Deck 9: Noninvasive Monitoring in Neonatal and Pediatric Care
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Noninvasive Monitoring in Neonatal and Pediatric Care
1
As the therapist applies a pulse oximeter finger probe to a neonate who is receiving supplemental oxygen, she notices that the SpO2 reading is 100%. What should the therapist do in this situation?
A) The therapist should continue monitoring the patient because the reading is accurate.
B) The therapist should obtain an arterial blood sample to confirm SpO2 level.
C) The therapist should switch to using a capnometer.
D) The therapist should reduce the fraction of inspired oxygen.
A) The therapist should continue monitoring the patient because the reading is accurate.
B) The therapist should obtain an arterial blood sample to confirm SpO2 level.
C) The therapist should switch to using a capnometer.
D) The therapist should reduce the fraction of inspired oxygen.
B
The sensitivity of pulse oximetry to detect the presence and degree of hyperoxia may be limited in the neonatal patient. If the oximeter is reading an SpO2 of 100%, the arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) could be between 90 and 250 mm Hg. However, many neonatal intensive care units will target an SpO2 below a certain threshold in order to reduce the risk of retinopathy of prematurity in premature babies.
The sensitivity of pulse oximetry to detect the presence and degree of hyperoxia may be limited in the neonatal patient. If the oximeter is reading an SpO2 of 100%, the arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) could be between 90 and 250 mm Hg. However, many neonatal intensive care units will target an SpO2 below a certain threshold in order to reduce the risk of retinopathy of prematurity in premature babies.
2
While working in the NICU with a mechanically ventilated newborn who is being monitored for PetCO2, the therapist observes the following capnogram. 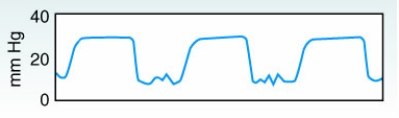 What interpretation should the therapist make of this capnogram?
What interpretation should the therapist make of this capnogram?
A) This capnogram is normal.
B) The patient is receiving about 10 cm H2O positive end-expiratory pressure.
C) The patient is rebreathing his own exhaled gas.
D) The neonate is being hyperventilated.
 What interpretation should the therapist make of this capnogram?
What interpretation should the therapist make of this capnogram?A) This capnogram is normal.
B) The patient is receiving about 10 cm H2O positive end-expiratory pressure.
C) The patient is rebreathing his own exhaled gas.
D) The neonate is being hyperventilated.
C
Rebreathing is characterized by an elevation in the A-B phase of the capnogram, with a corresponding increase in ETCO2. It indicates the rebreathing of previously exhaled carbon dioxide. Rebreathing can be caused by allowing an insufficient expiratory time or by inadequate inspiratory flow (see Figure 9-7 in the textbook).
Rebreathing is characterized by an elevation in the A-B phase of the capnogram, with a corresponding increase in ETCO2. It indicates the rebreathing of previously exhaled carbon dioxide. Rebreathing can be caused by allowing an insufficient expiratory time or by inadequate inspiratory flow (see Figure 9-7 in the textbook).
3
What clinical parameter is critically important to monitor when mechanical ventilation is administered?
A) Blood pressure
B) Heart rate
C) Temperature
D) Respiratory rate
A) Blood pressure
B) Heart rate
C) Temperature
D) Respiratory rate
A
In mechanically ventilated children, increasing intrathoracic pressure (by increasing positive end expiratory pressure, for example) can reduce venous return, resulting in decreased blood pressure.
In mechanically ventilated children, increasing intrathoracic pressure (by increasing positive end expiratory pressure, for example) can reduce venous return, resulting in decreased blood pressure.
4
While attending to a neonatal patient in the NICU, the therapist notices that a transcutaneous electrode is affixed to the upper chest of the neonate. What should the therapist do at this time?
A) The therapist should only continue monitoring the patient since the transcutaneous electrode is properly placed.
B) The therapist should reposition the electrode on the neonate's abdomen.
C) The therapist needs to move the transcutaneous electrode to the infant's right shoulder.
D) The therapist should relocate the electrode on the sternum as close as possible to the heart.
A) The therapist should only continue monitoring the patient since the transcutaneous electrode is properly placed.
B) The therapist should reposition the electrode on the neonate's abdomen.
C) The therapist needs to move the transcutaneous electrode to the infant's right shoulder.
D) The therapist should relocate the electrode on the sternum as close as possible to the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following features or characteristics apply to mainstream capnography?
I) The mainstream capnograph contains narrow tubing that can become occluded with mucus.
II) Mainstream capnography generally employs infrared spectrometers.
III) The mainstream capnograph does not add much weight to the breathing circuit.
IV) The mainstream capnograph is placed at the proximal end of the endotracheal tube.
A) I and II only
B) II and IV only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, III, and IV only
I) The mainstream capnograph contains narrow tubing that can become occluded with mucus.
II) Mainstream capnography generally employs infrared spectrometers.
III) The mainstream capnograph does not add much weight to the breathing circuit.
IV) The mainstream capnograph is placed at the proximal end of the endotracheal tube.
A) I and II only
B) II and IV only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The therapist is assessing a mechanically ventilated infant and observes that the transcutaneous electrode temperature is set between 41 and 44°C. What action does the therapist need to take at this time?
A) The temperature range set is appropriate; therefore, no action is necessary.
B) The therapist should increase the temperature range to 46 to 48°C.
C) The temperature of the transcutaneous electrode needs to be reduced to 36 to 38°C.
D) The electrode needs to be repositioned and maintained at the same temperature.
A) The temperature range set is appropriate; therefore, no action is necessary.
B) The therapist should increase the temperature range to 46 to 48°C.
C) The temperature of the transcutaneous electrode needs to be reduced to 36 to 38°C.
D) The electrode needs to be repositioned and maintained at the same temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following conditions will preclude the use of indirect calorimetry?
I) Cuffed endotracheal tubes
II) Circuit leaks
III) FiO2 0.40
IV) HFOV
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) II and IV only
D) I, III, and IV only
I) Cuffed endotracheal tubes
II) Circuit leaks
III) FiO2 0.40
IV) HFOV
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) II and IV only
D) I, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the main physiologic factor responsible for deriving accurate transcutaneous data?
A) Heart rate
B) Minute ventilation
C) Peripheral perfusion
D) Ventilation-perfusion ratios
A) Heart rate
B) Minute ventilation
C) Peripheral perfusion
D) Ventilation-perfusion ratios

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The therapist has been asked to measure preductal oxygen saturation. Where could the therapist place the pulse oximeter probe?
A) Right thumb
B) Left leg
C) Right leg
D) Left earlobe
A) Right thumb
B) Left leg
C) Right leg
D) Left earlobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the purpose of indirect calorimetry?
A) To measure heat produced and lost from the body
B) To calculate energy expenditure by measuring VO2 and VCO2
C) To calculate resting energy expenditure
D) To measure gas exchange
A) To measure heat produced and lost from the body
B) To calculate energy expenditure by measuring VO2 and VCO2
C) To calculate resting energy expenditure
D) To measure gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A therapist is monitoring a child on the mechanical ventilator who is hemodynamically stable. The PetCO2 is 48 mm Hg. If accurate, what should be the PaCO2?
A) 43 to 48 mm Hg
B) 45 to 48 mm Hg
C) 50 to 53 mm Hg
D) Exactly the same as PetCO2
A) 43 to 48 mm Hg
B) 45 to 48 mm Hg
C) 50 to 53 mm Hg
D) Exactly the same as PetCO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why do transcutaneous oxygen tension (PO2) and carbon dioxide tension (PCO2) values differ from PaO2 and PaCO2 measurements?
A) Because of the lag time between the cardiac output and the time the blood reaches the transcutaneous electrode site
B) Because the skin is much more permeable to oxygen than carbon dioxide
C) Because oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is produced in transit from the left ventricle to the electrode site
D) Because metabolism in the tissue consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide at the site of the electrode
A) Because of the lag time between the cardiac output and the time the blood reaches the transcutaneous electrode site
B) Because the skin is much more permeable to oxygen than carbon dioxide
C) Because oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is produced in transit from the left ventricle to the electrode site
D) Because metabolism in the tissue consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide at the site of the electrode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following capnogram was obtained from a newborn infant receiving mechanical ventilation. 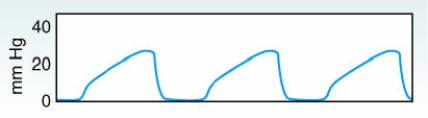 How should the therapist evaluate this capnogram?
How should the therapist evaluate this capnogram?
A) Airway obstruction
B) Hypoventilation
C) Hyperventilation
D) Increased dead space ventilation
 How should the therapist evaluate this capnogram?
How should the therapist evaluate this capnogram?A) Airway obstruction
B) Hypoventilation
C) Hyperventilation
D) Increased dead space ventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How is the percentage of functional hemoglobin that is saturated with oxygen determined via pulse oximetry?
A) The percentage of red light that lands on the photodiode represents the SpO2 (oxygen saturation as determined by pulse oximetry).
B) The percentage of infrared light that reaches the photodetector reflects the SpO2.
C) The ratio of the red and infrared light that reaches the photodiode signifies the SpO2.
D) The sum of the amount of red and infrared absorbed by the tissue determines the SpO2.
A) The percentage of red light that lands on the photodiode represents the SpO2 (oxygen saturation as determined by pulse oximetry).
B) The percentage of infrared light that reaches the photodetector reflects the SpO2.
C) The ratio of the red and infrared light that reaches the photodiode signifies the SpO2.
D) The sum of the amount of red and infrared absorbed by the tissue determines the SpO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is volumetric capnography able to determine?
I) Airway dead space
II) Alveolar tidal volume
III) Shunt fraction
IV) Alveolar minute volume
A) III and IV only
B) II, III, and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) I, II, and III only
I) Airway dead space
II) Alveolar tidal volume
III) Shunt fraction
IV) Alveolar minute volume
A) III and IV only
B) II, III, and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) I, II, and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The therapist has applied a bandage-type pulse oximetry probe too tightly to an infant's finger. What problem can be expected to occur in this situation?
A) The SpO2 will read erroneously low.
B) The SpO2 will read erroneously high.
C) The monitor will display a message indicating inadequate pulse.
D) The monitor will display fluctuating SpO2 values between being erroneously low and high.
A) The SpO2 will read erroneously low.
B) The SpO2 will read erroneously high.
C) The monitor will display a message indicating inadequate pulse.
D) The monitor will display fluctuating SpO2 values between being erroneously low and high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



