Deck 10: Fiscal Policy and Debt
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/366
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Fiscal Policy and Debt
1
Countries such as China often purchase U.S. debt to help manage their exchange rates against the U.S. dollar.
True
2
Which of these is NOT a withdrawal that reduces the size of the spending multiplier?
A) purchases of imports
B) personal income tax
C) savings
D) personal investment in human capital
A) purchases of imports
B) personal income tax
C) savings
D) personal investment in human capital
personal investment in human capital
3
_____ are securities issued by the government with terms to maturity ranging from 1 to 10 years.
A) Treasury bills
B) Treasury notes
C) Treasury bonds
D) U.S. savings bonds
A) Treasury bills
B) Treasury notes
C) Treasury bonds
D) U.S. savings bonds
Treasury notes
4
_____ government spending, _____ transfer payments, and _____ taxes are all examples of contractionary fiscal policy.
A) Reducing; reducing; reducing
B) Reducing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; increasing; raising
D) Raising; increasing; raising
A) Reducing; reducing; reducing
B) Reducing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; increasing; raising
D) Raising; increasing; raising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement(s) is/are TRUE? I. Automatic stabilizers require overt action by Congress or other policymakers to implement.
II) Discretionary increases in government spending are classified as automatic stabilizers.
III) When the economy is growing, tax receipts increase and transfer payments decrease, helping to automatically stabilize the economy by preventing it from growing too fast.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
II) Discretionary increases in government spending are classified as automatic stabilizers.
III) When the economy is growing, tax receipts increase and transfer payments decrease, helping to automatically stabilize the economy by preventing it from growing too fast.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the economy is below full employment and the government uses expansionary fiscal policy in an attempt to reduce unemployment
A) output and the price level will rise.
B) it will have no effect, as fiscal policy does not work during times of unemployment.
C) output and the price level will fall.
D) output will rise, but the price level will fall.
A) output and the price level will rise.
B) it will have no effect, as fiscal policy does not work during times of unemployment.
C) output and the price level will fall.
D) output will rise, but the price level will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement does NOT refer to a potential problem associated with cyclically balancing the federal budget?
A) Different phases of the business cycle are not of equal length or severity.
B) Forecasting the turning point of the economy is very difficult.
C) Most economists agree that the federal budget should be balanced annually to avoid adding to the deficit.
D) Politicians find it difficult to cut spending or raise taxes.
A) Different phases of the business cycle are not of equal length or severity.
B) Forecasting the turning point of the economy is very difficult.
C) Most economists agree that the federal budget should be balanced annually to avoid adding to the deficit.
D) Politicians find it difficult to cut spending or raise taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The public debt is the
A) debt held by public corporations.
B) portion of the national debt that is held by individuals, companies, and pension funds, along with foreign entities and foreign governments.
C) amount by which government spending exceeds tax revenues in a given year.
D) amount government agencies owe to other agencies.
A) debt held by public corporations.
B) portion of the national debt that is held by individuals, companies, and pension funds, along with foreign entities and foreign governments.
C) amount by which government spending exceeds tax revenues in a given year.
D) amount government agencies owe to other agencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
_____ are all examples of mandatory spending.
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The total accumulation of past deficits less surpluses is called the
A) public debt.
B) national deficit.
C) public surplus.
D) national debt.
A) public debt.
B) national deficit.
C) public surplus.
D) national debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Economists who favor a(n) _____ approach to the federal budget believe that the first priority of policymakers should be to keep the economy at full employment with stable prices.
A) functional finance
B) annually balanced budget
C) cyclically balanced budget
D) laissez-faire
A) functional finance
B) annually balanced budget
C) cyclically balanced budget
D) laissez-faire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the economy is growing steadily, rising tax revenues and declining transfer payments have a contractionary effect on the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Transfer payments are
A) monies paid directly to individuals by the government.
B) not part of the government budget.
C) a vital part of discretionary fiscal policy.
D) payments made to government officials who transfer them back to private companies.
A) monies paid directly to individuals by the government.
B) not part of the government budget.
C) a vital part of discretionary fiscal policy.
D) payments made to government officials who transfer them back to private companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A deficit occurs when tax revenues exceed government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The nearly $800 billion stimulus package passed in the United States in 2009 focused more on spending than on taxes partly because
A) increased spending leads to a larger increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
B) increased spending leads to a smaller increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
C) the government tax multiplier is more than the government spending multiplier.
D) the government revenue multiplier is about the same as the government tax multiplier.
A) increased spending leads to a larger increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
B) increased spending leads to a smaller increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
C) the government tax multiplier is more than the government spending multiplier.
D) the government revenue multiplier is about the same as the government tax multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Voters who want federal government revenues to equal federal government expenditures every year would agree with the _____ approach to federal finance.
A) annually balanced budget
B) cyclically balanced budget
C) functional finance
D) trade-balanced budget
A) annually balanced budget
B) cyclically balanced budget
C) functional finance
D) trade-balanced budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Of the share of the U.S. national debt that is held by the public, foreigners hold nearly the same amount as do Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
_____ are all examples of discretionary spending.
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these illustrates the information lag?
A) Real GDP, an indicator of economic growth, is predicted to increase by 0.1% in July, but the numbers are revised in August to reflect an actual 2% decrease.
B) Current data have been provided to policymakers, but they decide to wait and see what happens in the next quarter.
C) The government responds to the 2% decrease in real GDP, and private investment is crowded out of the investment market.
D) The government decides not to respond to the 2% decrease in real GDP because it is worried about the possibility of inflation.
A) Real GDP, an indicator of economic growth, is predicted to increase by 0.1% in July, but the numbers are revised in August to reflect an actual 2% decrease.
B) Current data have been provided to policymakers, but they decide to wait and see what happens in the next quarter.
C) The government responds to the 2% decrease in real GDP, and private investment is crowded out of the investment market.
D) The government decides not to respond to the 2% decrease in real GDP because it is worried about the possibility of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to public choice economists, the federal government has expanded because
A) the public likes to pay higher taxes to finance more programs.
B) the federal government is efficient in its spending.
C) deficit spending has reduced the perceived cost of current government operations.
D) taxpayers pay the full cost of current government operations.
A) the public likes to pay higher taxes to finance more programs.
B) the federal government is efficient in its spending.
C) deficit spending has reduced the perceived cost of current government operations.
D) taxpayers pay the full cost of current government operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the economy reaches the positively sloped portion of the aggregate supply curve, the value of the multiplier increases, as some of the increase in output is absorbed into price increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which item is NOT public debt?
A) Treasury notes held by individuals
B) Treasury bonds held by banks
C) T-Bills held by the Fed
D) U.S. savings bonds held by pension funds
A) Treasury notes held by individuals
B) Treasury bonds held by banks
C) T-Bills held by the Fed
D) U.S. savings bonds held by pension funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Contractionary fiscal policy is typically used to
A) combat inflation stemming from an overheated economy.
B) combat a recession due to deficient demand.
C) restore the balance of payments.
D) balance the federal budget.
A) combat inflation stemming from an overheated economy.
B) combat a recession due to deficient demand.
C) restore the balance of payments.
D) balance the federal budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The crowding-out effect recognizes that if the government sells bonds to finance spending, it can cause interest rates to _____ consumer spending and investment.
A) fall, thereby reducing
B) fall, thereby stimulating
C) rise, thereby reducing
D) rise, thereby stimulating
A) fall, thereby reducing
B) fall, thereby stimulating
C) rise, thereby reducing
D) rise, thereby stimulating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The recognition lag occurs when it takes several quarters to receive macroeconomic data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Investment tax credits are intended to _____ productivity, shifting the _____ curve to the _____.
A) increase; long-run aggregate supply; right
B) increase; long-run aggregate supply; left
C) increase; aggregate demand; left
D) decrease; long-run aggregate supply; left
A) increase; long-run aggregate supply; right
B) increase; long-run aggregate supply; left
C) increase; aggregate demand; left
D) decrease; long-run aggregate supply; left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Taxes constitute the removal of income from the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which U.S. president reduced marginal tax rates to promote work and business risk taking?
A) Kennedy
B) Reagan
C) Clinton
D) Obama
A) Kennedy
B) Reagan
C) Clinton
D) Obama

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
One strength of the use of discretionary fiscal policy is the timing lags.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose a government finances its expansionary fiscal policy by borrowing from the public. Joseph is concerned that this will increase the demand for loanable funds, drive up interest rates, and leave less loanable money available for consumers and businesses. Joseph is concerned about the _____ effect.
A) boomerang
B) opposite expansionary
C) ricochet
D) crowding-out
A) boomerang
B) opposite expansionary
C) ricochet
D) crowding-out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the government borrows money from the Federal Reserve
A) the quantity of publicly held bonds will rise.
B) the quantity of money in circulation will rise.
C) the quantity of money in circulation will fall.
D) inflation will decrease.
A) the quantity of publicly held bonds will rise.
B) the quantity of money in circulation will rise.
C) the quantity of money in circulation will fall.
D) inflation will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The concept of intergenerational imbalance refers to
A) fiscally sustainable fiscal policy.
B) the amount of fiscal burden future generations place on the present generation.
C) the tax burden the current generation incurs for infrastructure that benefits future generations.
D) future generations funding the current generation's benefits.
A) fiscally sustainable fiscal policy.
B) the amount of fiscal burden future generations place on the present generation.
C) the tax burden the current generation incurs for infrastructure that benefits future generations.
D) future generations funding the current generation's benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When government spending increases, the aggregate demand curve shifts to the _____ and the multiplier effect is dampened by a _____ in the aggregate price level.
A) right; fall
B) right; rise
C) left; fall
D) left; rise
A) right; fall
B) right; rise
C) left; fall
D) left; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which fiscal policy will increase aggregate supply?
A) increasing tax rates on consumers
B) increasing tax rates on businesses
C) allocating more money for federal student loans
D) instituting more regulations on businesses
A) increasing tax rates on consumers
B) increasing tax rates on businesses
C) allocating more money for federal student loans
D) instituting more regulations on businesses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consumers reduce their spending by the exact amount of a tax increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The budget deficit is the sum of past public debts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Laffer curve has aggregate expenditure and income on its axes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of these is a withdrawal of spending in the economy?
A) imports
B) investment
C) exports
D) government spending
A) imports
B) investment
C) exports
D) government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Of the U.S. national debt that is held by the public, _____ hold about ____.
A) foreigners; 74%
B) foreigners; 30%
C) Americans; 30%
D) foreigners; 40%
A) foreigners; 74%
B) foreigners; 30%
C) Americans; 30%
D) foreigners; 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Because taxes withdraw spending from the economy, equilibrium income falls when a tax is imposed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The graph that plots hypothetical tax revenues at various income tax rates is commonly called the _____ curve.
A) revenue-enhancement
B) Phillips
C) Laffer
D) tax efficiency
A) revenue-enhancement
B) Phillips
C) Laffer
D) tax efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For fiscal policy to be sustainable, the present value of all projected future revenues must equal the present value of projected future spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Automatic stabilizers include all of these EXCEPT
A) tax revenues.
B) transfer payments.
C) research and development funding.
D) unemployment insurance.
A) tax revenues.
B) transfer payments.
C) research and development funding.
D) unemployment insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose the government increases aggregate demand to a level that increases GDP above its long-run equilibrium level. What sequence of events would follow?
A) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP drops
B) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
C) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; long-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP falls
D) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
A) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP drops
B) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
C) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; long-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP falls
D) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of these is MOST likely to have a large intergenerational imbalance?
A) construction of a new dam
B) agricultural price supports
C) Medicare
D) payments to research facilities
A) construction of a new dam
B) agricultural price supports
C) Medicare
D) payments to research facilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Trying to annually balance the federal budget during a recession may harm the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Reducing tax rates affects only aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
As GDP increases, tax revenues _____ and transfer payments _____.
A) decline; decline
B) decline; increase
C) increase; decline
D) increase; increase
A) decline; decline
B) decline; increase
C) increase; decline
D) increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Spending money to battle flooding on the Mississippi River is an example of an automatic stabilizer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The interest paid on internally held debt is
A) a real claim on American goods and services.
B) roughly 20% of the federal budget.
C) paid out to one group of Americans from the taxes collected from another group of Americans.
D) a real burden on the U.S. economy.
A) a real claim on American goods and services.
B) roughly 20% of the federal budget.
C) paid out to one group of Americans from the taxes collected from another group of Americans.
D) a real burden on the U.S. economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose the economy is growing at 4% a year, inflation is measured at 0.5% a year, and the federal deficit is relatively high. An economist who suggests that nothing needs to be done is advocating a(n)
A) annually balanced budget.
B) cyclically balanced budget.
C) functional finance approach to federal budgeting.
D) full employment balanced budget.
A) annually balanced budget.
B) cyclically balanced budget.
C) functional finance approach to federal budgeting.
D) full employment balanced budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Interest on debt as a percentage of GDP was at its highest
A) during World War II.
B) during the 1970s.
C) during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
D) in 2009.
A) during World War II.
B) during the 1970s.
C) during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
D) in 2009.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The use of supply-side fiscal policy always requires a tradeoff between output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement regarding supply-side fiscal policy is INCORRECT?
A) It tends to have a longer impact on the economy than demand-side policies.
B) It is geared toward short-term increases in employment.
C) It attempts to increase the long-run equilibrium level of GDP.
D) It tends to lower prices in the economy.
A) It tends to have a longer impact on the economy than demand-side policies.
B) It is geared toward short-term increases in employment.
C) It attempts to increase the long-run equilibrium level of GDP.
D) It tends to lower prices in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Supply-side fiscal policies include all of these EXCEPT
A) investment in human capital.
B) projects that encourage new technologies.
C) increasing transfer payments.
D) policies that encourage investment in research and development.
A) investment in human capital.
B) projects that encourage new technologies.
C) increasing transfer payments.
D) policies that encourage investment in research and development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The _____ lag is the time policymakers must wait for economic data to be collected, processed, and reported.
A) information
B) recognition
C) implementation
D) decision
A) information
B) recognition
C) implementation
D) decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Annually balancing the federal budget has been the prevailing approach since the 1930s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Reducing tax rates can _____ aggregate demand and _____ aggregate supply.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which graph BEST depicts the impact of a policy that reduces burdensome regulations?
A)
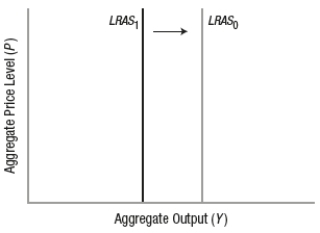
B)
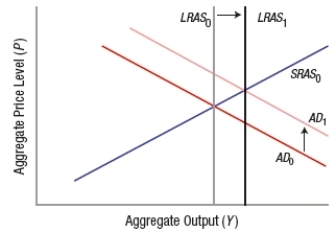
C)
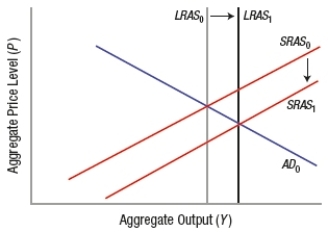
D)
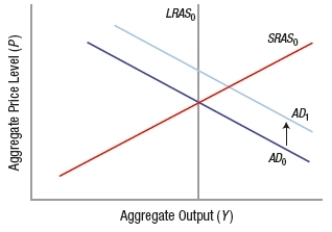
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Expansionary fiscal policy is typically used to _____ aggregate demand in order to _____.
A) increase; avoid a recession
B) decrease; avoid a recession
C) increase; slow down an overheated economy
D) decrease; slow down an overheated economy
A) increase; avoid a recession
B) decrease; avoid a recession
C) increase; slow down an overheated economy
D) decrease; slow down an overheated economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Politicians eagerly use contractionary policies that control inflation, since unemployment is not a concern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The _____ lag is the time required to turn fiscal policy into law to have an impact on the economy.
A) information
B) recognition
C) implementation
D) decision
A) information
B) recognition
C) implementation
D) decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
(Figure: Understanding SRAS and LRAS Shifts) This graph shows _____ policies. 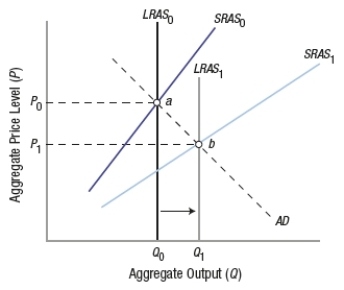
A) demand-side fiscal
B) supply-side fiscal
C) a combination of supply-side and demand-side fiscal
D) demand-side monetary

A) demand-side fiscal
B) supply-side fiscal
C) a combination of supply-side and demand-side fiscal
D) demand-side monetary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An intergenerational tax burden means that future generations will pay for the spending of the current generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of these is NOT an element of expansionary fiscal policy?
A) expanding immigration policies
B) increasing government spending
C) cutting taxes
D) increasing transfer payments
A) expanding immigration policies
B) increasing government spending
C) cutting taxes
D) increasing transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An automatic stabilizer
A) injects money into the economy during booms.
B) extracts money from the economy during recessions.
C) is exemplified by a program such as unemployment compensation.
D) is exemplified by a program such as the Corps of Engineers dam-building program.
A) injects money into the economy during booms.
B) extracts money from the economy during recessions.
C) is exemplified by a program such as unemployment compensation.
D) is exemplified by a program such as the Corps of Engineers dam-building program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Functional finance emphasizes economic growth and price level stability with full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
As GDP increases, tax revenues _____, which in turn _____ GDP growth.
A) decline; slows
B) decline; expands
C) increase; slows
D) increase; expands
A) decline; slows
B) decline; expands
C) increase; slows
D) increase; expands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Expansionary demand-side fiscal policies set up a tradeoff between increasing output at the expense of raising prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Over the past few decades, external debt has become a less important source of funds for the U.S. federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Externally held debt is public debt held by foreigners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The time required to comprehend that a recession has in fact begun is called the recognition lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which measure is NOT a channel through which the government can influence aggregate demand?
A) direct spending on goods and services
B) transfer payments to households and firms
C) taxes on households and firms
D) regulation on businesses
A) direct spending on goods and services
B) transfer payments to households and firms
C) taxes on households and firms
D) regulation on businesses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the Laffer curve, when tax rates are zero
A) tax revenues are positive.
B) tax revenues are negative.
C) tax revenues are zero.
D) There is no relationship between tax revenues and tax rates.
A) tax revenues are positive.
B) tax revenues are negative.
C) tax revenues are zero.
D) There is no relationship between tax revenues and tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which groups must be in agreement to implement fiscal policy?
A) the Senate, the House of Representatives, and the president
B) the legislative branch, the president, and the judicial branch
C) the legislative branch, the president, and the Federal Reserve
D) the Senate, the House of Representatives, and the Federal Reserve
A) the Senate, the House of Representatives, and the president
B) the legislative branch, the president, and the judicial branch
C) the legislative branch, the president, and the Federal Reserve
D) the Senate, the House of Representatives, and the Federal Reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The interest paid on public debt held by _____ is a real claim on American goods and services.
A) U.S. banks
B) foreigners
C) U.S. citizens
D) the Federal Reserve
A) U.S. banks
B) foreigners
C) U.S. citizens
D) the Federal Reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Examples of discretionary government spending include national defense, transportation, and education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Figure: Effects of Policy Shifts) If the economy starts below full employment, an expansionary fiscal policy will shift the aggregate demand curve from _____ to _____, and equilibrium will move from point _____ to _____. 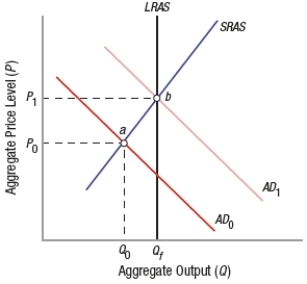
A) AD1; AD0; a; b
B) AD1; AD0; b; a
C) AD0; AD1; b; a
D) AD0; AD1; a; b

A) AD1; AD0; a; b
B) AD1; AD0; b; a
C) AD0; AD1; b; a
D) AD0; AD1; a; b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of these will increase aggregate supply?
A) The president raises tariffs on Chinese imports.
B) The president asks Congress for $200 billion for rebuilding roads and bridges.
C) The Secretary of Education finalizes rules that make it more difficult for students to obtain federal loans.
D) The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announces new, tighter standards for lead in dust on floors and windowsills.
A) The president raises tariffs on Chinese imports.
B) The president asks Congress for $200 billion for rebuilding roads and bridges.
C) The Secretary of Education finalizes rules that make it more difficult for students to obtain federal loans.
D) The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announces new, tighter standards for lead in dust on floors and windowsills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
(Figure: Laffer Curve 3) A supply-side economist is advocating reducing income tax rates. She is probably assuming that the economy is at point _____ in the graph. 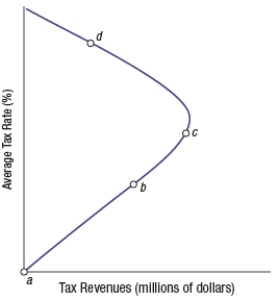
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 366 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



