Deck 10: Externalities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Externalities
1
Negative consumption externalities will have a socially optimal quantity that is smaller than the quantity determined by the private market.
True
2
Taxation is often able to correct market externalities at a lower cost than regulations designed to achieve the same goal.
True
3
Policy responses that try to deal with market failure resulting from externalities are largely restricted to various forms of taxation.
False
4
According to the Coase theorem, parties will bargain among themselves to reach an efficient solution without intervention.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The externality associated with the production of electricity will lead the market to produce a larger quantity than socially desirable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When regulating a market in which an externality arises, the government can only command how much of the good companies are allowed to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When weighing the costs and benefits of pollution, the costs always exceed the benefits because the benefit equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Market outcomes cannot be improved by government policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Internet is a good example of a negative externality because it has aspects which may be inappropriate for some users.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Government can internalise an externality by taxing the goods that have negative externalities and subsidising the goods that have positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Externalities can be solved if parties are able to bargain without cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The ability of individuals to arrive at a private solution to an externality is dependent on the initial distribution of rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the social cost of producing robots is less than the private cost of producing robots, the private market produces too few robots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Government can solve externality problems that are too costly for private parties to solve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Internalising a negative consumption externality will cause the market supply curve to shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The size and scope of technology spillovers is easy for governments to measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Education has negative externalities for society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Despite the appealing logic of the Coase theorem, private actors often fail to resolve on their own the problems caused by externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Government can accurately measure the social value of an externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The owner of a luxury 4WD enjoys a positive externality because the luxury 4WD offers added safety when compared to a small car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Vaccinations are heavily subsidised in order to get the optimal number of people vaccinated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Because a driver's private motoring costs do not completely reflect the costs he imposes on others, he is likely to use the car more than is socially desirable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
All remedies that attempt to solve an externality problem share the goal of moving the allocation of resources closer to the private optimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Private parties can negotiate a solution to an externality in all cases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A market for pollution permits can efficiently allocate the right to pollute through the forces of supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When Jake takes into account how his actions affect Jill, and then changes his behaviour, an externality is solved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The main goal of a tax on pollution is to raise revenue for the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Pigovian taxes enhance efficiency but the cost of administering such taxes frequently exceeds the revenue they raise for the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Luckily, the free market corrects for the cost to bystanders of a crying child, because the parent is irritated as much as, if not more than the bystander.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Firms that can reduce pollution easily will be willing to sell their emissions permits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Aaron and Katie are building a house. They want to make sure they have a good relationship with the neighbours and do not want to impose any negative externalities on them. Which of the following are measures to avoid negative externalities on Aaron and Katie's neighbours?
(i) making sure their windows do not look into the neighbours' yarD.
(ii) carefully insulating their house so that sound doesn't carry when they play loud musiC.
(iii) building an environmentally friendly house.
A) (i), (ii) and (iii)
B) only (i) and (iii)
C) only (ii) and (iii)
D) only (i) and (ii)
(i) making sure their windows do not look into the neighbours' yarD.
(ii) carefully insulating their house so that sound doesn't carry when they play loud musiC.
(iii) building an environmentally friendly house.
A) (i), (ii) and (iii)
B) only (i) and (iii)
C) only (ii) and (iii)
D) only (i) and (ii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Charities are an example of a private solution to an externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In essence, the Pigovian tax places a price on the right to pollute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When the government decides to dredge a bay to let big ships into the port, they are causing:
A) a positive externality because dredging will allow bigger ships into the bay
B) a positive externality because the dredging will create profit for the dredging company
C) a negative externality because marine life will be displaced by the dredging
D) a negative externality because the dredging will take a long time to complete
A) a positive externality because dredging will allow bigger ships into the bay
B) a positive externality because the dredging will create profit for the dredging company
C) a negative externality because marine life will be displaced by the dredging
D) a negative externality because the dredging will take a long time to complete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Contracts cannot solve the inefficiency that arises from externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Policies aimed at reducing an externality sometimes have unintended consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Government policies to encourage technology spillovers may go to industries with the most political clout rather than industries with the largest spillovers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a tax is used to give buyers and sellers in a market the incentive to take into account the external effects of their actions, it is said to be 'internalising an externality'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Social welfare can be enhanced by allowing firms to trade their carbon credits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When there are transaction costs to resolving an externality, the distribution of rights does not matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Airports can generate a negative externality with the noise the landing aircraft makes on neighbourhoods. Policies to reduce this noise problem include:
A) charging passengers an airport departure tax
B) charging excise taxes on airline fuel
C) encouraging people to drive rather than fly
D) requiring aircraft to use 'whisper' technology to quieten their engines
A) charging passengers an airport departure tax
B) charging excise taxes on airline fuel
C) encouraging people to drive rather than fly
D) requiring aircraft to use 'whisper' technology to quieten their engines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Graph 10-1
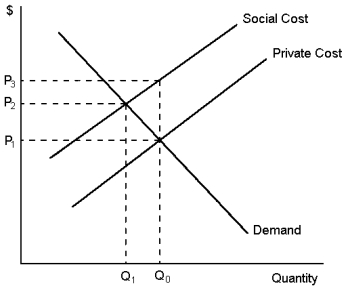
Refer to Graph 10-1. In the figure shown, an optimal government policy would be a tax on production to the value of:
A) P3 - P1
B) P3 - P2
C) P3 - P1.
D) The value of the optimal tax cannot be measured

Refer to Graph 10-1. In the figure shown, an optimal government policy would be a tax on production to the value of:
A) P3 - P1
B) P3 - P2
C) P3 - P1.
D) The value of the optimal tax cannot be measured

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Graph 10-1

Refer to Graph 10-1. This graph reflects the presence of a:
A) negative production externality
B) positive production externality
C) negative consumption externality
D) positive consumption externality

Refer to Graph 10-1. This graph reflects the presence of a:
A) negative production externality
B) positive production externality
C) negative consumption externality
D) positive consumption externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tom is very tall. When he goes to a music festival it is likely he will create:
A) no externality because there are lots of people at the festival
B) a positive externality because he can hear the music very well, being above the crowd
C) a positive externality because he can easily find his friends if he loses them
D) a negative externality because he will block the view of shorter people who find themselves standing behind him
A) no externality because there are lots of people at the festival
B) a positive externality because he can hear the music very well, being above the crowd
C) a positive externality because he can easily find his friends if he loses them
D) a negative externality because he will block the view of shorter people who find themselves standing behind him

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A positive externality exists when:
A) a person engages in an activity that has a spillover that makes a bystander better off
B) the market has only one seller
C) a firm sells its product in an external foreign market
D) a person engages in an activity that has a spillover that makes a bystander worse off
A) a person engages in an activity that has a spillover that makes a bystander better off
B) the market has only one seller
C) a firm sells its product in an external foreign market
D) a person engages in an activity that has a spillover that makes a bystander worse off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose that a fish-food manufacturing company is located up the river from a fishing firm and often releases some of the food into the river. This means:
A) the fish food manufacturing company is imposing a negative externality on the fishing firm
B) the fish food manufacturing company is imposing a positive externality on the fishing firm
C) under the Coase theorem the two companies should be able to negotiate away the externality
D) unless the government imposes a tax on river pollution, the fishing firm will continue to be negatively impacted by the fish-food manufacturing company
A) the fish food manufacturing company is imposing a negative externality on the fishing firm
B) the fish food manufacturing company is imposing a positive externality on the fishing firm
C) under the Coase theorem the two companies should be able to negotiate away the externality
D) unless the government imposes a tax on river pollution, the fishing firm will continue to be negatively impacted by the fish-food manufacturing company

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Graph 10-2
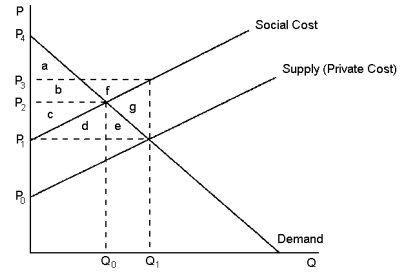 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. The difference between the social cost curve and the supply curve reflects the:
A) profit margin of each kiwifruit tray
B) cost of spillover effects from the kiwifruit orchards (replacing bees, lost honey output)
C) value of kiwifruit to society as a whole
D) amount by which the government should subsidise the kiwifruit orchardists
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. The difference between the social cost curve and the supply curve reflects the:
A) profit margin of each kiwifruit tray
B) cost of spillover effects from the kiwifruit orchards (replacing bees, lost honey output)
C) value of kiwifruit to society as a whole
D) amount by which the government should subsidise the kiwifruit orchardists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Markets are often inefficient when negative production externalities are present because:
A) private costs exceed social costs at the private market solution
B) externalities can never be corrected without government regulation
C) social costs exceed private costs at the private market solution
D) production externalities lead to consumption externalities
A) private costs exceed social costs at the private market solution
B) externalities can never be corrected without government regulation
C) social costs exceed private costs at the private market solution
D) production externalities lead to consumption externalities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A _________ is enacted to correct the effects of a negative externality:
A) regulation
B) deadweight loss
C) corrective tax
D) tradeable permit
A) regulation
B) deadweight loss
C) corrective tax
D) tradeable permit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An externality will:
A) usually be characterised as a form of market failure
B) cause markets to allocate resources efficiently
C) strengthen the role of the 'invisible hand' in the marketplace
D) always require the producer to compensate society
A) usually be characterised as a form of market failure
B) cause markets to allocate resources efficiently
C) strengthen the role of the 'invisible hand' in the marketplace
D) always require the producer to compensate society

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
To produce honey, beekeepers place hives of bees in orchards and crop fields. As bees gather nectar that they use to produce honey, they pollinate the orchards and fields increasing their yields of fruit and grain. This arrangement results in:
A) positive externalities that benefit both the beekeeper and the owner of the fields of fruit and grain
B) no significant additional benefit to anyone
C) a positive externality that benefits only the owner of the fields of fruit and grain
D) a positive externality that solely benefits the beekeeper
A) positive externalities that benefit both the beekeeper and the owner of the fields of fruit and grain
B) no significant additional benefit to anyone
C) a positive externality that benefits only the owner of the fields of fruit and grain
D) a positive externality that solely benefits the beekeeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Graph 10-1

Refer to Graph 10-1. Which price and quantity combination represents the social optimum?
A) P1, Q1
B) P2, Q1
C) P1, Q2
D) P2, Q2

Refer to Graph 10-1. Which price and quantity combination represents the social optimum?
A) P1, Q1
B) P2, Q1
C) P1, Q2
D) P2, Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose people plant flowering trees near their homes to encourage rare native birds to feed. If people believe that an increase in native bird populations is valuable, people who plant these trees:
A) generate a negative consumption externality for their neighbours
B) generate a positive production externality for their neighbours
C) generate a positive consumption externality for their neighbours
D) generate a negative production externality for their neighbours
A) generate a negative consumption externality for their neighbours
B) generate a positive production externality for their neighbours
C) generate a positive consumption externality for their neighbours
D) generate a negative production externality for their neighbours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Using the information in question 30, what would be a private solution to the above externality?
A) under the Coase theorem the two companies should be able to negotiate away the externality
B) the two companies would need to trade permits for river pollution in order to achieve an optimal outcome
C) the fishing firm could buy the fish-food manufacturing company
D) the fishing firm should continue to make the most of the positive externality
A) under the Coase theorem the two companies should be able to negotiate away the externality
B) the two companies would need to trade permits for river pollution in order to achieve an optimal outcome
C) the fishing firm could buy the fish-food manufacturing company
D) the fishing firm should continue to make the most of the positive externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
It is generally difficult or impossible for private markets to take externalities into account because:
A) decision makers in the market fail to take account of the spillover effects of their behaviour
B) buyers and sellers in private markets are only interested in social wellbeing
C) people are only interested in short-term gains
D) governments are responsible for externality problems
A) decision makers in the market fail to take account of the spillover effects of their behaviour
B) buyers and sellers in private markets are only interested in social wellbeing
C) people are only interested in short-term gains
D) governments are responsible for externality problems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the social cost of an externality is lower than its private cost:
A) society is likely to benefit from a corrective tax
B) the externality is a positive one and society will not consume enough of the good
C) the externality is a positive one and society will consume too much of the good
D) society will benefit from the introduction of tradeable permits for production of the good
A) society is likely to benefit from a corrective tax
B) the externality is a positive one and society will not consume enough of the good
C) the externality is a positive one and society will consume too much of the good
D) society will benefit from the introduction of tradeable permits for production of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a particular market is associated with an externality, the social optimum should include the wellbeing of:
A) buyers, sellers and bystanders
B) bystanders and buyers
C) bystanders and sellers
D) buyers and sellers only
A) buyers, sellers and bystanders
B) bystanders and buyers
C) bystanders and sellers
D) buyers and sellers only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Jack loves surfing but prefers to go in winter instead of summer and always tries to find spots most surfers usually avoid. What could be one of the reasons for which Jack chooses to surf in this way?
A) he only likes to surf in dangerous circumstances
B) having other surfers around imposes a negative externality on Jack
C) the spots most surfers avoid usually have the best conditions
D) he doesn't want to impose a negative externality on other surfers by taking their waves
A) he only likes to surf in dangerous circumstances
B) having other surfers around imposes a negative externality on Jack
C) the spots most surfers avoid usually have the best conditions
D) he doesn't want to impose a negative externality on other surfers by taking their waves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. The social cost curve is above the supply curve because:
A) it takes into account the external costs imposed on society by the kiwifruit farmers
B) honeybees are also a cost to society
C) kiwifruits are likely to cost more than growing the kiwifruit costs the organisers
D) workers on kiwifruit orchards also benefit from the job opportunities
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. The social cost curve is above the supply curve because:
A) it takes into account the external costs imposed on society by the kiwifruit farmers
B) honeybees are also a cost to society
C) kiwifruits are likely to cost more than growing the kiwifruit costs the organisers
D) workers on kiwifruit orchards also benefit from the job opportunities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Negative externalities occur when one person's actions:
A) cause another person to lose money in a stock-market transaction.
B) cause his or her employer to lose business.
C) adversely affect the wellbeing of a bystander (or bystanders) who is (are) not party to a market exchange.
D) reveal his or her preference for foreign produced goods.
A) cause another person to lose money in a stock-market transaction.
B) cause his or her employer to lose business.
C) adversely affect the wellbeing of a bystander (or bystanders) who is (are) not party to a market exchange.
D) reveal his or her preference for foreign produced goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose that a steel factory emits a certain amount of air pollution and that this pollution constitutes a negative externality. If this market is not required to internalise this externality:
A) the supply curve would adequately reflect the marginal social cost of production
B) consumers will be required to pay a higher price for steel than they would have if the externality were internalised
C) the market equilibrium would not be the socially optimal quantity
D) producers will produce less steel than they otherwise would have if the externality were internalised
A) the supply curve would adequately reflect the marginal social cost of production
B) consumers will be required to pay a higher price for steel than they would have if the externality were internalised
C) the market equilibrium would not be the socially optimal quantity
D) producers will produce less steel than they otherwise would have if the externality were internalised

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Internalising a positive production externality will cause the demand curve faced by an industry to:
A) shift to the right
B) shift to the left
C) become more elastic
D) remain unchanged
A) shift to the right
B) shift to the left
C) become more elastic
D) remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. Assume that the kiwifruit orchardists must purchase a pesticide application permit (the cost for the permit is included in private cost) before spraying their fruit. What criteria should the government use in determining whether or not to issue a permit?
A) the majority vote of the affected beekeepers should determine whether a permit is issued
B) as long as the value to consumers of kiwifruit exceeds the cost of kiwifruit (including the external costs), the permit should be issued
C) as long as kiwifruit orchardists are willing to replace the dead honeybees, the permit should be issued
D) the permit should not be issued as long as there are identifiable external costs imposed on local beekeepers.
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. Assume that the kiwifruit orchardists must purchase a pesticide application permit (the cost for the permit is included in private cost) before spraying their fruit. What criteria should the government use in determining whether or not to issue a permit?
A) the majority vote of the affected beekeepers should determine whether a permit is issued
B) as long as the value to consumers of kiwifruit exceeds the cost of kiwifruit (including the external costs), the permit should be issued
C) as long as kiwifruit orchardists are willing to replace the dead honeybees, the permit should be issued
D) the permit should not be issued as long as there are identifiable external costs imposed on local beekeepers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements about a market that is affected by a positive production externality is correct?
A) the optimum level of output is less than the free market level of output and the optimum price is greater than the free market price
B) the optimum level of output is greater than the free market level of output and the optimum price is less than the free market price
C) the optimum level of output is greater than the free market level of output and the optimum price is greater than the free market price
D) the optimum level of output is less than the free market level of output and the optimum price is less than the free market price
A) the optimum level of output is less than the free market level of output and the optimum price is greater than the free market price
B) the optimum level of output is greater than the free market level of output and the optimum price is less than the free market price
C) the optimum level of output is greater than the free market level of output and the optimum price is greater than the free market price
D) the optimum level of output is less than the free market level of output and the optimum price is less than the free market price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. At the private market outcome, the equilibrium price of kiwifruit will be:
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. At the private market outcome, the equilibrium price of kiwifruit will be:
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. At the private market outcome, quantity Q1 represents the:
A) quantity of kiwifruit consumers will buy
B) quantity of kiwifruit and honey consumers will buy
C) socially optimal quantity of kiwifruit that should be produced
D) optimal price of a kiwifruit from the standpoint of society as a whole
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. At the private market outcome, quantity Q1 represents the:
A) quantity of kiwifruit consumers will buy
B) quantity of kiwifruit and honey consumers will buy
C) socially optimal quantity of kiwifruit that should be produced
D) optimal price of a kiwifruit from the standpoint of society as a whole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose fertiliser use on pastoral land causes water quality in surrounding areas to fall. If a tax on fertiliser was set at the optimal level:
A) farmers would choose not to use any fertiliser
B) farmers fully internalise the pollution costs of the fertiliser
C) farm output would be maximised
D) the value to consumers of pastoral products would exceeds the cost of production (including tax) at the market equilibrium
A) farmers would choose not to use any fertiliser
B) farmers fully internalise the pollution costs of the fertiliser
C) farm output would be maximised
D) the value to consumers of pastoral products would exceeds the cost of production (including tax) at the market equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. What price and quantity combination best represents the optimum price and number of kiwifruit trays that should be produced?
A) P1, Q1
B) P2, Q0
C) P3, Q1
D) The optimum quantity is zero kiwifruit as long as honey production by beekeepers is lower because of pesticide use.
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. What price and quantity combination best represents the optimum price and number of kiwifruit trays that should be produced?
A) P1, Q1
B) P2, Q0
C) P3, Q1
D) The optimum quantity is zero kiwifruit as long as honey production by beekeepers is lower because of pesticide use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Graph 10-2
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
Refer to Graph 10-2. The producer surplus derived from the most efficient kiwifruit production levels is represented by the area:
A) g
B) e + g
C) a + b
D) a + b + c
 This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.
This graph reflects the market for kiwifruit, where pesticide used by kiwifruit orchardists also unintentionally kills honey bees.Refer to Graph 10-2. The producer surplus derived from the most efficient kiwifruit production levels is represented by the area:
A) g
B) e + g
C) a + b
D) a + b + c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Technology spillover occurs when:
A) the firm's innovations allow it to establish monopoly power
B) new products by high-tech firms create harmful wastes
C) research by a firm creates innovations that are easily applied and used by others
D) patent laws are used to hinder other firms adopting new technology
A) the firm's innovations allow it to establish monopoly power
B) new products by high-tech firms create harmful wastes
C) research by a firm creates innovations that are easily applied and used by others
D) patent laws are used to hinder other firms adopting new technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Internalising a positive production externality will cause the supply curve faced by an industry to:
A) shift to the right
B) shift to the left
C) expand
D) remain unchanged
A) shift to the right
B) shift to the left
C) expand
D) remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Markets are inefficient when positive production externalities are present because:
A) private benefits of consumption exceed social benefits of consumption when the market is in equilibrium
B) social costs of production exceed private costs of production when the market is in equilibrium
C) social benefits of consumption exceed private benefits of consumption when the market is in equilibrium
D) private costs of production exceed social costs of production when the market is in equilibrium
A) private benefits of consumption exceed social benefits of consumption when the market is in equilibrium
B) social costs of production exceed private costs of production when the market is in equilibrium
C) social benefits of consumption exceed private benefits of consumption when the market is in equilibrium
D) private costs of production exceed social costs of production when the market is in equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements is most correct about a market that is characterised by a negative production externality?
A) the equilibrium quantity of output is equal to the socially optimal quantity
B) the equilibrium quantity of output is greater than the socially optimal quantity
C) government intervention is only required for negative externalities
D) the equilibrium quantity of output is less than the socially optimal quantity
A) the equilibrium quantity of output is equal to the socially optimal quantity
B) the equilibrium quantity of output is greater than the socially optimal quantity
C) government intervention is only required for negative externalities
D) the equilibrium quantity of output is less than the socially optimal quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When a producer operates in a market characterised by negative production externalities, a tax that forces them to internalise the externality will:
A) give sellers the incentive to take account of the external effects of their actions
B) have an offsetting effect that reduces the producer's private production costs
C) increase the amount of the commodity exchanged in market equilibrium
D) restrict the producer's ability to take the costs of the externality into account when deciding how much to supply
A) give sellers the incentive to take account of the external effects of their actions
B) have an offsetting effect that reduces the producer's private production costs
C) increase the amount of the commodity exchanged in market equilibrium
D) restrict the producer's ability to take the costs of the externality into account when deciding how much to supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A positive production externality will cause a market to produce:
A) less than is socially desirable
B) more than is socially desirable
C) more than is market optimal
D) less than is market optimal
A) less than is socially desirable
B) more than is socially desirable
C) more than is market optimal
D) less than is market optimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements about internalising a negative production externality is LEAST correct?
A) internalising a negative production externality will cause the supply curve for the good to shift to the left
B) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to decrease the quantity it supplies to the market and increase the price of the good produced
C) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to increase the quantity it supplies to the market and decrease the price of the good produced
D) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to move closer to the socially optimal price and quantity of the good
A) internalising a negative production externality will cause the supply curve for the good to shift to the left
B) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to decrease the quantity it supplies to the market and increase the price of the good produced
C) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to increase the quantity it supplies to the market and decrease the price of the good produced
D) internalising a negative production externality will cause an industry to move closer to the socially optimal price and quantity of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Melbourne city council is trying to quantify the social cost of smoking in order to determine the optimal value of a tax on smoking. What factors should they include when calculating the social cost of smoking?
A) The chewing gum costs of the smokers and the price consumers pay for cigarettes
B) The price consumers pay for cigarettes and the costs to bystanders affected by air pollution
C) The costs to the bystanders affected by the air pollution only
D) The price consumers pay for the cigarettes
A) The chewing gum costs of the smokers and the price consumers pay for cigarettes
B) The price consumers pay for cigarettes and the costs to bystanders affected by air pollution
C) The costs to the bystanders affected by the air pollution only
D) The price consumers pay for the cigarettes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Internalising a positive production externality through technology policy:
A) involves a subsidy to industries that yield the largest spillovers
B) requires that the government be able to measure the size of technology spillovers
C) does not have the support of economists who believe technology spillovers are difficult to measure
D) all of the above are true
A) involves a subsidy to industries that yield the largest spillovers
B) requires that the government be able to measure the size of technology spillovers
C) does not have the support of economists who believe technology spillovers are difficult to measure
D) all of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Internalising a positive production externality through a government subsidy will cause the industry's supply curve to:
A) remain unchanged
B) shift down by an amount less than the subsidy
C) shift down by an amount equal to the subsidy
D) shift down by an amount greater than the subsidy
A) remain unchanged
B) shift down by an amount less than the subsidy
C) shift down by an amount equal to the subsidy
D) shift down by an amount greater than the subsidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Encouraging firms to increase production via a subsidy will tend to be socially optimal when:
A) the firms are producing necessities
B) there is excess supply in the market
C) the firms output is associated with large technology spillovers
D) the market equilibrium output level is greater than the social optimum
A) the firms are producing necessities
B) there is excess supply in the market
C) the firms output is associated with large technology spillovers
D) the market equilibrium output level is greater than the social optimum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 149 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



