Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
1
At all points on the 458 line:
A) equilibrium GDP is possible.
B) aggregate expenditures exceed real GDP.
C) consumption exceeds investment.
D) aggregate expenditures are less than real GDP.
A) equilibrium GDP is possible.
B) aggregate expenditures exceed real GDP.
C) consumption exceeds investment.
D) aggregate expenditures are less than real GDP.
An inflationary expenditure gap will result in demand-pull inflation, because the government would need to lower the real GDP to meet full-employment level of GDP. This means that the supply of output is limited by the supply of labor. These high prices drive nominal GDP up.
Hence, the correct answer is a. demand-pull inflation.
Options c. and d. are incorrect because an inflationary expenditure gap means that full employment is met. Unemployment isn't relevant in this case.
Option b. is incorrect because cost-push inflation is caused by reductions in aggregate supply.
Hence, the correct answer is a. demand-pull inflation.
Options c. and d. are incorrect because an inflationary expenditure gap means that full employment is met. Unemployment isn't relevant in this case.
Option b. is incorrect because cost-push inflation is caused by reductions in aggregate supply.
2
Assume that, without taxes, the consumption schedule of an economy is as follows: LO4 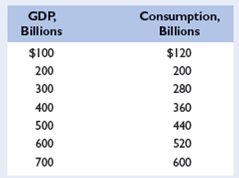
a. Graph this consumption schedule and determine the MPC.
b. Assume now that a lump-sum tax is imposed such that the government collects $10 billion in taxes at all levels of GDP. Graph the resulting consumption schedule and compare the MPC and the multiplier with those of the pretax consumption schedule.

a. Graph this consumption schedule and determine the MPC.
b. Assume now that a lump-sum tax is imposed such that the government collects $10 billion in taxes at all levels of GDP. Graph the resulting consumption schedule and compare the MPC and the multiplier with those of the pretax consumption schedule.
a. The information is reproduced below: 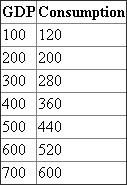 MPC is calculated as follows:
MPC is calculated as follows:  The graph below shows the consumption schedule. The slope of the schedule is the MPC.
The graph below shows the consumption schedule. The slope of the schedule is the MPC. 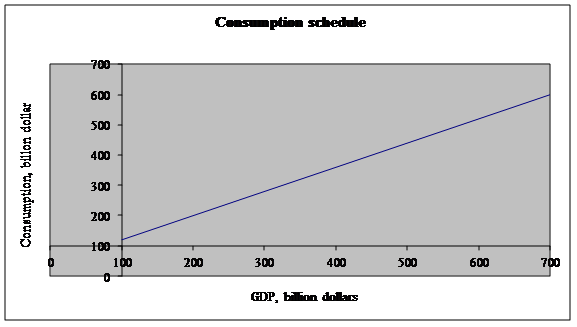 b. After the tax, disposable income falls by $10 billion at every level of GDP. The MPC does not change, but he level of consumption shifts downward by $8 billion:
b. After the tax, disposable income falls by $10 billion at every level of GDP. The MPC does not change, but he level of consumption shifts downward by $8 billion: 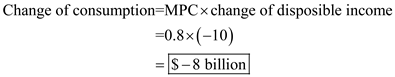 The new level of consumption is calculated as follows.
The new level of consumption is calculated as follows. 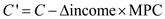 The table for the new level of consumption is as follows:
The table for the new level of consumption is as follows: 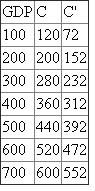

 The graph below shows the change of the consumption schedule from C to C'.
The graph below shows the change of the consumption schedule from C to C'. 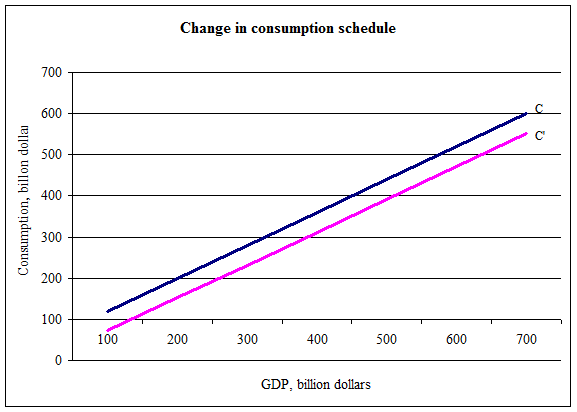
 MPC is calculated as follows:
MPC is calculated as follows:  The graph below shows the consumption schedule. The slope of the schedule is the MPC.
The graph below shows the consumption schedule. The slope of the schedule is the MPC.  b. After the tax, disposable income falls by $10 billion at every level of GDP. The MPC does not change, but he level of consumption shifts downward by $8 billion:
b. After the tax, disposable income falls by $10 billion at every level of GDP. The MPC does not change, but he level of consumption shifts downward by $8 billion: 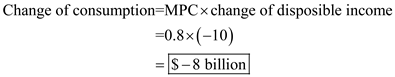 The new level of consumption is calculated as follows.
The new level of consumption is calculated as follows. 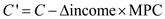 The table for the new level of consumption is as follows:
The table for the new level of consumption is as follows: 

 The graph below shows the change of the consumption schedule from C to C'.
The graph below shows the change of the consumption schedule from C to C'. 
3
If total spending is just sufficient to purchase an economy's output, then the economy is:
A) In equilibrium.
B) In recession.
C) In debt.
D) In expansion.
A) In equilibrium.
B) In recession.
C) In debt.
D) In expansion.
The equilibrium level of GDP for a private closed economy is the point where aggregate spending and the real output are equal.
Hence, the correct answer is a. In equilibrium.
All the other answers are false because they either occur when aggregate spending and real output are not balanced.
Hence, the correct answer is a. In equilibrium.
All the other answers are false because they either occur when aggregate spending and real output are not balanced.
4
A depression abroad will tend to ________ our exports, which in turn will _______ net exports, which in turn will _______ equilibrium real GDP.
A) Reduce; reduce; reduce.
B) Increase; increase; increase.
C) Reduce; increase; increase.
D) Increase; reduce; reduce.
A) Reduce; reduce; reduce.
B) Increase; increase; increase.
C) Reduce; increase; increase.
D) Increase; reduce; reduce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is saving called a leakage ? Why is planned investment called an injection ? Why must saving equal planned investment at equilibrium GDP in the private closed economy? Are unplanned changes in inventories rising, falling, or constant at equilibrium GDP? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is a recessionary expenditure gap? An inflationary expenditure gap? Which is associated with a positive GDP gap? A negative GDP gap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
By how much will GDP change if firms increase their investment by $8 billion and the MPC is.80? If the MPC is.67? LO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to columns 1 and 6 in the table for problem 5. Incorporate government into the table by assuming that it plans to tax and spend $20 billion at each possible level of GDP. Also assume that the tax is a personal tax and that government spending does not induce a shift in the private aggregate expenditures schedule. What is the change in equilibrium GDP caused by the addition of government? LO4 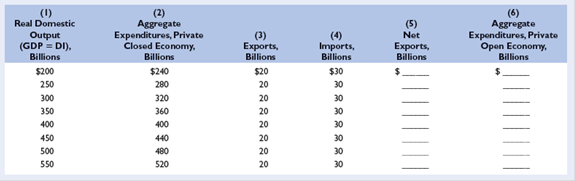


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The recessionary expenditure gap depicted will cause:
A) demand-pull inflation.
B) cost-push inflation.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.
A) demand-pull inflation.
B) cost-push inflation.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Explain graphically the determination of equilibrium GDP for a private economy through the aggregate expenditures model. Now add government purchases (any amount you choose) to your graph, showing its impact on equilibrium GDP. Finally, add taxation (any amount of lump-sum tax that you choose) to your graph and show its effect on equilibrium GDP. Looking at your graph, determine whether equilibrium GDP has increased, decreased, or stayed the same given the sizes of the government purchases and taxes that you selected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The $490 billion level of real GDP is not at equilibrium because:
A) investment exceeds consumption.
B) consumption exceeds investment.
C) planned C + I g exceeds real GDP.
D) planned C + I g is less than real GDP.
A) investment exceeds consumption.
B) consumption exceeds investment.
C) planned C + I g exceeds real GDP.
D) planned C + I g is less than real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
LAST WORD What is Say's law? How does it relate to the view held by classical economists that the economy generally will operate at a position on its production possibilities curve (Chapter 1)? Use production possibilities analysis to demonstrate Keynes' view on this matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
True or False: If spending exceeds output, real GDP will decline as firms cut back on production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Advanced Analysis Assume that the consumption schedule for a private open economy is such that consumption C = 50 + 0.8 Y. Assume further that planned investment Ig and net exports Xn are independent of the level of real GDP and constant at Ig = 30 and Xn = 10. Recall also that, in equilibrium, the real output produced ( Y ) is equal to aggregate expenditures: Y = C + Ig + Xn. LO4
a. Calculate the equilibrium level of income or real GDP for this economy.
b. What happens to equilibrium Y if Ig changes to 10? What does this outcome reveal about the size of the multiplier?
a. Calculate the equilibrium level of income or real GDP for this economy.
b. What happens to equilibrium Y if Ig changes to 10? What does this outcome reveal about the size of the multiplier?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following changes independently have on the equilibrium level of real GDP in the private closed economy? LO3
a. A decline in the real interest rate.
b. An overall decrease in the expected rate of return on investment.
c. A sizeable, sustained increase in stock prices.
a. A decline in the real interest rate.
b. An overall decrease in the expected rate of return on investment.
c. A sizeable, sustained increase in stock prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The economy's current level of equilibrium GDP is $780 billion. The full employment level of GDP is $800 billion. The multiplier is 4. Given those facts, we know that the economy faces _______ expenditure gap of _______.
A) An inflationary; $5 billion.
B) An inflationary; $10 billion.
C) An inflationary; $20 billion.
D) A recessionary; $5 billion.
E) A recessionary; $10 billion.
F) A recessionary; $20 billion.
A) An inflationary; $5 billion.
B) An inflationary; $10 billion.
C) An inflationary; $20 billion.
D) A recessionary; $5 billion.
E) A recessionary; $10 billion.
F) A recessionary; $20 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is an investment schedule and how does it differ from an investment demand curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose that a certain country has an MPC of.9 and a real GDP of $400 billion. If its investment spending decreases by $4 billion, what will be its new level of real GDP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the accompanying table in answering the questions that follow: LO5 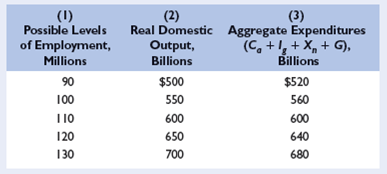
a. If full employment in this economy is 130 million, will there be an inflationary expenditure gap or a recessionary expenditure gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary expenditure gap or the recessionary expenditure gap? What is the multiplier in this example?
b. Will there be an inflationary expenditure gap or a recessionary expenditure gap if the full-employment level of output is $500 billion? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the gap? What is the multiplier in this example?
c. Assuming that investment, net exports, and government expenditures do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?

a. If full employment in this economy is 130 million, will there be an inflationary expenditure gap or a recessionary expenditure gap? What will be the consequence of this gap? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the inflationary expenditure gap or the recessionary expenditure gap? What is the multiplier in this example?
b. Will there be an inflationary expenditure gap or a recessionary expenditure gap if the full-employment level of output is $500 billion? By how much would aggregate expenditures in column 3 have to change at each level of GDP to eliminate the gap? What is the multiplier in this example?
c. Assuming that investment, net exports, and government expenditures do not change with changes in real GDP, what are the sizes of the MPC, the MPS, and the multiplier?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Assuming the level of investment is $16 billion and independent of the level of total output, complete the accompanying table and determine the equilibrium levels of output and employment in this private closed economy. What are the sizes of the MPC and MPS?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the economy depicted, the $5 billion inflationary expenditure gap:
A) expands real GDP to $530 billion.
B) leaves real GDP at $510 billion but causes inflation.
C) could be remedied by equal $5 billion increases in taxes and government spending.
D) implies that real GDP exceeds nominal GDP.
A) expands real GDP to $530 billion.
B) leaves real GDP at $510 billion but causes inflation.
C) could be remedied by equal $5 billion increases in taxes and government spending.
D) implies that real GDP exceeds nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If an economy has an inflationary expenditure gap, the government could attempt to bring the economy back toward the full-employment level of GDP by _______ taxes or _______ government expenditures.
A) Increasing; increasing.
B) Increasing; decreasing.
C) Decreasing; increasing.
D) Decreasing; decreasing.
A) Increasing; increasing.
B) Increasing; decreasing.
C) Decreasing; increasing.
D) Decreasing; decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the economy depicted:
A) the MPS is 0.50.
B) the MPC is 0.75.
C) the full-employment level of real GDP is $530 billion.
D) nominal GDP always equals real GDP.
A) the MPS is 0.50.
B) the MPC is 0.75.
C) the full-employment level of real GDP is $530 billion.
D) nominal GDP always equals real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The $430 billion level of real GDP is not at equilibrium because:
A) investment exceeds consumption.
B) consumption exceeds investment.
C) planned C + I g exceeds real GDP.
D) planned C + I g is less than real GDP.
A) investment exceeds consumption.
B) consumption exceeds investment.
C) planned C + I g exceeds real GDP.
D) planned C + I g is less than real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Answer the following questions, which relate to the aggregate expenditures model: LO5
a. If C is $100, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, what is the economy's equilibrium GDP?
b. If real GDP in an economy is currently $200, C is $100, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, will the economy's real GDP rise, fall, or stay the same?
c. Suppose that full-employment (and full-capacity) output in an economy is $200. If C is $150, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, what will be the macroeconomic result?
a. If C is $100, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, what is the economy's equilibrium GDP?
b. If real GDP in an economy is currently $200, C is $100, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, will the economy's real GDP rise, fall, or stay the same?
c. Suppose that full-employment (and full-capacity) output in an economy is $200. If C is $150, Ig is $50, Xn is -$10, and G is $30, what will be the macroeconomic result?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In this figure, the slope of the aggregate expenditures schedule C + I g :
A) increases as real GDP increases.
B) falls as real GDP increases.
C) is constant and equals the MPC.
D) is constant and equals the MPS.
A) increases as real GDP increases.
B) falls as real GDP increases.
C) is constant and equals the MPC.
D) is constant and equals the MPS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If inventories unexpectedly rise, then production sales _________ and firms will respond by _______ output.
A) Trails; expanding.
B) Trails; reducing.
C) Exceeds; expanding.
D) Exceeds; reducing.
A) Trails; expanding.
B) Trails; reducing.
C) Exceeds; expanding.
D) Exceeds; reducing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
True or False: The aggregate expenditures model assumes flexible prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Depict graphically the aggregate expenditures model for a private closed economy. Now show a decrease in the aggregate expenditures schedule and explain why the decline in real GDP in your diagram is greater than the decline in the aggregate expenditures schedule. What is the term used for the ratio of a decline in real GDP to the initial drop in aggregate expenditures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why does equilibrium real GDP occur where C + I g = GDP in a private closed economy? What happens to real GDP when C + I g exceeds GDP? When C + I g is less than GDP? What two expenditure components of real GDP are purposely excluded in a private closed economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The data in columns 1 and 2 in the accompanying table are for a private closed economy: LO4 
a. Use columns 1 and 2 to determine the equilibrium GDP for this hypothetical economy.
b. Now open up this economy to international trade by including the export and import figures of columns 3 and 4. Fill in columns 5 and 6 and determine the equilibrium GDP for the open economy. What is the change in equilibrium GDP caused by the addition of net exports?
c. Given the original $20 billion level of exports, what would be net exports and the equilibrium GDP if imports were $10 billion greater at each level of GDP?
d. What is the multiplier in this example?

a. Use columns 1 and 2 to determine the equilibrium GDP for this hypothetical economy.
b. Now open up this economy to international trade by including the export and import figures of columns 3 and 4. Fill in columns 5 and 6 and determine the equilibrium GDP for the open economy. What is the change in equilibrium GDP caused by the addition of net exports?
c. Given the original $20 billion level of exports, what would be net exports and the equilibrium GDP if imports were $10 billion greater at each level of GDP?
d. What is the multiplier in this example?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the consumption and saving data in problem 1 and assuming investment is $16 billion, what are saving and planned investment at the $380 billion level of domestic output? What are saving and actual investment at that level? What are saving and planned investment at the $300 billion level of domestic output? What are the levels of saving and actual investment? In which direction and by what amount will unplanned investment change as the economy moves from the $380 billion level of GDP to the equilibrium level of real GDP? From the $300 billion level of real GDP to the equilibrium level of GDP? LO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the multiplier is 5 and investment increases by $3 billion, equilibrium real GDP will increase by:
A) $2 billion.
B) $3 billion.
C) $8 billion.
D) $15 billion.
E) None of the above.
A) $2 billion.
B) $3 billion.
C) $8 billion.
D) $15 billion.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The inflationary expenditure gap depicted will cause:
A) demand-pull inflation.
B) cost-push inflation.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.
A) demand-pull inflation.
B) cost-push inflation.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assuming the economy is operating below its potential output, what is the impact of an increase in net exports on real GDP? Why is it difficult, if not impossible, for a country to boost its net exports by increasing its tariffs during a global recession?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



