Deck 27: The Wealth of Nations and Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/155
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: The Wealth of Nations and Economic Growth
1
Workers who put 10 percent of their income into a retirement account each year are
A) consuming all of their income.
B) smoothing consumption.
C) dissaving.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) consuming all of their income.
B) smoothing consumption.
C) dissaving.
D) None of the answers is correct.
B
2
According to the consumption-smoothing theory, people with a longer life expectancy
A) invest more in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
B) have the same saving rates in their lifetimes as those with shorter life expectancy.
C) have higher savings rates in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
D) have lower saving rates in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
A) invest more in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
B) have the same saving rates in their lifetimes as those with shorter life expectancy.
C) have higher savings rates in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
D) have lower saving rates in their lifetimes than those with shorter life expectancy.
C
3
All else equal, time preference is the desire to
A) have goods and services sooner rather than later.
B) delay the purchase of goods and services.
C) have goods and services in retirement years.
D) have goods and services that are made in the current year.
A) have goods and services sooner rather than later.
B) delay the purchase of goods and services.
C) have goods and services in retirement years.
D) have goods and services that are made in the current year.
A
4
Investment is
A) the purchase of new capital goods.
B) the purchase of new consumption goods.
C) the purchase of gold and silver during inflationary times.
D) the purchase of shares of stock on the New York Stock Exchange.
A) the purchase of new capital goods.
B) the purchase of new consumption goods.
C) the purchase of gold and silver during inflationary times.
D) the purchase of shares of stock on the New York Stock Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is savings so minimal in nations with a high population of AIDS victims?
A) People with a short-life expectancy tend to save less.
B) Governments provide an extensive social safety net.
C) Interest rates are not high enough.
D) Unemployment rates are too high.
A) People with a short-life expectancy tend to save less.
B) Governments provide an extensive social safety net.
C) Interest rates are not high enough.
D) Unemployment rates are too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why do people save during their working lifetimes?
A) They save for retirement especially if average life expectancy is higher.
B) They save to prepare for those periods of unemployment.
C) They may want to save for unexpected hospitalizations and illnesses.
D) Each of these answers provides a valid explanation for why people save.
A) They save for retirement especially if average life expectancy is higher.
B) They save to prepare for those periods of unemployment.
C) They may want to save for unexpected hospitalizations and illnesses.
D) Each of these answers provides a valid explanation for why people save.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Fluctuations in income cause most people to
A) invest.
B) save.
C) spend all their income each year.
D) retire at an early age.
A) invest.
B) save.
C) spend all their income each year.
D) retire at an early age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the consumption-smoothing theory, a person typically saves the most
A) during working years.
B) during retirement years.
C) as an infant.
D) as a full-time student.
A) during working years.
B) during retirement years.
C) as an infant.
D) as a full-time student.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Time preference is the desire to
A) save for a time when income will be reduced.
B) have goods and services sooner rather than later.
C) maximize return on investment in the shortest amount of time.
D) increase longevity in order to have a greater income.
A) save for a time when income will be reduced.
B) have goods and services sooner rather than later.
C) maximize return on investment in the shortest amount of time.
D) increase longevity in order to have a greater income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Savings is
A) the purchase of new capital goods.
B) the purchase of new consumption goods.
C) income that is not spent on capital goods.
D) income that is not spent on consumption goods.
A) the purchase of new capital goods.
B) the purchase of new consumption goods.
C) income that is not spent on capital goods.
D) income that is not spent on consumption goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following can be defined as saving according to economics?
A) General Motors issues corporate bonds.
B) Microsoft sells stock at an initial public offering.
C) Sandra purchases a certificate of deposit from a bank.
D) Andrea finances her new car through an auto loan.
A) General Motors issues corporate bonds.
B) Microsoft sells stock at an initial public offering.
C) Sandra purchases a certificate of deposit from a bank.
D) Andrea finances her new car through an auto loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why do people save during their working lifetimes?
A) So they do not have to drastically reduce their consumption once they retire.
B) To consume later in life.
C) To take precautionary measures in case of job loss.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) So they do not have to drastically reduce their consumption once they retire.
B) To consume later in life.
C) To take precautionary measures in case of job loss.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What do we call income that is NOT spent on consumption goods?
A) investment
B) profit
C) asset retention
D) saving
A) investment
B) profit
C) asset retention
D) saving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The supply of savings function shows the relationship between saving and
A) consumption.
B) income.
C) age.
D) the interest rate.
A) consumption.
B) income.
C) age.
D) the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a person's income is greater than her spending on consumption goods, then she is
A) dissaving.
B) saving.
C) investing.
D) disinvesting.
A) dissaving.
B) saving.
C) investing.
D) disinvesting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is an example of impatience in economic behavior?
A) taking the first job you are offered
B) insisting on getting a physical exam every year
C) asking for your grade right after finishing a test
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) taking the first job you are offered
B) insisting on getting a physical exam every year
C) asking for your grade right after finishing a test
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The main reason people save during their working years is
A) a preference towards a smooth consumption path over time.
B) a high time preference for the present.
C) an expectation to die early.
D) a preference towards matching income with spending over time.
A) a preference towards a smooth consumption path over time.
B) a high time preference for the present.
C) an expectation to die early.
D) a preference towards matching income with spending over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A seasonal worker saves more when her income rises, and saves less when her income falls. This behavior is referred to as
A) dissaving.
B) consumption smoothing.
C) not being very smart.
D) time preference.
A) dissaving.
B) consumption smoothing.
C) not being very smart.
D) time preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Mario is saving if he does which of the following?
A) makes a deposit in a savings account at the bank
B) buys a share of stock in a computer company
C) buys a corporate bond
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) makes a deposit in a savings account at the bank
B) buys a share of stock in a computer company
C) buys a corporate bond
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All else being equal, a working-age person who has more patience tends to have
A) more savings.
B) fewer savings.
C) more collateral.
D) less investment.
A) more savings.
B) fewer savings.
C) more collateral.
D) less investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At an interest rate of 8 percent, borrowers demand is $30 billion. At 4 percent, borrowers would want to borrow
A) $20 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $30 billion.
D) $45 billion
A) $20 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $30 billion.
D) $45 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why do firms and individuals borrow?
A) They want to smooth consumption.
B) Debt is often necessary for large purchases.
C) They believe their return will be greater than the interest rate.
D) Each of these explanations provides a reason for borrowing.
A) They want to smooth consumption.
B) Debt is often necessary for large purchases.
C) They believe their return will be greater than the interest rate.
D) Each of these explanations provides a reason for borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The supply of loanable funds comes from ______ and the demand for loanable funds comes from ______.
A) saving; investment
B) investment; saving
C) saving; consumption
D) investment; consumption
A) saving; investment
B) investment; saving
C) saving; consumption
D) investment; consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the interest rate increases, then
A) the quantity saved will decrease but the quantity supplied of loanable funds will increase.
B) the quantity saved will increase but the quantity supplied of loanable funds will decrease.
C) both the quantity saved and the quantity supplied of loanable funds will decrease.
D) both the quantity saved and the quantity supplied of loanable funds will increase.
A) the quantity saved will decrease but the quantity supplied of loanable funds will increase.
B) the quantity saved will increase but the quantity supplied of loanable funds will decrease.
C) both the quantity saved and the quantity supplied of loanable funds will decrease.
D) both the quantity saved and the quantity supplied of loanable funds will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If $100 is saved at an annual interest rate of 10 percent, what will be the return in one year?
A) $11
B) $110
C) $10
D) $111
A) $11
B) $110
C) $10
D) $111

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the interest rate rises from 5 percent to 9 percent, the number of new businesses will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) sharply increase, then level off.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) sharply increase, then level off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The demand to borrow function is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What theory describes a pattern of early borrowing, a period of saving, and then dissaving during a worker's lifetime?
A) The Lifecycle Theory of Savings
B) The Career Theory of Dissaving
C) The Demand Theory of Borrowing
D) The Theory of Cyclical Smoothing
A) The Lifecycle Theory of Savings
B) The Career Theory of Dissaving
C) The Demand Theory of Borrowing
D) The Theory of Cyclical Smoothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is the demand for loanable funds downward sloping?
A) People save less when the interest rates are low.
B) More people borrow money when interest rates are low than when they are high.
C) Fewer investment projects have returns that can beat higher interest rates, so people are more willing to invest at higher interest rates.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) People save less when the interest rates are low.
B) More people borrow money when interest rates are low than when they are high.
C) Fewer investment projects have returns that can beat higher interest rates, so people are more willing to invest at higher interest rates.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In economics, investment refers to
A) saving.
B) dissaving.
C) the purchase of consumption goods.
D) the purchase of capital goods.
A) saving.
B) dissaving.
C) the purchase of consumption goods.
D) the purchase of capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The supply of savings is positively sloped because
A) firms borrow more when interest rates are low.
B) people are enticed to forgo consumption when interest rates are higher.
C) when people have more incomes they save more.
D) of time preference.
A) firms borrow more when interest rates are low.
B) people are enticed to forgo consumption when interest rates are higher.
C) when people have more incomes they save more.
D) of time preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why do people borrow?
A) to engage in consumption smoothing
B) to sustain themselves through periods of unemployment
C) to fund unexpected expenditures
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) to engage in consumption smoothing
B) to sustain themselves through periods of unemployment
C) to fund unexpected expenditures
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The supply of savings function is
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why is the ability to borrow positively related to the rate of economic growth?
A) Lenders obtain additional wealth.
B) It provides motivation to keep spending to a minimum.
C) The incentive to invest is enhanced by economic growth.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) Lenders obtain additional wealth.
B) It provides motivation to keep spending to a minimum.
C) The incentive to invest is enhanced by economic growth.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is TRUE about the lifecycle theory of savings?
A) People tend to save during the early years of their lifetimes, dissave during their prime working years, and borrow during their retirement years.
B) People tend to borrow during the early years of their lifetimes, invest during their prime working years, and save during their retirement years.
C) People tend to borrow during the early years of their lifetimes, save during their prime working years, and dissave during their retirement years.
D) People tend to save during the early years of their lifetimes, borrow during their prime working years, and invest during their retirement years.
A) People tend to save during the early years of their lifetimes, dissave during their prime working years, and borrow during their retirement years.
B) People tend to borrow during the early years of their lifetimes, invest during their prime working years, and save during their retirement years.
C) People tend to borrow during the early years of their lifetimes, save during their prime working years, and dissave during their retirement years.
D) People tend to save during the early years of their lifetimes, borrow during their prime working years, and invest during their retirement years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The demand to borrow function shows the relationship between borrowing money and
A) consumption.
B) income.
C) age.
D) the interest rate.
A) consumption.
B) income.
C) age.
D) the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The lifecycle theory of savings predicts individuals will save during
A) the early years of life.
B) the middle years of life.
C) the later years of life.
D) all phases of life.
A) the early years of life.
B) the middle years of life.
C) the later years of life.
D) all phases of life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
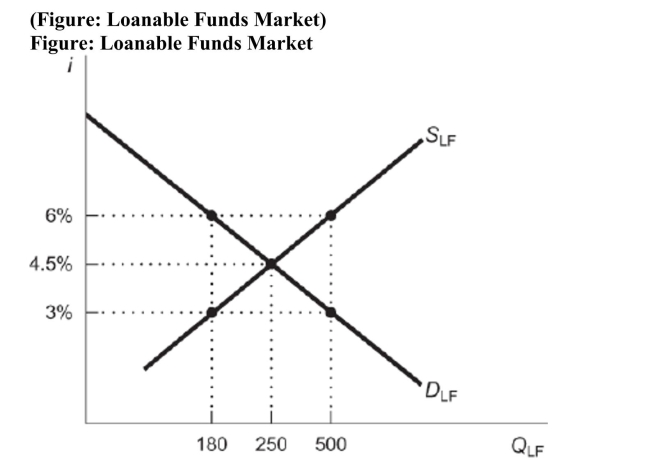 At an interest rate of 3 percent in this market, there is a ______ of loanable funds of ______ million.
At an interest rate of 3 percent in this market, there is a ______ of loanable funds of ______ million.A) shortage; $300
B) surplus; $150
C) shortage; $150
D) surplus; $300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Modigliani's lifecycle theory of savings proposes that in order to maximize lifetime satisfaction, consumers
A) practice consumption smoothing by borrowing and saving.
B) borrow equal amounts throughout the life cycle.
C) save equal amounts throughout their life cycle.
D) consume what they earn each year.
A) practice consumption smoothing by borrowing and saving.
B) borrow equal amounts throughout the life cycle.
C) save equal amounts throughout their life cycle.
D) consume what they earn each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
At lower interest rates, the cost of investing ______ and the funds that are demanded for investment ______.
A) decreases; increase
B) increases; decrease
C) increases; increase
D) decreases; decrease
A) decreases; increase
B) increases; decrease
C) increases; increase
D) decreases; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When business firms become more pessimistic about the state of the economy, the interest rate ______ and borrowing ______.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An investment tax credit will cause the interest rate to ______ and borrowing to ______.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following would be the most likely to cause an increase in the demand for loanable funds?
A) a decrease in the interest rate
B) an increase in savings
C) a decrease in consumption
D) an increase in government borrowing
A) a decrease in the interest rate
B) an increase in savings
C) a decrease in consumption
D) an increase in government borrowing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What effect will an investment tax credit have on interest rates and the quantity of savings?
A) None, investment tax credits only affect the amount of taxes paid by firms.
B) Both interest rates and the quantity of savings will increase.
C) Interest rates will decrease and the quantity of savings will increase.
D) Interest rates will not change, but the quantity of savings decreases.
A) None, investment tax credits only affect the amount of taxes paid by firms.
B) Both interest rates and the quantity of savings will increase.
C) Interest rates will decrease and the quantity of savings will increase.
D) Interest rates will not change, but the quantity of savings decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the government raises taxes on investment returns, then
A) the demand for loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
B) the demand for loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
C) the supply of loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
A) the demand for loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
B) the demand for loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
C) the supply of loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Trading in the market for loanable funds determines the equilibrium
A) level of savings.
B) amount of borrowing.
C) interest rate.
D) It determines all three of these.
A) level of savings.
B) amount of borrowing.
C) interest rate.
D) It determines all three of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A decrease in investment demand
A) results in the same equilibrium as an increase in savings.
B) decreases both the amount saved and the interest rate.
C) increases the amount saved but decreases the interest rate.
D) increases the demand for loanable funds.
A) results in the same equilibrium as an increase in savings.
B) decreases both the amount saved and the interest rate.
C) increases the amount saved but decreases the interest rate.
D) increases the demand for loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What economic activity did many South Korean citizens engage in during the 1960s and 1970s to help their country increase its growth rate?
A) increased consumer spending
B) increased saving
C) buying and selling stocks and bonds
D) only buying goods made in South Korea
A) increased consumer spending
B) increased saving
C) buying and selling stocks and bonds
D) only buying goods made in South Korea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If consumers expect to have shorter life expectancy and desire to save less, then the
A) demand for loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
B) demand for loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
C) supply of loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
A) demand for loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
B) demand for loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.
C) supply of loanable funds will decrease, and the equilibrium interest rate will increase.
D) the supply of loanable funds will increase, and the equilibrium interest rate will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which variable is determined in the market for loanable funds?
A) income
B) consumption
C) investment
D) the interest rate
A) income
B) consumption
C) investment
D) the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
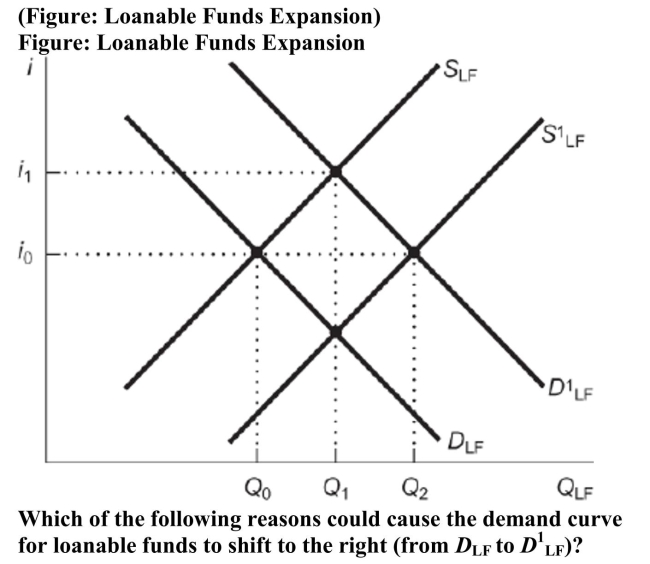
A) The economy is expected to boom thereby increasing investment returns.
B) Larger investment projects with potentially higher returns get funded.
C) Falling interest rates make it less expensive for firms to borrow.
D) Rising interest rates make it more attractive for savers to save.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
At an 8 percent interest rate, the quantity of savings is $250 billion. What would the quantity of savings be if the interest rate falls to 5 percent?
A) $190 billion
B) $250 billion
C) $300 billion
D) $500 billion
A) $190 billion
B) $250 billion
C) $300 billion
D) $500 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When individuals become more willing to save because their incomes have increased, the interest rate ______ and borrowing ______.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An increase in the supply of savings will cause the interest rate
A) to remain unchanged.
B) to decrease.
C) to increase.
D) to increase or decrease depending on the elasticity of demand for loanable funds.
A) to remain unchanged.
B) to decrease.
C) to increase.
D) to increase or decrease depending on the elasticity of demand for loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
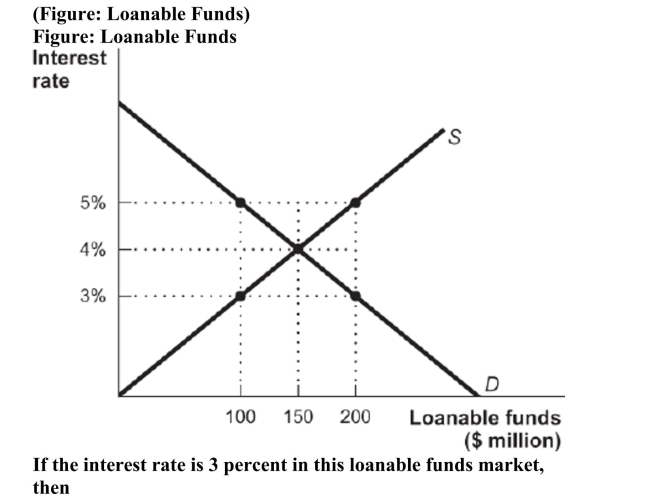
A) investment exceeds savings by $200 million.
B) investment exceeds savings by $100 million.
C) borrowing demands exceed savings by $200 million.
D) borrowing demands exceed savings by $100 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When business firms become more pessimistic about the state of the economy, the
A) demand to borrow shifts outward.
B) demand to borrow shifts inward.
C) supply of savings shifts outward.
D) supply of savings shifts inward.
A) demand to borrow shifts outward.
B) demand to borrow shifts inward.
C) supply of savings shifts outward.
D) supply of savings shifts inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Firms primarily raise money by using which two methods?
A) selling stocks and issuing treasury bills
B) selling stocks and issuing corporate bonds
C) borrowing from banks and borrowing from the government
D) borrowing from international countries and the government
A) selling stocks and issuing treasury bills
B) selling stocks and issuing corporate bonds
C) borrowing from banks and borrowing from the government
D) borrowing from international countries and the government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is a frequent temporary government solution to combat the decreased investment demand during a recession?
A) decrease government spending
B) reduce regulation affecting firms
C) sell more bonds
D) offer an investment tax credit
A) decrease government spending
B) reduce regulation affecting firms
C) sell more bonds
D) offer an investment tax credit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When individuals become more willing to save, the
A) demand to borrow shifts outward.
B) demand to borrow shifts inward.
C) supply of savings shifts outward.
D) supply of savings shifts inward.
A) demand to borrow shifts outward.
B) demand to borrow shifts inward.
C) supply of savings shifts outward.
D) supply of savings shifts inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
(Figure: Loanable Funds Contraction) Figure: Loanable Funds Contraction 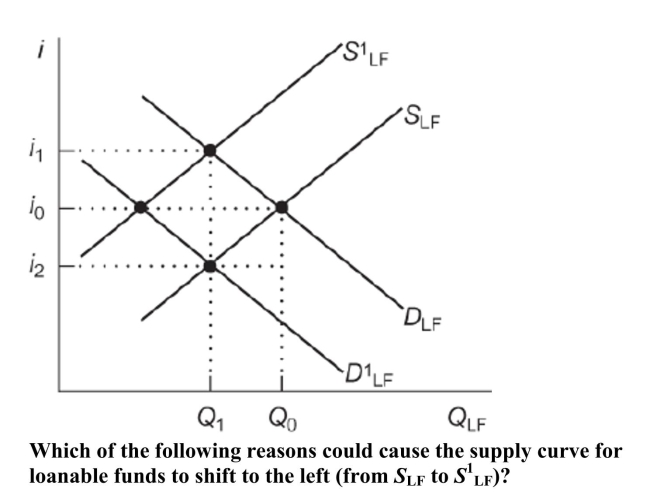
A) The economy is expected to go into a recession.
B) An existing investment tax credit is abolished.
C) The government ceases taxing interest earnings.
D) Consumers display stronger time preference.

A) The economy is expected to go into a recession.
B) An existing investment tax credit is abolished.
C) The government ceases taxing interest earnings.
D) Consumers display stronger time preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do banks engage in specialization and division of labor?
A) Banks are the only avenue for savers to save their money and for borrowers to borrow for projects.
B) Banks specialize in lending to risky borrowers.
C) Banks coordinate the collection of lenders' funds and employ specialists in risk assessment to assure their safety.
D) Banks specialize in the use of ATM cards.
A) Banks are the only avenue for savers to save their money and for borrowers to borrow for projects.
B) Banks specialize in lending to risky borrowers.
C) Banks coordinate the collection of lenders' funds and employ specialists in risk assessment to assure their safety.
D) Banks specialize in the use of ATM cards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the potential of a bond lender not being able to repay the bond holder called?
A) moral hazard
B) default risk
C) payment jeopardy
D) repayment peril
A) moral hazard
B) default risk
C) payment jeopardy
D) repayment peril

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Stock shares represent __________ and bonds represent __________.
A) corporate debt; corporate ownership
B) corporate debt; corporate debt
C) corporate ownership; corporate ownership
D) corporate ownership; corporate debt
A) corporate debt; corporate ownership
B) corporate debt; corporate debt
C) corporate ownership; corporate ownership
D) corporate ownership; corporate debt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is an example of a financial intermediary?
A) commercial banks
B) the bond market
C) the stock market
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) commercial banks
B) the bond market
C) the stock market
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The crowding out effect of government borrowing refers to a decrease in I. private consumption. II. private savings. III. investment.
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A bond is a(n)
A) liability for the issuer.
B) asset for the purchaser.
C) promise by the issuer to pay.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) liability for the issuer.
B) asset for the purchaser.
C) promise by the issuer to pay.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is a financial intermediary? I. a commercial bank II. a mutual fund III. the government
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is a service that banks specialize in providing?
A) providing the highest return available in the market
B) seeking to pass all of the returns on investment to the savers
C) evaluating the quality of investment opportunities
D) making sure all funds are distributed in the most equitable fashion
A) providing the highest return available in the market
B) seeking to pass all of the returns on investment to the savers
C) evaluating the quality of investment opportunities
D) making sure all funds are distributed in the most equitable fashion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the U.S. government borrows, it sells
A) federal paper.
B) treasury bonds.
C) government stocks.
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) federal paper.
B) treasury bonds.
C) government stocks.
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the loanable funds market, an increase in government borrowing will most likely
A) decrease bond prices and increase interest rates.
B) increase bond prices and decrease interest rates.
C) increase both bond prices and interest rates.
D) decrease both bond prices and interest rates.
A) decrease bond prices and increase interest rates.
B) increase bond prices and decrease interest rates.
C) increase both bond prices and interest rates.
D) decrease both bond prices and interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Crowding out occurs because the government increases the demand for loanable funds, drives up interest rates, and I. stops private savers from saving. II. causes investment to fall. III. causes consumption to fall.
A) I only
B) II only
C) II and III only
D) I and III only
A) I only
B) II only
C) II and III only
D) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Junk bonds are bonds
A) issued by garbage companies.
B) backed by subprime mortgages.
C) rated lower than BBB-.
D) that mature 30 years into the future.
A) issued by garbage companies.
B) backed by subprime mortgages.
C) rated lower than BBB-.
D) that mature 30 years into the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A corporation is planning to finance the construction of new offices but has limited funds. The corporation is likely to
A) supply loanable funds by selling bonds.
B) supply loanable funds by buying bonds.
C) demand loanable funds by selling bonds.
D) demand loanable funds by buying bonds.
A) supply loanable funds by selling bonds.
B) supply loanable funds by buying bonds.
C) demand loanable funds by selling bonds.
D) demand loanable funds by buying bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in government borrowing will cause the
A) demand for borrowing to shift outward.
B) demand for borrowing to shift inward.
C) supply of savings to shift outward.
D) supply of savings to shift inward.
A) demand for borrowing to shift outward.
B) demand for borrowing to shift inward.
C) supply of savings to shift outward.
D) supply of savings to shift inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a Treasury Bill (T-bill)?
A) It has an implicit interest rate.
B) It reaches maturity after 30 years.
C) It is sold at a discount from its face value.
D) It has almost zero default risk.
A) It has an implicit interest rate.
B) It reaches maturity after 30 years.
C) It is sold at a discount from its face value.
D) It has almost zero default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is NOT a Treasury Bill (T-bill) characteristic?
A) It has coupon payments.
B) It has a maturity of 26 weeks or less.
C) It is sold at a discount from its face value.
D) Its price fluctuates with T-bill demand.
A) It has coupon payments.
B) It has a maturity of 26 weeks or less.
C) It is sold at a discount from its face value.
D) Its price fluctuates with T-bill demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An increase in government borrowing will cause the interest rate to
A) rise and private spending to rise.
B) rise and private spending to fall.
C) fall and private spending to fall.
D) fall and private spending to rise.
A) rise and private spending to rise.
B) rise and private spending to fall.
C) fall and private spending to fall.
D) fall and private spending to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why do ratings agencies rate bonds?
A) to indicate the chance of a bond being repaid
B) to show a bond's probable rate of return
C) to validate the amount of collateral involved
D) Each of these answers is correct.
A) to indicate the chance of a bond being repaid
B) to show a bond's probable rate of return
C) to validate the amount of collateral involved
D) Each of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following chains of logic explain the functions of banks in the process of economic growth?
A) Savers deposit their savings in banks. Banks direct these funds to firms that invest and engage in capital accumulation that furthers economic growth.
B) Savers deposit their savings in banks. Banks engage in capital accumulation, which plays an important role in economic growth.
C) Firms borrow from stock and bond markets. These funds are used for investment, which leads to the capital accumulation that furthers economic growth.
D) The demand for loanable funds shows an inverse relationship between the real interest rate that banks charge and the quantity of loans demanded.
A) Savers deposit their savings in banks. Banks direct these funds to firms that invest and engage in capital accumulation that furthers economic growth.
B) Savers deposit their savings in banks. Banks engage in capital accumulation, which plays an important role in economic growth.
C) Firms borrow from stock and bond markets. These funds are used for investment, which leads to the capital accumulation that furthers economic growth.
D) The demand for loanable funds shows an inverse relationship between the real interest rate that banks charge and the quantity of loans demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following functions is NOT performed by banks?
A) They provide a safe opportunity for us to earn interest on our savings.
B) They direct money to its highest valued uses.
C) They form the bridge between savers and investors.
D) They organize initial public offerings for firms.
A) They provide a safe opportunity for us to earn interest on our savings.
B) They direct money to its highest valued uses.
C) They form the bridge between savers and investors.
D) They organize initial public offerings for firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



