Deck 25: Consumer Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/141
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Consumer Choice
1
The correlation between infant mortality and per capita GDP is
A) zero.
B) positive.
C) negative.
D) unpredictable.
A) zero.
B) positive.
C) negative.
D) unpredictable.
C
2
Most children live in countries where infant survival rates are lower than those in the United States because I. wealthier countries have fewer civil wars and riots. II. wealthier countries have better neonatal care. III. people in poor countries have more children because of the low survival rates.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
D
3
If 10 percent of the population had an average income of $46,000 and the population as a whole had an average income of $10,000, what would the average income be for the other 90 percent of the population?
A) $6,000
B) $10,000
C) $9,000
D) There is not enough information provided to answer the question.
A) $6,000
B) $10,000
C) $9,000
D) There is not enough information provided to answer the question.
A
4
Suppose a country has real GDP of $10,000 at the beginning of the year 2005. Each year the economy grows by 5 percent. By how much will GDP rise by the end of 2007?
A) $500
B) $1,576.25
C) $1,500
D) $1,025
A) $500
B) $1,576.25
C) $1,500
D) $1,025

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What percentage of the world's population lives in a country that has a GDP per capita above the world's average of $9,133?
A) 10 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 55 percent
A) 10 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 55 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The United States and Western European countries began to experience accelerated economic growth during which century?
A) 12th
B) 16th
C) 17th
D) 19th
A) 12th
B) 16th
C) 17th
D) 19th

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the year 2000, the world's average per capita GDP was $9,133. What percent of the world's population lived in a country with per capita GDP that was below $9,133?
A) 40 percent
B) 50 percent
C) 65 percent
D) 80 percent
A) 40 percent
B) 50 percent
C) 65 percent
D) 80 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
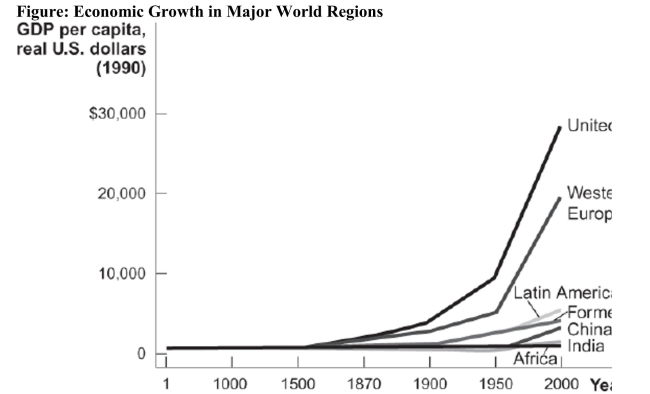 Reference: Ref 7-2 (Figure: Economic Growth in Major World Regions) Refer to the figure, which shows us how real GDP per capita has been changing over time in different regions of the world. Studying the chart shows
Reference: Ref 7-2 (Figure: Economic Growth in Major World Regions) Refer to the figure, which shows us how real GDP per capita has been changing over time in different regions of the world. Studying the chart showsA) that all these regions and countries were poor at one time.
B) the distribution of wealth within the various regions over time.
C) the rate of infant mortality within the various regions over time.
D) the level of life expectancy within the various regions at various points in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
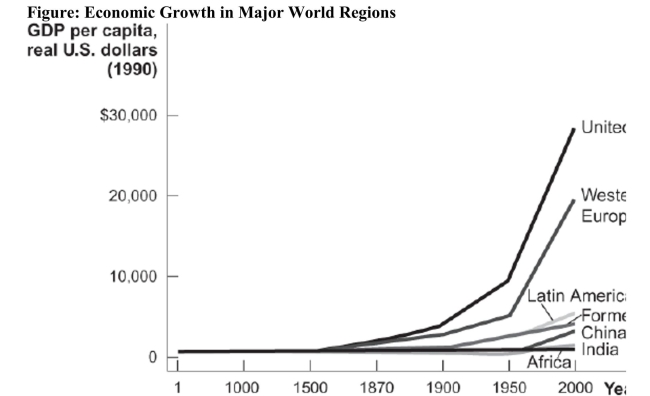 Reference: Ref 7-2 (Figure: Economic Growth in Major World Regions) Refer to the figure, which shows us how real GDP per capita has been changing over time in different regions and countries of the world. Studying the chart shows I. that growth in Africa has stagnated. II. that the world only saw significant growth in real GDP per capita after 1950. III. that life expectancy has risen tremendously across the world regions.
Reference: Ref 7-2 (Figure: Economic Growth in Major World Regions) Refer to the figure, which shows us how real GDP per capita has been changing over time in different regions and countries of the world. Studying the chart shows I. that growth in Africa has stagnated. II. that the world only saw significant growth in real GDP per capita after 1950. III. that life expectancy has risen tremendously across the world regions.A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Refer to the figure. Based on the data in the figure, about how many times wealthier is the richest country when compared to the poorest country?
Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Refer to the figure. Based on the data in the figure, about how many times wealthier is the richest country when compared to the poorest country?A) 500 times
B) 50 times
C) 10 times
D) 30 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Wealthier nations tend to have
A) better educational opportunities.
B) lower infant survival rates.
C) lower life expectancy rates.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) better educational opportunities.
B) lower infant survival rates.
C) lower life expectancy rates.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure: The Distribution of World Income (2000) 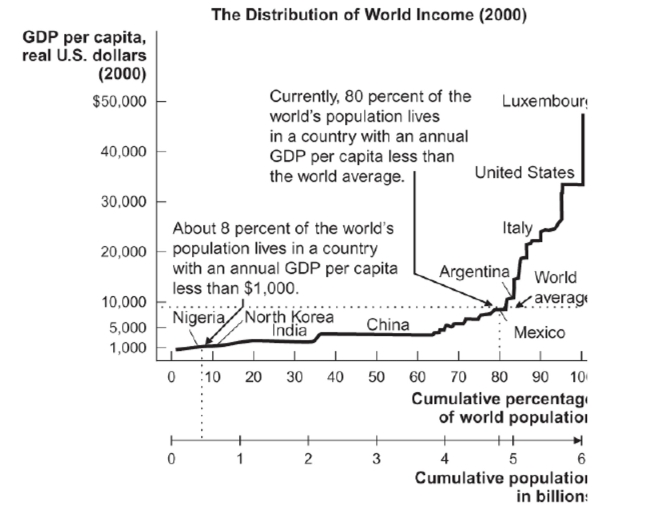 Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Based on the data in the figure, people in the United States are about how many times wealthier than the world average GDP per capita?
Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Based on the data in the figure, people in the United States are about how many times wealthier than the world average GDP per capita?
A) 50 times
B) 10 times
C) 4 times
D) 30 times
 Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Based on the data in the figure, people in the United States are about how many times wealthier than the world average GDP per capita?
Reference: Ref 7-1 (Figure: The Distribution of World Income) Based on the data in the figure, people in the United States are about how many times wealthier than the world average GDP per capita?A) 50 times
B) 10 times
C) 4 times
D) 30 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
One of the indicators of a country's economic well-being is infant mortality. Most of the world's children live in countries with an infant mortality rate that is
A) about the same as the infant mortality rate in the United States.
B) well above the infant mortality rate in the United States.
C) below the infant mortality rate in the United States.
D) close to zero.
A) about the same as the infant mortality rate in the United States.
B) well above the infant mortality rate in the United States.
C) below the infant mortality rate in the United States.
D) close to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Throughout human history we know that
A) all countries were able to establish periods of high levels of real GDP per capita.
B) most countries were only able to establish a few decades of high levels of real GDP per capita.
C) not until the early 19th century were a few countries able to establish sustained long-run economic growth.
D) all countries will eventually return to very low levels of real GDP per capita.
A) all countries were able to establish periods of high levels of real GDP per capita.
B) most countries were only able to establish a few decades of high levels of real GDP per capita.
C) not until the early 19th century were a few countries able to establish sustained long-run economic growth.
D) all countries will eventually return to very low levels of real GDP per capita.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Approximately how many people in the world live on less than $2 per day?
A) 5 million
B) 25 million
C) 1 billion
D) 2 billion
A) 5 million
B) 25 million
C) 1 billion
D) 2 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One of the indicators of a country's economic well-being is infant mortality. Piped water and flush toilets together reduce infant mortality by approximately
A) 40 percent.
B) 50 percent.
C) 60 percent.
D) 70 percent.
A) 40 percent.
B) 50 percent.
C) 60 percent.
D) 70 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the year 2000, what percent of the world population lived in a country with an annual GDP per capita less than the world's average annual GDP per capita?
A) 50 percent
B) 60 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 80 percent
A) 50 percent
B) 60 percent
C) 40 percent
D) 80 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The world's average level of GDP per capita is $9,133. This is about the same as which nation?
A) China
B) Mexico
C) Nigeria
D) India
A) China
B) Mexico
C) Nigeria
D) India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When considering human history we see that ______ growth in real per capita GDP generally did not occur before the beginning of the 19th century ______.
A) long-run sustainable; and even now only for a few countries
B) short-run; in some parts of the world
C) long-run sustainable; but now exists in many countries around the world
D) None of these answers is correct.
A) long-run sustainable; and even now only for a few countries
B) short-run; in some parts of the world
C) long-run sustainable; but now exists in many countries around the world
D) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
At the beginning of the 19th century, growth rates in per capita GDP for different countries began to
A) diverge.
B) converge.
C) equalize.
D) fall.
A) diverge.
B) converge.
C) equalize.
D) fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When did South Korea's period of high growth occur?
A) 1900-1950
B) 1945-1970
C) 1950-1970
D) 1970-1990
A) 1900-1950
B) 1945-1970
C) 1950-1970
D) 1970-1990

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The rule of 70 indicates that if the growth rate of a variable is X percent per year, the variable will double in
A) 70 + X years.
B) 70 - X years.
C) 70 × X years.
D) 70 ÷ X years.
A) 70 + X years.
B) 70 - X years.
C) 70 × X years.
D) 70 ÷ X years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What two countries are known for growth disasters since 1950?
A) South Korea and Argentina
B) South Korea and China
C) Nigeria and Argentina
D) Nigeria and South Africa
A) South Korea and Argentina
B) South Korea and China
C) Nigeria and Argentina
D) Nigeria and South Africa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the annual growth rate of a nation is 5 percent, how many years would it take for the GDP per capita to double?
A) 10
B) 12
C) 14
D) 17.5
A) 10
B) 12
C) 14
D) 17.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Over one billion of the world's people live on less than _______ per day.
A) $2.00
B) $5.00
C) $10.00
D) $12.00
A) $2.00
B) $5.00
C) $10.00
D) $12.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the annual real GDP per capita in the United States is currently $50,000 and growing at 2.5 percent per year, how many years will it take to reach an annual real GDP per capita of $100,000?
A) approximately 20 years
B) approximately 28 years
C) approximately 40 years
D) approximately 35 years
A) approximately 20 years
B) approximately 28 years
C) approximately 40 years
D) approximately 35 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A nation's real per capita GDP is $7,788 in 2004 and $8,080 in 2005. What is the growth rate of real GDP per capita?
A) 2.75 percent
B) 3.5 percent
C) 3.61 percent
D) 3.75 percent
A) 2.75 percent
B) 3.5 percent
C) 3.61 percent
D) 3.75 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The text defines economic growth as an increase in
A) GDP.
B) real GDP.
C) per capita GDP.
D) real per capita GDP.
A) GDP.
B) real GDP.
C) per capita GDP.
D) real per capita GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a nation doubles its GDP per capita in 20 years, what is its annual growth rate?
A) 3.5 percent
B) 4.2 percent
C) 6.5 percent
D) 7 percent
A) 3.5 percent
B) 4.2 percent
C) 6.5 percent
D) 7 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure: Two Growth Miracles and Two Growth Disasters 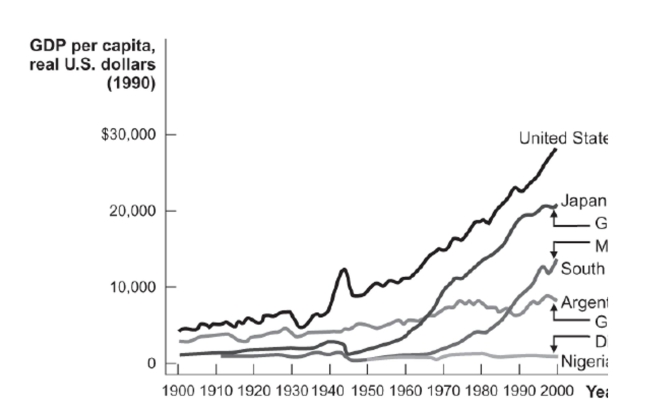 Reference: Ref 7-3 (Figure: Two Growth Miracles and Two Growth Disasters) Based on the figure, which country has stagnated in terms of growth?
Reference: Ref 7-3 (Figure: Two Growth Miracles and Two Growth Disasters) Based on the figure, which country has stagnated in terms of growth?
A) Argentina
B) Nigeria
C) South Korea
D) Japan
 Reference: Ref 7-3 (Figure: Two Growth Miracles and Two Growth Disasters) Based on the figure, which country has stagnated in terms of growth?
Reference: Ref 7-3 (Figure: Two Growth Miracles and Two Growth Disasters) Based on the figure, which country has stagnated in terms of growth?A) Argentina
B) Nigeria
C) South Korea
D) Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If per capita real GDP was $30,000 in the year 2000 and $31,000 in 2001, the growth rate of per capita GDP in 2001 was approximately
A) 0.3 percent.
B) 3.3 percent.
C) 33 percent.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) 0.3 percent.
B) 3.3 percent.
C) 33 percent.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the method used for approximating the length of time necessary for GDP per capita to double?
A) rule of 50
B) rule of 60
C) rule of 70
D) rule of 80
A) rule of 50
B) rule of 60
C) rule of 70
D) rule of 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If you received a constant annual rate of return of 7 percent on an investment of $10,000, how many years will it take before you have $20,000?
A) 10 years
B) 7 years
C) 35 years
D) 2.86 years
A) 10 years
B) 7 years
C) 35 years
D) 2.86 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A small economy has a current real GDP per capita level of $2,000 and a GDP growth rate of 2 percent. Use the Rule of 70 to estimate how long it would take for this economy to quadruple its GDP per capita.
A) 10 years
B) 14 years
C) 70 years
D) 35 years
A) 10 years
B) 14 years
C) 70 years
D) 35 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If real GDP per capita in the United States is currently $50,000 and grows at 2.5 percent per year, how many years will it take to reach $200,000?
A) approximately 56 years
B) approximately 28 years
C) approximately 84 years
D) approximately 112 years
A) approximately 56 years
B) approximately 28 years
C) approximately 84 years
D) approximately 112 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a country's annual growth rate is 2 percent, how many years will it take for this country's real per capita GDP to double?
A) 140
B) 70
C) 35
D) never
A) 140
B) 70
C) 35
D) never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a country's initial real GDP is $60,000 and its yearly growth rate of GDP is 5 percent, use the Rule of 70 to determine approximately how many years it would take for this economy to double its GDP.
A) 20 years
B) 14 years
C) 70 years
D) 12 years
A) 20 years
B) 14 years
C) 70 years
D) 12 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What term do economists use to describe the growth rate of GDP per capita?
A) national growth
B) aggregate growth
C) real growth
D) economic growth
A) national growth
B) aggregate growth
C) real growth
D) economic growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose economies A and B have the same initial level of GDP per capita at $15,000, and each economy begins with a constant growth rate of 1 percent per year. (Neither country has good institutions for economic growth at first.) Then Country A enters an era of political stability, establishes property rights, and installs incentives for entrepreneurship. Country A's economic growth rate consequently improves to 5 percent. Assuming population growth rates remain unaffected, how much longer will it take Country B to double its per capita GDP level compared to Country A?
A) 70 years
B) 14 years
C) 56 years
D) 28 years
A) 70 years
B) 14 years
C) 56 years
D) 28 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
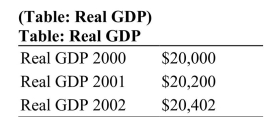 What is the annual growth rate in this economy?
What is the annual growth rate in this economy?A) 10 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 2.01 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Physical capital is the
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Factors of production that contribute to growth in per capita GDP include
A) proximal and ultimate factors of production.
B) physical capital, skilled labor, and technological know- how.
C) organization of resources.
D) institutions.
A) proximal and ultimate factors of production.
B) physical capital, skilled labor, and technological know- how.
C) organization of resources.
D) institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A rural village in a developing country has an economy based on agriculture. Then the government of the country provides the village with newly developed hybrid seeds that more than double the agricultural yield per acre. This story illustrates the growth of per capita GDP in the village through which factor(s) of production?
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) both human capital and technological knowledge
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) both human capital and technological knowledge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are the four factors of production that combine to contribute to the wealth of nations?
A) incentives, institutions, organization, and technical knowledge
B) international trading partners, natural resources, efficient government, and low taxes
C) human capital, physical capital, technical knowledge, and organization
D) property rights, honest government, political stability, and a dependable legal system
A) incentives, institutions, organization, and technical knowledge
B) international trading partners, natural resources, efficient government, and low taxes
C) human capital, physical capital, technical knowledge, and organization
D) property rights, honest government, political stability, and a dependable legal system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A country increases human capital by engaging in activities that improve ________.
A) research and development
B) education
C) income distribution
D) physical capital
A) research and development
B) education
C) income distribution
D) physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A country increases technological knowledge by engaging in activities that improve ________.
A) research and development
B) education
C) workers health
D) physical capital
A) research and development
B) education
C) workers health
D) physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A firm that pays for workers to attend a technical college is increasing its
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) gains from trade.
D) technical knowledge.
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) gains from trade.
D) technical knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Human capital is the
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is another term for proximate causes for wealth of nations?
A) direct causes
B) indirect causes
C) ultimate causes
D) physical causes
A) direct causes
B) indirect causes
C) ultimate causes
D) physical causes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Farmers who use tractors instead of horse-drawn plows have greater yields. Which factor of production explains this result?
A) organizational skills
B) natural resources
C) technical knowledge
D) physical capital
A) organizational skills
B) natural resources
C) technical knowledge
D) physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following are proximate causes for the wealth of nations?
A) institutions and incentives
B) technical knowledge and human capital
C) customs, practices, and social norms
D) property rights and honest government
A) institutions and incentives
B) technical knowledge and human capital
C) customs, practices, and social norms
D) property rights and honest government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Workers ability to use various tools is known as _____________.
A) technological knowledge
B) human capital
C) knowledge
D) experience
A) technological knowledge
B) human capital
C) knowledge
D) experience

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT an example of physical capital?
A) tractor
B) cell phone
C) computer
D) a share of Caterpillar InD. stock
A) tractor
B) cell phone
C) computer
D) a share of Caterpillar InD. stock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Countries that have high per capita GDP have
A) high levels of physical capital per worker.
B) high levels of human capital per worker.
C) high levels of technology per worker.
D) high levels of all three factors of production.
A) high levels of physical capital per worker.
B) high levels of human capital per worker.
C) high levels of technology per worker.
D) high levels of all three factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A developing country could buy (or be given) ____________ and ___________ more easily than ___________________.
A) technological knowledge; physical capital; human capital
B) physical capital; human capital; technological capital
C) human capital; technological capital; physical capital
D) human capital; work experience; technological capital
A) technological knowledge; physical capital; human capital
B) physical capital; human capital; technological capital
C) human capital; technological capital; physical capital
D) human capital; work experience; technological capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Technological knowledge is the
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.
A) stock of tools including machines, structures, and equipment.
B) productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
C) knowledge about how the world works that is used to produce goods and services.
D) organizational skills of business owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the most proximate (or direct) cause of growth in real GDP per capita?
A) the factors of production
B) institutions
C) political system in the economy
D) incentives
A) the factors of production
B) institutions
C) political system in the economy
D) incentives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
One measure of student output is number of completed math problems produced. Using pen and paper only, a student can complete 50 math problems in 2 hours. Using pen, paper and calculator, this same student can complete 100 math problems in 2 hours. (The student is already familiar with, and knows how to use, the calculator.) This scenario illustrates the use of which factor of production?
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) technological knowledge.
D) both human capital and technological knowledge.
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) technological knowledge.
D) both human capital and technological knowledge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is NOT directly related to human capital?
A) a life-saving drug
B) work experience
C) schooling
D) an understanding of chemistry
A) a life-saving drug
B) work experience
C) schooling
D) an understanding of chemistry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Increasing the amount of physical capital tends to _______ output per hour of workers and _______ the value of workers.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Enforced property rights are important to increase which of the following?
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) All of the factors listed are correct.
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) All of the factors listed are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Between 1978 and 1983, food production in China rose by 50 percent and 170 million people rose above the international poverty line. This occurred because of
A) the institution of the ―it is glorious to be rich‖ policy.
B) the return to private property rights in farming.
C) the fall of communism in China.
D) the teaching of Mao Zedong.
A) the institution of the ―it is glorious to be rich‖ policy.
B) the return to private property rights in farming.
C) the fall of communism in China.
D) the teaching of Mao Zedong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why is there such a great difference between the GDP per capita of North Korea and South Korea?
A) South Korea has greater natural resources.
B) North Korea invested heavily in its industries.
C) South Korea uses markets to organize production.
D) North Korea has a 100% literacy rate.
A) South Korea has greater natural resources.
B) North Korea invested heavily in its industries.
C) South Korea uses markets to organize production.
D) North Korea has a 100% literacy rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Institutions and incentives are ____________ causes and factors of productions are ________ causes of wealth of nations.
A) ultimate; proximate
B) proximate; ultimate
C) ultimate; indirect
D) proximate; direct
A) ultimate; proximate
B) proximate; ultimate
C) ultimate; indirect
D) proximate; direct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why does South Korea have a higher level of real GDP per capita than North Korea?
A) South Korea has more human capital than North Korea.
B) South Korea has more physical capital than North Korea.
C) South Korea has a better system of incentives for producers than North Korea does.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) South Korea has more human capital than North Korea.
B) South Korea has more physical capital than North Korea.
C) South Korea has a better system of incentives for producers than North Korea does.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following would be most effective in ensuring sustained long-term economic growth?
A) increasing technological knowledge
B) increasing human capital
C) increasing government control of land use
D) increasing physical capital
A) increasing technological knowledge
B) increasing human capital
C) increasing government control of land use
D) increasing physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Why does South Korea have a higher level of physical and human capital than North Korea? I. Markets constitute much more of the primary organizations of economic activity in South Korea than they do in North Korea. II. Economic incentives are better installed in South Korea. III. South Korea has a different culture from North Korea.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would be most effective in reducing free ridership on a communal farming system?
A) assigning property rights
B) increasing supervision of workers
C) increasing penalties for low production
D) increasing physical capital
A) assigning property rights
B) increasing supervision of workers
C) increasing penalties for low production
D) increasing physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following has the greatest potential for solving free rider problems?
A) property rights
B) stable political system
C) education
D) rule of law
A) property rights
B) stable political system
C) education
D) rule of law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The institutions of economic growth include
A) property rights.
B) a dependable legal system.
C) competitive and open markets.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) property rights.
B) a dependable legal system.
C) competitive and open markets.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following activities generates the greatest potential for free riding?
A) activities to increase technological knowledge
B) activities to increase human capital
C) activities to increase physical capital
D) None of these responses has the potential to generate free- riding problems.
A) activities to increase technological knowledge
B) activities to increase human capital
C) activities to increase physical capital
D) None of these responses has the potential to generate free- riding problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the Communist Party took over China, they instituted ―The Great Leap Forward‖ as a system of reforms to encourage the growth of agricultural production in China. Yet, during this time, thousands of farmers starved. Why did this occur?
A) Farmer self-interest was not aligned with social interest.
B) The land and its output were assigned to individuals.
C) The farmers had violated government policy.
D) The farmers were being jailed.
A) Farmer self-interest was not aligned with social interest.
B) The land and its output were assigned to individuals.
C) The farmers had violated government policy.
D) The farmers were being jailed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Communal returns to work often lead to low worker effort. Why does this happen? I. It happens because of the free-rider problem. II. Since the final payout depends on the number of people in the pool rather than an individual worker's effort, a worker does not have much incentive to work. III. It happens because workers learned from seeing the Chinese experience during ―The Great Leap Forward.‖
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is NOT an institution that leads to sustained long-term economic growth?
A) a dependable legal system
B) a stable political system
C) an honest government
D) an equitable income redistribution system
A) a dependable legal system
B) a stable political system
C) an honest government
D) an equitable income redistribution system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
All of the high income economies of the world have _____________ that generally incentivize individuals' self- interest by using ____________.
A) institutions; profit-seeking motives
B) government mandates; legal penalties
C) central planners; profit-seeking motives
D) institutions; legal penalties
A) institutions; profit-seeking motives
B) government mandates; legal penalties
C) central planners; profit-seeking motives
D) institutions; legal penalties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Countries with high per capita GDP have institutions that make it in people's self-interest to invest in
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) technology.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) technology.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What defines the ―rules of the game‖ that structure economic incentives?
A) institutions
B) economic laws
C) property rights
D) open markets
A) institutions
B) economic laws
C) property rights
D) open markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The main institutions necessary for economic growth are
A) good government and well-functioning markets.
B) property rights and absence of the rule of law.
C) collectivized farming.
D) separation of effort from payoff.
A) good government and well-functioning markets.
B) property rights and absence of the rule of law.
C) collectivized farming.
D) separation of effort from payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Institutions
A) are unimportant in market economies.
B) provide structure for economic incentives.
C) matter only when backed by law.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) are unimportant in market economies.
B) provide structure for economic incentives.
C) matter only when backed by law.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A country that has enforceable property rights, a non-corrupt political system, abundant factors of production, and a bloody coup every few years, should suspect that economic growth will be ______ because _______.
A) slow; of a lack of a dependable legal system
B) slow; of uncertainty due to an unstable political system
C) high; most of the institutions needed for growth are in place
D) high; once a group comes to power all the institutions needed for growth exist
A) slow; of a lack of a dependable legal system
B) slow; of uncertainty due to an unstable political system
C) high; most of the institutions needed for growth are in place
D) high; once a group comes to power all the institutions needed for growth exist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 141 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



