Deck 6: Chromosome Mutations: Variation in Number and Arrangement
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Chromosome Mutations: Variation in Number and Arrangement
1
In what way might gene duplication play a role in evolution?
In 1970,Ohno proposed that gene duplication provides a way in which new genes arise.By duplicating a gene,the duplicated copy or the original gene is able to mutate without necessarily having an adverse influence on the phenotype.
2
Trisomics are observed in humans; monosomics are not.Why?
Monosomics are inviable.Such haploinsufficiency combines the loss of multiple genes.
3
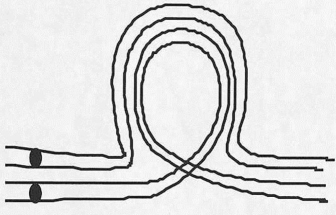
Clearly illustrate the pairing configuration of an inversion (paracentric)heterokaryotype.
The pairing of homologous chromosomes of an inversion heterokaryotype is typically one of an "outside" loop filled by an "inside loop."

4
What explanation is generally given for lethality of monosomic individuals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Name the polyploid condition that is formed from the addition of one or more extra sets of chromosomes identical to the normal haploid complement of the same species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given that a human normally contains 46 chromosomes,give the chromosome number for each of the following conditions:
Turner syndrome (female,no Barr bodies)
Klinefelter syndrome (male,one Barr body)
triploid
Down syndrome (trisomic)
trisomy 13
Turner syndrome (female,no Barr bodies)
Klinefelter syndrome (male,one Barr body)
triploid
Down syndrome (trisomic)
trisomy 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A genomic condition that may be responsible for some forms of fragile-X syndrome,as well as Huntington disease,involves ________.
A)F plasmids inserted into the FMR-1 gene
B)various lengths of trinucleotide repeats
C)multiple breakpoints fairly evenly dispersed along the X chromosome
D)multiple inversions in the X chromosome
E)single translocations in the X chromosome
A)F plasmids inserted into the FMR-1 gene
B)various lengths of trinucleotide repeats
C)multiple breakpoints fairly evenly dispersed along the X chromosome
D)multiple inversions in the X chromosome
E)single translocations in the X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The condition that exists when an organism gains or loses one or more chromosomes but not a complete haploid set is known as ________.
A)polyploidy
B)euploidy
C)aneuploidy
D)triploidy
E)trisomy
A)polyploidy
B)euploidy
C)aneuploidy
D)triploidy
E)trisomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Deletions are chromosomal aberrations in which some portion of a chromosome is missing.Describe a method using Drosophila deletions to determine the actual,physical location of a gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Provide an example of gene redundancy that occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The condition known as cri-du-chat syndrome in humans has a genetic constitution designated as ________.
A)45,X
B)heteroplasmy
C)46,5p-
D)triploidy
E)trisomy
A)45,X
B)heteroplasmy
C)46,5p-
D)triploidy
E)trisomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Recently,a gene located on chromosome 3 in humans,FHIT,has been shown to be associated with the significant human malady known as ________.
A)cancer
B)Huntington disease
C)"mad-cow" disease
D)Klinefelter syndrome
E)XYY/XY mosaicism
A)cancer
B)Huntington disease
C)"mad-cow" disease
D)Klinefelter syndrome
E)XYY/XY mosaicism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Although the most frequent forms of Down syndrome are caused by a random error,nondisjunction of chromosome 21,Down syndrome occasionally runs in families.The cause of this form of familial Down syndrome is ________.
A)an inversion involving chromosome 21
B)a chromosomal aberration involving chromosome 1
C)too many X chromosomes
D)a translocation between chromosome 21 and a member of the D chromosome group
E)a maternal age effect
A)an inversion involving chromosome 21
B)a chromosomal aberration involving chromosome 1
C)too many X chromosomes
D)a translocation between chromosome 21 and a member of the D chromosome group
E)a maternal age effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe Bar mutations in Drosophila melanogaster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Trisomy 21,or Down syndrome,occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement but one (extra)chromosome 21.Although fertility is reduced in both sexes,females have higher fertility rates than males.Van Dyke et al.(1995; Down Syndrome Research and Practice 3[2]:65-69)summarize data involving children born of Down syndrome individuals.Assume that children are born to a female with Down syndrome and a normal 46-chromosome male.What proportion of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome?
A)One-third of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)Two-thirds of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)None of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)One-half of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
A)One-third of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)Two-thirds of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)None of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)One-half of the offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Inversion heterokaryotypes are often characterized as having reduced crossing over and reduced fertility.Assume that you were examining a strain of organisms you knew to be inversion heterokaryotypes and saw a relatively high number of double chromatid bridges extending between anaphase I nuclei.What would be a likely explanation for this observation? Explain with a labeled diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Trisomy 21,or Down syndrome,occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement but one (extra)chromosome 21.Although fertility is reduced in both sexes,females have higher fertility than males.Van Dyke et al.(1995; Down Syndrome Research and Practice 3[2]:65-69)summarize data involving children born of Down syndrome individuals.Given the fact that conceptuses with 48 chromosomes (four chromosome 21s)are not likely to survive early development,what percentage of surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome if both parents have Down syndrome?
A)One-third of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)None of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)Two-thirds of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)One-half of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
A)One-third of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
B)All the children would be expected to have Down syndrome.
C)None of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
D)Two-thirds of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.
E)One-half of the surviving offspring would be expected to have Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Name two methods used in genetic prenatal diagnostic testing in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Describe the maternal age effect associated with Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Colchicine is an alkaloid derived from plants.What is its effect on chromosome behavior?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Fragile-X syndrome (or Martin-Bell syndrome)is the most common form of inherited mental retardation in humans.Is it more common in males or females? What is FMR1?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Nondisjunction is viewed as a major cause of aneuploidy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is meant by the terms acentric and dicentric?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Gene duplications provide an explanation for the origin of gene families.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
rDNA in eukaryotes is typically redundant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under what circumstance can an individual with Down syndrome have 46 chromosomes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The term aneuploidy is synonymous with the term segmental deletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A paracentric inversion is one whose break points do not flank the centromere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An autotriploid may arise when three sperm cells are involved in fertilization of a single egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Inversions suppress crossing over by providing a chemical imbalance because of breakpoints within certain genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assume that an organism has a haploid chromosome number of 7.There would be 14 chromosomes in a monoploid individual of that species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An expected meiotic pairing configuration in a triploid would be a trivalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)is sometimes preferred to amniocentesis because results can be provided earlier in the pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Doubling the chromosomes of a sterile species hybrid with colchicine or cold shock is a method used to produce a fertile species hybrid (amphidiploid).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assume that a species has a diploid chromosome number of 24.The term applied to an individual with 25 chromosomes would be triploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume that a species has a diploid chromosome number of 24.The term applied to an individual with 36 chromosomes would be triploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An individual with Patau syndrome would be called a triploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A deletion may set up a genetic circumstance known as overdominance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In Drosophila melanogaster (2n = 8),a fly with seven chromosomes could be called a haplo-IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assume that an organism has a diploid chromosome number of 14.There would be 28 chromosomes in a tetraploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A position effect occurs when a gene's expression is altered by virtue of a change in its position.One might expect position effects to occur with inversions and translocations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Familial Down syndrome can be caused by a translocation between chromosomes 1 and 14.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Familial Down syndrome is caused by a translocation involving chromosome 21.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Individuals with familial Down syndrome are trisomic and have 47 chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In general,inversion and translocation heterozygotes are as fertile as organisms whose chromosomes are in the standard arrangement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A pericentric inversion includes the centromere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Inversions and translocations are without evolutionary significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Translocations may be pericentric or paracentric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



