Deck 18: Labor Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/148
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Labor Markets
1
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only excludable and nonrival goods from the table?
A) cable Internet service, toll highways, public roads, soup kitchen meals
B) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C) public beaches, soup kitchen meals, public roads, smog reduction
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction, cable Internet service
A) cable Internet service, toll highways, public roads, soup kitchen meals
B) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C) public beaches, soup kitchen meals, public roads, smog reduction
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction, cable Internet service
B
2
An excludable good is:
A) one that is excluded from the common basket of goods consumed by households.
B) one that producers will exclude from production.
C) one where people can be prevented from using the good.
D) not necessary to consume, a luxury.
A) one that is excluded from the common basket of goods consumed by households.
B) one that producers will exclude from production.
C) one where people can be prevented from using the good.
D) not necessary to consume, a luxury.
C
3
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only rival, excludable goods from the table?
A) a watermelon, toll highways, a private beach, a chair
B) a watermelon, cable Internet service, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C) a watermelon, a chair, a pencil
D) online video games, a watermelon, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
A) a watermelon, toll highways, a private beach, a chair
B) a watermelon, cable Internet service, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C) a watermelon, a chair, a pencil
D) online video games, a watermelon, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C
4
A person ________ be cheaply prevented from using national defense, a(n) ________ good.
A) can; excludable
B) cannot; nonexcludable
C) cannot; excludable
D) can; nonexcludable
A) can; excludable
B) cannot; nonexcludable
C) cannot; excludable
D) can; nonexcludable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A public good is:
A) nonrival and nonexcludable.
B) rival and nonexcludable.
C) rival and excludable.
D) nonrival and excludable.
A) nonrival and nonexcludable.
B) rival and nonexcludable.
C) rival and excludable.
D) nonrival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that a private-sector firm produces two goods: Good 1 is a private good and Good 2 is a public good. Which of the following statements is true?
A) If a consumer spends more money on Good 1, she gets more Good 1.
B) If a consumer spends more money on Good 2, she gets more Good 2.
C) If a consumer spends less money on Good 1, she gets less Good 2.
D) If a consumer spends less money on Good 2, she gets less Good 1.
A) If a consumer spends more money on Good 1, she gets more Good 1.
B) If a consumer spends more money on Good 2, she gets more Good 2.
C) If a consumer spends less money on Good 1, she gets less Good 2.
D) If a consumer spends less money on Good 2, she gets less Good 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only common resources from the table?
A) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
B) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
C) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
D) online video games, a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
A) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
B) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
C) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
D) online video games, a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A good is excludable if:
A) the government can regulate the availability of the good.
B) it is a normal good.
C) several people can enjoy the good simultaneously.
D) people can be prevented from using it.
A) the government can regulate the availability of the good.
B) it is a normal good.
C) several people can enjoy the good simultaneously.
D) people can be prevented from using it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only private goods from the table?
A) a watermelon, toll highways, a private beach, a chair
B) a watermelon, cable Internet service, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C) a watermelon, a chair, a pencil
D) online video games, a watermelon, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
A) a watermelon, toll highways, a private beach, a chair
B) a watermelon, cable Internet service, a private beach, a pencil, a chair
C) a watermelon, a chair, a pencil
D) online video games, a watermelon, a private beach, a pencil, a chair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A rival good is one where:
A) one person's use does not impinge on another person's ability to enjoy the same good.
B) one person's use prevents another person's ability to use that good at the same time.
C) two people can use the same good at the same time.
D) the good is simultaneously nonexcludable and public.
A) one person's use does not impinge on another person's ability to enjoy the same good.
B) one person's use prevents another person's ability to use that good at the same time.
C) two people can use the same good at the same time.
D) the good is simultaneously nonexcludable and public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only nonexcludable and rival goods from the table?
A) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
B) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
D) online video games, a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
A) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
B) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
C) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
D) online video games, a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only public goods from the table?
A) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
B) online video games, a public beach, national defense, a lighthouse
C) a public beach, a lighthouse, toll highways, public roads
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
A) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads
B) online video games, a public beach, national defense, a lighthouse
C) a public beach, a lighthouse, toll highways, public roads
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Toilet paper is a rival good because:
A) there is a lot of competition in the toilet paper market.
B) it is a substitute good for a bidet.
C) one person's use of toilet paper reduces the ability of another person to use the same sheets.
D) it is made from natural resources.
A) there is a lot of competition in the toilet paper market.
B) it is a substitute good for a bidet.
C) one person's use of toilet paper reduces the ability of another person to use the same sheets.
D) it is made from natural resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only nonexcludable, nonrival goods from the table?
A) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
B) a public beaches, soup kitchen meals, public roads
C) online video games, a public beach, national defense, a lighthouse
D) a public beach, a lighthouse, toll highways, public roads
A) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction
B) a public beaches, soup kitchen meals, public roads
C) online video games, a public beach, national defense, a lighthouse
D) a public beach, a lighthouse, toll highways, public roads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Table: Example Goods A Watermelon A Lighthouse Smog Reduction Online Video Games Cable Internet Service National Defense A Private Beach A Public Beach A Pencil Soup Kitchen Meals A Chair Toll Highways Public Roads Reference: Ref 18-2 (Table: Example Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following contains only nonrival private goods from the table?
A) cable Internet service, toll highways, public roads, soup kitchen meals
B) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads, smog reduction
C) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction, cable Internet service
A) cable Internet service, toll highways, public roads, soup kitchen meals
B) a public beach, soup kitchen meals, public roads, smog reduction
C) online video games, a private beach, toll highways, cable Internet service
D) national defense, a lighthouse, smog reduction, cable Internet service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If you give a firm $1,000 to protect the earth from asteroids:
A) your contribution will not have an effect on whether the firm will be successful in protecting the earth.
B) your contribution will be vital in determining whether the firm will have enough resources to combat asteroids.
C) your family will now have adequate protection.
D) you are considered a free-rider of public goods.
A) your contribution will not have an effect on whether the firm will be successful in protecting the earth.
B) your contribution will be vital in determining whether the firm will have enough resources to combat asteroids.
C) your family will now have adequate protection.
D) you are considered a free-rider of public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
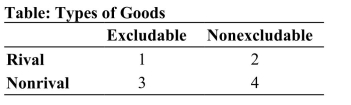 Reference: Ref 18-1 (Table: Types of Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following statements is true? I. Section 1 may contain fruit, chicken, and underwear. II. Section 2 may contain fish in the ocean, public roads, and public hunting grounds. III. Section 3 may contain Wi-Fi, cable TV, and digital music. IV. Section 4 may contain asteroid deflection, national defense, and radio.
Reference: Ref 18-1 (Table: Types of Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following statements is true? I. Section 1 may contain fruit, chicken, and underwear. II. Section 2 may contain fish in the ocean, public roads, and public hunting grounds. III. Section 3 may contain Wi-Fi, cable TV, and digital music. IV. Section 4 may contain asteroid deflection, national defense, and radio.A) I, II, and IV
B) III and IV
C) II only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a good is excludable:
A) one person's use of the good prevents another's ability to use it.
B) everyone is excluded from using the good.
C) people can be prevented from using the good.
D) no more than one person can use the good at one time.
A) one person's use of the good prevents another's ability to use it.
B) everyone is excluded from using the good.
C) people can be prevented from using the good.
D) no more than one person can use the good at one time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that a firm plans to provide defense against asteroids striking the earth. Which of the following is TRUE?
A) Most people will find it in their self-interest to pay the firm to protect the earth.
B) Asteroid protection is a private good, so the firm will make a lot of profit.
C) In case of an earth bound asteroid, the firm will not protect people who refused to pay for asteroid defense.
D) Most people will not pay a firm for asteroid defense.
A) Most people will find it in their self-interest to pay the firm to protect the earth.
B) Asteroid protection is a private good, so the firm will make a lot of profit.
C) In case of an earth bound asteroid, the firm will not protect people who refused to pay for asteroid defense.
D) Most people will not pay a firm for asteroid defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
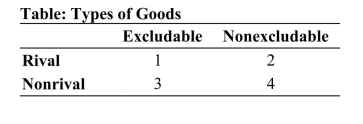 Reference: Ref 18-1 (Table: Types of Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following statements is true?
Reference: Ref 18-1 (Table: Types of Goods) Refer to the table. Which of the following statements is true?A) Section 1 includes national defense.
B) Section 2 includes a can of soda.
C) Section 3 includes wireless Internet.
D) Section 4 includes an MP3 song.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Goods that are not excludable include both:
A) common resources and public goods.
B) private and public goods.
C) natural monopolies and common resources.
D) only public goods, since no other goods are not excludable.
A) common resources and public goods.
B) private and public goods.
C) natural monopolies and common resources.
D) only public goods, since no other goods are not excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Goods that are rival in consumption include both:
A) public goods and common resources.
B) common resources and natural monopolies.
C) common resources and private goods.
D) public goods and private goods.
A) public goods and common resources.
B) common resources and natural monopolies.
C) common resources and private goods.
D) public goods and private goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A good is nonexcludable if it is:
A) easy to prevent people from using the good at low cost.
B) easy to make people use the good at low cost.
C) difficult to prevent people from using the good at low cost.
D) difficult to make people use the good at low cost.
A) easy to prevent people from using the good at low cost.
B) easy to make people use the good at low cost.
C) difficult to prevent people from using the good at low cost.
D) difficult to make people use the good at low cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a good is rival in consumption:
A) people can be excluded from using the good.
B) one person's use of the good prevents another's ability to use it.
C) no more than one person can use the good at the same time.
D) people can be prevented from using the good.
A) people can be excluded from using the good.
B) one person's use of the good prevents another's ability to use it.
C) no more than one person can use the good at the same time.
D) people can be prevented from using the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a private good?
A) national defense
B) cable TV
C) soft drinks
D) the environment
A) national defense
B) cable TV
C) soft drinks
D) the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A tornado warning siren is an example of a:
A) private good.
B) public good.
C) common resource.
D) rival public good.
A) private good.
B) public good.
C) common resource.
D) rival public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An example of a private good would be:
A) a tornado siren.
B) a fireworks display.
C) a piece of fruit.
D) cable TV.
A) a tornado siren.
B) a fireworks display.
C) a piece of fruit.
D) cable TV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Compared to private goods, the free market would ________ public goods.
A) overproduce
B) efficiently produce
C) underproduce
D) sometimes overproduce but most often underproduce
A) overproduce
B) efficiently produce
C) underproduce
D) sometimes overproduce but most often underproduce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Goods that are excludable include both:
A) public goods and common resources.
B) natural monopolies and public goods.
C) public and private goods.
D) rival and nonrival private goods.
A) public goods and common resources.
B) natural monopolies and public goods.
C) public and private goods.
D) rival and nonrival private goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is NOT considered a private good?
A) pizza
B) tennis rackets
C) cable TV
D) French fries
A) pizza
B) tennis rackets
C) cable TV
D) French fries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is a public good?
A) city parking spots
B) protection of the ozone layer
C) computers
D) the Internet
A) city parking spots
B) protection of the ozone layer
C) computers
D) the Internet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
People have little incentive to produce a public good because:
A) fixed costs are usually too high.
B) production is impossible.
C) of the free rider problem.
D) social benefits are typically less than total costs.
A) fixed costs are usually too high.
B) production is impossible.
C) of the free rider problem.
D) social benefits are typically less than total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Uncongested, non-toll roads are a good example of a:
A) public good.
B) common resource.
C) private good.
D) natural monopoly.
A) public good.
B) common resource.
C) private good.
D) natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If one person's use of a good prevents another person's ability to use it, then the good is:
A) rival in consumption.
B) nonrival in consumption.
C) normal.
D) excludable.
A) rival in consumption.
B) nonrival in consumption.
C) normal.
D) excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Private goods are both:
A) rival and nonexcludable.
B) nonrival and excludable.
C) nonrival and nonexcludable.
D) rival and excludable.
A) rival and nonexcludable.
B) nonrival and excludable.
C) nonrival and nonexcludable.
D) rival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A good is nonrival if:
A) the good does not cause rivalry between the people using the good.
B) the good potentially creates rivalry between the people using the good.
C) one person's use of the good reduces the ability of another person to use the same good.
D) one person's use of the good does not reduce the ability of another person to use the same good.
A) the good does not cause rivalry between the people using the good.
B) the good potentially creates rivalry between the people using the good.
C) one person's use of the good reduces the ability of another person to use the same good.
D) one person's use of the good does not reduce the ability of another person to use the same good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is rival and not excludable?
A) cable TV
B) lobsters in the ocean
C) national defense
D) clothing
A) cable TV
B) lobsters in the ocean
C) national defense
D) clothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following goods is not rival and not excludable?
A) a boat
B) a public road
C) an ice cream cone
D) a street light
A) a boat
B) a public road
C) an ice cream cone
D) a street light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A free rider is a person who:
A) avoids paying taxes by using tax code loopholes.
B) produces goods at no cost.
C) receives the benefits of a good but avoids paying for it.
D) will purchase products only when on sale.
A) avoids paying taxes by using tax code loopholes.
B) produces goods at no cost.
C) receives the benefits of a good but avoids paying for it.
D) will purchase products only when on sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Both public goods and common resources are:
A) rival in consumption.
B) nonexcludable.
C) excludable.
D) nonrival in consumption.
A) rival in consumption.
B) nonexcludable.
C) excludable.
D) nonrival in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Hamburgers are example of goods that are:
A) rival and excludable.
B) rival and nonexcludable.
C) nonrival and excludable.
D) nonrival and nonexcludable.
A) rival and excludable.
B) rival and nonexcludable.
C) nonrival and excludable.
D) nonrival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is TRUE? I. In order for society to have a sufficient level of national defense, the government must tax the public to raise funds for a standing army. II. For every 100 people that use a public good, approximately 500 people are prevented from using it. III. People do not have an incentive to voluntarily pay for nonexcludable goods.
A) I and II only
B) III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Private goods can be provided by competitive markets because they are:
A) excludable, providing an incentive to pay for and thus to produce these goods.
B) excludable, since the market for buying and selling these goods is distinguishable.
C) nonexcludable, providing an incentive to pay for and thus to produce these goods.
D) nonexcludable, since the market for buying and selling these goods cannot be distinguished.
A) excludable, providing an incentive to pay for and thus to produce these goods.
B) excludable, since the market for buying and selling these goods is distinguishable.
C) nonexcludable, providing an incentive to pay for and thus to produce these goods.
D) nonexcludable, since the market for buying and selling these goods cannot be distinguished.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The total benefit of a public good equals the sum of the benefits to each person.
B) It is harder for society to produce optimal amounts of public goods than it is for private goods.
C) The United States Postal Service is not a public good.
D) People value public goods differently.
A) The total benefit of a public good equals the sum of the benefits to each person.
B) It is harder for society to produce optimal amounts of public goods than it is for private goods.
C) The United States Postal Service is not a public good.
D) People value public goods differently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose your city has had an increase in crime and the city government decides that more police are needed to patrol at night. Which of the following funding solutions avoids the free-rider problem involved with additional police officers?
A) taxation of the city's top 50 percent of income earners
B) donation-based police service
C) voluntary police officers
D) an increase in the city's sales tax
A) taxation of the city's top 50 percent of income earners
B) donation-based police service
C) voluntary police officers
D) an increase in the city's sales tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A major difference between a private good and a public good is that:
A) private goods are excludable, public goods are not.
B) private goods can be produced in efficient quantities while public goods generally are not.
C) private goods are rival in consumption, public goods are not.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) private goods are excludable, public goods are not.
B) private goods can be produced in efficient quantities while public goods generally are not.
C) private goods are rival in consumption, public goods are not.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The problem of free riders is most apparent for:
A) private goods.
B) nonrival private goods.
C) public goods.
D) textbooks.
A) private goods.
B) nonrival private goods.
C) public goods.
D) textbooks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Private goods: I. are excludable. II. can be priced. III. are rival in consumption.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following would NOT be considered as an example of public good?
A) asteroid deflection
B) national defense
C) mosquito control
D) public roads
A) asteroid deflection
B) national defense
C) mosquito control
D) public roads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
It is difficult to get people to pay for public goods voluntarily because these goods are:
A) excludable, and therefore markets tend to overprovide them.
B) excludable, and therefore markets tend to underprovide them.
C) nonexcludable, and therefore markets tend to overprovide them.
D) nonexcludable, and therefore, markets tend to underprovide them.
A) excludable, and therefore markets tend to overprovide them.
B) excludable, and therefore markets tend to underprovide them.
C) nonexcludable, and therefore markets tend to overprovide them.
D) nonexcludable, and therefore, markets tend to underprovide them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In which of the cases can you identify the potential for a free- rider problem?
A) half-off sales at department stores
B) voluntary payments for a smog reduction program
C) group projects where all members have clearly assigned tasks and are responsible for presenting their work
D) cable Internet service
A) half-off sales at department stores
B) voluntary payments for a smog reduction program
C) group projects where all members have clearly assigned tasks and are responsible for presenting their work
D) cable Internet service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The need to produce public goods provides a strong argument for:
A) regulation and subsidy.
B) regulation and government provision.
C) taxation and subsidy.
D) taxation and government provision.
A) regulation and subsidy.
B) regulation and government provision.
C) taxation and subsidy.
D) taxation and government provision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Free riders are people who:
A) enjoy public goods without paying for them.
B) pay for public goods but do not end up enjoying them.
C) pay for both private and public goods.
D) ride public transportation without paying.
A) enjoy public goods without paying for them.
B) pay for public goods but do not end up enjoying them.
C) pay for both private and public goods.
D) ride public transportation without paying.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Asteroid deflection would be considered a:
A) public good since it is rival and nonexcludable.
B) public good since it is nonrival and nonexcludable.
C) private good since it is rival and excludable.
D) private good since it is nonrival and excludable.
A) public good since it is rival and nonexcludable.
B) public good since it is nonrival and nonexcludable.
C) private good since it is rival and excludable.
D) private good since it is nonrival and excludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A forced rider is someone who:
A) pays a share of the costs of public good but who does not enjoy the benefits.
B) pays a share of the costs of public good and enjoys the benefits.
C) does not pay a share of the costs of public good but who enjoys the benefits.
D) does not pay a share of the costs of public good and does not enjoy the benefits.
A) pays a share of the costs of public good but who does not enjoy the benefits.
B) pays a share of the costs of public good and enjoys the benefits.
C) does not pay a share of the costs of public good but who enjoys the benefits.
D) does not pay a share of the costs of public good and does not enjoy the benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Mosquito control must be provided by government because if:
A) a lot of people free ride then mosquito control would be overprovided by the market.
B) a lot of people free ride then mosquito control would be underprovided by the market.
C) only few people are benefited then mosquito control would be overprovided by the market.
D) only few people are benefited then mosquito control would be underprovided by the market.
A) a lot of people free ride then mosquito control would be overprovided by the market.
B) a lot of people free ride then mosquito control would be underprovided by the market.
C) only few people are benefited then mosquito control would be overprovided by the market.
D) only few people are benefited then mosquito control would be underprovided by the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The sun has features of a:
A) public good.
B) common resource-everyone in society can use it for warmth and light.
C) rival good that can easily be made excludable.
D) private good since solar energy can be marketed.
A) public good.
B) common resource-everyone in society can use it for warmth and light.
C) rival good that can easily be made excludable.
D) private good since solar energy can be marketed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Public goods are: I. excludable. II. nonrival. III. free to those who do not pay.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why is national defense a public good? I. because it is expensive to produce II. because people who don't pay for national defense still benefit from having it III. because one person's benefit from national defense doesn't reduce anyone else's benefit from it IV. because it is provided by the government
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, and III only
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The city government taxes its residents to pay for mosquito control. Betty is not happy about paying the tax, for mosquitoes never bite her. Betty is a:
A) free rider.
B) forced rider.
C) taxed rider.
D) lonesome rider.
A) free rider.
B) forced rider.
C) taxed rider.
D) lonesome rider.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is TRUE? I. Excludability leads to efficiency. II. The benefits of public goods provide an argument for government provision of these goods. III. Taxation turns some people into free riders.
A) I and II only
B) II only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following solutions allows for an efficient allocation of a public good?
A) widespread taxation
B) government command and control policies
C) donation-based funding
D) advertising
A) widespread taxation
B) government command and control policies
C) donation-based funding
D) advertising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Nonrival private goods are likely to have ________ fixed costs and ________ marginal costs.
A) small; large
B) no; small
C) large; small
D) large; no
A) small; large
B) no; small
C) large; small
D) large; no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The O'Reilly Factor is a popular cable television news show. To watch the show requires a paid subscription. Therefore, which of the following is TRUE?
A) This show is a nonrival private good because 1) nonpayers can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.
B) This show is a public good because payers and nonpayers alike are watching a rival show.
C) This show is a public good because 1) no one can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.
D) This show is a common good because 1) nonpayers can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.
A) This show is a nonrival private good because 1) nonpayers can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.
B) This show is a public good because payers and nonpayers alike are watching a rival show.
C) This show is a public good because 1) no one can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.
D) This show is a common good because 1) nonpayers can be excluded and 2) when one person watches it does not diminish another person's ability to watch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During the Middle Ages, many villages had areas reserved for families to take their cows or sheep to graze. All families were welcome to use this land without charge. The land for grazing can be characterized as a:
A) public good.
B) private good.
C) natural resource.
D) common resource.
A) public good.
B) private good.
C) natural resource.
D) common resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Nonrival private goods are likely to be:
A) overprovided by the market.
B) underprovided by the market.
C) nonrival and nonexclusive.
D) rival and nonexclusive.
A) overprovided by the market.
B) underprovided by the market.
C) nonrival and nonexclusive.
D) rival and nonexclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following explains why it is difficult to determine the optimal quantity of public goods that the government should produce?
A) It is difficult to determine how much budget the government should have each year.
B) It is difficult to assess exactly how much each individual values a public good.
C) It is difficult to identify how public goods really benefit the society.
D) It is difficult to find out how demographics change over time.
A) It is difficult to determine how much budget the government should have each year.
B) It is difficult to assess exactly how much each individual values a public good.
C) It is difficult to identify how public goods really benefit the society.
D) It is difficult to find out how demographics change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A television show like The Sopranos, for example, is:
A) rival and excludable.
B) nonrival but excludable.
C) rival but nonexcludable.
D) nonrival and nonexcludable.
A) rival and excludable.
B) nonrival but excludable.
C) rival but nonexcludable.
D) nonrival and nonexcludable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During the Middle Ages, many villages had areas reserved for families to take their cows or sheep to graze. All families were welcome to use this land without charge. This situation likely led to a(n):
A) tragedy of the commons.
B) finite of proportions.
C) marketable public good.
D) exhaustive equilibrium.
A) tragedy of the commons.
B) finite of proportions.
C) marketable public good.
D) exhaustive equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When entrepreneurs use advertising to pay for the provision of a public good, the outcome is typically:
A) efficient because the market price is zero and hence equal to the marginal cost of providing the public good.
B) efficient because the market price is equal to the benefits received from the public gooB.
C) inefficient because people are not paying for the benefits that they receive from the public gooC.
D) inefficient because while advertising generates some revenue for the producers, it typically does not generate enough to equal the social benefits received from the public good.
A) efficient because the market price is zero and hence equal to the marginal cost of providing the public good.
B) efficient because the market price is equal to the benefits received from the public gooB.
C) inefficient because people are not paying for the benefits that they receive from the public gooC.
D) inefficient because while advertising generates some revenue for the producers, it typically does not generate enough to equal the social benefits received from the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Though markets can provide goods which are excludable but nonrival, they do so at the price of:
A) efficiency.
B) inefficiency.
C) equity.
D) inequity.
A) efficiency.
B) inefficiency.
C) equity.
D) inequity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following solutions for public goods funding avoids both the problems of "forced riders" and "free riders"?
A) widespread taxation
B) advertising
C) donation based funding
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) widespread taxation
B) advertising
C) donation based funding
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A common resource is:
A) likely to be overutilized.
B) a good that, when used by one person, leaves less for everyone else.
C) rival but nonexcludable.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) likely to be overutilized.
B) a good that, when used by one person, leaves less for everyone else.
C) rival but nonexcludable.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For some public goods, such as Internet search engines, which are nonrival but potentially excludable, it is more profitable for the providers to:
A) exclude people who don't pay for its service.
B) sell advertising and provide its services for free.
C) sell advertising and also charge people for using the services.
D) offer the service to anyone for free.
A) exclude people who don't pay for its service.
B) sell advertising and provide its services for free.
C) sell advertising and also charge people for using the services.
D) offer the service to anyone for free.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following methods would help to produce optimal amounts of public goods?
A) antitrust law
B) regulation
C) privatization
D) taxation
A) antitrust law
B) regulation
C) privatization
D) taxation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) It is paradoxical that people can be made better off by requiring them to do something that they would choose to do voluntarily.
B) It is paradoxical that people cannot be made better off by requiring them to do something that they would choose to do voluntarily.
C) Even though none contribute voluntarily, all would agree to be taxed as long as everyone else is also taxed.
D) Even though everyone contributes voluntarily, none would agree to be taxed if everyone else is not taxed.
A) It is paradoxical that people can be made better off by requiring them to do something that they would choose to do voluntarily.
B) It is paradoxical that people cannot be made better off by requiring them to do something that they would choose to do voluntarily.
C) Even though none contribute voluntarily, all would agree to be taxed as long as everyone else is also taxed.
D) Even though everyone contributes voluntarily, none would agree to be taxed if everyone else is not taxed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Google provides a(n) ________ good, but uses advertising to make its good ________.
A) excludable; nonexcludable
B) common; more scarce
C) nonexcludable; excludable
D) public; private
A) excludable; nonexcludable
B) common; more scarce
C) nonexcludable; excludable
D) public; private

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An example of a common resource would be:
A) a street light.
B) the environment.
C) clothing.
D) cable TV.
A) a street light.
B) the environment.
C) clothing.
D) cable TV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following conditions would turn some people into forced riders?
A) People who must contribute to the public good because their benefit from the public good is high.
B) People who must contribute to the public good even though they will not benefit from the public good.
C) People who are not required to contribute to the public good if they will not receive any benefit from it.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) People who must contribute to the public good because their benefit from the public good is high.
B) People who must contribute to the public good even though they will not benefit from the public good.
C) People who are not required to contribute to the public good if they will not receive any benefit from it.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Although the provision of nonrival private goods is ________, we typically consider it ________.
A) efficient; an inefficient allocation due to its nonrival nature
B) inefficient; not that big a deal because we value diversity and creativity
C) inefficient; a big deal because it leads to many forced riders
D) efficient; a big deal because it leads to other types of market inefficiencies
A) efficient; an inefficient allocation due to its nonrival nature
B) inefficient; not that big a deal because we value diversity and creativity
C) inefficient; a big deal because it leads to many forced riders
D) efficient; a big deal because it leads to other types of market inefficiencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



