Deck 5: Pulmonary Function Testing and Bedside Pulmonary Mechanics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Pulmonary Function Testing and Bedside Pulmonary Mechanics
1
Why must caution be exercised when using a face mask while performing pulmonary function testing on neonates?
A) To prevent trigeminal nerve stimulation
B) To avoid necrosis of the facial skin
C) To prevent vagal reflexes
D) To prevent gastric insufflations
A) To prevent trigeminal nerve stimulation
B) To avoid necrosis of the facial skin
C) To prevent vagal reflexes
D) To prevent gastric insufflations
A
A face mask is required when testing neonates and infants. Caution must be exercised because using a face mask can cause trigeminal nerve stimulation and induce vagal reflexes that may alter the pattern of heart or respiratory rhythm.
A face mask is required when testing neonates and infants. Caution must be exercised because using a face mask can cause trigeminal nerve stimulation and induce vagal reflexes that may alter the pattern of heart or respiratory rhythm.
2
What is the clinical purpose for measuring the maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP)?
A) To assess lung function before and after bronchodilator administration
B) To help patients with asthma management at home
C) To evaluate the strength of respiratory muscles
D) To assist in performing bronchial hygiene techniques
A) To assess lung function before and after bronchodilator administration
B) To help patients with asthma management at home
C) To evaluate the strength of respiratory muscles
D) To assist in performing bronchial hygiene techniques
C
MIP is an important measure to help differentiate weakness from other causes of restrictive lung disease. It can be an important differentiating point for children and young adults with various neuromuscular diseases. These patients usually have a combination of scoliosis and muscle weakness, both of which might contribute to reduced lung volumes. Measuring MIP helps in determining how much reduction might be caused by weakness. Because many neuromuscular diseases are progressive, MIP helps to document this progression. MIP may also indicate the patient's physical ability to take a deep breath and is often measured when weaning a patient from mechanical ventilation is being considered.
MIP is an important measure to help differentiate weakness from other causes of restrictive lung disease. It can be an important differentiating point for children and young adults with various neuromuscular diseases. These patients usually have a combination of scoliosis and muscle weakness, both of which might contribute to reduced lung volumes. Measuring MIP helps in determining how much reduction might be caused by weakness. Because many neuromuscular diseases are progressive, MIP helps to document this progression. MIP may also indicate the patient's physical ability to take a deep breath and is often measured when weaning a patient from mechanical ventilation is being considered.
3
A reduction in the DlCO may indicate the presence of which of the following conditions?
I) Pulmonary fibrosis
II) Pulmonary edema
III) Hematologic disorders
IV) Acute hemorrhageous bleeds
A) I and II only
B) I and IV only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, III, and IV
I) Pulmonary fibrosis
II) Pulmonary edema
III) Hematologic disorders
IV) Acute hemorrhageous bleeds
A) I and II only
B) I and IV only
C) I, II, and III only
D) I, III, and IV
C
Indications for testing in the pediatric population that may produce a reduced DlCO include pulmonary fibrosis (primary disease or secondary to radiation treatment or chemotherapy), immunologic disorders (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus), bronchiolitis obliterans, pulmonary edema, and hematologic disorders.
Indications for testing in the pediatric population that may produce a reduced DlCO include pulmonary fibrosis (primary disease or secondary to radiation treatment or chemotherapy), immunologic disorders (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus), bronchiolitis obliterans, pulmonary edema, and hematologic disorders.
4
Which of the following factors is the most important determinant of high airway resistance and air trapping in small infants?
A) The small tidal volume
B) Small diameter of the airways
C) Excessive amount of mucus production
D) The length of the airways
A) The small tidal volume
B) Small diameter of the airways
C) Excessive amount of mucus production
D) The length of the airways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The respiratory therapist is looking at a flow-volume curve that displays a concave shape on the expiratory tracing. What is this change most consistent with?
A) Neuromuscular disease
B) Abnormal chest wall configuration
C) Interstitial fibrosis
D) Asthma
A) Neuromuscular disease
B) Abnormal chest wall configuration
C) Interstitial fibrosis
D) Asthma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
On the basis of the data presented below, calculate the time constant.
Tidal volume (VT), 600 mL
Respiratory rate (RR), 12 breaths per minute
Lung compliance (C), 0.2 L/cm H2O
Airway resistance (Raw), 2.5 cm H2O/L/second
Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP), 30 cm H2O
Inspiratory time (TI), 2 seconds
Expiratory time (TE), 1 second
A) 4.5 seconds
B) 3.0 seconds
C) 0.5 second
D) 0.1 second
Tidal volume (VT), 600 mL
Respiratory rate (RR), 12 breaths per minute
Lung compliance (C), 0.2 L/cm H2O
Airway resistance (Raw), 2.5 cm H2O/L/second
Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP), 30 cm H2O
Inspiratory time (TI), 2 seconds
Expiratory time (TE), 1 second
A) 4.5 seconds
B) 3.0 seconds
C) 0.5 second
D) 0.1 second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A child has been diagnosed with vocal cord dysfunction. Which of the following flow-volume loops demonstrates this condition?
A) Figure 5-9C
B) Figure 5-9A
C) Figure 5-9B
D) Figure 5-8B
A) Figure 5-9C
B) Figure 5-9A
C) Figure 5-9B
D) Figure 5-8B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following methods can be used to measure airway caliber on a 4-year-old patient with asthma?
A) Peak expiratory flow measurement
B) Impulse oscillometry
C) Nitrogen washout method
D) Helium dilution method
A) Peak expiratory flow measurement
B) Impulse oscillometry
C) Nitrogen washout method
D) Helium dilution method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The respiratory therapist places a face mask on an infant to measure FRC. What should the therapist do to minimize the presence of air leaks and improve accuracy of the test?
A) Place a nose clip on the infant.
B) Minimize the amount of helium used during the test.
C) Minimize oxygen concentration and increase nitrogen concentration.
D) Apply petroleum jelly on the edges of the mask before applying the mask to the face.
A) Place a nose clip on the infant.
B) Minimize the amount of helium used during the test.
C) Minimize oxygen concentration and increase nitrogen concentration.
D) Apply petroleum jelly on the edges of the mask before applying the mask to the face.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
On the basis of the bronchial provocation data presented in the following table, identify the PD20. 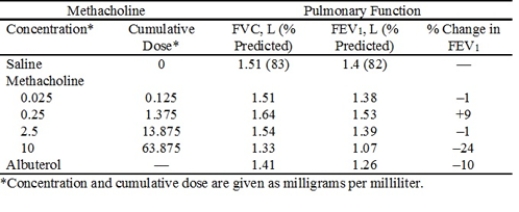
A) 0.025 mg/mL
B) 0.25 mg/mL
C) 2.5 mg/mL
D) 10 mg/mL

A) 0.025 mg/mL
B) 0.25 mg/mL
C) 2.5 mg/mL
D) 10 mg/mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A pre- and postbronchodilator, partial expiratory pressure-volume maneuver was performed on a 9-month-old boy. The child's prebronchodilator maxFRC was 67 mL/second and the postbronchodilator maxFRC was 94 mL/second. How should the therapist interpret these data?
A) The data are erroneous.
B) The data are inconclusive.
C) The patient will not clinically improve with bronchodilator administration.
D) The patient has demonstrated clinically significant improvement with bronchodilator administration.
A) The data are erroneous.
B) The data are inconclusive.
C) The patient will not clinically improve with bronchodilator administration.
D) The patient has demonstrated clinically significant improvement with bronchodilator administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following pulmonary function values characterizes an obstructive lung disorder?
I. The forced vital capacity (FVC) is normal or decreased.
II. The forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) is decreased.
III. The ratio of residual volume to total lung capacity (RV/TLC) is decreased.
IV. RV is increased.
A) II and IV only
B) I and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I. The forced vital capacity (FVC) is normal or decreased.
II. The forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) is decreased.
III. The ratio of residual volume to total lung capacity (RV/TLC) is decreased.
IV. RV is increased.
A) II and IV only
B) I and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On the partial expiratory flow-volume loop shown here, identify the point depicting the maximal expiratory flow at FRC. 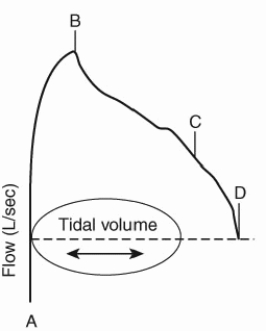
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The therapist is reviewing a flow-volume loop obtained from a pediatric patient and observes decreased volume and normal flows. On the basis of this observation, how should the therapist interpret this finding?
A) Obstructive pattern
B) Restrictive pattern
C) Fixed airway obstruction
D) Variable extrathoracic obstruction
A) Obstructive pattern
B) Restrictive pattern
C) Fixed airway obstruction
D) Variable extrathoracic obstruction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Pulmonary function testing has been ordered in an infant. Which of the following represents a potential risk to this infant?
A) The infant may require sedation for up to 3 hours.
B) If the infant cries, it will make the test invalid or open to misinterpretation.
C) The gases used for the PFT may be toxic for the infant.
D) The inability to feed the child 24 hours prior to the test.
A) The infant may require sedation for up to 3 hours.
B) If the infant cries, it will make the test invalid or open to misinterpretation.
C) The gases used for the PFT may be toxic for the infant.
D) The inability to feed the child 24 hours prior to the test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How is airway resistance calculated?
A) By dividing the airway occlusion pressure by the expiratory flow
B) By dividing the transpulmonary pressure by the expiratory flow
C) By multiplying the expiratory flow by the pressure gradient responsible for initiating inspiration
D) By multiplying the expiratory occlusion pressure by the transpulmonary pressure gradient
A) By dividing the airway occlusion pressure by the expiratory flow
B) By dividing the transpulmonary pressure by the expiratory flow
C) By multiplying the expiratory flow by the pressure gradient responsible for initiating inspiration
D) By multiplying the expiratory occlusion pressure by the transpulmonary pressure gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following major forces opposes inspiration?
A) Inspiratory flow
B) Surface tension
C) Airway resistance
D) Respiratory rate
A) Inspiratory flow
B) Surface tension
C) Airway resistance
D) Respiratory rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the ATS-ERS acceptability criteria for an FVC maneuver performed on a 7-year-old child, what is considered a satisfactory exhalation time?
A) 1 second
B) 2 seconds
C) 3 seconds
D) 6 seconds
A) 1 second
B) 2 seconds
C) 3 seconds
D) 6 seconds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How should the therapist interpret the following pressure-volume loop obtained from a mechanically ventilated infant? 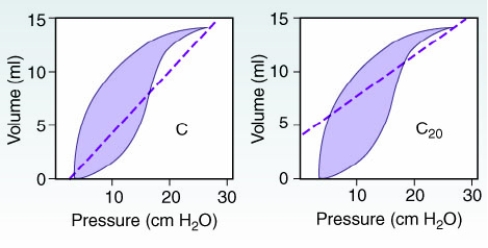
A) A leak has developed in the ventilator patient system.
B) The patient's lungs are being overinflated.
C) The patient is displaying trigger dyssynchrony.
D) The patient's lungs are exhibiting increased compliance.

A) A leak has developed in the ventilator patient system.
B) The patient's lungs are being overinflated.
C) The patient is displaying trigger dyssynchrony.
D) The patient's lungs are exhibiting increased compliance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



