Deck 23: Stock Markets and Personal Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Stock Markets and Personal Finance
1
 Reference: Ref 23-4 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. What is the relative price of music downloads to movie downloads?
Reference: Ref 23-4 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. What is the relative price of music downloads to movie downloads?A) 3
B) 1/3
C) 5
D) 4
B
2
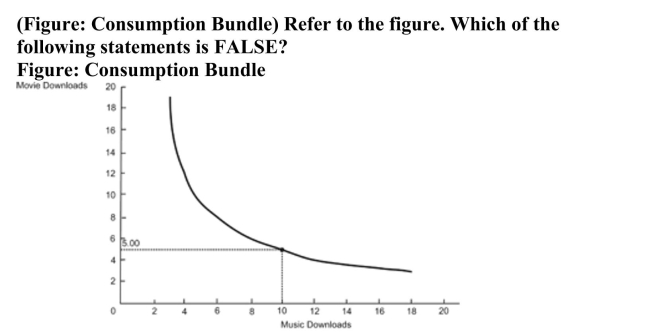
A) The optimal consumption bundle contains five movie downloads and 10 music downloads.
B) The MRS is 0.50 at the optimal consumption bundle.
C) The price per music download is half as expensive as the price per movie download.
D) In the optimum consumption bundle, the marginal utility of movie downloads equals half the marginal utility of music downloads.
D
3
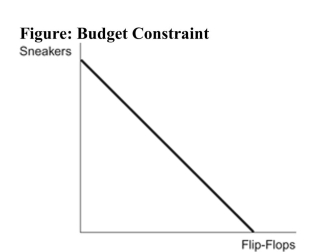 Reference: Ref 23-3 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. If the price of sneakers rises, then the budget constraint in the figure will:
Reference: Ref 23-3 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. If the price of sneakers rises, then the budget constraint in the figure will:A) not change.
B) become steeper.
C) become flatter.
D) shift to the left.
C
4
Which of the following best illustrates the concept of diminishing marginal utility?
A) Gladys is hungry and the first piece of pizza she eats tastes wonderful! The second tastes great, the third good, the fourth okay, and the fifth piece of pizza she eats makes her sick.
B) Thomas likes tomatoes more than Janice, and thus gets more utility from tomatoes than Janice does.
C) High Fly is a new low-cost airline. Initially it is very expensive for High Fly to offer flights to customers because of the high start-up costs, but after fixed costs are covered the additional cost of adding one more consumer falls significantly.
D) Sarah likes hamburgers, but the price she is willing to pay for them is low as compared to another good.
A) Gladys is hungry and the first piece of pizza she eats tastes wonderful! The second tastes great, the third good, the fourth okay, and the fifth piece of pizza she eats makes her sick.
B) Thomas likes tomatoes more than Janice, and thus gets more utility from tomatoes than Janice does.
C) High Fly is a new low-cost airline. Initially it is very expensive for High Fly to offer flights to customers because of the high start-up costs, but after fixed costs are covered the additional cost of adding one more consumer falls significantly.
D) Sarah likes hamburgers, but the price she is willing to pay for them is low as compared to another good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
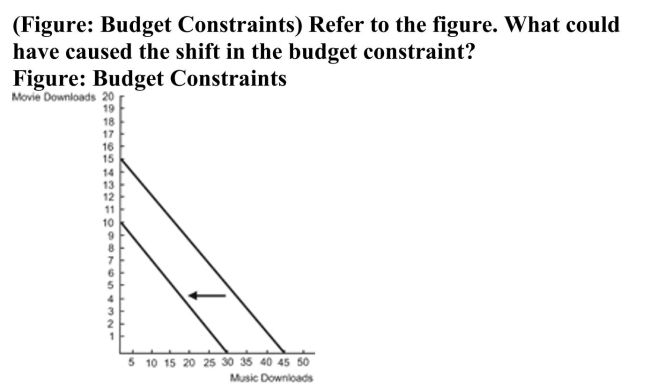
A) The price of music downloads decreased.
B) The price of movie downloads increased.
C) This consumer's income increased.
D) This consumer's income decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
By assuming diminishing marginal utility, we mean that:
A) consumers get less overall value from goods as their income rises.
B) consumers value some goods more than others.
C) the cost of producing goods declines as output increases.
D) consumers value additional units of a good less than the previous unit.
A) consumers get less overall value from goods as their income rises.
B) consumers value some goods more than others.
C) the cost of producing goods declines as output increases.
D) consumers value additional units of a good less than the previous unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
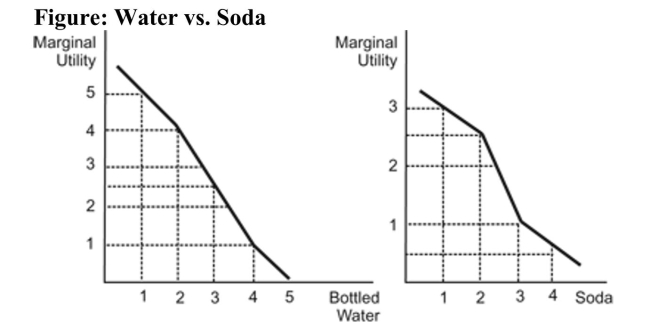 Reference: Ref 23-1 (Figure: Water vs. Soda) Refer to the figure. The figure represents the marginal utility Janet receives when she consumes bottled water and soda. The prices of bottled water and sodas are both $1 each. Janet has $2 to spend and consumes two bottles of water and no soda.
Reference: Ref 23-1 (Figure: Water vs. Soda) Refer to the figure. The figure represents the marginal utility Janet receives when she consumes bottled water and soda. The prices of bottled water and sodas are both $1 each. Janet has $2 to spend and consumes two bottles of water and no soda.A) She would be better off if she consumed one bottle of water and one soda.
B) She would be better off if she consumed two sodas instead of two bottles of water.
C) She is maximizing her utility.
D) The marginal utility of soda will be higher than the marginal utility of bottled water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Amy purchased four cantaloupes at $2 each and three watermelons at $4 each. If Amy is following the optimal consumption rule, the marginal utility of the fourth cantaloupe and third watermelon are:
A) 12 and 24, respectively.
B) four and three, respectively.
C) 40 and 10, respectively.
D) six and eight, respectively.
A) 12 and 24, respectively.
B) four and three, respectively.
C) 40 and 10, respectively.
D) six and eight, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure: Coffee and Comic Books 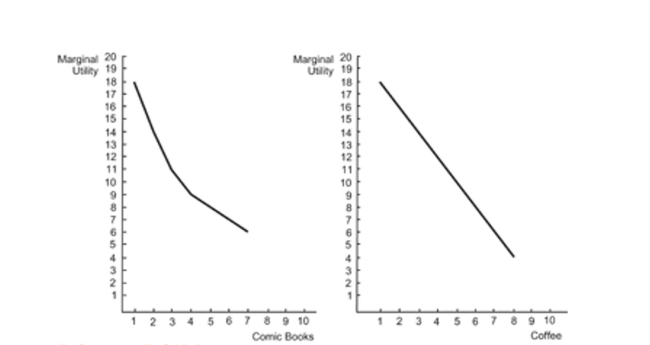 Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. The price of comic books is $0.50. Using the diagram, the marginal utility per dollar for the third comic book is:
Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. The price of comic books is $0.50. Using the diagram, the marginal utility per dollar for the third comic book is:
A) 11.
B) 5.5.
C) 22.
D) 11.5.
 Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. The price of comic books is $0.50. Using the diagram, the marginal utility per dollar for the third comic book is:
Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. The price of comic books is $0.50. Using the diagram, the marginal utility per dollar for the third comic book is:A) 11.
B) 5.5.
C) 22.
D) 11.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
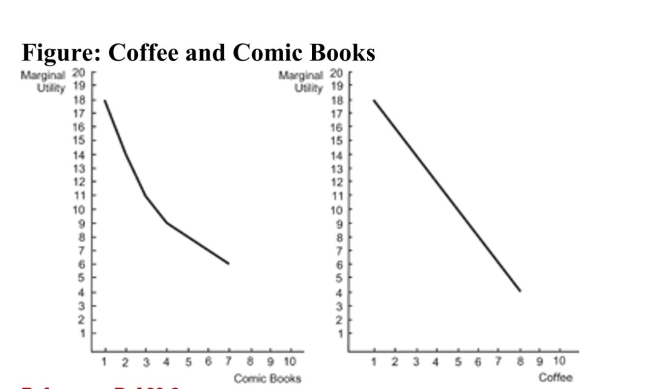 Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $2 to spend on comic books (priced at $1 per comic book) and coffee (priced at $1 per cup). To maximize utility, should this consumer buy two cups of coffee?
Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $2 to spend on comic books (priced at $1 per comic book) and coffee (priced at $1 per cup). To maximize utility, should this consumer buy two cups of coffee?A) Yes, buying two cups of coffee maximizes the consumer's total utility.
B) Yes, because the marginal utility of the second comic book is less than the marginal utility of the second cup of coffee.
C) No, the consumer should put back one cup of coffee (losing 16 utils) and replace it with a comic book (gaining 18 utils).
D) No, the consumer should buy two comic books to maximize utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
(Figure: Marginal Rate of Substitution) Refer to the figure. What is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) between Bundle A and Bundle B? 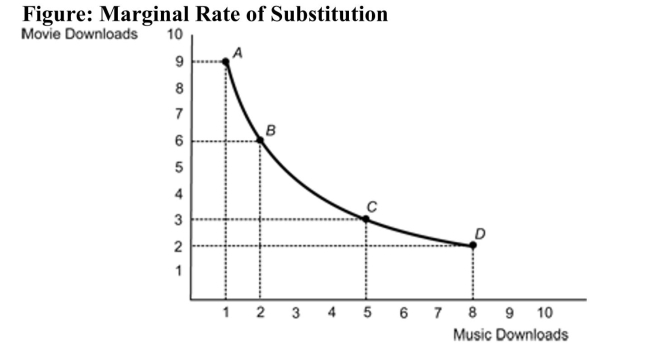
A) 4.5; the consumer is willing to trade 4.5 movie downloads for one music download.
B) three; the consumer is willing to give up three movie downloads for an additional music download.
C) 1.5; the consumer will buy 1.5 times as many music downloads as movie downloads.
D) one; the consumer faces a one-to-one trade-off.

A) 4.5; the consumer is willing to trade 4.5 movie downloads for one music download.
B) three; the consumer is willing to give up three movie downloads for an additional music download.
C) 1.5; the consumer will buy 1.5 times as many music downloads as movie downloads.
D) one; the consumer faces a one-to-one trade-off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
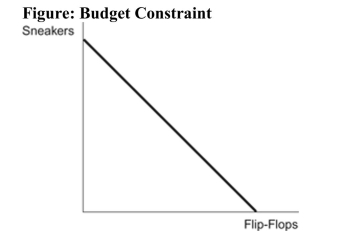 Reference: Ref 23-3 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. The slope of the budget constraint in the figure above is equal to:
Reference: Ref 23-3 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. The slope of the budget constraint in the figure above is equal to:A) the price of sneakers divided by the price of flip- flops.
B) the price of flip-flops divided by the price of gas.
C) the quantity of flip-flops divided by the quantity of sneakers.
D) the quantity of sneakers divided by the quantity of flip- flops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The consumption bundle that maximizes utility for a consumer is the bundle that:
A) equates the slope of the budget constraint with the slope of the indifference curve.
B) maximizes marginal utility across all goods.
C) minimizes the costs of production.
D) maximizes the marginal rate of substitution.
A) equates the slope of the budget constraint with the slope of the indifference curve.
B) maximizes marginal utility across all goods.
C) minimizes the costs of production.
D) maximizes the marginal rate of substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $5 to spend on comic books (priced at $1 per comic book) and coffee (priced at $1 per cup). Using the figure, how many comic books and cups of coffee will this consumer purchase?
Reference: Ref 23-2 (Figure: Coffee and Comic Books) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $5 to spend on comic books (priced at $1 per comic book) and coffee (priced at $1 per cup). Using the figure, how many comic books and cups of coffee will this consumer purchase?A) three comic books and two cups of coffee
B) two comic books and three cups of coffee
C) 2.5 comic books and 2.5 cups of coffee
D) one comic book and four cups of coffee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
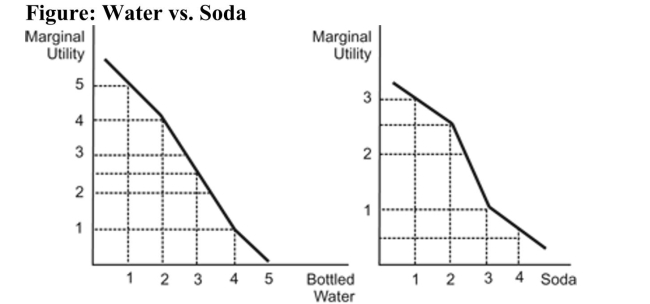 Reference: Ref 23-1 (Figure: Water vs. Soda) Refer to the figure. The figure represents the marginal utility Janet receives when she consumes bottled water and soda. The prices of bottled water and sodas are both $1 each. Janet has $5 to spend. What mix of bottled water and soda will maximize Janet's utility?
Reference: Ref 23-1 (Figure: Water vs. Soda) Refer to the figure. The figure represents the marginal utility Janet receives when she consumes bottled water and soda. The prices of bottled water and sodas are both $1 each. Janet has $5 to spend. What mix of bottled water and soda will maximize Janet's utility?A) five bottles of water
B) four bottles of water and one soda
C) three bottles of water and two sodas
D) 2.5 bottles of water and 2.5 sodas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Reference: Ref 23-4 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $45 to spend on movie and music downloads per month. What is the price per movie and music download?
Reference: Ref 23-4 (Figure: Budget Constraint) Refer to the figure. A consumer has $45 to spend on movie and music downloads per month. What is the price per movie and music download?A) $15 per movie download and $0.45 per music download
B) $3 per movie download and $1 per music download
C) $2.50 per movie download and $1.50 per music download
D) $10 per movie download and $0.80 per music download

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An increase in the price of a good leads to a(n) ______ in the marginal utility per dollar of that good, and thus a(n) ______ in the quantity purchased.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
At the consumer's optimal consumption bundle, the MRSXY is 4, and the marginal utility of Good X is 8. What is the marginal utility of Good Y?
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 24
D) 16
A) 1/2
B) 2
C) 24
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
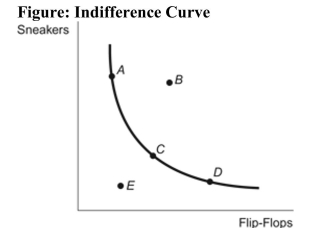 Reference: Ref 23-5 (Figure: Indifference Curve) Refer to the figure. Which of the following points generates the highest level of utility for the consumer?
Reference: Ref 23-5 (Figure: Indifference Curve) Refer to the figure. Which of the following points generates the highest level of utility for the consumer?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consumers maximize their utility when:
A) the total benefits are greater than total costs.
B) the marginal utility per dollar is equal across all goods consumed and all income is spent.
C) they consume the good on which they place the highest overall value.
D) they diversify their consumption across goods.
A) the total benefits are greater than total costs.
B) the marginal utility per dollar is equal across all goods consumed and all income is spent.
C) they consume the good on which they place the highest overall value.
D) they diversify their consumption across goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(Figure: Labor Supply) Refer to the figure. The figure represents the budget constraint and indifference curves for the labor-leisure decision of a consumer when the wage rate falls from $20 to $10. For this worker: 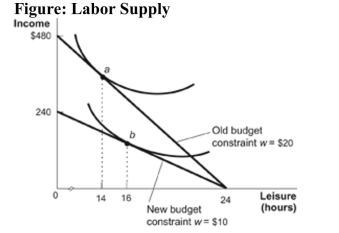
A) the income effect will dominate and the consumer will work more.
B) the substitution effect will dominate and the consumer will work more.
C) the income effect will dominate and the consumer will work less.
D) the substitution effect will dominate and the consumer will work less.

A) the income effect will dominate and the consumer will work more.
B) the substitution effect will dominate and the consumer will work more.
C) the income effect will dominate and the consumer will work less.
D) the substitution effect will dominate and the consumer will work less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the marginal utility per dollar for hamburgers is higher than the marginal utility per dollar for Tacos, then in order to maximize utility the consumer should only consume hamburgers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A partner at a major law firm spent $90 for a ticket to the Rockstar Energy Mayhem Festival, featuring Disturbed, Godsmack, and Megadeth and then lost it. Should he buy another $90 ticket?
A) Yes, there is no substitution effect and the income effect is trivial given his wealth.
B) Yes, there is a positive substitution effect and the income effect is large given his wealth.
C) No, there is some substitution effect and the income effect is trivial given his wealth.
D) No, there is a positive substitution effect and the income effect is large given his wealth.
A) Yes, there is no substitution effect and the income effect is trivial given his wealth.
B) Yes, there is a positive substitution effect and the income effect is large given his wealth.
C) No, there is some substitution effect and the income effect is trivial given his wealth.
D) No, there is a positive substitution effect and the income effect is large given his wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If there are only two goods in the economy, chocolate and peanut butter, and the price of chocolate falls, the new utility maximizing bundle for a typical consumer would entail consuming ______ peanut butter and ______ chocolate.
A) less; more
B) more; less
C) more; more
D) less; less
A) less; more
B) more; less
C) more; more
D) less; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
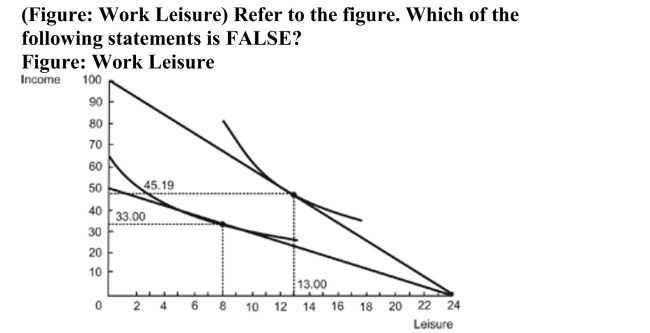
A) At 13 hours of leisure and income of $45.19, the worker earns a wage of $4.17 an hour.
B) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
C) The substitution effect dominates the income effect.
D) This worker chooses to work more hours if paid higher wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the marginal utility per dollar for hamburgers is 2, and the marginal utility per dollar for pizza is 1, then this consumer should consume more hamburgers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
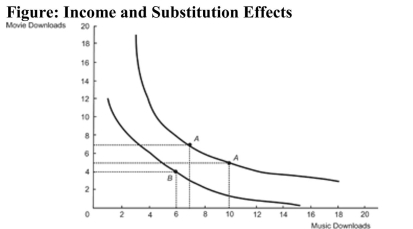 Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. What caused this consumer to switch optimal consumption bundles from Bundle A to Bundle B?
Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. What caused this consumer to switch optimal consumption bundles from Bundle A to Bundle B?A) a decrease in consumer income available for music downloads
B) a decrease in the price of music downloads
C) an increase in the price of music downloads
D) an increase in the price of movie downloads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
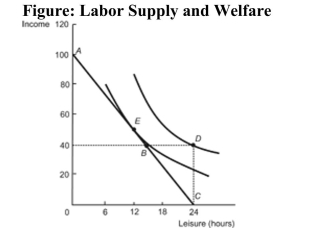 Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The presence of the welfare program causes this person to:
Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The presence of the welfare program causes this person to:A) reduce hours of work from 12 to 0.
B) increase hours of work from 0 to 12.
C) reduce hours of work from 12 to 9.
D) reduce hours of work from 8 to 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
After purchasing and then losing a ticket to a concert, a rational consumer would:
A) not repurchase the ticket since the lost ticket is a sunk cost.
B) always repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed.
C) repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed and the income effect is high.
D) repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed and the income effect is low.
A) not repurchase the ticket since the lost ticket is a sunk cost.
B) always repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed.
C) repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed and the income effect is high.
D) repurchase the ticket as long as the price hasn't changed and the income effect is low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The income effect of a wage increase is to consume less leisure.
B) The substitution effect of a wage decrease is to consume less leisure.
C) The price of leisure decreases with a decrease in wages.
D) The price of leisure increases with an increase in income.
A) The income effect of a wage increase is to consume less leisure.
B) The substitution effect of a wage decrease is to consume less leisure.
C) The price of leisure decreases with a decrease in wages.
D) The price of leisure increases with an increase in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
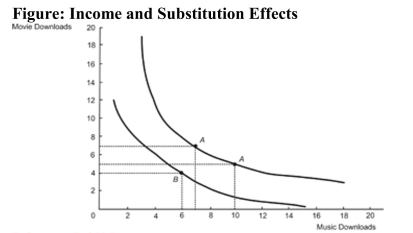 Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the substitution effect from the price change?
Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the substitution effect from the price change?A) the reduction of the number of music downloads by three
B) the reduction of the number of music downloads by four
C) the increase of the number of music downloads by one
D) the increase of the number of music downloads by three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure: Income and Substitution Effects 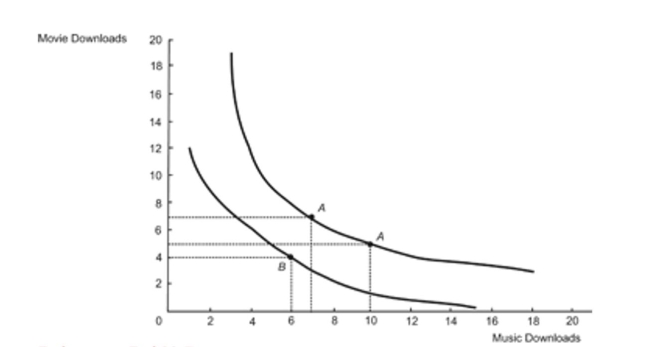 Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the income effect from the price change?
Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the income effect from the price change?
A) the increase of the number of music downloads by three
B) the increase of the number of music downloads by four
C) the reduction of the number of music downloads by one
D) the reduction of the number of music downloads by three
 Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the income effect from the price change?
Reference: Ref 23-7 (Figure: Income and Substitution Effects) Refer to the figure. The consumer is initially in equilibrium at Point A than moves to Point B. What is the income effect from the price change?A) the increase of the number of music downloads by three
B) the increase of the number of music downloads by four
C) the reduction of the number of music downloads by one
D) the reduction of the number of music downloads by three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
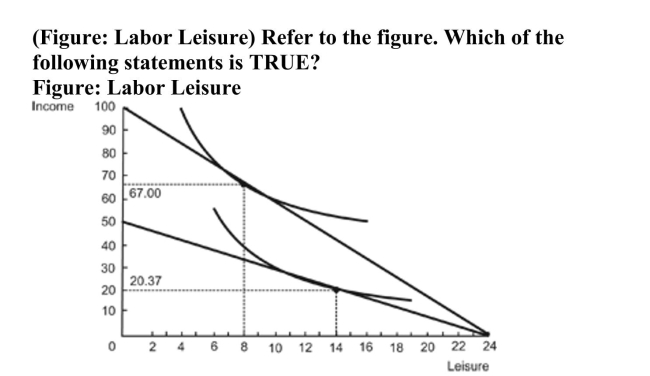
A) The labor supply curve is downward sloping.
B) The labor supply curve is upward sloping.
C) The income effect denominates the substitution effect.
D) The worker earns $6.00 an hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If an individual's labor supply curve is downward sloping, this indicates that:
A) the individual has become wealthier.
B) the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
C) the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
D) the individual faces a diminishing marginal utility for leisure.
A) the individual has become wealthier.
B) the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
C) the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
D) the individual faces a diminishing marginal utility for leisure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Barry's wage increased and he responded by working more hours. Which of the following must be true?
A) Leisure is an inferior good.
B) The substitution effect of the wage increase dominated the income effect.
C) The income effect of the wage increase dominated the substitution effect.
D) The substitution and income effect both increased hours of work.
A) Leisure is an inferior good.
B) The substitution effect of the wage increase dominated the income effect.
C) The income effect of the wage increase dominated the substitution effect.
D) The substitution and income effect both increased hours of work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following methods have been used to reduce the disincentive effects of welfare on labor supply? I. The government reduces welfare benefits by $1 of every $1 of labor income earned. II. The government limits the amount of time that someone can collect welfare. III. The government provides an Earned Income Tax Credit that supplements the income of the working poor.
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) II only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) II only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
(Figure: Sam's Club) Refer to the figure. How much should Sam's Club charge for membership? 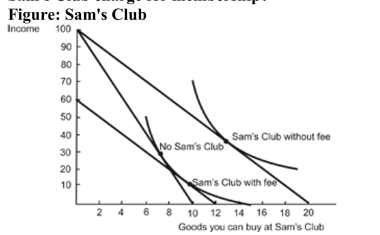
A) $60
B) $100
C) $40
D) $10

A) $60
B) $100
C) $40
D) $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Countries in Western Europe tend to have more generous unemployment benefits for their workers than the United States. All else equal, you would expect workers in Western Europe to:
A) work more hours on average.
B) work fewer hours on average.
C) have higher wages.
D) have lower wages.
A) work more hours on average.
B) work fewer hours on average.
C) have higher wages.
D) have lower wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The income effect is:
A) represented by a pivot in the budget constraint from a change in price.
B) the change in consumption caused by a change in purchasing power from a price change.
C) an increase in price caused by a change in market demand from an increase in income.
D) the increase in the price of leisure caused by higher wages.
A) represented by a pivot in the budget constraint from a change in price.
B) the change in consumption caused by a change in purchasing power from a price change.
C) an increase in price caused by a change in market demand from an increase in income.
D) the increase in the price of leisure caused by higher wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare 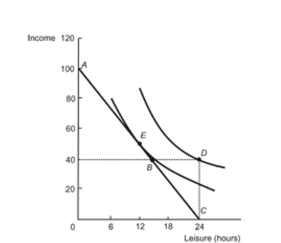 Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The budget constraint is:
Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The budget constraint is:
A) ABC.
B) BD.
C) ABDC.
D) ABD.
 Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The budget constraint is:
Reference: Ref 23-8 (Figure: Labor Supply and Welfare) Refer to the figure. The budget constraint is:A) ABC.
B) BD.
C) ABDC.
D) ABD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the price of Good X is $10 and price of Good Y is $15, the slope of the budget constraint is -1.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The table given shows the marginal utility a consumer receives from purchasing take-out food and lattes each week. The price of a take-out meal is $15, and the price of a latte is $5. What is the utility-maximizing bundle of take-out and lattes for a consumer with a weekly income of $45 (all of which will be spent on take-out and lattes)? How does it change if income increases to $75? What is the bundle then? 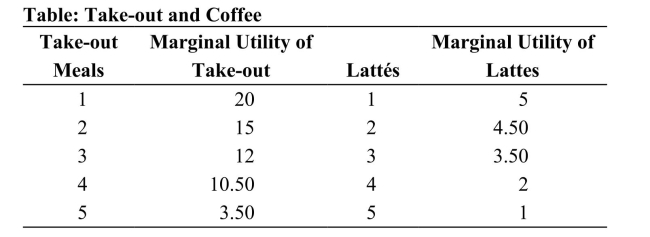


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose the price of apples rises making oranges relatively less expensive. The increase in orange consumption as a result of the price change is an example of the income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand curve is downward sloping due to diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The slope of the indifference curve is equal to the marginal rate of substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If another unit of Good X gives a consumer 15 additional units of satisfaction, and another unit of Good Y gives 45 additional units of satisfaction, the MRS is equal to 1/3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A bar owner must decide how best to raise revenues. A cover charge will allow him to offer cheaper drink prices. If the owner does decide to require a cover charge and offer cheaper drinks, how much should it be to avoid losing customers? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The utility maximizing consumption bundle for a consumer is the bundle that maximizes marginal utility across all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the marginal utility of apples is 4 and marginal utility of grapes is 4, the consumer is maximizing utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the wage rate increases and the income effect exactly offsets the substitution effect, the labor supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
As wages rise, will labor supply increase or decrease? Discuss and explain each possible scenario.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Indifference curves can never cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consumption Bundle A contains six donuts and 2 cups of coffee, and consumption Bundle B contains four donuts and 1.5 cups of coffee. Bundle A and Bundle B could lie on the same indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



