for learning disabilities
D) hire more special needs educators for the public school system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When IBM paid programmers by the line, IBM programmers produced:
A) small amounts of low-quality code.
B) small amounts of high-quality code.
C) large amounts of low-quality code.
D) large amounts of high-quality code.
A) small amounts of low-quality code.
B) small amounts of high-quality code.
C) large amounts of low-quality code.
D) large amounts of high-quality code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following would be the LEAST likely result of efficient private prisons replacing inefficient public prisons?
A) Strong profit motive gives private prisons stronger incentives than public prisons to cut costs.
B) Strong profit incentives would encourage private prisons to increase quality rather than cut costs.
C) When quality and cost-cutting go together, private prisons have a strong incentive to increase quality.
D) Lower costs result, but at the expense of quality since public prisons have no incentive to cut costs and only care about producing high quality.
A) Strong profit motive gives private prisons stronger incentives than public prisons to cut costs.
B) Strong profit incentives would encourage private prisons to increase quality rather than cut costs.
C) When quality and cost-cutting go together, private prisons have a strong incentive to increase quality.
D) Lower costs result, but at the expense of quality since public prisons have no incentive to cut costs and only care about producing high quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The famous economist ________ studied teacher cheating in ________ public schools.
A) Steven Levitt; Chicago
B) Carl Menger; Detroit
C) Robert Barro; Boston
D) Joseph Schumpeter; Philadelphia
A) Steven Levitt; Chicago
B) Carl Menger; Detroit
C) Robert Barro; Boston
D) Joseph Schumpeter; Philadelphia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following programs would NOT be favored by economists Hart, Shleifer, and Vishny (HSV) and why?
A) Public prisons replace private prisons because tight budget constraints reduce the incentive to increase quality.
B) Public prisons replace private prisons because the profit motive increases the incentive to increase quality.
C) Private prisons replace public prisons because the profit motive encourages cost-cutting at the expense of quality.
D) Private prisons replace pubic prisons because slack budget constraints increase the incentive to increase quality.
A) Public prisons replace private prisons because tight budget constraints reduce the incentive to increase quality.
B) Public prisons replace private prisons because the profit motive increases the incentive to increase quality.
C) Private prisons replace public prisons because the profit motive encourages cost-cutting at the expense of quality.
D) Private prisons replace pubic prisons because slack budget constraints increase the incentive to increase quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Tying executive compensation to stock prices may create incentives for:
A) CEOs to work harder and increase the profitability of the firm.
B) CEOs to overstate the firm's financial status.
C) Enron-type scandals.
D) All of these possibilities are correct.
A) CEOs to work harder and increase the profitability of the firm.
B) CEOs to overstate the firm's financial status.
C) Enron-type scandals.
D) All of these possibilities are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
CEOs in the 1980s were given much stronger incentives to increase their firm's stock price by receiving:
A) an extraordinary amount of salary.
B) stock options.
C) a lucrative benefit package.
D) an annual vacation package.
A) an extraordinary amount of salary.
B) stock options.
C) a lucrative benefit package.
D) an annual vacation package.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The stronger the incentives:
A) the less it pays to invest in careful measurement and auditing.
B) the more it pays to invest in careful measurement and auditing.
C) the less important the effects.
D) the stronger the effects.
A) the less it pays to invest in careful measurement and auditing.
B) the more it pays to invest in careful measurement and auditing.
C) the less important the effects.
D) the stronger the effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
It is true that incentives matter, and:
A) getting incentives right is not a major issue.
B) the right incentives can be hard to figure out.
C) the ideal would be to remove all incentives.
D) wrong incentives are not important.
A) getting incentives right is not a major issue.
B) the right incentives can be hard to figure out.
C) the ideal would be to remove all incentives.
D) wrong incentives are not important.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The incentive to cut costs is ________ for ________ prisons (as/than) it is for ________ prisons.
A) about the same; private; public
B) smaller; private; public
C) greater; private; public
D) greater; public; private
A) about the same; private; public
B) smaller; private; public
C) greater; private; public
D) greater; public; private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the two statements: I. The closer "what you pay for" is to "what you want," then the more you can rely on strong incentives. II. If you can't bridge the gap between "what you pay for" and "what you want" then strong incentive schemes can be better than weak incentive schemes.
A) I is true; II is false
B) I is false; II is true
C) I and II are both true.
D) I and II are both false.
A) I is true; II is false
B) I is false; II is true
C) I and II are both true.
D) I and II are both false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
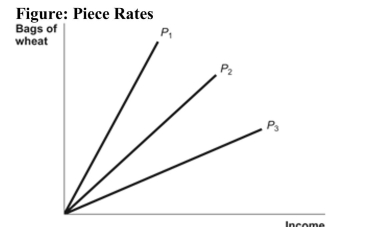 Reference: Ref 21-1 (Figure: Piece Rates) Refer to the figure. A piece rate is offered for every 10 bags of wheat that workers fill. Which of the three piece rates plotted in the figure above has the highest dollar value?
Reference: Ref 21-1 (Figure: Piece Rates) Refer to the figure. A piece rate is offered for every 10 bags of wheat that workers fill. Which of the three piece rates plotted in the figure above has the highest dollar value?A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) All three piece rates are of equal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A piece rate is:
A) any payment system that pays workers directly for their input.
B) any payment system that pays workers directly for their output.
C) any payment paid in pieces to workers.
D) the percentage of a payment paid weekly to workers.
A) any payment system that pays workers directly for their input.
B) any payment system that pays workers directly for their output.
C) any payment paid in pieces to workers.
D) the percentage of a payment paid weekly to workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is the most correct statement about piece rates?
A) A piece rate firm would attract less productive workers because piece rates reduce the incentive to work hard.
B) A piece rate firm would attract more productive workers because piece rates usually require some form of quality control.
C) A piece rate firm would attract less productive workers because piece rates do not work well when quality is important.
D) A piece rate firm would attract more productive workers because piece rates give productive workers a chance to earn more money.
A) A piece rate firm would attract less productive workers because piece rates reduce the incentive to work hard.
B) A piece rate firm would attract more productive workers because piece rates usually require some form of quality control.
C) A piece rate firm would attract less productive workers because piece rates do not work well when quality is important.
D) A piece rate firm would attract more productive workers because piece rates give productive workers a chance to earn more money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is TRUE? I. Piece rate systems will attract more productive workers than hourly-wage plans. II. Workers may fear that the piece rate could be lowered in the future. III. Factory managers who increased productivity in the Soviet Union were accused of previous laziness.
A) I and II only
B) III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The difference between a price rate and an hourly rate is:
A) a piece rate is a wage for each piece of work completed whereas an hourly rate is a rate for each hour of work completed.
B) a piece rate is only offered for noncontractual workers whereas an hourly rate is only offered for contractual workers.
C) a piece rate is not tied to effort whereas an hourly wage is tied to effort.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) a piece rate is a wage for each piece of work completed whereas an hourly rate is a rate for each hour of work completed.
B) a piece rate is only offered for noncontractual workers whereas an hourly rate is only offered for contractual workers.
C) a piece rate is not tied to effort whereas an hourly wage is tied to effort.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Even though firms and workers can both benefit from piece rates, piece rates are sometimes not implemented because of:
A) government regulation.
B) a shortage of workers.
C) issues of distrust.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) government regulation.
B) a shortage of workers.
C) issues of distrust.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When using a piece rate system:
A) it is important to measure and observe worker quality.
B) a firm may attract more unproductive workers.
C) a firm will experience a decrease in output.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) it is important to measure and observe worker quality.
B) a firm may attract more unproductive workers.
C) a firm will experience a decrease in output.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The main advantage of piece rate pay is:
A) decreased labor costs.
B) increased quality.
C) increased productivity.
D) easy implementation.
A) decreased labor costs.
B) increased quality.
C) increased productivity.
D) easy implementation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The riskier the payments are to workers, the:
A) more a firm must pay on average.
B) less a firm must pay on average.
C) more a firm must rely on piece rate pay.
D) fewer the workers who will take on work.
A) more a firm must pay on average.
B) less a firm must pay on average.
C) more a firm must rely on piece rate pay.
D) fewer the workers who will take on work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A piece rate system ________ earnings inequality.
A) has no effect on
B) increases
C) decreases
D) first increases then decreases
A) has no effect on
B) increases
C) decreases
D) first increases then decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
As performance pay is becoming more common in an economy:
A) wage rates would increase more than productivity in the economy.
B) the number of unemployed workers in the economy would also increase.
C) the inequality of earnings in the economy would also increase.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) wage rates would increase more than productivity in the economy.
B) the number of unemployed workers in the economy would also increase.
C) the inequality of earnings in the economy would also increase.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In order for a piece rate to result in high-quality output by workers, it requires:
A) no environmental risk.
B) the piece rate to be lower than the hourly wage.
C) good quality control.
D) workers to have equal abilities.
A) no environmental risk.
B) the piece rate to be lower than the hourly wage.
C) good quality control.
D) workers to have equal abilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The establishment of a piece rate system can lead to increased productivity and higher quality work if: I. the piece rate is considerably higher than existing wages. II. the workers are held responsible for the jobs that they personally complete. III. there is a reliable measure of quality control.
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A piece rate is:
A) the discounted present value of a day's worth of production output.
B) an hourly rate paid to mid-level managers.
C) a method to compensate workers for the number of units of output they produce.
D) the interest rate paid to finance a firm's output costs.
A) the discounted present value of a day's worth of production output.
B) an hourly rate paid to mid-level managers.
C) a method to compensate workers for the number of units of output they produce.
D) the interest rate paid to finance a firm's output costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a firm's owner is better able than the sales staff to bear the risk of a recession, weak incentives:
A) are worse than strong incentives.
B) may be mutually profitable.
C) should not be used.
D) would not be profitable.
A) are worse than strong incentives.
B) may be mutually profitable.
C) should not be used.
D) would not be profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
IBM paid programmers by the number of lines of code written, which resulted in:
A) too many lines of poor-quality code.
B) primarily high-quality code.
C) increased profits.
D) increased sales revenue.
A) too many lines of poor-quality code.
B) primarily high-quality code.
C) increased profits.
D) increased sales revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Piece rates do not work well when:
A) quality is important but quality control is expensive.
B) quality is important and quality control is not costly.
C) quality is not important and quality control is not costly.
D) quality is not important but quality control is expensive.
A) quality is important but quality control is expensive.
B) quality is important and quality control is not costly.
C) quality is not important and quality control is not costly.
D) quality is not important but quality control is expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
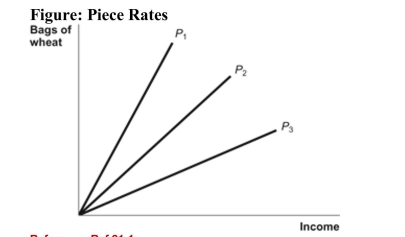 Reference: Ref 21-1 (Figure: Piece Rates) Refer to the figure. A piece rate is offered for every 10 bags of wheat that workers fill. Which of the three piece rates plotted in the figure above has the lowest dollar value?
Reference: Ref 21-1 (Figure: Piece Rates) Refer to the figure. A piece rate is offered for every 10 bags of wheat that workers fill. Which of the three piece rates plotted in the figure above has the lowest dollar value?A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) All three piece rates are of equal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Rajesh owns a pizza shop and pays his workers per pizza made. His ingredients are fresh and the recipe is good but he has few repeat customers and his pizzas are not tasty. He wants to redesign his incentive scheme. What would you suggest that Rajesh do?
A) pay his workers by the hour with a bonus tied to increased sales and customer satisfaction
B) threaten to fire them if they do not improve the quality of the pizza
C) continue paying the workers per pizza made
D) provide an extra bonus based on worker productivity
A) pay his workers by the hour with a bonus tied to increased sales and customer satisfaction
B) threaten to fire them if they do not improve the quality of the pizza
C) continue paying the workers per pizza made
D) provide an extra bonus based on worker productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Bjorn is a lazy worker with low productivity who works because he has to, not because he wants to. Amal is a very productive worker, enjoys what he does, and works quickly and accurately. Based on this information, which of the following is true?
A) The piece rate incentive scheme would be equally appropriate for both these workers.
B) Bjorn should be offered an hourly wage, whereas Amal should be offered a piece rate.
C) Amal should be offered an hourly wage, whereas Bjorn should be offered a piece rate.
D) The hourly wage incentive scheme would be equally appropriate for both these workers.
A) The piece rate incentive scheme would be equally appropriate for both these workers.
B) Bjorn should be offered an hourly wage, whereas Amal should be offered a piece rate.
C) Amal should be offered an hourly wage, whereas Bjorn should be offered a piece rate.
D) The hourly wage incentive scheme would be equally appropriate for both these workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Two students are given a project to work on together. Each student could either work or shirk. There is no individual accountability, each student receives the same grade regardless of how much work he or she contributes. One student is a weak student who prefers partying and the other is a serious student who prefers working hard. What is the most likely outcome in this scenario?
A) The serious student will end up completing most of the project alone.
B) The weak student will end up completing most of the project alone.
C) Both students will work equally hard on the project.
D) Neither student will complete the project.
A) The serious student will end up completing most of the project alone.
B) The weak student will end up completing most of the project alone.
C) Both students will work equally hard on the project.
D) Neither student will complete the project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a college professor implements a grading scale based on tournament theory:
A) students' grades cannot fall below a certain point.
B) students' grades will depend on how they perform relative to others in the class.
C) an absolute grading scale is used.
D) studying extra will not improve your overall grade.
A) students' grades cannot fall below a certain point.
B) students' grades will depend on how they perform relative to others in the class.
C) an absolute grading scale is used.
D) studying extra will not improve your overall grade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Job X pays a yearly salary of $55,000, regardless of the state of the economy. Job Y pays a yearly salary of $10,000 in a bad economy and $70,000 in a good economy. The probability of a bad economy is 0.30. Which job would most people prefer?
A) Job Y because the expected payoff of $80,000 is greater than $55,000.
B) Job X because $55,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y of $52,000.
C) Job X because $55,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y by $6,000.
D) Job Y because the expected payoff of $70,000 is greater than $55,000.
A) Job Y because the expected payoff of $80,000 is greater than $55,000.
B) Job X because $55,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y of $52,000.
C) Job X because $55,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y by $6,000.
D) Job Y because the expected payoff of $70,000 is greater than $55,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tournaments can tie rewards more closely to actions that an agent controls thereby:
A) increasing effort and risk.
B) reducing shirk and slack.
C) improving productivity and pay.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) increasing effort and risk.
B) reducing shirk and slack.
C) improving productivity and pay.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Tournaments are useful for rewarding worker effort whenever:
A) external factors, such as the quality of the good and the state of the economy, have little effect on workers' success.
B) workers are myopic and unaware that external factors play a significant role on sales.
C) workers are utility maximizers primarily concerned about their reputation in the community.
D) external factors, such as the quality of the good and the state of the economy, do affect workers success.
A) external factors, such as the quality of the good and the state of the economy, have little effect on workers' success.
B) workers are myopic and unaware that external factors play a significant role on sales.
C) workers are utility maximizers primarily concerned about their reputation in the community.
D) external factors, such as the quality of the good and the state of the economy, do affect workers success.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Job X pays a yearly salary of $52,000, regardless of the state of the economy. Job Y pays a yearly salary of $10,000 in a bad economy and $70,000 in a good economy. The probability of a bad economy is 0.30. Which job would most people prefer?
A) Job Y because the expected payoff is $70,000 seventy percent of the time.
B) Job X because it is more certain than the $52,000 expected payoff of Job Y.
C) Job X because $52,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y by $3,000.
D) Job Y because the expected payoff of $70,000 is greater than $55,000.
A) Job Y because the expected payoff is $70,000 seventy percent of the time.
B) Job X because it is more certain than the $52,000 expected payoff of Job Y.
C) Job X because $52,000 exceeds the expected payoff of Job Y by $3,000.
D) Job Y because the expected payoff of $70,000 is greater than $55,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In situations where worker productivity largely depends on factors outside the worker's control (e.g., the state of the economy):
A) piece rate systems are generally preferred to fixed salary.
B) workers may prefer stable pay to larger bonuses.
C) workers are more willing to trade-off stable pay for larger sales bonuses.
D) workers will see their salary increase during recessions.
A) piece rate systems are generally preferred to fixed salary.
B) workers may prefer stable pay to larger bonuses.
C) workers are more willing to trade-off stable pay for larger sales bonuses.
D) workers will see their salary increase during recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In ideal circumstances, tournaments ________ risk and ________ worker effort with rewards.
A) enhance; link
B) reduce; align
C) reduce; enhance
D) enhance; decrease
A) enhance; link
B) reduce; align
C) reduce; enhance
D) enhance; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When the owner of a firm sells "recession insurance" to her employees, it means that the:
A) employees sacrifice larger bonuses during good economic times in return for higher salaries during bad economic times.
B) owner of the firm earns higher profits during bad economic times by skimming off the workers' salaries.
C) employees are not allowed to quit the firm for higher pay during good economic times.
D) employees are not allowed to quit the firm during bad economic times.
A) employees sacrifice larger bonuses during good economic times in return for higher salaries during bad economic times.
B) owner of the firm earns higher profits during bad economic times by skimming off the workers' salaries.
C) employees are not allowed to quit the firm for higher pay during good economic times.
D) employees are not allowed to quit the firm during bad economic times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Paying sales staff bonuses based on the agents with the highest, second- and third-highest sales is called a:
A) strict ranking game.
B) players event.
C) tournament.
D) horse race scheme.
A) strict ranking game.
B) players event.
C) tournament.
D) horse race scheme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of tournament pay?
A) giving a bonus to the sales agent with the highest sales
B) giving a bonus to sales agents based on the gross amount of their sales
C) giving a bonus to the sales agent with the most hours of working
D) giving a bonus to sales agents based on the hours of overtime work
A) giving a bonus to the sales agent with the highest sales
B) giving a bonus to sales agents based on the gross amount of their sales
C) giving a bonus to the sales agent with the most hours of working
D) giving a bonus to sales agents based on the hours of overtime work

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Economists call a compensation scheme in which pay is based on relative performance a:
A) profit sharing plan.
B) bonus plan.
C) salary.
D) tournament.
A) profit sharing plan.
B) bonus plan.
C) salary.
D) tournament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One way a manager can reduce an agent's risk is to tie:
A) penalties more closely to the agent's effort.
B) bonuses more closely to the agent's sales.
C) rewards more closely to the actions that the agent can control.
D) pay directly to past performance.
A) penalties more closely to the agent's effort.
B) bonuses more closely to the agent's sales.
C) rewards more closely to the actions that the agent can control.
D) pay directly to past performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A good compensation scheme:
A) ties rewards to actions that an agent does not control.
B) ties rewards to actions that an agent controls.
C) will not increase performance in a poor economy.
D) is based on luck.
A) ties rewards to actions that an agent does not control.
B) ties rewards to actions that an agent controls.
C) will not increase performance in a poor economy.
D) is based on luck.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Today, a large fraction of executives' pay is tied to:
A) the level of sales of their firm.
B) bonuses of other executives.
C) the effort and work ethic of the executive.
D) the stock price of their firm.
A) the level of sales of their firm.
B) bonuses of other executives.
C) the effort and work ethic of the executive.
D) the stock price of their firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A very motivated and skilled salesperson may not have good sales if which of the following factors occurs? I. The product is of a low quality. II. The economy is in a recession. III. The price of the product is too high compared to competing products.
A) II only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) II only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When sales depend heavily on outside factors such as the state of the economy, strong incentives may:
A) be more expensive than they are worth.
B) be less expensive than they are worth.
C) equal what they are worth.
D) be worthless.
A) be more expensive than they are worth.
B) be less expensive than they are worth.
C) equal what they are worth.
D) be worthless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two students are given a project to work on together. Each student could either work or shirk. There is no individual accountability, each student receives the same grade regardless of how much work he or she contributes. One student is a weak student who prefers partying and the other is a serious student who prefers working hard. How can the teacher adjust the incentive scheme to ensure equal effort by both students?
A) Ask each student to evaluate the other and use that assessment in grading the project.
B) Ask the more serious student to put in as much effort as possible.
C) Ask the weaker student to put in as much effort as possible.
D) Leave the incentive scheme as is-the students will automatically put in equal effort.
A) Ask each student to evaluate the other and use that assessment in grading the project.
B) Ask the more serious student to put in as much effort as possible.
C) Ask the weaker student to put in as much effort as possible.
D) Leave the incentive scheme as is-the students will automatically put in equal effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following may make weak incentives mutually profitable for both owner and sales staff of an auto dealer?
A) If the sales staff is better able than the owner to bear the risk of a recession.
B) If the owner is better able than the sales staff to bear the risk of a recession.
C) If the owner and sales staff can equally bear the risk of a recession.
D) If neither the owner nor the sales staff has to bear the risk of a recession.
A) If the sales staff is better able than the owner to bear the risk of a recession.
B) If the owner is better able than the sales staff to bear the risk of a recession.
C) If the owner and sales staff can equally bear the risk of a recession.
D) If neither the owner nor the sales staff has to bear the risk of a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose the economy is in a recession. Which of the following is the best incentive scheme for the manager of a large auto sales center?
A) Threat of termination if one sale is not made each day.
B) Equal salary for all sales agents regardless of sales.
C) Bonuses for the sales agents with the highest gross level of sales.
D) Bonuses for the sales agents with the highest sales relative to other sales agents.
A) Threat of termination if one sale is not made each day.
B) Equal salary for all sales agents regardless of sales.
C) Bonuses for the sales agents with the highest gross level of sales.
D) Bonuses for the sales agents with the highest sales relative to other sales agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If executives were paid based on relative performance:
A) compensation would largely be based on luck.
B) there would be less volatility in executive pay.
C) stockholders would find it more difficult to monitor how much the executives are being paid.
D) executives would have less incentive to work hard since ability risk is now high.
A) compensation would largely be based on luck.
B) there would be less volatility in executive pay.
C) stockholders would find it more difficult to monitor how much the executives are being paid.
D) executives would have less incentive to work hard since ability risk is now high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Executive pay based on relative performance:
A) makes little sense, but has still been widely adopted.
B) makes little sense and has not been widely adopted.
C) makes a lot of sense and has been widely adopted.
D) makes a lot of sense, but has not been widely adopted.
A) makes little sense, but has still been widely adopted.
B) makes little sense and has not been widely adopted.
C) makes a lot of sense and has been widely adopted.
D) makes a lot of sense, but has not been widely adopted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following risks increases when a bad teacher grades on an absolute scale?
A) ability risk
B) environment risk
C) incentive risk
D) competition risk
A) ability risk
B) environment risk
C) incentive risk
D) competition risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When a teacher grades on a curve, it increases the incentive to study, particularly when:
A) students are of very different abilities.
B) students are of similar abilities.
C) the teacher is bad.
D) the teacher is good.
A) students are of very different abilities.
B) students are of similar abilities.
C) the teacher is bad.
D) the teacher is good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose an average student gets mistakenly enrolled in an honors class in high school. In the context of a tournament, which of the following risks is most likely to occur?
A) environment risk
B) registrar risk
C) school board risk
D) ability risk
A) environment risk
B) registrar risk
C) school board risk
D) ability risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Environment risk in sales can be described as:
A) the risk that an external factor such as customer preferences, recessionary pressures, or the quality of the product will depress sales.
B) the risk that certain members of the sales force will have better sales tactics than other members of the same sales force.
C) the risk that certain products will affect the availability of natural resources and the environment.
D) None of these answers describes environment risk.
A) the risk that an external factor such as customer preferences, recessionary pressures, or the quality of the product will depress sales.
B) the risk that certain members of the sales force will have better sales tactics than other members of the same sales force.
C) the risk that certain products will affect the availability of natural resources and the environment.
D) None of these answers describes environment risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Well-structured tournaments not only encourage competition but also:
A) encourage cooperation.
B) discourage cooperation.
C) encourage shirking.
D) discourage participation.
A) encourage cooperation.
B) discourage cooperation.
C) encourage shirking.
D) discourage participation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The problem with tying executive pay to stock prices is that:
A) many factors other than executive effort and ability affect stock prices.
B) executives can manipulate stock prices.
C) it is a complicated evaluation to make, riddled with strong assumptions.
D) executives prefer more straightforward compensation schemes that reduce their risk.
A) many factors other than executive effort and ability affect stock prices.
B) executives can manipulate stock prices.
C) it is a complicated evaluation to make, riddled with strong assumptions.
D) executives prefer more straightforward compensation schemes that reduce their risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Grading on a curve ________ environmental risk but ________ ability risk.
A) increases; decreases
B) reduces; increases
C) eliminates; increases
D) reduces; eliminates
A) increases; decreases
B) reduces; increases
C) eliminates; increases
D) reduces; eliminates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following would reduce ability risk in tournaments?
A) excluding players with low ability from contesting in tournaments
B) creating strong incentive for effort in tournaments
C) enhancing the rewards for players in tournaments
D) structuring tournaments so that rewards are closely tied to effort
A) excluding players with low ability from contesting in tournaments
B) creating strong incentive for effort in tournaments
C) enhancing the rewards for players in tournaments
D) structuring tournaments so that rewards are closely tied to effort

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
On American Idol, the winner of the competition gets a recording contract. An average person is randomly picked as a surprise entrant in the final round. Which of the following risks is most likely to occur in this tournament?
A) environment risk
B) sales risk
C) risk of recession
D) ability risk
A) environment risk
B) sales risk
C) risk of recession
D) ability risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Ability risk can be described as the risk that:
A) external factors such as customer preferences, the economy, or product quality will affect sales.
B) some members of a sales force will have a higher ability than others.
C) agents may appear to be high ability when they are actually low ability.
D) tournament pay may hide the true ability of some agents.
A) external factors such as customer preferences, the economy, or product quality will affect sales.
B) some members of a sales force will have a higher ability than others.
C) agents may appear to be high ability when they are actually low ability.
D) tournament pay may hide the true ability of some agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What proportion of U.S. corporations evaluate employees based upon relative performance?
A) over half
B) almost all
C) about a third
D) less than a quarter
A) over half
B) almost all
C) about a third
D) less than a quarter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A tournament removes risks from outside factors but adds another type of risk called:
A) internal risk.
B) ability risk.
C) personal risk.
D) competition risk.
A) internal risk.
B) ability risk.
C) personal risk.
D) competition risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
You and Bill Gates are junior executives of a software company. If both of you are in a tournament vying for promotion to CEO, there is likely to be substantial:
A) ability risk.
B) effort on your part to get promoted.
C) effort on Bill Gates's part to get promoted.
D) All the answers are correct.
A) ability risk.
B) effort on your part to get promoted.
C) effort on Bill Gates's part to get promoted.
D) All the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Tournaments work best when the risk from the outside environment is ________ the ability risk.
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) unrelated to
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) unrelated to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In schools, ability risk can be mitigated in tournaments by:
A) using an absolute grading scale.
B) grading students relative to each other.
C) grouping students with similar abilities together.
D) standardizing test scores.
A) using an absolute grading scale.
B) grading students relative to each other.
C) grouping students with similar abilities together.
D) standardizing test scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Premed students (who compete for a limited number of slots in medical schools) sometimes sabotage the experiments of other premed students. This is an example of:
A) system risk.
B) ability risk.
C) tournaments discouraging cooperation.
D) environmental risk.
A) system risk.
B) ability risk.
C) tournaments discouraging cooperation.
D) environmental risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following risks increases when a bad teacher is grading on a curve?
A) ability risk
B) environmental risk
C) incentive risk
D) competition risk
A) ability risk
B) environmental risk
C) incentive risk
D) competition risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How can tournaments be structured to eliminate ability risk?
A) The weakest players/workers can be eliminated in the early rounds.
B) Different tournament classes can be created: beginner, intermediate, and advanceB.
C) Tournaments for junior and senior positions for each class of employee can be createC.
D) All of these solutions would serve to eliminate ability risk.
A) The weakest players/workers can be eliminated in the early rounds.
B) Different tournament classes can be created: beginner, intermediate, and advanceB.
C) Tournaments for junior and senior positions for each class of employee can be createC.
D) All of these solutions would serve to eliminate ability risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



