Deck 36: The Federal Budget: Taxes and Spending
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/158
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: The Federal Budget: Taxes and Spending
1
A situation in which the value of a country's exports exceeds the value of its imports is called a(n)
A) trade surplus.
B) capital surplus.
C) balance of payments surplus.
D) exchange rate surplus.
A) trade surplus.
B) capital surplus.
C) balance of payments surplus.
D) exchange rate surplus.
A
2
A situation where foreign capital inflows exceed domestic capital outflows to other nations is called a(n)
A) trade surplus.
B) capital surplus.
C) balance of payments surplus.
D) exchange rate surplus.
A) trade surplus.
B) capital surplus.
C) balance of payments surplus.
D) exchange rate surplus.
B
3
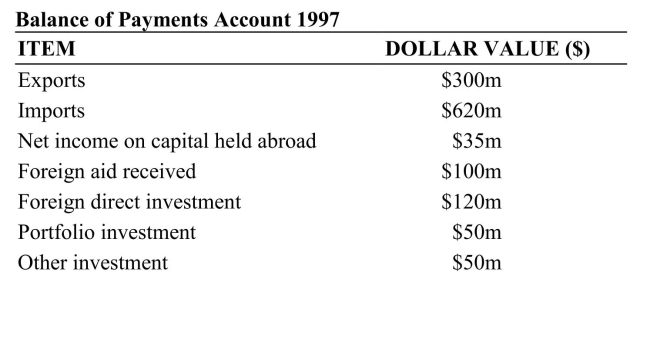 Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, which of the following statements is true for the year 1997?
Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, which of the following statements is true for the year 1997?A) This country had a balance of trade surplus of $620 million.
B) This country had a balance of trade deficit of $320 million.
C) This country had a current account deficit of $320 million.
D) This country had a current account surplus of $185 million.
B
4
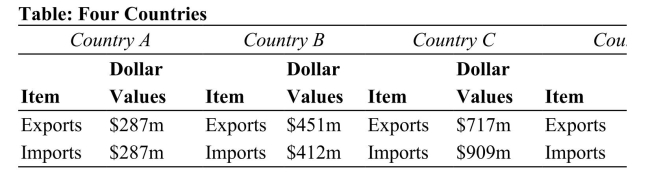 Values $132m $121m Reference: Ref 20-1 (Table: Four Countries) Refer to the table. Which of these countries has a trade surplus? I. Country A II. Country B III. Country C IV. Country D
Values $132m $121m Reference: Ref 20-1 (Table: Four Countries) Refer to the table. Which of these countries has a trade surplus? I. Country A II. Country B III. Country C IV. Country DA) I only
B) III only
C) I and III only
D) II and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When Koreans buy stock on the NYSE
A) this does not immediately create new investment in the United States.
B) portfolio investment in the United States increases.
C) the U.S. capital account increases.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) this does not immediately create new investment in the United States.
B) portfolio investment in the United States increases.
C) the U.S. capital account increases.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If this year's current account balance is -$100 billion and the capital account balance is $150 billion, then the amount of official reserves will
A) increase by $50 billion.
B) decrease by $50 billion.
C) increase by $250 billion.
D) decrease by $250 billion.
A) increase by $50 billion.
B) decrease by $50 billion.
C) increase by $250 billion.
D) decrease by $250 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The United States has a trade deficit with China. Because of this, U.S. Congresswoman Nancy Pelosi has called for
A) a tariff on goods exported to China.
B) a tariff on goods imported from China.
C) the export of toxic loans to China.
D) the purchase of Chinese currency by the U.S. Federal Reserve.
A) a tariff on goods exported to China.
B) a tariff on goods imported from China.
C) the export of toxic loans to China.
D) the purchase of Chinese currency by the U.S. Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When Koreans buy stock on the NYSE
A) the U.S. balance of trade increases.
B) the Korean capital account increases.
C) the U.S. capital account decreases.
D) the U.S. capital account increases.
A) the U.S. balance of trade increases.
B) the Korean capital account increases.
C) the U.S. capital account decreases.
D) the U.S. capital account increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
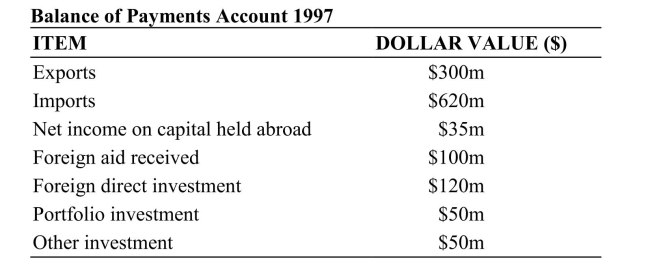 Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, what is the capital account balance for this country in 1997?
Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, what is the capital account balance for this country in 1997?A) $220 million
B) -$185 million
C) $1,055 million
D) $170 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Transactions included in the balance of payments are I. foreign direct investment. II. government deficits. III. imports.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The trade deficit and the _____ surplus essentially balance out and offset each other.
A) capital
B) trade
C) saving
D) reserve
A) capital
B) trade
C) saving
D) reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Transactions in the current account include I. official reserves. II. net income on capital held abroad. III. imports.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What occurs when the value of a country's exports exceeds the value of its imports?
A) a trade deficit
B) a trade surplus
C) a payment imbalance
D) a capital surplus
A) a trade deficit
B) a trade surplus
C) a payment imbalance
D) a capital surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
We call the yearly summary of all the economic transactions between residents of one country and the rest of the world a
A) trade deficit.
B) trade surplus.
C) balance of payments.
D) capital account.
A) trade deficit.
B) trade surplus.
C) balance of payments.
D) capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

 Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, what is the current account balance for this country in 1997?
Reference: Ref 20-2 (Table: Balance of Payments) According to the data in this table, what is the current account balance for this country in 1997?A) -$320 million
B) -$185 million
C) $135 million
D) $1,055 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A trade deficit occurs when
A) the total value of exports exceeds the total value of imports.
B) the total value of imports exceeds the total value of exports.
C) the total money payment to other countries exceeds the total money payment from other countries.
D) the total money payment from other countries exceeds the total money payment to other countries.
A) the total value of exports exceeds the total value of imports.
B) the total value of imports exceeds the total value of exports.
C) the total money payment to other countries exceeds the total money payment from other countries.
D) the total money payment from other countries exceeds the total money payment to other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
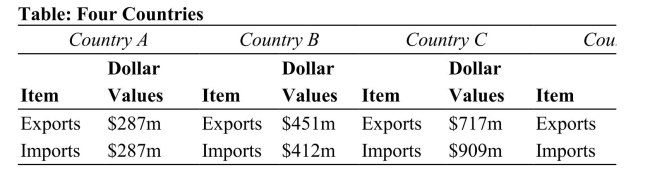 es Reference: Ref 20-1 (Table: Four Countries) Refer to the table. Which of these countries has a trade deficit?
es Reference: Ref 20-1 (Table: Four Countries) Refer to the table. Which of these countries has a trade deficit?A) Country A
B) Country B
C) Country C
D) Country D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The United States currently has a net ________ with the rest of the world.
A) trade deficit
B) capital deficit
C) balance of payments deficit
D) exchange rate deficit
A) trade deficit
B) capital deficit
C) balance of payments deficit
D) exchange rate deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When you shop at Old Navy, you run a private _____ with Old Navy.
A) trade deficit
B) trade surplus
C) payment imbalance
D) capital surplus
A) trade deficit
B) trade surplus
C) payment imbalance
D) capital surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a yearly summary of all the economic transactions between residents of one country and residents of the rest of the world?
A) the balance of trade
B) the balance of the capital account
C) the balance of the current account
D) the balance of payments
A) the balance of trade
B) the balance of the capital account
C) the balance of the current account
D) the balance of payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When Chinese investors purchase U.S. commercial real estate, the ______ increases in the United States.
A) trade deficit
B) balance of payments
C) capital account
D) current account
A) trade deficit
B) balance of payments
C) capital account
D) current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following includes the activity of a foreign firm constructing a new manufacturing plant in the United States?
A) foreign transfer payment
B) current account surplus
C) foreign direct investment
D) foreign portfolio investment
A) foreign transfer payment
B) current account surplus
C) foreign direct investment
D) foreign portfolio investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The difference between foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign aid is
A) not significant because both items are counted as part of the current account.
B) FDI refers to foreign businesses opening factories or operations, while foreign aid is monetary assistance.
C) FDI earns interest while foreign aid is a gift of money with no interest component.
D) FDI is monetary aid while foreign aid is the establishment of operations by foreign-owned businesses.
A) not significant because both items are counted as part of the current account.
B) FDI refers to foreign businesses opening factories or operations, while foreign aid is monetary assistance.
C) FDI earns interest while foreign aid is a gift of money with no interest component.
D) FDI is monetary aid while foreign aid is the establishment of operations by foreign-owned businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following transactions can be classified as foreign direct investment for the United States?
A) A Beijing antique dealer opens a store in downtown New York City.
B) The purchase of a Maserati Gran Turismo from a Maserati dealer in New Jersey.
C) A Korean businessman, living in South Korea, purchases stock on the NYSE.
D) A Bangladeshi-American purchases a home in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
A) A Beijing antique dealer opens a store in downtown New York City.
B) The purchase of a Maserati Gran Turismo from a Maserati dealer in New Jersey.
C) A Korean businessman, living in South Korea, purchases stock on the NYSE.
D) A Bangladeshi-American purchases a home in Dhaka, Bangladesh.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose a country's official reserves do not change. If it has a $20 billion deficit in its current account, then it must also have a $20 billion
A) surplus in its balance of payments.
B) deficit in its balance of payments.
C) surplus in its capital account.
D) deficit in its capital account.
A) surplus in its balance of payments.
B) deficit in its balance of payments.
C) surplus in its capital account.
D) deficit in its capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When the United States has a current account deficit, the U.S. capital account
A) will have a deficit also.
B) will be balanced.
C) will have a surplus.
D) must be falling.
A) will have a deficit also.
B) will be balanced.
C) will have a surplus.
D) must be falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Other investment takes place when foreigners
A) construct new business plants in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) construct new business plants in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Portfolio investment takes place when foreigners
A) construct new business plants in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) construct new business plants in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
All current account transactions take place in
A) future periods only.
B) the current period only.
C) the current and future periods.
D) the current and past periods.
A) future periods only.
B) the current period only.
C) the current and future periods.
D) the current and past periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The presence of a saving glut in other countries is one possible reason for the United States's
A) current account deficit.
B) capital account surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) current account deficit.
B) capital account surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Foreign portfolio investment is included in the __________ account.
A) current
B) trade
C) direct investment
D) capital
A) current
B) trade
C) direct investment
D) capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is included in the current account?
A) the balance of trade
B) net transfer payments
C) net income on capital held abroad
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) the balance of trade
B) net transfer payments
C) net income on capital held abroad
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The presence of a low saving rate in the United States is one possible reason for the United States's
A) current account deficit.
B) capital account surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) current account deficit.
B) capital account surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which transactions cause the U.S. capital account to increase?
A) Japanese citizens purchase U.S. exports.
B) Japanese citizens purchase U.S. imports.
C) Japanese citizens purchase real estate in the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) Japanese citizens purchase U.S. exports.
B) Japanese citizens purchase U.S. imports.
C) Japanese citizens purchase real estate in the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Increases in the U.S. capital surpluses since 1980s were caused by increases in
A) current account deficits.
B) American saving rates.
C) the balance of payments.
D) U.S. official reserves.
A) current account deficits.
B) American saving rates.
C) the balance of payments.
D) U.S. official reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
U.S. capital account surpluses are related to I. government deficits. II. high money supply growth. III. increases in the trade gap.
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A trade deficit is balanced with a
A) trade surplus.
B) capital account surplus.
C) capital account deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) trade surplus.
B) capital account surplus.
C) capital account deficit.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Foreign direct investment takes place when foreigners
A) construct a new business plant in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) construct a new business plant in the United States.
B) buy U.S. stocks and bonds.
C) shift bank deposits into the United States from outside the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a capital account transaction?
A) foreign purchases of U.S. stocks
B) foreign purchases of U.S. bonds
C) foreign purchases of U.S. buildings
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) foreign purchases of U.S. stocks
B) foreign purchases of U.S. bonds
C) foreign purchases of U.S. buildings
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A country with a negative current account (trade deficit) has
A) a negative capital account.
B) a positive capital account.
C) no capital account.
D) large budget deficits.
A) a negative capital account.
B) a positive capital account.
C) no capital account.
D) large budget deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
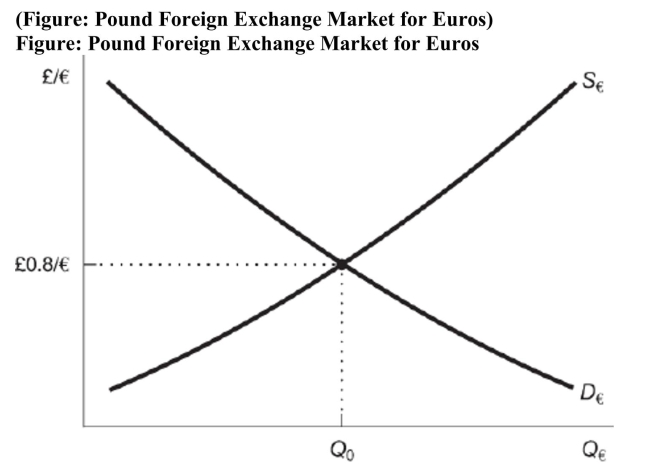 Use the figure to answer the following question: If the British become wealthier and begin importing more goods from the European Union, which shift would occur in the foreign exchange market for euros?
Use the figure to answer the following question: If the British become wealthier and begin importing more goods from the European Union, which shift would occur in the foreign exchange market for euros?A) The demand for euros would shift to the right.
B) The demand for euros would shift to the left.
C) The supply of euros would shift to the right.
D) The supply of euros would shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A decrease in the value of the domestic currency in terms of other currencies is called __________ of the domestic currency.
A) a parity
B) a discount
C) an appreciation
D) a depreciation
A) a parity
B) a discount
C) an appreciation
D) a depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A trade deficit might signal a problem of
A) high unemployment.
B) high taxes.
C) low savings.
D) low spending.
A) high unemployment.
B) high taxes.
C) low savings.
D) low spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is most likely to significantly increase the U.S. savings rate?
A) imports quotas
B) import tariffs
C) reducing the federal government deficit
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) imports quotas
B) import tariffs
C) reducing the federal government deficit
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars 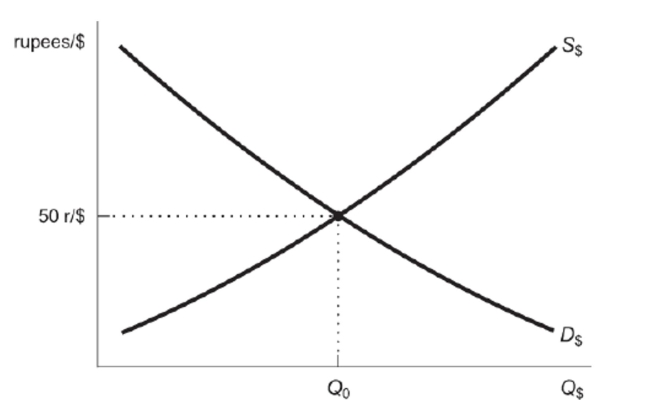 Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a decrease in the money supply by the Federal Reserve cause?
Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a decrease in the money supply by the Federal Reserve cause?
A) the demand for dollars to shift to the right
B) the demand for dollars to shift to the left
C) the supply of dollars to shift to the right
D) the supply of dollars to shift to the left
 Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a decrease in the money supply by the Federal Reserve cause?
Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a decrease in the money supply by the Federal Reserve cause?A) the demand for dollars to shift to the right
B) the demand for dollars to shift to the left
C) the supply of dollars to shift to the right
D) the supply of dollars to shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2004 the price of 1 euro in terms of Japanese yen was
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2004 the price of 1 euro in terms of Japanese yen wasA) �200.
B) �100.
C) �250.
D) �400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
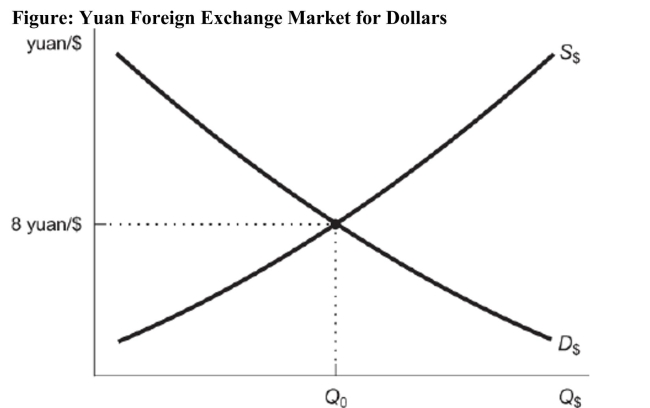 Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, if Americans begin to import more from China, which of the following is a possible outcome for the price of the dollar?
Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, if Americans begin to import more from China, which of the following is a possible outcome for the price of the dollar?A) 10 yuan per dollar
B) 9 yuan per dollar
C) 8 yuan per dollar
D) 7 yuan per dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An exchange rate is the cost, or price, of
A) exporting goods.
B) importing goods.
C) borrowing in a foreign country.
D) one currency in terms of another.
A) exporting goods.
B) importing goods.
C) borrowing in a foreign country.
D) one currency in terms of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

A) the yen appreciated against the dollar.
B) the yen depreciated against the dollar.
C) both the yen and the dollar appreciated.
D) both the yen and the dollar depreciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2004 the price of 1 Japanese yen in terms of U.S. dollars was
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2004 the price of 1 Japanese yen in terms of U.S. dollars wasA) �200.
B) �1.
C) $200.
D) $0.005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Canadian dollar was US$1.25 for C$1, then a shirt that costs US$20 would cost
A) C$25.
B) C$21.25.
C) C$18.75.
D) C$16.
A) C$25.
B) C$21.25.
C) C$18.75.
D) C$16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The United States is the perfect place for other countries to invest in, if they expect to experience
A) higher capital accounts.
B) balanced trade.
C) lower trade deficits.
D) lower interest payments.
A) higher capital accounts.
B) balanced trade.
C) lower trade deficits.
D) lower interest payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?A) In 2004, the U.S. dollar had not changed relative to all of the other currencies.
B) In 2004, the Japanese yen had depreciated relative to the U.S. dollar.
C) In 2004, the Japanese yen had appreciated relative to the European euro.
D) In 2004, the European euro had appreciated relative to the British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2000 the price of 1 euro in terms of British pounds was
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information for the two years in the table, in the year 2000 the price of 1 euro in terms of British pounds wasA) �1.25.
B) �0.8.
C) �2.
D) �1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
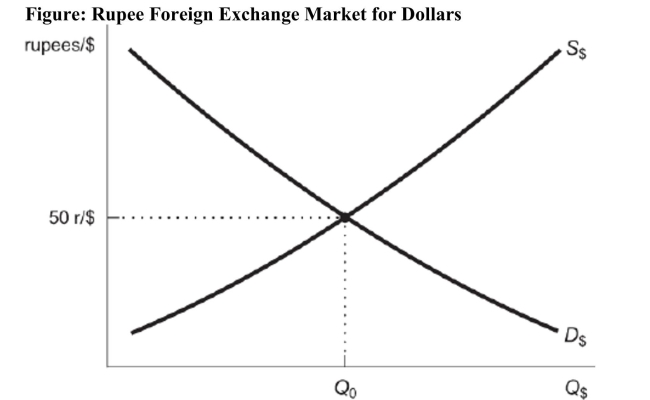 Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a rise in real interest rates in the United States cause?
Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on the figure, what will a rise in real interest rates in the United States cause?A) the demand for dollars to shift to the right
B) the demand for dollars to shift to the left
C) the supply of dollars to shift to the right
D) the supply of dollars to shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?A) In 2004, the Japanese yen had become stronger relative to all other currencies.
B) In 2004, the American dollar had become weaker relative to all other currencies.
C) In 2004, the price of 1 European euro had doubled relative to Japanese yen.
D) In 2004, the price of 1 British pound had not changed relative to European euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars 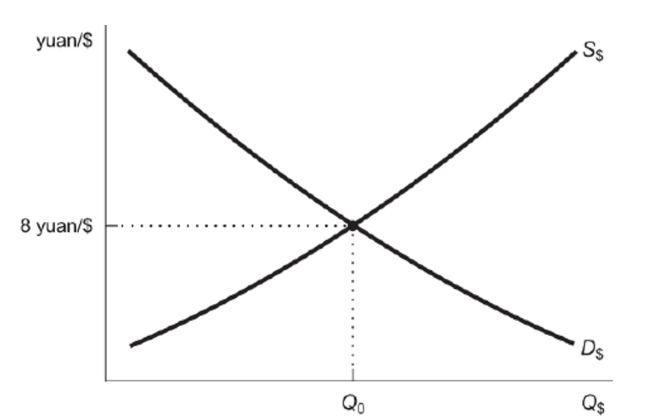 Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, which of the following statements is correct?
Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, which of the following statements is correct?
A) Moving up the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to all world currencies.
B) Moving up the y-axis, the American dollar depreciates relative to the Chinese yuan.
C) Moving down the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to the U.S. dollar.
D) Moving up the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to the U.S. dollar.
 Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, which of the following statements is correct?
Reference: Ref 20-4 (Figure: Yuan Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Based on this figure, which of the following statements is correct?A) Moving up the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to all world currencies.
B) Moving up the y-axis, the American dollar depreciates relative to the Chinese yuan.
C) Moving down the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to the U.S. dollar.
D) Moving up the y-axis, the Chinese yuan depreciates relative to the U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
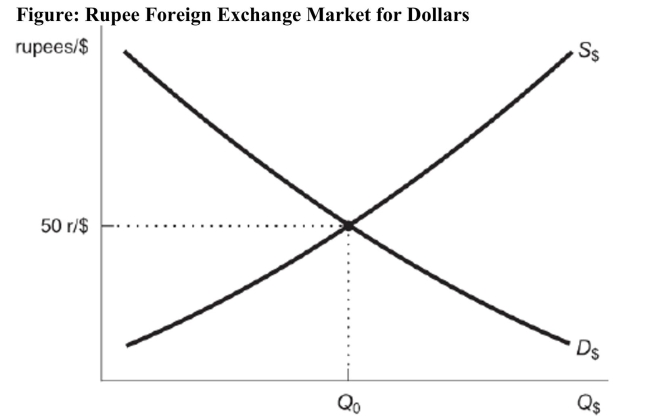 Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Use the figure to answer this question: Suppose war breaks out in India, and there is a great deal of political instability. Which of the scenarios would likely occur in the rupee/dollar foreign exchange market? I. The demand for U.S. dollars would shift to the right. II. The demand for U.S. dollars would shift to the left. III. The supply of U.S. dollars would shift to the right. IV. The supply of U.S. dollars would shift to the left.
Reference: Ref 20-5 (Figure: Rupee Foreign Exchange Market for Dollars) Use the figure to answer this question: Suppose war breaks out in India, and there is a great deal of political instability. Which of the scenarios would likely occur in the rupee/dollar foreign exchange market? I. The demand for U.S. dollars would shift to the right. II. The demand for U.S. dollars would shift to the left. III. The supply of U.S. dollars would shift to the right. IV. The supply of U.S. dollars would shift to the left.A) I and III only
B) I and IV only
C) II and III only
D) II and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?
Reference: Ref 20-3 (Table: Exchange Rates) Using the hypothetical exchange rate information in the table, which of the following statements is correct?A) In 2004, the British pound had become stronger relative to all other currencies.
B) In 2004, the European Euro had become stronger relative to all other currencies.
C) In 2004, the U.S. dollar had become stronger relative to all other currencies.
D) In 2004, the Japanese yen had become stronger relative to all other currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What does knowing that $1.25 buys one euro tell you?
A) the currency reserve ratio
B) the exchange rate
C) the foreign money replacement rate
D) the capital index conversion rate
A) the currency reserve ratio
B) the exchange rate
C) the foreign money replacement rate
D) the capital index conversion rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
With a floating exchange rate, an increase in the U.S. demand for Japanese exports will cause
A) the yen to appreciate.
B) the dollar to depreciate.
C) an increase in the number of yen exchanged.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) the yen to appreciate.
B) the dollar to depreciate.
C) an increase in the number of yen exchanged.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the exchange rate is written as dollars per yen, the exchange rate represents the
A) official government price of the dollar.
B) official government price of the yen.
C) price of 1 yen in dollars.
D) price of 1 dollar in yen.
A) official government price of the dollar.
B) official government price of the yen.
C) price of 1 yen in dollars.
D) price of 1 dollar in yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When the exchange rate is written as dollars per yen, an increase in the exchange rate means that
A) the yen is increasing in value.
B) the dollar is decreasing in value.
C) Japanese goods are becoming more expensive in the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) the yen is increasing in value.
B) the dollar is decreasing in value.
C) Japanese goods are becoming more expensive in the United States.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the short run, a tighter monetary policy by the U.S. Federal Reserve leads to
A) an increase in the supply of dollars and a dollar depreciation.
B) a decrease in the supply of dollars and a dollar appreciation.
C) an increase in the demand for dollars and a dollar depreciation.
D) a decrease in the demand for dollars and a dollar appreciation.
A) an increase in the supply of dollars and a dollar depreciation.
B) a decrease in the supply of dollars and a dollar appreciation.
C) an increase in the demand for dollars and a dollar depreciation.
D) a decrease in the demand for dollars and a dollar appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The nominal exchange rate in Kenya is 94 Kenyan shillings per U.S. dollar. A burger in the United States costs $2. A similar burger at ―Steers Restaurant‖ in Kenya costs 94 shillings. The real exchange rate in terms of U.S. burgers for Kenyan burgers is
A) 1:1.
B) 1:2.
C) 1:1/2.
D) 2:1.
A) 1:1.
B) 1:2.
C) 1:1/2.
D) 2:1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If U.S. producers export more wine to France, then
A) the demand for dollars will increase.
B) the supply of euros will increase.
C) the supply for both dollars and euros will increase.
D) the demand for both dollars and euros will increase.
A) the demand for dollars will increase.
B) the supply of euros will increase.
C) the supply for both dollars and euros will increase.
D) the demand for both dollars and euros will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
With a floating exchange rate, an increase in the U.S. demand for Japanese exports will cause the supply of yen to
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become less elastic.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become less elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is an increase in the price of currency in terms of another currency called?
A) exchange rate
B) elevation
C) accumulation
D) appreciation
A) exchange rate
B) elevation
C) accumulation
D) appreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the short run, with floating exchange rates, the exchange rate is determined by
A) the supply of the currency only.
B) the demand for the currency only.
C) both the supply and demand for the currency.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) the supply of the currency only.
B) the demand for the currency only.
C) both the supply and demand for the currency.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
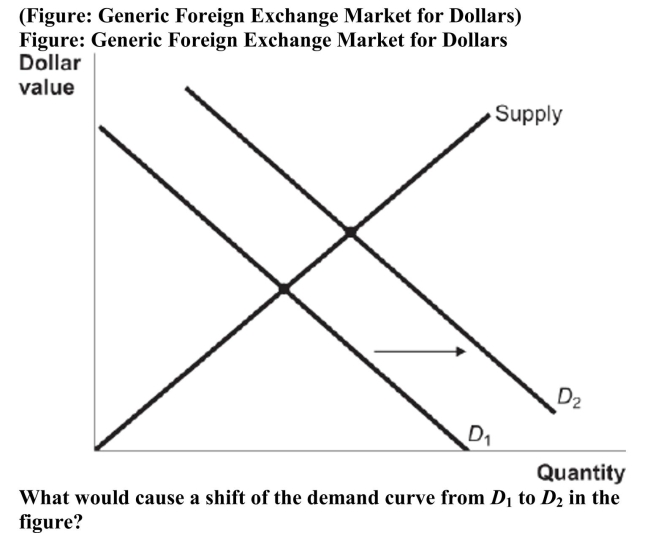
A) an increase in the export of U.S. beef to China
B) a purchase of Japanese corporate bonds by Americans
C) a sale of U.S. Treasury bonds by Chinese bondholders
D) an increase of the dollar supply by the U.S. Federal Reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Higher interest rates, a stable government, and increased exports contribute to
A) high taxes.
B) trade deficits.
C) a strong currency.
D) high GDP per capita.
A) high taxes.
B) trade deficits.
C) a strong currency.
D) high GDP per capita.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The increased supply of a currency will cause its
A) purchasing power parity to rise.
B) value to depreciate.
C) reserves to increase.
D) value to appreciate.
A) purchasing power parity to rise.
B) value to depreciate.
C) reserves to increase.
D) value to appreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When a country becomes more attractive for foreign investment we would expect an
A) increase in foreign direct investment in the country.
B) appreciation in the country's exchange rate.
C) increase in the demand for that country's currency.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) increase in foreign direct investment in the country.
B) appreciation in the country's exchange rate.
C) increase in the demand for that country's currency.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An appreciation of the Mexican peso would most likely be a result of
A) an increase in Mexican imports in the United States.
B) an increase in the supply of pesos.
C) an increase of foreign investment in Mexico.
D) a decrease in Mexican exports to the United States.
A) an increase in Mexican imports in the United States.
B) an increase in the supply of pesos.
C) an increase of foreign investment in Mexico.
D) a decrease in Mexican exports to the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
With a floating exchange rate, an increase in the U.S. interest rate will cause
A) capital to flow into the United States.
B) an increase in the demand for dollars.
C) an appreciation of the dollar.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) capital to flow into the United States.
B) an increase in the demand for dollars.
C) an appreciation of the dollar.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
With a floating exchange rate, an increase in the U.S. demand for Japanese exports will cause the demand for yen to
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become less elastic.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become less elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
With a floating exchange rate, when the Federal Reserve increases the U.S. money supply the U.S. dollar will
A) appreciate.
B) depreciate.
C) become more scarce.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) appreciate.
B) depreciate.
C) become more scarce.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An increase in the demand for a country's exports will have what effect on its currency?
A) Its value will not change.
B) Its value will increase.
C) Its value will decrease.
D) Its value will depreciate.
A) Its value will not change.
B) Its value will increase.
C) Its value will decrease.
D) Its value will depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the exchange market for the U.S. dollar versus the Japanese yen. The demand for yen comes from
A) the United States only.
B) Japan only.
C) both the United States and Japan.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) the United States only.
B) Japan only.
C) both the United States and Japan.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the exchange market for the U.S. dollar versus the Japanese yen. The supply of yen comes from
A) the United States only.
B) Japan only.
C) both the United States and Japan.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) the United States only.
B) Japan only.
C) both the United States and Japan.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 158 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



