Deck 10: Basic Macroeconomic Relationships
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Basic Macroeconomic Relationships
1
In this figure, if the real interest rate falls from 6 to 4 percent:
A) investment will increase from 0 to $30 billion.
B) investment will decrease by $5 billion.
C) the expected rate of return will rise by $5 billion.
D) investment will increase from $25 billion to $30 billion.
A) investment will increase from 0 to $30 billion.
B) investment will decrease by $5 billion.
C) the expected rate of return will rise by $5 billion.
D) investment will increase from $25 billion to $30 billion.
The marginal propensity to consume is illustrated by the consumption schedule line. Therefore, since we have a straight line that is not curved, the marginal propensity to consume is constant at all levels of income, and the answer is 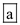 Consumption is not inversely related to disposable income as suggested by the graph, nor is saving inversely related to disposable income.
Consumption is not inversely related to disposable income as suggested by the graph, nor is saving inversely related to disposable income.
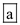 Consumption is not inversely related to disposable income as suggested by the graph, nor is saving inversely related to disposable income.
Consumption is not inversely related to disposable income as suggested by the graph, nor is saving inversely related to disposable income. 2
True or False: Real GDP is more volatile (variable) than gross investment.
This statement is false. In the history of the United States, the percentage swings in investment have been greater than the percentage swings in real GDP.
3
In this figure:
A) the marginal propensity to consume is constant at all levels of income.
B) the marginal propensity to save rises as disposable income rises.
C) consumption is inversely (negatively) related to disposable income.
D) saving is inversely (negatively) related to disposable income.
A) the marginal propensity to consume is constant at all levels of income.
B) the marginal propensity to save rises as disposable income rises.
C) consumption is inversely (negatively) related to disposable income.
D) saving is inversely (negatively) related to disposable income.
At an interest rate of 6 percent, investment is at 25 billion. At an interest rate of 4 percent, investment is at 30 billion. Therefore, as the interest rate goes down from 6 percent to 4 percent, investment increases by 5 billion, from 25 to 30 billion, and our answer is 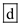
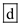
4
Why is the actual multiplier in the U.S. economy less than the multiplier in this chapter's example?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the MPS rises, then the MPC will:
A) Fall.
B) Rise.
C) Stay the same.
A) Fall.
B) Rise.
C) Stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Refer to the table in Figure 27.5 in the book and suppose that the real interest rate is 6 percent. Next, assume that some factor changes such that that the expected rate of return declines by 2 percentage points at each prospective level of investment. Assuming no change in the real interest rate, by how much and in what direction will investment change? Which of the following might cause this change: (a) a decision to increase inventories; (b) an increase in excess production capacity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In what direction will each of the following occurrences shift the investment demand curve, other things equal? LO4
a. An increase in unused production capacity occurs.
b. Business taxes decline.
c. The costs of acquiring equipment fall.
d. Widespread pessimism arises about future business conditions and sales revenues.
e. A major new technological breakthrough creates prospects for a wide range of profitable new products.
a. An increase in unused production capacity occurs.
b. Business taxes decline.
c. The costs of acquiring equipment fall.
d. Widespread pessimism arises about future business conditions and sales revenues.
e. A major new technological breakthrough creates prospects for a wide range of profitable new products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a $50 billion initial increase in spending leads to a $250 billion change in real GDP, how big is the multiplier?
A) 1.0.
B) 2.5.
C) 4.0.
D) 5.0.
A) 1.0.
B) 2.5.
C) 4.0.
D) 5.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Precisely how do the MPC and the APC differ? How does the MPC differ from the MPS? Why must the sum of MPC and the MPS equal 1?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Advanced Analysis Linear equations for the consumption and saving schedules take the general form C = a + bY and S= -a + (1-b)Y where C , S , and Y are consumption, saving, and national income, respectively. The constant a represents the vertical intercept, and b represents the slope of the consumption schedule. LO1, LO2
a. Use the following data to substitute numerical values for a and b in the consumption and saving equations.
b. What is the economic meaning of b ? Of (1 - b )?
c. Suppose that the amount of saving that occurs at each level of national income falls by $20 but that the values of b and (1 - b ) remain unchanged. Restate the saving and consumption equations inserting the new numerical values, and cite a factor that might have caused the change.
a. Use the following data to substitute numerical values for a and b in the consumption and saving equations.

b. What is the economic meaning of b ? Of (1 - b )?
c. Suppose that the amount of saving that occurs at each level of national income falls by $20 but that the values of b and (1 - b ) remain unchanged. Restate the saving and consumption equations inserting the new numerical values, and cite a factor that might have caused the change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
LAST WORD What is the central economic idea humorously illustrated in Art Buchwald's piece, "Squaring the Economic Circle"? How does the central idea relate to economic recessions, on the one hand, and vigorous economic expansions, on the other?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the incomplete table below. LO1 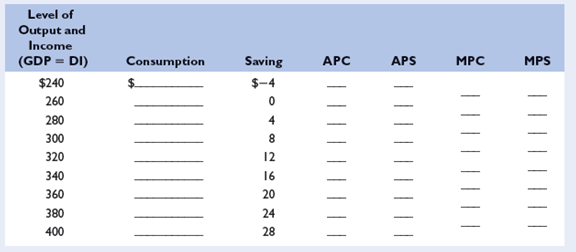
a. Fill in the missing numbers in the table.
b. What is the break-even level of income in the table? What is the term that economists use for the saving situation shown at the $240 level of income?
c. For each of the following items indicate whether the value in the table is either constant or variable as income changes: the MPS, the APC, the MPC, the APS.

a. Fill in the missing numbers in the table.
b. What is the break-even level of income in the table? What is the term that economists use for the saving situation shown at the $240 level of income?
c. For each of the following items indicate whether the value in the table is either constant or variable as income changes: the MPS, the APC, the MPC, the APS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In this figure, investment will be:
A) zero if the real interest rate is zero.
B) $40 billion if the real interest rate is 16 percent.
C) $30 billion if the real interest rate is 4 percent.
D) $20 billion if the real interest rate is 12 percent.
A) zero if the real interest rate is zero.
B) $40 billion if the real interest rate is 16 percent.
C) $30 billion if the real interest rate is 4 percent.
D) $20 billion if the real interest rate is 12 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What will the multiplier be when the MPS is 0,.4,.6, and 1? What will it be when the MPC is 1,.90,.67,.50, and 0? How much of a change in GDP will result if firms increase their level of investment by $8 billion and the MPC is.80? If the MPC instead is.67?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The investment demand curve:
A) reflects a direct (positive) relationship between the real interest rate and investment.
B) reflects an inverse (negative) relationship between the real interest rate and investment.
C) shifts to the right when the real interest rate rises.
D) shifts to the left when the real interest rate rises.
A) reflects a direct (positive) relationship between the real interest rate and investment.
B) reflects an inverse (negative) relationship between the real interest rate and investment.
C) shifts to the right when the real interest rate rises.
D) shifts to the left when the real interest rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When consumption equals disposable income:
A) the marginal propensity to consume is zero.
B) the average propensity to consume is zero.
C) consumption and saving must be equal.
D) saving must be zero.
A) the marginal propensity to consume is zero.
B) the average propensity to consume is zero.
C) consumption and saving must be equal.
D) saving must be zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
True or False: Larger MPCs imply larger multipliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The slope of the consumption schedule in this figure is 0.75. Thus, the:
A) slope of the saving schedule is 1.33.
B) marginal propensity to consume is 0.75.
C) average propensity to consume is 0.25.
D) slope of the saving schedule is also 0.75.
A) slope of the saving schedule is 1.33.
B) marginal propensity to consume is 0.75.
C) average propensity to consume is 0.25.
D) slope of the saving schedule is also 0.75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In what direction will each of the following occurrences shift the consumption and saving schedules, other things equal? LO2
a. A large decrease in real estate values, including private homes.
b. A sharp, sustained increase in stock prices.
c. A 5-year increase in the minimum age for collecting Social Security benefits.
d. An economy-wide expectation that a recession is over and that a robust expansion will occur.
e. A substantial increase in household borrowing to finance auto purchases.
a. A large decrease in real estate values, including private homes.
b. A sharp, sustained increase in stock prices.
c. A 5-year increase in the minimum age for collecting Social Security benefits.
d. An economy-wide expectation that a recession is over and that a robust expansion will occur.
e. A substantial increase in household borrowing to finance auto purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that an initial $10 billion increase in investment spending expands GDP by $10 billion in the first round of the multiplier process. If GDP and consumption both rise by $6 billion in the second round of the process, what is the MPC in this economy? What is the size of the multiplier? If, instead, GDP and consumption both rose by $8 billion in the second round, what would have been the size of the multiplier?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What are the variables (the items measured on the axes) in a graph of the (a) consumption schedule and (b) saving schedule? Are the variables inversely (negatively) related or are they directly (positively) related? What is the fundamental reason that the levels of consumption and saving in the United States are each higher today than they were a decade ago?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How is it possible for investment spending to increase even in a period in which the real interest rate rises?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why does a downshift of the consumption schedule typically involve an equal upshift of the saving schedule? What is the exception to this relationship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use your completed table for problem 1 to solve this problem. Suppose the wealth effect is such that $10 changes in wealth produce $1 changes in consumption at each level of income. If real estate prices tumble such that wealth declines by $80, what will be the new level of consumption at the $340 billion level of disposable income? The new level of saving?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that disposable income, consumption, and saving in some country are $200 billion, $150 billion, and $50 billion, respectively. Next, assume that disposable income increases by $20 billion, consumption rises by $18 billion and saving goes up by $2 billion. What is the economy's MPC? Its MPS? What was the APC before the increase in disposable income? After the increase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Irving owns a chain of movie theaters. He is considering whether he should build a new theater downtown. The expected rate of return is 15 percent per year. He can borrow money at a 12 percent interest rate to finance the project. Should Irving proceed with this project?
A) Yes.
B) No.
A) Yes.
B) No.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In this figure:
A) greater cumulative amounts of investment are associated with lower real interest rates.
B) lesser cumulative amounts of investment are associated with lower expected rates of return on investment.
C) higher interest rates are associated with higher expected rates of return on investment, and therefore greater amounts of investment.
D) interest rates and investment move in the same direction.
A) greater cumulative amounts of investment are associated with lower real interest rates.
B) lesser cumulative amounts of investment are associated with lower expected rates of return on investment.
C) higher interest rates are associated with higher expected rates of return on investment, and therefore greater amounts of investment.
D) interest rates and investment move in the same direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why is investment spending unstable?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In this figure, when consumption is a positive amount, saving:
A) must be a negative amount.
B) must also be a positive amount.
C) can be either a positive or a negative amount.
D) is zero.
A) must be a negative amount.
B) must also be a positive amount.
C) can be either a positive or a negative amount.
D) is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose a handbill publisher can buy a new duplicating machine for $500 and the duplicator has a 1-year life. The machine is expected to contribute $550 to the year's net revenue. What is the expected rate of return? If the real interest rate at which funds can be borrowed to purchase the machine is 8 percent, will the publisher choose to invest in the machine? Will it invest in the machine if the real interest rate is 9 percent? If it is 11 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In year one, Adam earns $1,000 and saves $100. In year 2, Adam gets a $500 raise so that he earns a total of $1,500. Out of that $1,500, he saves $200. What is Adam's MPC out of his $500 raise?
A) 0.50.
B) 0.75.
C) 0.80.
D) 1.00.
A) 0.50.
B) 0.75.
C) 0.80.
D) 1.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following scenarios will shift the investment demand curve right?
Select one or more answers from the choices shown.
a. Business taxes increase.
b. The expected return on capital increases.
c. Firms have a lot of unused production capacity.
d. Firms are planning on increasing their inventories.
Select one or more answers from the choices shown.
a. Business taxes increase.
b. The expected return on capital increases.
c. Firms have a lot of unused production capacity.
d. Firms are planning on increasing their inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why will a reduction in the real interest rate increase investment spending, other things equal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Is the relationship between changes in spending and changes in real GDP in the multiplier effect a direct (positive) relationship or is it an inverse (negative) relationship? How does the size of the multiplier relate to the size of the MPC? The MPS? What is the logic of the multiplier-MPC relationship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Advanced Analysis Suppose that the linear equation for consumption in a hypothetical economy is C = 40 +.8 Y. Also suppose that income ( Y ) is $400. Determine (a) the marginal propensity to consume, (b) the marginal propensity to save, (c) the level of consumption, (d) the average propensity to consume, (e) the level of saving, and (f) the average propensity to save.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume there are no investment projects in the economy that yield an expected rate of return of 25 percent or more. But suppose there are $10 billion of investment projects yielding expected returns of between 20 and 25 percent; another $10 billion yielding between 15 and 20 percent; another $10 billion between 10 and 15 percent; and so forth. Cumulate these data and present them graphically, putting the expected rate of return (and the real interest rate) on the vertical axis and the amount of investment on the horizontal axis. What will be the equilibrium level of aggregate investment if the real interest rate is (a) 15 percent, (b) 10 percent, and (c) 5 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



