Deck 12: Airway Clearance Techniques and Hyperinflation Therapy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Airway Clearance Techniques and Hyperinflation Therapy
1
On the basis of the following diagram, which of the following lung segments is being drained? 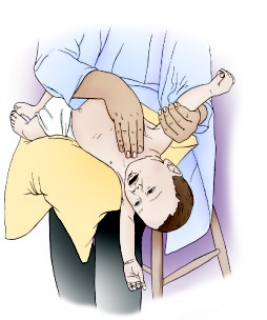
A) Right middle lobe
B) Left lingular segment of the lower lobe
C) Lateral basal segment of the right lower lobe
D) Apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe

A) Right middle lobe
B) Left lingular segment of the lower lobe
C) Lateral basal segment of the right lower lobe
D) Apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe
A
What is shown here (and in Figure 12-4H in the textbook) is the postural drainage position for draining the right middle lobe.
What is shown here (and in Figure 12-4H in the textbook) is the postural drainage position for draining the right middle lobe.
2
During autogenic drainage, at which of the following levels does the patient begin breathing?
A) Total lung capacity
B) Inspiratory reserve volume
C) Expiratory reserve volume
D) Inspiratory capacity
A) Total lung capacity
B) Inspiratory reserve volume
C) Expiratory reserve volume
D) Inspiratory capacity
C
AD is a series of breathing exercises designed to mobilize secretions in patients with bronchiectasis or CF. To loosen secretions from the smallest airways, the patient begins breathing in a slow, controlled manner, first at the expiratory reserve volume level. The volume of ventilation is then increased, with the patient breathing in the normal tidal volume range but exhaling approximately halfway into the expiratory reserve volume.
AD is a series of breathing exercises designed to mobilize secretions in patients with bronchiectasis or CF. To loosen secretions from the smallest airways, the patient begins breathing in a slow, controlled manner, first at the expiratory reserve volume level. The volume of ventilation is then increased, with the patient breathing in the normal tidal volume range but exhaling approximately halfway into the expiratory reserve volume.
3
By which of the following mechanisms are high-frequency chest compressions purported to mobilize tracheobronchial secretions?
A) By dislodging mucus directly from bronchial walls
B) By advancing the mucociliary escalator at a faster than normal rate
C) By mechanically lysing long molecules of mucus into smaller, more mobile segments
D) By generating brief periods of high expiratory airflow
A) By dislodging mucus directly from bronchial walls
B) By advancing the mucociliary escalator at a faster than normal rate
C) By mechanically lysing long molecules of mucus into smaller, more mobile segments
D) By generating brief periods of high expiratory airflow
D
Commercially available devices have been developed that compress the entire chest wall at high frequencies by means of a snug-fitting inflatable vest connected to a high-performance air compressor (see Figure 12-6 in the textbook). Intermittent chest wall compression produces brief periods of high expiratory airflow, which loosens and mobilizes mucus from bronchial walls. This type of device is widely used in patients with CF.
Commercially available devices have been developed that compress the entire chest wall at high frequencies by means of a snug-fitting inflatable vest connected to a high-performance air compressor (see Figure 12-6 in the textbook). Intermittent chest wall compression produces brief periods of high expiratory airflow, which loosens and mobilizes mucus from bronchial walls. This type of device is widely used in patients with CF.
4
A respiratory therapist has been assigned to administer ACT to a number of patients on the ward. In which of the following conditions may ACT be beneficial?
A) Asthma
B) Pneumonia
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Atelectasis
A) Asthma
B) Pneumonia
C) Bronchiolitis
D) Atelectasis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A respiratory therapist has been assigned to administer CPT to a patient with cystic fibrosis. What areas of the body should the RT avoid when percussing the patient?
A) Intercostal spaces
B) Areas of subcutaneous emphysema
C) Precordium
D) Areas between the scapulas
A) Intercostal spaces
B) Areas of subcutaneous emphysema
C) Precordium
D) Areas between the scapulas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the most important variable used to assess the efficacy of CPT?
A) Quality of the chest radiograph
B) Degree and persistence of coughing
C) Changes in the color and consistency of mucus
D) Amount of mucus obtained during and after treatment
A) Quality of the chest radiograph
B) Degree and persistence of coughing
C) Changes in the color and consistency of mucus
D) Amount of mucus obtained during and after treatment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are the main components of the traditional airway clearance techniques?
I) Palpation of the chest wall
II) Postural drainage
III) Percussion
IV) Coughing
A) II only
B) I and III only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV
I) Palpation of the chest wall
II) Postural drainage
III) Percussion
IV) Coughing
A) II only
B) I and III only
C) II, III, and IV only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following postural drainage positions are shown for an infant patient. 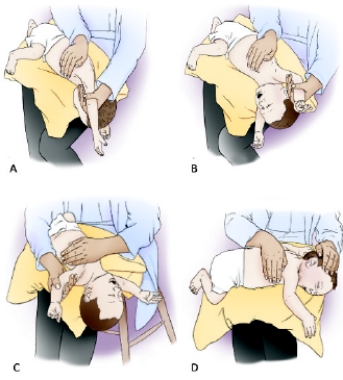 Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the lingular segments of the left upper lobe in an infant?
Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the lingular segments of the left upper lobe in an infant?
A) Image A
B) Image B
C) Image C
D) Image D
 Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the lingular segments of the left upper lobe in an infant?
Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the lingular segments of the left upper lobe in an infant?A) Image A
B) Image B
C) Image C
D) Image D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
On the basis of the following diagram, which of the following lung segments is being drained? 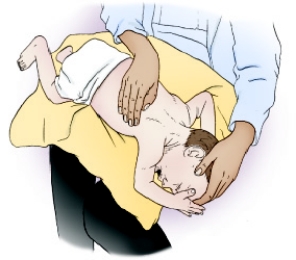
A) Posterior segment of the right upper lobe
B) Apical segment of the right upper lobe
C) Posterior basal segments of both lower lobes
D) Anterior segments of both upper lobes

A) Posterior segment of the right upper lobe
B) Apical segment of the right upper lobe
C) Posterior basal segments of both lower lobes
D) Anterior segments of both upper lobes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following maneuvers is characterized by having a patient forcibly exhale, from a middle to low lung volume, through an open glottis?
A) Autogenic drainage
B) Forced expiratory technique
C) Positive expiratory pressure
D) Active cycle of breathing
A) Autogenic drainage
B) Forced expiratory technique
C) Positive expiratory pressure
D) Active cycle of breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A respiratory therapist has been assigned to administer FET to a 5-year-old patient. Since small children are typically unable to perform such a maneuver, what should the RT do at this time?
A) Request to cancel the order and change therapy.
B) Try to instruct the child on how to perform FET.
C) Apply gentle chest wall compression during the expiratory phase.
D) Ask the child to forcefully cough after a deep breath.
A) Request to cancel the order and change therapy.
B) Try to instruct the child on how to perform FET.
C) Apply gentle chest wall compression during the expiratory phase.
D) Ask the child to forcefully cough after a deep breath.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What do postural drainage, positive expiratory pressure therapy, autogenic drainage, forced expiration techniques, and high-frequency chest compressions have in common?
A) They dislodge mucus from the bronchial walls of patients.
B) They attempt to prevent dynamic airway collapse.
C) They work toward increasing the functional residual capacity of patients.
D) They are intended to promote the ability of patients to generate effective coughs.
A) They dislodge mucus from the bronchial walls of patients.
B) They attempt to prevent dynamic airway collapse.
C) They work toward increasing the functional residual capacity of patients.
D) They are intended to promote the ability of patients to generate effective coughs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following clinical parameters are important to determine a positive response to ACT?
I) Changes in sputum color
II) Breath sounds
III) Vital signs
IV) Lung mechanics
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I) Changes in sputum color
II) Breath sounds
III) Vital signs
IV) Lung mechanics
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The following postural drainage positions are shown for a pediatric patient. 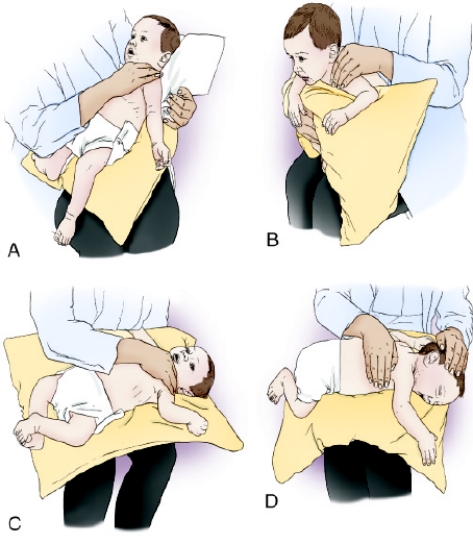 Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the posterior subsegment of the apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe?
Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the posterior subsegment of the apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe?
A) Image B
B) Image C
C) Image A
D) Image D
 Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the posterior subsegment of the apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe?
Which of the diagrams demonstrates the postural drainage position for draining the posterior subsegment of the apical-posterior segment of the left upper lobe?A) Image B
B) Image C
C) Image A
D) Image D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A respiratory therapist has been assigned to administer ACT to a patient with acute lobar atelectasis. What should the RT consider to determine the length and frequency of the treatment?
I) Most pediatric patients require ACTs for at least 60 minutes.
II) ACT is rarely needed more than every 4 hours.
III) ACT orders should be evaluated at least every 48 hours for patients in the ICU.
IV) ACT for patients with atelectasis due to CF requires at least 30 to 45 minutes.
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only
I) Most pediatric patients require ACTs for at least 60 minutes.
II) ACT is rarely needed more than every 4 hours.
III) ACT orders should be evaluated at least every 48 hours for patients in the ICU.
IV) ACT for patients with atelectasis due to CF requires at least 30 to 45 minutes.
A) I, II, and III only
B) II and III only
C) III and IV only
D) II, III, and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the best explanation of why the therapist should routinely avoid advancing the catheter tip beyond the distal end of the endotracheal tube when performing endotracheal suctioning on a neonate?
A) To reduce the risk of inadvertent extubation with the suction catheter
B) To prevent the development of bronchial stenosis and granulomas
C) To decrease the chance of removing too much lung volume
D) To minimize the risk of oxygen desaturation
A) To reduce the risk of inadvertent extubation with the suction catheter
B) To prevent the development of bronchial stenosis and granulomas
C) To decrease the chance of removing too much lung volume
D) To minimize the risk of oxygen desaturation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A respiratory therapist has been assigned to administer ACT to a number of patients on the ward. In which of the following conditions may ACT be contraindicated?
I) Bronchial secretions
II) Frank hemoptysis
III) Empyema
IV) Untreated pneumothorax
A) II, III, and IV
B) I, II, and IV only
C) III and IV only
D) I and IV only
I) Bronchial secretions
II) Frank hemoptysis
III) Empyema
IV) Untreated pneumothorax
A) II, III, and IV
B) I, II, and IV only
C) III and IV only
D) I and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient with an excessive amount of secretions and atelectasis has been receiving ACT. The most commonly cited complication is _____________________________.
A) hypoxemia
B) hypercapnia
C) alterations of blood pressure
D) tachycardia
A) hypoxemia
B) hypercapnia
C) alterations of blood pressure
D) tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



