Deck 26: Pediatric Airway Disorders and Parenchymal Lung Diseases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Pediatric Airway Disorders and Parenchymal Lung Diseases
1
A therapist has been asked to evaluate a child suspected of having foreign body aspiration. Which of the following clinical conditions would guide the therapist to the diagnosis?
A) Recurrent bronchitis
B) Wheezing partially responsive to bronchodilators
C) Unilateral wheezing
D) Stridor
A) Recurrent bronchitis
B) Wheezing partially responsive to bronchodilators
C) Unilateral wheezing
D) Stridor
C
Signs and symptoms of foreign body aspiration vary with the location of impaction and the degree of airway obstruction. They can range from unilateral wheezing or recurrent pneumonia, as when peanuts or popcorn obstruct the smaller airways, to immediate occlusion of the upper airway with complete absence of air movement and rapid death from suffocation, as seen in hot dog or balloon aspiration fatalities.
Signs and symptoms of foreign body aspiration vary with the location of impaction and the degree of airway obstruction. They can range from unilateral wheezing or recurrent pneumonia, as when peanuts or popcorn obstruct the smaller airways, to immediate occlusion of the upper airway with complete absence of air movement and rapid death from suffocation, as seen in hot dog or balloon aspiration fatalities.
2
Tracheomalacia is a condition of dynamic tracheal collapse. Which of the following injurious events can be associated with this condition?
A) Neonatal ventilation with high pressures
B) Excessive use of racemic epinephrine
C) Tracheal trauma due to CPT
D) Neonatal ventilation with high oxygen concentrations
A) Neonatal ventilation with high pressures
B) Excessive use of racemic epinephrine
C) Tracheal trauma due to CPT
D) Neonatal ventilation with high oxygen concentrations
A
Common injurious events include neonatal ventilation with high pressures, chronic trauma to the trachea from a malpositioned ETT or aggressive endotracheal suctioning, and external compressive structures, such as a vascular ring.
Common injurious events include neonatal ventilation with high pressures, chronic trauma to the trachea from a malpositioned ETT or aggressive endotracheal suctioning, and external compressive structures, such as a vascular ring.
3
Which of the following lateral neck radiographic presentations is characteristic of laryngotracheobronchitis? 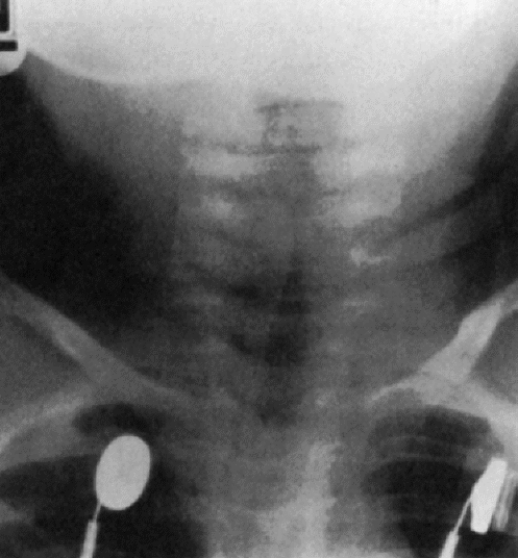
A) Posterior pharyngeal shadow
B) Thumb sign
C) Steeple sign
D) Penumbra effect

A) Posterior pharyngeal shadow
B) Thumb sign
C) Steeple sign
D) Penumbra effect
C
A lateral neck radiograph, sometimes obtained to help differentiate laryngotracheobronchitis from epiglottitis, demonstrates a large retropharyngeal air shadow without epiglottic swelling. The anteroposterior (A-P) chest radiograph reveals the classic steeple sign, a sharply sloped, wedge-shaped, linear narrowing of the trachea. This demonstrates the subglottic tracheal edema that extends from the larynx to the thoracic trachea.
A lateral neck radiograph, sometimes obtained to help differentiate laryngotracheobronchitis from epiglottitis, demonstrates a large retropharyngeal air shadow without epiglottic swelling. The anteroposterior (A-P) chest radiograph reveals the classic steeple sign, a sharply sloped, wedge-shaped, linear narrowing of the trachea. This demonstrates the subglottic tracheal edema that extends from the larynx to the thoracic trachea.
4
Which of the following medications should be administered to a 4-year-old child with symptomatic LTB and respiratory compromise?
A) Phenylephrine
B) Racemic epinephrine
C) Albuterol
D) Antibiotics
A) Phenylephrine
B) Racemic epinephrine
C) Albuterol
D) Antibiotics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An 11-month-old child has been treated with bronchodilators for persistent wheezing without a positive clinical response. Which of the following conditions should the therapist suspect?
A) Bronchitis
B) Aspergillosis
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Endobronchial compression
A) Bronchitis
B) Aspergillosis
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Endobronchial compression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 30-month-old child is brought to the emergency room (ER) by the parents. The child appears to have a sore throat along with dysphagia, fever, and voice changes. The child exhibits a "hot potato voice." Visualization of the posterior pharynx reveals a displaced retropharynx. What condition does this child likely have?
A) Peritonsillar abscess
B) Retropharyngeal abscess
C) Tonsillar enlargement
D) Pierre Robin syndrome
A) Peritonsillar abscess
B) Retropharyngeal abscess
C) Tonsillar enlargement
D) Pierre Robin syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Relative to an adult's larynx, where is an infant's larynx situated?
A) C1-2
B) C2-3
C) C3-4
D) C4-5
A) C1-2
B) C2-3
C) C3-4
D) C4-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why does a respiratory syncytial viral infection have little adverse effect on an older child but is often life-threatening to a younger child?
A) The older child has a better developed immune system.
B) The younger child has a less effective cough mechanism.
C) The older child has a better developed mucociliary escalator.
D) The younger child has fewer respiratory bronchioles.
A) The older child has a better developed immune system.
B) The younger child has a less effective cough mechanism.
C) The older child has a better developed mucociliary escalator.
D) The younger child has fewer respiratory bronchioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A 10-month-old child has been brought into the emergency room (ER) by his or her parents, who state that after few days with low-grade fever, malaise, and rhinorrhea, their child presented with a "barking" cough and increased work of breathing. What condition is this child likely exhibiting?
A) Epiglottitis
B) Laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB)
C) Bronchitis
D) Bronchiolitis
A) Epiglottitis
B) Laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB)
C) Bronchitis
D) Bronchiolitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An 18-month-old child has been admitted with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis due to RSV. The therapist has administered a single dose of albuterol and racemic epinephrine, but the child shows no signs of improvement. What should the therapist suggest at this time?
A) Alternate albuterol and racemic epinephrine every 4 hours
B) Use albuterol every 1 hour for 4 hours and then space treatments to every 4 hours
C) Discontinue therapy
D) Add an inhaled corticosteroid to the albuterol every 12 hours
A) Alternate albuterol and racemic epinephrine every 4 hours
B) Use albuterol every 1 hour for 4 hours and then space treatments to every 4 hours
C) Discontinue therapy
D) Add an inhaled corticosteroid to the albuterol every 12 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The therapist is evaluating a child in the emergency department who displays the following signs: inability to cry, ineffective cough, high-pitched inspiratory sound, and cyanosis. What should the therapist suspect?
A) Tracheomalacia
B) Severe or complete airway obstruction
C) Vascular ring
D) Status asthmaticus
A) Tracheomalacia
B) Severe or complete airway obstruction
C) Vascular ring
D) Status asthmaticus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A 4-year-old child is brought into the emergency room (ER) by her parents, who state that an abrupt high fever developed along with a severe sore throat, dysphagia with drooling, and cough. In the ER, the girl exhibits stridor, muffled voice without hoarseness, air hunger, and cyanosis. She also has suprasternal, substernal, and intercostal retractions, with nasal flaring, bradypnea, and dyspnea. The child is sitting upright with her chin thrust forward and her neck hyperextended in a tripod position. What condition is she likely exhibiting?
A) Laryngotracheobronchitis
B) Tracheomalacia
C) Bacterial tracheitis
D) Epiglottitis
A) Laryngotracheobronchitis
B) Tracheomalacia
C) Bacterial tracheitis
D) Epiglottitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following radiographic techniques is best for determining the presence of a ball-valve type obstruction?
A) A standard portable A-P chest X-ray
B) A lateral neck radiograph
C) Either a right or left lateral decubitus film
D) Inspiratory and expiratory A-P chest X-rays
A) A standard portable A-P chest X-ray
B) A lateral neck radiograph
C) Either a right or left lateral decubitus film
D) Inspiratory and expiratory A-P chest X-rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As the therapist auscultates over an infant's larynx, he hears a very low-pitched sound. On the basis of this finding, what impression is he or she likely to have regarding the nature of the upper airway obstruction?
A) Mild obstruction
B) Moderate obstruction
C) Severe obstruction
D) Complete obstruction
A) Mild obstruction
B) Moderate obstruction
C) Severe obstruction
D) Complete obstruction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why does an infant's respiratory distress from choanal atresia seem to lessen when the infant cries?
A) Because the anterior nares widen more
B) Because the infant breathes more through the mouth
C) Because the infant is able to generate a stronger inspiratory effort
D) Because accessory muscles of ventilation help stabilize the chest wall
A) Because the anterior nares widen more
B) Because the infant breathes more through the mouth
C) Because the infant is able to generate a stronger inspiratory effort
D) Because accessory muscles of ventilation help stabilize the chest wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A 3-year-old child has the following clinical presentations in the ER:
Profound nasal congestion and productive cough
Chest auscultation revealing diffuse coarse, "sticky" crackles (sounding like Velcro)
Chest radiograph revealing lung hyperinflation with flattened hemidiaphragms
What pulmonary condition does this infant likely have?
A) Bronchiectasis
B) Primary ciliary dyskinesia
C) Supralaryngeal obstruction
D) Bronchiolitis
Profound nasal congestion and productive cough
Chest auscultation revealing diffuse coarse, "sticky" crackles (sounding like Velcro)
Chest radiograph revealing lung hyperinflation with flattened hemidiaphragms
What pulmonary condition does this infant likely have?
A) Bronchiectasis
B) Primary ciliary dyskinesia
C) Supralaryngeal obstruction
D) Bronchiolitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A 3-year-old child has been diagnosed with epiglottitis and was intubated due to severe respiratory distress. After 24 hours of antibiotics, the therapist is considering extubation. What will be an acceptable leak before considering extubation?
A) 10 to 20 cm H2O.
B) 20 to 30 cm H2O.
C) 30 to 35 cm H2O.
D) An audible leak at any pressure level is enough to consider extubation.
A) 10 to 20 cm H2O.
B) 20 to 30 cm H2O.
C) 30 to 35 cm H2O.
D) An audible leak at any pressure level is enough to consider extubation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The therapist has been asked to evaluate the chest radiograph of a 3-month-old boy with atelectasis. Which pulmonary lobe has the greatest tendency to collapse in young infants?
A) RUL
B) RML
C) Lingula
D) LUL
A) RUL
B) RML
C) Lingula
D) LUL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
While performing auscultation on a 2-month-old child, the therapist hears wheezes equal in pitch across all regions of the chest; however, they seem loudest in the vicinity of the sternum. From which of the following anatomic structures is the wheezing likely originating?
A) Trachea
B) Terminal bronchioles
C) Segmental bronchi
D) Alveoli
A) Trachea
B) Terminal bronchioles
C) Segmental bronchi
D) Alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the ER, a chest radiograph reveals dilation of the segmental and subsegmental bronchi. The patient complains of expectorating copious amounts of thick mucus and frequent lung infections over the last year. Which of the following conditions does this child likely have?
A) Atelectasis
B) Bronchiectasis
C) Foreign body aspiration
D) Postoperative laryngotracheobronchitis
A) Atelectasis
B) Bronchiectasis
C) Foreign body aspiration
D) Postoperative laryngotracheobronchitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Diagnosis of TB in children requires which of the following special considerations?
A) Three consecutive days of gastric washings
B) A positive skin test
C) A positive chest X-ray
D) One positive respiratory washing
A) Three consecutive days of gastric washings
B) A positive skin test
C) A positive chest X-ray
D) One positive respiratory washing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following clinical interventions are used to treat complications of sickle cell anemia?
I) Supplemental oxygen
II) Bronchodilators
III) Diuretics
IV) Red blood cell transfusions
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I) Supplemental oxygen
II) Bronchodilators
III) Diuretics
IV) Red blood cell transfusions
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following agents has been shown to be effective and safe in treating infants with bronchiolitis?
A) Prednisone
B) Nebulized 3% hypertonic saline
C) Dexamethasone
D) Theophylline
A) Prednisone
B) Nebulized 3% hypertonic saline
C) Dexamethasone
D) Theophylline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid is considered positive for VAP when which of the following conditions occur?
I. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils are greater than 25 per optic field at a magnification *100.
II. Squamous epithelial cells are less than 1%.
III. Axilary temperature of greater than 37°C.
IV. One or more microorganisms are seen per optic field at a magnification of 1:1000.
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils are greater than 25 per optic field at a magnification *100.
II. Squamous epithelial cells are less than 1%.
III. Axilary temperature of greater than 37°C.
IV. One or more microorganisms are seen per optic field at a magnification of 1:1000.
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A child presents to the emergency department with fever, tachypnea, nasal flaring, and shallow breathing. The physical exam of the chest reveals the presence of crackles, increased tactile fremitus, and dullness to percussion. What should the therapist suspect the diagnosis is?
A) Bronchitis
B) Bronchiectasis
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Pneumonia
A) Bronchitis
B) Bronchiectasis
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Pneumonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



