Deck 9: Unemploymentand the Labor Market
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Unemploymentand the Labor Market
1
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 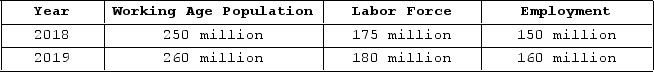 What was the unemployment rate in 2018?
What was the unemployment rate in 2018?
A) 14 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 17.5 percent
D) 15 percent
 What was the unemployment rate in 2018?
What was the unemployment rate in 2018?A) 14 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 17.5 percent
D) 15 percent
14 percent
2
The labor force participation rate:
A) can be measured by dividing the total population by the proportion of people who want to work.
B) tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment.
C) typically increases during periods of recession.
D) is measured by dividing the working-age population by the percentage of people employed.
A) can be measured by dividing the total population by the proportion of people who want to work.
B) tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment.
C) typically increases during periods of recession.
D) is measured by dividing the working-age population by the percentage of people employed.
tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment.
3
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 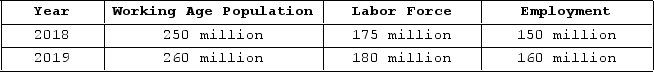 What was the labor force participation rate in 2018?
What was the labor force participation rate in 2018?
A) 70 percent
B) 75 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 69 percent
 What was the labor force participation rate in 2018?
What was the labor force participation rate in 2018?A) 70 percent
B) 75 percent
C) 50 percent
D) 69 percent
70 percent
4
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 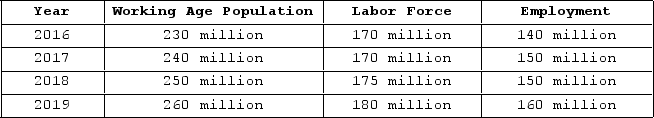 In which year was the labor force participation rate the lowest?
In which year was the labor force participation rate the lowest?
A) 2016
B) 2017
C) 2018
D) 2019
 In which year was the labor force participation rate the lowest?
In which year was the labor force participation rate the lowest?A) 2016
B) 2017
C) 2018
D) 2019

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which government office is in charge of collecting official employment statistics?
A) Bureau of Labor Statistics
B) Bureau of Economic Analysis
C) Bureau of Industry and Security
D) Bureau of the Census
A) Bureau of Labor Statistics
B) Bureau of Economic Analysis
C) Bureau of Industry and Security
D) Bureau of the Census

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The unemployment rate tells us:
A) what percentage of the labor force wants to work but can't find a job.
B) what will happen in the labor market in the future.
C) why the unemployed can't find work.
D) the number of people who don't want to work.
A) what percentage of the labor force wants to work but can't find a job.
B) what will happen in the labor market in the future.
C) why the unemployed can't find work.
D) the number of people who don't want to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During a recession, unemployment is:
A) more common.
B) less common.
C) unpredictable.
D) the same for all demographic groups.
A) more common.
B) less common.
C) unpredictable.
D) the same for all demographic groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The labor force does not include people in the working-age population who are:
A) employed.
B) not actively trying to find a job.
C) retired, a full-time student, or a stay-at-home parent.
D) employed part time.
A) employed.
B) not actively trying to find a job.
C) retired, a full-time student, or a stay-at-home parent.
D) employed part time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Economists report changes in unemployment as:
A) percentage points, not percentages.
B) percentages, not percentage points.
C) percentage points or percentages, interchangeably.
D) nominal figures.
A) percentage points, not percentages.
B) percentages, not percentage points.
C) percentage points or percentages, interchangeably.
D) nominal figures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Unemployment:
A) exists at any time during the business cycle.
B) only occurs during times of recession.
C) is highest during times of peak economic activity.
D) tends to increase during times of economic recovery.
A) exists at any time during the business cycle.
B) only occurs during times of recession.
C) is highest during times of peak economic activity.
D) tends to increase during times of economic recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Unemployment occurs when someone:
A) wants to work but cannot find a job.
B) is not working full-time.
C) should be working but chooses not to.
D) is not utilizing their full set of skills.
A) wants to work but cannot find a job.
B) is not working full-time.
C) should be working but chooses not to.
D) is not utilizing their full set of skills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the United States, the working-age population includes people:
A) in prison.
B) in the military.
C) who are less than 16 years of age.
D) aged 16 years or older.
A) in prison.
B) in the military.
C) who are less than 16 years of age.
D) aged 16 years or older.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 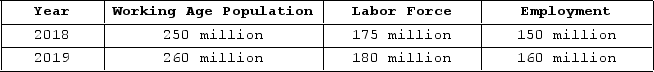 What was the unemployment rate in 2019?
What was the unemployment rate in 2019?
A) 1.1 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 16 percent
D) 11 percent
 What was the unemployment rate in 2019?
What was the unemployment rate in 2019?A) 1.1 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 16 percent
D) 11 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 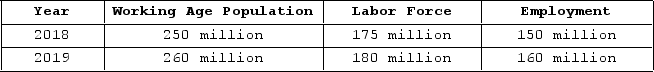 What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?
What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?
A) 70 percent
B) 80 percent
C) 69 percent
D) 26 percent
 What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?
What was the labor force participation rate in 2019?A) 70 percent
B) 80 percent
C) 69 percent
D) 26 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 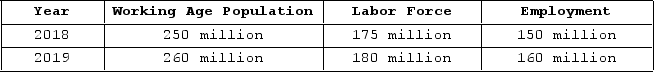 The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.
The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.
A) 3; higher
B) 3; lower
C) 14; higher
D) 11; lower
 The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.
The unemployment rate in 2019 was _______ percentage points _______ than in 2018.A) 3; higher
B) 3; lower
C) 14; higher
D) 11; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The table shown displays employment statistics for two years. 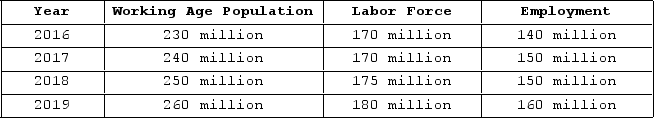 In which year was unemployment the highest?
In which year was unemployment the highest?
A) 2016
B) 2017
C) 2018
D) 2019
 In which year was unemployment the highest?
In which year was unemployment the highest?A) 2016
B) 2017
C) 2018
D) 2019

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the United States, to count as unemployed, you must be:
A) younger than 65 years of age.
B) actively looking for work.
C) skilled enough to hold a job.
D) All of these are true.
A) younger than 65 years of age.
B) actively looking for work.
C) skilled enough to hold a job.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the United States, the working-age population does not include people:
A) in the military.
B) who are 16 years of age.
C) who are 65 years of age.
D) who do not have a driver's license.
A) in the military.
B) who are 16 years of age.
C) who are 65 years of age.
D) who do not have a driver's license.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Unemployment rates tend to be highest during periods of:
A) recession.
B) expansion.
C) recovery.
D) stagflation.
A) recession.
B) expansion.
C) recovery.
D) stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Unemployment:
A) wastes the productive potential of the economy.
B) makes it easier for firms in other countries to find the labor they need.
C) disproportionally affects highly educated workers.
D) occurs most often during the summer.
A) wastes the productive potential of the economy.
B) makes it easier for firms in other countries to find the labor they need.
C) disproportionally affects highly educated workers.
D) occurs most often during the summer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The unemployment rate may_______ the effect of a recession on unemployment because some people ______ the labor force.
A) understate; leave
B) understate; enter
C) overstate; leave
D) overstate; enter
A) understate; leave
B) understate; enter
C) overstate; leave
D) overstate; enter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The labor supply curve:
A) shows the relationship between the total quantity of labor supplied by all firms in the economy and the wage rate.
B) shows that, all things being equal, more workers will want to work when wages are higher and fewer will want to work when wages are lower.
C) has a negative slope.
D) All of these are true.
A) shows the relationship between the total quantity of labor supplied by all firms in the economy and the wage rate.
B) shows that, all things being equal, more workers will want to work when wages are higher and fewer will want to work when wages are lower.
C) has a negative slope.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In 2018, the labor force participation rate was 63.1 percent. This means that:
A) 63.1 percent of all working-age people wanted a job.
B) there was 36.9 percent unemployment.
C) 63.1 percent of all working-age people were employed.
D) only 63.1 percent of the labor force was of working age.
A) 63.1 percent of all working-age people wanted a job.
B) there was 36.9 percent unemployment.
C) 63.1 percent of all working-age people were employed.
D) only 63.1 percent of the labor force was of working age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
All else equal, if unemployment falls by 2 percentage points to 6 percent, this indicates that:
A) 2 out of every 10 in the labor force lost a job.
B) 20 out of every 1,000 unemployed found a job.
C) 2 out of every 100 in the labor force lost a job.
D) 4 out of every 100 unemployed found a job.
A) 2 out of every 10 in the labor force lost a job.
B) 20 out of every 1,000 unemployed found a job.
C) 2 out of every 100 in the labor force lost a job.
D) 4 out of every 100 unemployed found a job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The price of labor is called:
A) the wage.
B) income.
C) opportunity cost.
D) the leisure trade-off.
A) the wage.
B) income.
C) opportunity cost.
D) the leisure trade-off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In terms of supply and demand, unemployment is:
A) a surplus of labor.
B) a shortage of labor.
C) an increase in the quantity of labor demanded.
D) a decrease in the quantity of labor supplied.
A) a surplus of labor.
B) a shortage of labor.
C) an increase in the quantity of labor demanded.
D) a decrease in the quantity of labor supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Jennifer has a PhD in economics and has been working for three years as a part-time instructor, but she would like to be hired as a full-time faculty member. Jennifer is best described as:
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) overemployed.
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) overemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Sonia has a BA in art history and is currently working full-time as a waitress. The BLS would classify Sonia as:
A) employed.
B) underemployed.
C) unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.
A) employed.
B) underemployed.
C) unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The labor demand curve shows:
A) the number of workers firms want to hire at each given wage.
B) the number of people who want to work at each given wage.
C) the number of workers who are willing and able to work at higher wages.
D) that the number of people who want to work increases as the wage increases.
A) the number of workers firms want to hire at each given wage.
B) the number of people who want to work at each given wage.
C) the number of workers who are willing and able to work at higher wages.
D) that the number of people who want to work increases as the wage increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During times of recession, the labor force participation rate typically:
A) rises, as labor demand increases during a recession.
B) rises, as more incomes per household are needed to make ends meet.
C) falls, as more people give up and stop looking for work.
D) stays roughly the same, as people make decisions about work independent of the overall health of the economy.
A) rises, as labor demand increases during a recession.
B) rises, as more incomes per household are needed to make ends meet.
C) falls, as more people give up and stop looking for work.
D) stays roughly the same, as people make decisions about work independent of the overall health of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Some people drop out of the labor force during times of recession:
A) to go back to college, because the opportunity cost is lower during a recession.
B) because they age out of the workforce.
C) because the cost of living is lower.
D) All of these are true.
A) to go back to college, because the opportunity cost is lower during a recession.
B) because they age out of the workforce.
C) because the cost of living is lower.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The BLS collects _______ measures of unemployment.
A) four
B) five
C) six
D) seven
A) four
B) five
C) six
D) seven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All else equal, if unemployment rises to 8 percent after a 3.5 percentage point increase, this indicates that:
A) 35 out of every 100 in the labor force have lost a job.
B) 35 out of every 1,000 in the labor force have lost a job.
C) 8 out of every 1,000 in the labor force can't find a job.
D) 8 out of every 100 in the labor force have stopped looking for work.
A) 35 out of every 100 in the labor force have lost a job.
B) 35 out of every 1,000 in the labor force have lost a job.
C) 8 out of every 1,000 in the labor force can't find a job.
D) 8 out of every 100 in the labor force have stopped looking for work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The labor demand curve:
A) shows the relationship between the total quantity of labor demanded by all the firms in the economy and the wage rate.
B) shows that, all things being equal, firms will want to hire a constant amount of labor at each wage rate.
C) shows the relationship between the total quantity of employment demanded by all the workers in the economy and the wage rate.
D) has a positive slope.
A) shows the relationship between the total quantity of labor demanded by all the firms in the economy and the wage rate.
B) shows that, all things being equal, firms will want to hire a constant amount of labor at each wage rate.
C) shows the relationship between the total quantity of employment demanded by all the workers in the economy and the wage rate.
D) has a positive slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The labor force participation rate:
A) tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment, whether or not they actually have a job.
B) typically rises during times of recession, as more people need work.
C) is used to assess the health of the overall economy.
D) All of these are true.
A) tells us what fraction of the working-age population wants employment, whether or not they actually have a job.
B) typically rises during times of recession, as more people need work.
C) is used to assess the health of the overall economy.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The labor supply curve:
A) is made up of firms who want to hire workers at each given wage.
B) is made up of workers who want to work for firms at each given wage.
C) shows the number of firms that are willing and able to hire workers at each given wage.
D) shows that the number of firms that want to hire workers decreases as the wage increases.
A) is made up of firms who want to hire workers at each given wage.
B) is made up of workers who want to work for firms at each given wage.
C) shows the number of firms that are willing and able to hire workers at each given wage.
D) shows that the number of firms that want to hire workers decreases as the wage increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Underemployment occurs when someone:
A) is employed part-time, but wants full-time employment.
B) is paid under the table for their work.
C) is hired for an entry-level position.
D) is paid less than the median wage in a specific profession.
A) is employed part-time, but wants full-time employment.
B) is paid under the table for their work.
C) is hired for an entry-level position.
D) is paid less than the median wage in a specific profession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Miguel is a corrections officer at a local prison, but he would like to go back to school to train to become a police officer someday. According to the BLS, Miguel is:
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) employed.
A) a discouraged worker.
B) unemployed.
C) underemployed.
D) employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Lian has a master's degree in writing and currently works full-time as a second grade classroom helper. She submits articles for the local paper on occasion, and gets paid only when the editor agrees to publish a submission. Lian would love to work full-time as a news reporter. Lian is best described as _______ and the BLS would classify Lian as _______.
A) underemployed; employed
B) employed; employed
C) discouraged; underemployed
D) underemployed; underemployed
A) underemployed; employed
B) employed; employed
C) discouraged; underemployed
D) underemployed; underemployed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Discouraged workers are people who have:
A) looked for work in the past year but have given up looking because of the condition of the labor market.
B) not looked for work in the past year but would take a job if one was offered to them.
C) looked for work in the past year but have since decided to leave the labor market to go back to school, retire, or be a stay-at-home parent.
D) spent longer than a year looking for work.
A) looked for work in the past year but have given up looking because of the condition of the labor market.
B) not looked for work in the past year but would take a job if one was offered to them.
C) looked for work in the past year but have since decided to leave the labor market to go back to school, retire, or be a stay-at-home parent.
D) spent longer than a year looking for work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is true when the prevailing market wage is above equilibrium?
A) The surplus of labor reflects the amount of unemployment in the market.
B) The difference between the quantity supplied and the quantity of labor demanded is unemployment.
C) Unemployment occurs.
D) All of these are true when the market wage is above equilibrium.
A) The surplus of labor reflects the amount of unemployment in the market.
B) The difference between the quantity supplied and the quantity of labor demanded is unemployment.
C) Unemployment occurs.
D) All of these are true when the market wage is above equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the prevailing market wage is above equilibrium:
A) there is no unemployment.
B) there is a surplus of labor.
C) the quantity of labor demanded is higher than the quantity supplied.
D) All of these are true.
A) there is no unemployment.
B) there is a surplus of labor.
C) the quantity of labor demanded is higher than the quantity supplied.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sarah was a great bookkeeper 20 years ago, but she left the workforce to stay home and raise her children. Now that her kids are in college, Sarah is looking for another bookkeeping job, but they all require computer skills that she doesn't have. Sarah is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) not in the labor force.
D) seasonally unemployed.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) not in the labor force.
D) seasonally unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Weizhe just quit his job as a phone salesman and is looking for work as an accountant. Weizhe is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Liam just quit his job as a librarian to pursue his lifelong dream of becoming a teacher. Liam is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) seasonally unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) seasonally unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
While working as a sales rep for a local firm, Felipe completes an MBA by taking online college courses at night. Felipe then quits his job to look for a management position at another firm. Felipe is:
A) underemployed.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) classically unemployed.
A) underemployed.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) classically unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Real-wage unemployment:
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) is also called cyclical unemployment.
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) is also called cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Sanjeev just graduated from college and has landed his first job with an accounting firm, which will start in one month. Sanjeev plans to use the next month adjusting to the new area. Sanjeev currently is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) employed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) employed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suke used to be a music teacher at a local high school, but got let go last year due to budget cuts. Suke now works part-time as a waitress while looking for another teaching job. Suke is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) underemployed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) real-wage unemployed.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) underemployed.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) real-wage unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The normal level of unemployment that persists in an economy in the long run is:
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the equilibrium rate of underemployment.
C) zero, as long as the market is equilibrium.
D) zero with effective public policy.
A) the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the equilibrium rate of underemployment.
C) zero, as long as the market is equilibrium.
D) zero with effective public policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Structural unemployment:
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) occurs when workers voluntarily quit their jobs.
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) occurs when workers voluntarily quit their jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Frictional unemployment:
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) is not connected to natural rate of unemployment.
A) occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills that are in demand.
B) is caused by workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
C) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
D) is not connected to natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Don, who has worked as a machinist all his life, was recently laid off because the plant where he worked shut down and the jobs were outsourced. There don't seem to be any machinist jobs in the area anymore. Don is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) real-wage unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) real-wage unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Millennials are stereotyped as changing jobs frequently to find their "dream" career. What type of unemployment is caused by these movements?
A) Frictional
B) Real-wage
C) Cyclical
D) Structural
A) Frictional
B) Real-wage
C) Cyclical
D) Structural

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The natural rate of unemployment is the normal level of unemployment:
A) in an economy in the short run.
B) in an economy in the long run.
C) that exists without government intervention.
D) in an economy with a high labor force participation rate.
A) in an economy in the short run.
B) in an economy in the long run.
C) that exists without government intervention.
D) in an economy with a high labor force participation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Barbara has been working in a coffee shop full-time while she attends college. When she graduates, she quits the coffee shop and begins to search for full-time employment related to her college degree. Barbara is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) classically unemployed.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) classically unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Carol is an autoworker who was laid off when the last factory in the area shut down. She has looked everywhere for another job as an autoworker, but cannot find one. Carol is:
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) real-wage unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.
A) frictionally unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) real-wage unemployed.
D) a discouraged worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which type of unemployment does not contribute to the natural rate of unemployment?
A) Frictional
B) Structural
C) Real-wage
D) Cyclical
A) Frictional
B) Structural
C) Real-wage
D) Cyclical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The country of Hortonia enters into a massive free trade agreement that sends most manufacturing jobs overseas. The country's workers who were previously employed in manufacturing now face:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which type of unemployment contributes to the natural rate of unemployment?
A) Real-wage unemployment
B) Cyclical unemployment
C) Unemployment of government workers
D) All of these contribute to the natural rate of unemployment
A) Real-wage unemployment
B) Cyclical unemployment
C) Unemployment of government workers
D) All of these contribute to the natural rate of unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One way a government can attempt to minimize the effects of structural unemployment is to:
A) subsidize retraining programs.
B) increase unemployment benefits.
C) mandate that employers cannot fire any employees.
D) regulate the wage rate.
A) subsidize retraining programs.
B) increase unemployment benefits.
C) mandate that employers cannot fire any employees.
D) regulate the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Real-wage unemployment can be caused by:
A) minimum wage laws.
B) retraining programs.
C) low-interest student loans.
D) None of these cause real-wage unemployment.
A) minimum wage laws.
B) retraining programs.
C) low-interest student loans.
D) None of these cause real-wage unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
After the financial crisis in 2007, many firms laid off workers who struggled to find new work during the recession. These workers experienced:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When the economy slows down:
A) the demand for labor stays the same, then increases as firms expand their operations.
B) the demand for labor decreases.
C) the demand for labor stays the same.
D) the demand for labor increases.
A) the demand for labor stays the same, then increases as firms expand their operations.
B) the demand for labor decreases.
C) the demand for labor stays the same.
D) the demand for labor increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Classical unemployment can be caused by:
A) minimum wage laws.
B) union bargaining.
C) efficiency wages.
D) All these cause classical unemployment.
A) minimum wage laws.
B) union bargaining.
C) efficiency wages.
D) All these cause classical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the economy is going strong:
A) firms expand their operations.
B) the demand for labor decreases.
C) GDP growth is negative.
D) firms tend to lay off workers.
A) firms expand their operations.
B) the demand for labor decreases.
C) GDP growth is negative.
D) firms tend to lay off workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The pattern of recession and recovery is called:
A) the liquidity cycle.
B) the business cycle.
C) structural unemployment.
D) inflation.
A) the liquidity cycle.
B) the business cycle.
C) structural unemployment.
D) inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Wages tend to be "sticky" because:
A) contracts are often negotiated for long periods of time and cannot be easily changed.
B) workers are less likely to work hard if their pay may be cut due to market performance.
C) changing wages create uncertainty and cost employers a lot of time and energy.
D) All of these are reasons why wages might be sticky.
A) contracts are often negotiated for long periods of time and cannot be easily changed.
B) workers are less likely to work hard if their pay may be cut due to market performance.
C) changing wages create uncertainty and cost employers a lot of time and energy.
D) All of these are reasons why wages might be sticky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When economists say wages are "sticky," they mean that wages:
A) are slow to adjust to changes in the economy.
B) are subject to a wide range of regulations from the government.
C) tend to change before other indicators of the business cycle.
D) are unpredictable in terms of how they will change.
A) are slow to adjust to changes in the economy.
B) are subject to a wide range of regulations from the government.
C) tend to change before other indicators of the business cycle.
D) are unpredictable in terms of how they will change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
After an economic boom, the new equilibrium wage will be _______ because the labor demand curve shifts to the _______.
A) lower; left
B) higher; left
C) lower; right
D) higher; right
A) lower; left
B) higher; left
C) lower; right
D) higher; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An economic slowdown would likely cause the labor _______ curve to shift to the _______.
A) demand; left
B) demand; right
C) supply; left
D) supply; right
A) demand; left
B) demand; right
C) supply; left
D) supply; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
We don't typically see wages fall in response to an economic downturn because:
A) labor supply adjusts so that the market stays at the original equilibrium wage level.
B) there is often little change in the labor market in response to economic conditions.
C) they are "sticky" and are slow to respond to shifts in the economy.
D) the government sets tight regulations on how firms compensate their employees.
A) labor supply adjusts so that the market stays at the original equilibrium wage level.
B) there is often little change in the labor market in response to economic conditions.
C) they are "sticky" and are slow to respond to shifts in the economy.
D) the government sets tight regulations on how firms compensate their employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Unemployment is a:
A) leading indicator, because the business cycle follows it.
B) lagging indicator, because the business cycle follows it.
C) leading indicator, because it follows the business cycle.
D) lagging indicator, because it follows the business cycle.
A) leading indicator, because the business cycle follows it.
B) lagging indicator, because the business cycle follows it.
C) leading indicator, because it follows the business cycle.
D) lagging indicator, because it follows the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in GDP growth would likely cause the labor _______ curve to shift to the _______.
A) demand; left
B) demand; right
C) supply; left
D) supply; right
A) demand; left
B) demand; right
C) supply; left
D) supply; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In 2017, the city of Seattle passed legislation implementing a $15 per hour minimum wage. Critics of the plan argued that this legislation would increase:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) real-wage unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
After an economic slowdown, the new equilibrium wage will be _______ because the labor demand curve shifts to the _______.
A) lower; left
B) higher; left
C) lower; right
D) higher; right
A) lower; left
B) higher; left
C) lower; right
D) higher; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cyclical unemployment:
A) is caused by short-term economic fluctuations.
B) results from a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills demanded.
C) results from workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
D) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.
A) is caused by short-term economic fluctuations.
B) results from a mismatch between the skills workers can offer and the skills demanded.
C) results from workers changing their locations, jobs, or careers.
D) is the effect of wages remaining persistently above the market-clearing level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The business cycle:
A) affects the demand for labor.
B) affects the supply of labor.
C) affects both the supply of and demand for labor.
D) does not affect the market for labor.
A) affects the demand for labor.
B) affects the supply of labor.
C) affects both the supply of and demand for labor.
D) does not affect the market for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What happens when an economy starts to contract?
A) Labor demand will increase.
B) Cyclical unemployment will decrease.
C) Wages will approach the market-clearing level.
D) Labor supply will decrease.
A) Labor demand will increase.
B) Cyclical unemployment will decrease.
C) Wages will approach the market-clearing level.
D) Labor supply will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Wage stickiness in an economic downturn can result in:
A) actual wages that are temporarily above the market-clearing level.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) a surplus of labor.
D) a shortage of labor.
A) actual wages that are temporarily above the market-clearing level.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) a surplus of labor.
D) a shortage of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



