Deck 14: Pricing Techniques and Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Pricing Techniques and Analysis
1
The price elasticity of demand for a textbook sold in the United States is estimated to be 2.0, whereas the price elasticity of demand for books sold overseas is 3.0. The U.S. market requires hardcover books with a marginal cost of $40; the overseas market is normally served with softcover texts on newsprint, having a marginal cost of only $15. Calculate the profit-maximizing price in each market.
[Hint: Remember that MR = P( 1 +1/ED)]
[Hint: Remember that MR = P( 1 +1/ED)]
Price elasticity of demand in U.S. is estimated to be
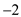 and price elasticity of demand is
and price elasticity of demand is
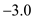 overseas markets. Overseas market is more elastic as comparison to the domestic market. Marginal cost is $40.
overseas markets. Overseas market is more elastic as comparison to the domestic market. Marginal cost is $40.
Following is the condition for equilibrium:

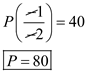 Elasticity of demand in overseas market is
Elasticity of demand in overseas market is
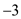 . Marginal cost is $15 in overseas market. Following is the equilibrium price in the overseas market:
. Marginal cost is $15 in overseas market. Following is the equilibrium price in the overseas market:

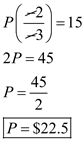 It has been proved that highly elastic demand reduces the price of output. Domestic price is higher in comparison to overseas for high elasticity of demand in overseas market.
It has been proved that highly elastic demand reduces the price of output. Domestic price is higher in comparison to overseas for high elasticity of demand in overseas market.
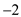 and price elasticity of demand is
and price elasticity of demand is 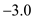 overseas markets. Overseas market is more elastic as comparison to the domestic market. Marginal cost is $40.
overseas markets. Overseas market is more elastic as comparison to the domestic market. Marginal cost is $40. Following is the condition for equilibrium:

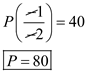 Elasticity of demand in overseas market is
Elasticity of demand in overseas market is 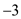 . Marginal cost is $15 in overseas market. Following is the equilibrium price in the overseas market:
. Marginal cost is $15 in overseas market. Following is the equilibrium price in the overseas market:
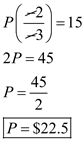 It has been proved that highly elastic demand reduces the price of output. Domestic price is higher in comparison to overseas for high elasticity of demand in overseas market.
It has been proved that highly elastic demand reduces the price of output. Domestic price is higher in comparison to overseas for high elasticity of demand in overseas market. 2
The price elasticity of demand for air travel differs radically from first-class ( 1.3) to unrestricted coach ( 1.4) to restricted discount coach ( 1.9). What do these elasticities mean for optimal prices (fares) on a cross-country trip with incremental variable costs (marginal costs) equal to $120
Price elasticity of demand for first class
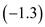 Price elasticity of demand for unrestricted coach
Price elasticity of demand for unrestricted coach
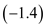 Price elasticity of demand for restricted discount coach
Price elasticity of demand for restricted discount coach
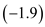 Following is the condition for equilibrium:
Following is the condition for equilibrium:


 Calculate the values of prices by equating the marginal revenue function with the marginal cost:
Calculate the values of prices by equating the marginal revenue function with the marginal cost:



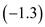 Price elasticity of demand for unrestricted coach
Price elasticity of demand for unrestricted coach 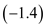 Price elasticity of demand for restricted discount coach
Price elasticity of demand for restricted discount coach 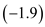 Following is the condition for equilibrium:
Following is the condition for equilibrium: 

 Calculate the values of prices by equating the marginal revenue function with the marginal cost:
Calculate the values of prices by equating the marginal revenue function with the marginal cost: 


3
American Export-Import Shipping Company operates a general cargo carrier service between New York and several Western European ports. It hauls two major categories of freight: manufactured items and semimanufactured raw materials. The demand functions for these two classes of goods are
P 1 = 100 2Q 1
P 2 = 80 Q 2
where Qi = tons of freight moved. The total cost function for American is
T C = 20 + 4(Q 1 + Q 2 )
a. Determine the firm's total profit function.
b. What are the profit-maximizing levels of price and output for the two freight categories
c. At these levels of output, calculate the marginal revenue in each market.
d. What are American's total profits if it is effectively able to charge different prices in the two markets
e. If American is required by law to charge the same per-ton rate to all users,
calculate the new profit-maximizing level of price and output. What are the profits in this situation
f. Explain the difference in profit levels between the differential pricing and uniform pricing cases. Hint: First calculate the point price elasticity of demand under the uniform price-output solution.
P 1 = 100 2Q 1
P 2 = 80 Q 2
where Qi = tons of freight moved. The total cost function for American is
T C = 20 + 4(Q 1 + Q 2 )
a. Determine the firm's total profit function.
b. What are the profit-maximizing levels of price and output for the two freight categories
c. At these levels of output, calculate the marginal revenue in each market.
d. What are American's total profits if it is effectively able to charge different prices in the two markets
e. If American is required by law to charge the same per-ton rate to all users,
calculate the new profit-maximizing level of price and output. What are the profits in this situation
f. Explain the difference in profit levels between the differential pricing and uniform pricing cases. Hint: First calculate the point price elasticity of demand under the uniform price-output solution.
a) Total Profit function
Demand function for two classes of goods
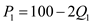 Total Revenue for manufactured item
Total Revenue for manufactured item
 Total Revenue for semi-manufactured item
Total Revenue for semi-manufactured item
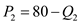
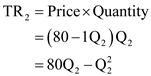 Total Cost function
Total Cost function
 Total Profit Function
Total Profit Function
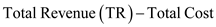
 b) Profit maximizing price and output
b) Profit maximizing price and output
Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the
 :-
:-


 Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the
Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the
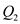 :-
:-
 Substituting the value of output in inverse demand function
Substituting the value of output in inverse demand function
 c) Marginal Revenue in each market
c) Marginal Revenue in each market

 Substituting the values of output
Substituting the values of output
 Marginal Cost for manufactured good is
Marginal Cost for manufactured good is
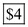

 Substituting the values of output
Substituting the values of output
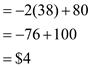 Marginal Cost for semi-manufactured good is
Marginal Cost for semi-manufactured good is
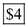 d) Profit if different prices are charged in markets
d) Profit if different prices are charged in markets
Total Profit Function
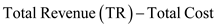

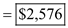 e) Profit if same price is charged
e) Profit if same price is charged
Price of both manufacture and semi-manufactured items should be equal.
Or

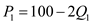
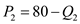
 Total Profit Function
Total Profit Function
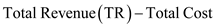
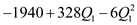 Differentiating it with respect to
Differentiating it with respect to

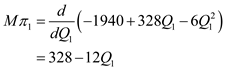 Equation the marginal profit with zero
Equation the marginal profit with zero
 Substituting the value of
Substituting the value of


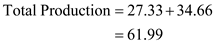 Following is the price of manufactured item:-
Following is the price of manufactured item:-
 Profit at equalized price
Profit at equalized price
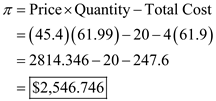 f) Difference in profit level between differential pricing and uniform pricing
f) Difference in profit level between differential pricing and uniform pricing
Elasticity of demand manufactured good


 Differentiating with respect to the price
Differentiating with respect to the price

 Elasticity of demand manufactured good
Elasticity of demand manufactured good
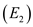
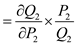
 Differentiating with respect to the price
Differentiating with respect to the price


Demand function for two classes of goods
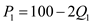 Total Revenue for manufactured item
Total Revenue for manufactured item  Total Revenue for semi-manufactured item
Total Revenue for semi-manufactured item 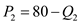
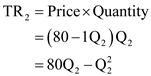 Total Cost function
Total Cost function  Total Profit Function
Total Profit Function 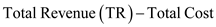
 b) Profit maximizing price and output
b) Profit maximizing price and output Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the
 :-
:-

 Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the
Differentiating the total profit function with respect to the 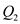 :-
:- Substituting the value of output in inverse demand function
Substituting the value of output in inverse demand function  c) Marginal Revenue in each market
c) Marginal Revenue in each market 
 Substituting the values of output
Substituting the values of output  Marginal Cost for manufactured good is
Marginal Cost for manufactured good is 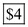

 Substituting the values of output
Substituting the values of output 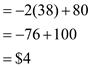 Marginal Cost for semi-manufactured good is
Marginal Cost for semi-manufactured good is 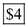 d) Profit if different prices are charged in markets
d) Profit if different prices are charged in markets Total Profit Function
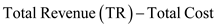

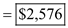 e) Profit if same price is charged
e) Profit if same price is charged Price of both manufacture and semi-manufactured items should be equal.
Or

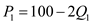
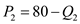
 Total Profit Function
Total Profit Function 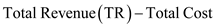
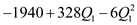 Differentiating it with respect to
Differentiating it with respect to 
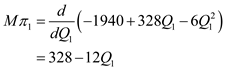 Equation the marginal profit with zero
Equation the marginal profit with zero  Substituting the value of
Substituting the value of 

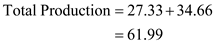 Following is the price of manufactured item:-
Following is the price of manufactured item:- Profit at equalized price
Profit at equalized price 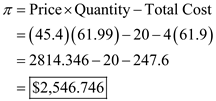 f) Difference in profit level between differential pricing and uniform pricing
f) Difference in profit level between differential pricing and uniform pricing Elasticity of demand manufactured good


 Differentiating with respect to the price
Differentiating with respect to the price 
 Elasticity of demand manufactured good
Elasticity of demand manufactured good 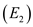
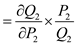
 Differentiating with respect to the price
Differentiating with respect to the price 

4
Sort the following products into those priced with two-part tariffs, user charges only, or lump sum access fees only: pay-per-view movies on cable TV, pay phones, Netflix, iTunes, country club membership, soda from vending machines, laundromats, cell phones, season ticket holders with seat rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Phillips Industries manufactures a certain product that can be sold directly to retail utlets or to the Superior Company for further processing and eventual sale as
a completely different product. The demand function for each of these markets is
Retail Outlets: P 1 = 60 2Q 1
Superior Company: P 2 = 40 Q 2
where P1 and P2 are the prices charged and Q1 and Q2 are the quantities sold in the respective markets. Phillips' total cost function for the manufacture of this product is
T C = 10 + 8(Q 1 + Q 2 )
a. Determine Phillips' total profit function.
b. What are the profit-maximizing price and output levels for the product in the two markets
c. At these levels of output, calculate the marginal revenue in each market.
d. What are Phillips' total profits if the firm is effectively able to charge different prices in the two markets
e. Calculate the profit-maximizing level of price and output if Phillips is required to charge the same price per unit in each market. What are Phillips' profits under this condition
a completely different product. The demand function for each of these markets is
Retail Outlets: P 1 = 60 2Q 1
Superior Company: P 2 = 40 Q 2
where P1 and P2 are the prices charged and Q1 and Q2 are the quantities sold in the respective markets. Phillips' total cost function for the manufacture of this product is
T C = 10 + 8(Q 1 + Q 2 )
a. Determine Phillips' total profit function.
b. What are the profit-maximizing price and output levels for the product in the two markets
c. At these levels of output, calculate the marginal revenue in each market.
d. What are Phillips' total profits if the firm is effectively able to charge different prices in the two markets
e. Calculate the profit-maximizing level of price and output if Phillips is required to charge the same price per unit in each market. What are Phillips' profits under this condition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the face of stable (or declining) enrollments and increasing costs, many colleges and universities, both public and private, find themselves in progressively tighter financial dilemmas that require basic reexamination of the pricing schemes used by institutions of higher learning. One proposal advocated by the Committee for Economic Development (CED) and others has been the use of more nearly fullcost pricing of higher education, combined with the government provision of sufficient loan funds to students who would not otherwise have access to reasonable loan terms in private markets. Advocates of such proposals argue that the private rate of return to student investors is sufficiently high to stimulate socially optimal levels of demand for education, even with the higher tuition rates. Others argue against the existence of significant external benefits to undergraduate education to warrant the current high levels of public support. As with current university pricing schemes, proponents of full-cost pricing generally argue for a standard fee (albeit higher than at present) for all students. Standard-fee proposals ignore relative cost and demand differences among activities in the university.
a. Discuss several possible rationales for charging different prices for different courses of study.
b. What are the income-distribution effects of a pricing scheme that charges the same fee to all students
c. If universities adopted a system of full-cost (or marginal cost) pricing for various courses, what would you expect the impact on the efficiency of resource allocations within the university to be
d. Would you complain less about large lecture sections taught by graduate students if these were priced significantly lower than small seminars taught by outstanding scholars
e. What problems could you see arising from a university that adopted such a pricing scheme
a. Discuss several possible rationales for charging different prices for different courses of study.
b. What are the income-distribution effects of a pricing scheme that charges the same fee to all students
c. If universities adopted a system of full-cost (or marginal cost) pricing for various courses, what would you expect the impact on the efficiency of resource allocations within the university to be
d. Would you complain less about large lecture sections taught by graduate students if these were priced significantly lower than small seminars taught by outstanding scholars
e. What problems could you see arising from a university that adopted such a pricing scheme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
General Medical makes disposable syringes for hospitals and doctor supply companies. The company uses cost-plus pricing and currently charges 150 percent of average variable costs. General Medical learned of an opportunity to sell 300,000 syringes to the Department of Defense if they can be delivered within three months at a price not in excess of $1 each. General Medical normally sells its syringes for $1.20 each. If General Medical accepts the Defense Department order, it will have to forgo sales of 100,000 syringes to its regular customers over this time period, although this loss of sales is not expected to affect future sales.
a. Should General Medical accept the Defense Department order
b. If sales for the balance of the year are expected to be 50,000 units less because of some lost customers who do not return, should the order be accepted (Ignore any effects beyond one year.)
a. Should General Medical accept the Defense Department order
b. If sales for the balance of the year are expected to be 50,000 units less because of some lost customers who do not return, should the order be accepted (Ignore any effects beyond one year.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Pear Computer Company just developed a totally revolutionary new personal computer. It estimates that it will take competitors at least two years to produce equivalent products. The demand function for the computer is estimated to be
P = 2,500 0.0005Q
The marginal (and average variable) cost of producing the computer is $900.
a. Compute the profit-maximizing price and output levels assuming Pear acts as a monopolist for its product.
b. Determine the total contribution to profits and fixed costs from the solution generated in Part (a). Pear Computer is considering an alternative pricing strategy of price skimming. It plans to set the following schedule of prices over the coming two years:
 c. Calculate the contribution to profit and overhead for each of the 10 time periods and prices.
c. Calculate the contribution to profit and overhead for each of the 10 time periods and prices.
d. Compare your results in Part (c) with your answers in Part (b).
e. Explain the major advantages and disadvantages of price skimming as a pricing strategy.
P = 2,500 0.0005Q
The marginal (and average variable) cost of producing the computer is $900.
a. Compute the profit-maximizing price and output levels assuming Pear acts as a monopolist for its product.
b. Determine the total contribution to profits and fixed costs from the solution generated in Part (a). Pear Computer is considering an alternative pricing strategy of price skimming. It plans to set the following schedule of prices over the coming two years:
 c. Calculate the contribution to profit and overhead for each of the 10 time periods and prices.
c. Calculate the contribution to profit and overhead for each of the 10 time periods and prices.d. Compare your results in Part (c) with your answers in Part (b).
e. Explain the major advantages and disadvantages of price skimming as a pricing strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
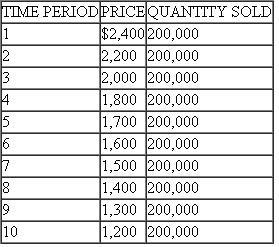
Explain the effect on capacity reallocations of advance sales data indicating mean demand of 55 rather than 60 during a slow travel week for business class, using the information in Figure, Table, and Equation.
Figure Optimal Differential Pricing and Capacity Allocation (45 Days in Advance) for Thursday 11:00 A.M. Flight from Dallas to Los Angeles
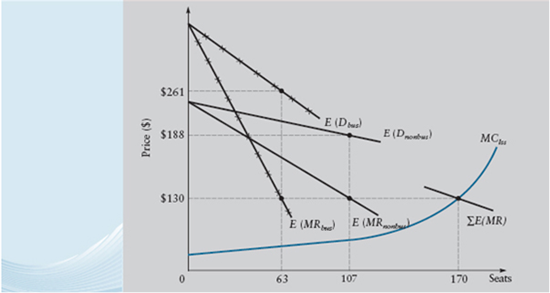
Table ALLOCATING AIRLINE CAPACITY WITH DIFFERENTIAL FARES FOR LEISURE AND BUSINESS
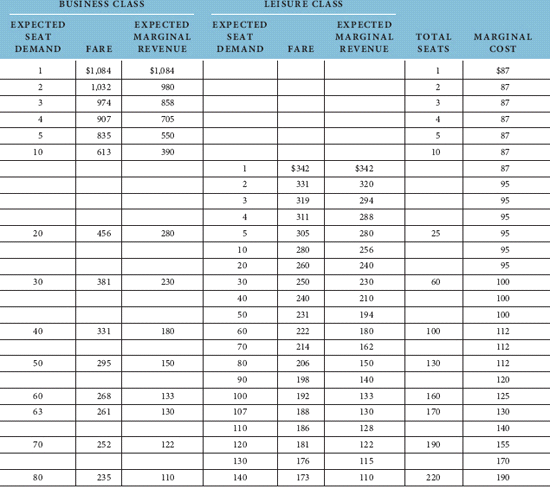
Equation
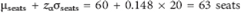
Figure Optimal Differential Pricing and Capacity Allocation (45 Days in Advance) for Thursday 11:00 A.M. Flight from Dallas to Los Angeles

Table ALLOCATING AIRLINE CAPACITY WITH DIFFERENTIAL FARES FOR LEISURE AND BUSINESS

Equation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose the frequent-flyer program raised the cost of high-yield spill twofold because business customers who are denied boarding now take their business to other carriers for several future trips, not just the current one. Reanalyze the overbooking decision in Figure under these circumstances. Will overbooking of business-class service increase or decrease
Figure How the Overbooking Decision Minimizes the Summed Cost of Spoilage and Spill
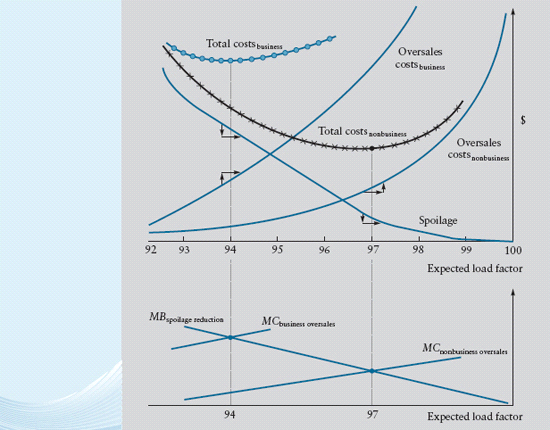
Figure How the Overbooking Decision Minimizes the Summed Cost of Spoilage and Spill


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An aircraft with 100 seats serves passengers through two types of fares: full ($550) and discount ($250). Extra passengers have $50 marginal cost. Demand for discount tickets is unlimited, while demand for full-fare tickets is evenly distributed between 11 and 30 seats. How many seats should be protected for full-fare passengers and not authorized for release to the discounted $250 segment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



