Deck 6: Governmentintervention
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/171
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Governmentintervention
1
Why might a government impose a minimum wage?
A) To correct a market failure
B) To redistribute surplus in a market
C) To encourage the consumption of inferior goods
D) To discourage the consumption of inferior goods
A) To correct a market failure
B) To redistribute surplus in a market
C) To encourage the consumption of inferior goods
D) To discourage the consumption of inferior goods
To redistribute surplus in a market
2
Which of the following exemplifies a market failure?
A) One person's consumption of a good imposes costs on others.
B) A firm selling a product faces competition from many other sellers.
C) A good is priced too high for poor families to afford.
D) The distribution of surplus in a market is unfair.
A) One person's consumption of a good imposes costs on others.
B) A firm selling a product faces competition from many other sellers.
C) A good is priced too high for poor families to afford.
D) The distribution of surplus in a market is unfair.
One person's consumption of a good imposes costs on others.
3
Governments can discourage the consumption of certain goods by:
A) giving a subsidy to consumers in those markets.
B) taxing substitute goods.
C) imposing a minimum price above the equilibrium price.
D) None of these policies decrease the consumption of goods.
A) giving a subsidy to consumers in those markets.
B) taxing substitute goods.
C) imposing a minimum price above the equilibrium price.
D) None of these policies decrease the consumption of goods.
imposing a minimum price above the equilibrium price.
4
What do we call situations in which the assumption of efficient, competitive markets fails to hold?
A) Market failures
B) Inelastic-response markets
C) Missing markets
D) Market interventions
A) Market failures
B) Inelastic-response markets
C) Missing markets
D) Market interventions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Normative analysis:
A) involves the formulation and testing of hypotheses.
B) is a value-free evaluation of a policy.
C) involves a value judgement regarding the desirability of a policy.
D) examines if a policy actually accomplished its goal.
A) involves the formulation and testing of hypotheses.
B) is a value-free evaluation of a policy.
C) involves a value judgement regarding the desirability of a policy.
D) examines if a policy actually accomplished its goal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A government might intervene in a market to:
A) increase the efficiency of the market.
B) reduce the consumption of a "bad" product.
C) correct a market failure.
D) All of these are reasons why a government might intervene in a market.
A) increase the efficiency of the market.
B) reduce the consumption of a "bad" product.
C) correct a market failure.
D) All of these are reasons why a government might intervene in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Price controls:
A) are regulations that set a maximum or minimum legal price for a particular good.
B) allow a market to reach equilibrium.
C) prevent a good from being bought or sold.
D) All of these are correct.
A) are regulations that set a maximum or minimum legal price for a particular good.
B) allow a market to reach equilibrium.
C) prevent a good from being bought or sold.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A price ceiling is:
A) a legal maximum price.
B) a legal minimum price.
C) a legal maximum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
D) a legal minimum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
A) a legal maximum price.
B) a legal minimum price.
C) a legal maximum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
D) a legal minimum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Governments might choose to intervene in a market in an attempt to:
A) encourage the consumption of certain goods.
B) discourage the consumption of certain goods.
C) redistribute surplus.
D) All of these are correct.
A) encourage the consumption of certain goods.
B) discourage the consumption of certain goods.
C) redistribute surplus.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A market failure is most likely to occur when:
A) a sole producer of a good faces no threat of competition.
B) several producers of a good compete for customers by having price wars.
C) several producers of a good search for the lowest-cost method of production.
D) many producers produce identical products, and only the consumers are affected by the transactions.
A) a sole producer of a good faces no threat of competition.
B) several producers of a good compete for customers by having price wars.
C) several producers of a good search for the lowest-cost method of production.
D) many producers produce identical products, and only the consumers are affected by the transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Positive analysis:
A) involves the formulation and testing of hypotheses.
B) involves value judgments concerning the desirability of alternative outcomes.
C) weighs the fairness of a policy.
D) examines if an outcome is desirable.
A) involves the formulation and testing of hypotheses.
B) involves value judgments concerning the desirability of alternative outcomes.
C) weighs the fairness of a policy.
D) examines if an outcome is desirable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Government attempts to lower, raise, or simply stabilize prices will usually:
A) maintain the distribution of surplus.
B) create unintended side effects.
C) improve the efficiency of a market.
D) All of these are correct.
A) maintain the distribution of surplus.
B) create unintended side effects.
C) improve the efficiency of a market.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Government attempts to set prices below market equilibrium can:
A) lead to more producer surplus.
B) encourage more production.
C) reduce the total surplus in the market.
D) always create a better outcome.
A) lead to more producer surplus.
B) encourage more production.
C) reduce the total surplus in the market.
D) always create a better outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a price ceiling to have an impact on a market it must be set:
A) above the equilibrium price.
B) below the equilibrium price.
C) equal to the equilibrium price.
D) anywhere along the demand curve.
A) above the equilibrium price.
B) below the equilibrium price.
C) equal to the equilibrium price.
D) anywhere along the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What type of public policy could a government set in response to rising prices of a basic necessity?
A) Make it illegal to charge higher prices for the good
B) Hire more producers of the good
C) Subsidize the price of the good
D) All of these are ways a government can try to address rising prices of a basic necessity.
A) Make it illegal to charge higher prices for the good
B) Hire more producers of the good
C) Subsidize the price of the good
D) All of these are ways a government can try to address rising prices of a basic necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How might a government attempt to protect dairy farmers from low milk prices?
A) Banning households from hoarding milk
B) Setting a minimum price on milk
C) Increasing taxes on dairy farmers
D) Reducing subsidies on the price of milk
A) Banning households from hoarding milk
B) Setting a minimum price on milk
C) Increasing taxes on dairy farmers
D) Reducing subsidies on the price of milk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a good has only one producer, with no threat of competition, the market for this good likely:
A) has greater consumer surplus than in a competitive equilibrium.
B) has the price set inefficiently high.
C) has the price set below the competitive equilibrium price.
D) is efficient.
A) has greater consumer surplus than in a competitive equilibrium.
B) has the price set inefficiently high.
C) has the price set below the competitive equilibrium price.
D) is efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a good has only one producer, with no threat of competition, it is likely that government intervention in the market will:
A) have no impact.
B) raise prices for consumers.
C) increase total surplus.
D) make buyers and sellers better off.
A) have no impact.
B) raise prices for consumers.
C) increase total surplus.
D) make buyers and sellers better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In evaluating policy effectiveness, economists rely on:
A) positive analysis.
B) normative analysis.
C) both normative and positive analysis.
D) Economists can never fully analyze any real-world policy effectiveness.
A) positive analysis.
B) normative analysis.
C) both normative and positive analysis.
D) Economists can never fully analyze any real-world policy effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Positive analysis:
A) evaluates whether a policy is a good idea.
B) leads to the best solutions.
C) is the only way to analyze a policy.
D) examines if a policy actually accomplished its goals.
A) evaluates whether a policy is a good idea.
B) leads to the best solutions.
C) is the only way to analyze a policy.
D) examines if a policy actually accomplished its goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why do governments tend to set price ceilings?
A) To ensure everyone can afford certain goods.
B) To encourage producers to make enough for everyone.
C) To help producers make enough profit to stay in the industry.
D) To prevent consumers from choosing the wrong goods.
A) To ensure everyone can afford certain goods.
B) To encourage producers to make enough for everyone.
C) To help producers make enough profit to stay in the industry.
D) To prevent consumers from choosing the wrong goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In order for a price ceiling to be binding, it must be set _______ the equilibrium price, and it will likely cause _______.
A) above; a shortage
B) below; a shortage
C) above; excess supply
D) below; excess supply
A) above; a shortage
B) below; a shortage
C) above; excess supply
D) below; excess supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
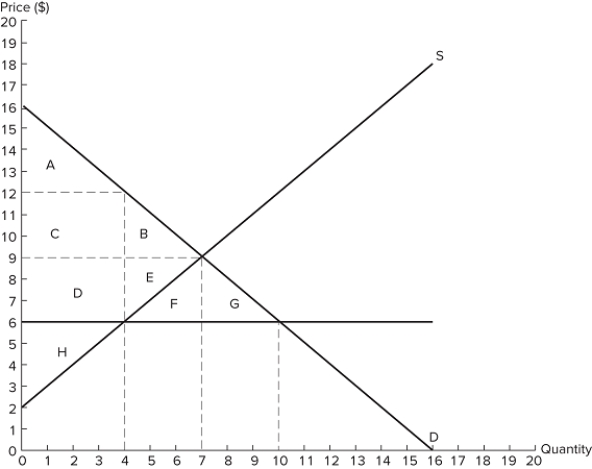
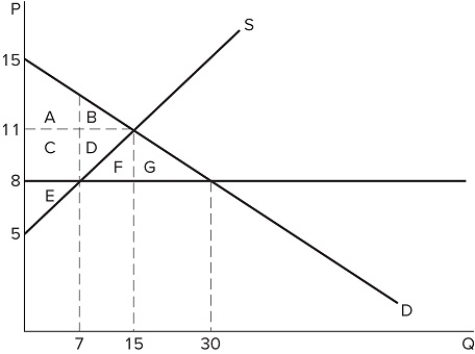 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market in the graph shown, the total number of units traded will:
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market in the graph shown, the total number of units traded will:A) fall by 8, relative to equilibrium.
B) fall by 15, relative to equilibrium.
C) fall by 23, relative to equilibrium.
D) increase by 15, relative to equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
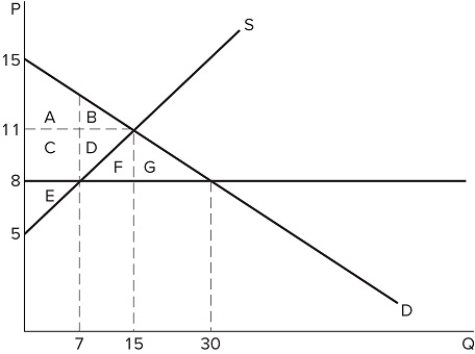 The graph shown best represents:
The graph shown best represents:A) a binding price ceiling.
B) a binding price floor.
C) a missing market.
D) a market for an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
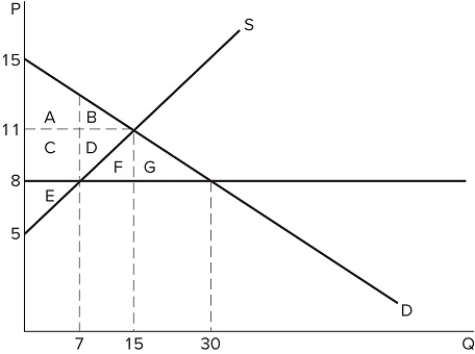 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which areas would represent total surplus?
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which areas would represent total surplus?A) A + B + C + D + E + F + G
B) A + B + C + D + E
C) A + C + E
D) A + B + C + D + E + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
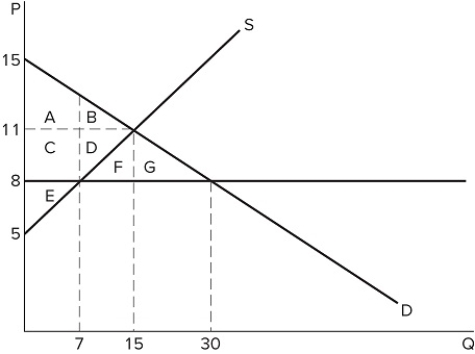 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent producer surplus?
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent producer surplus?A) C + D + E
B) C + D + F + G
C) E
D) A + C + E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
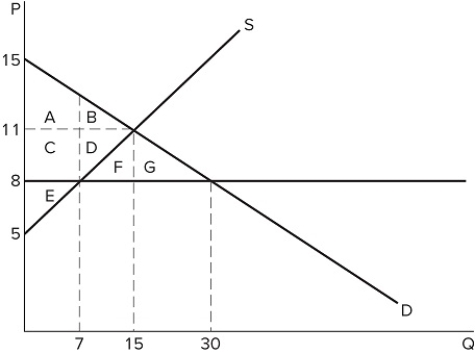 A price ceiling in the market shown in the graph would be non-binding if it were set at:
A price ceiling in the market shown in the graph would be non-binding if it were set at:A) $5.
B) $8.
C) $10.
D) $13.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
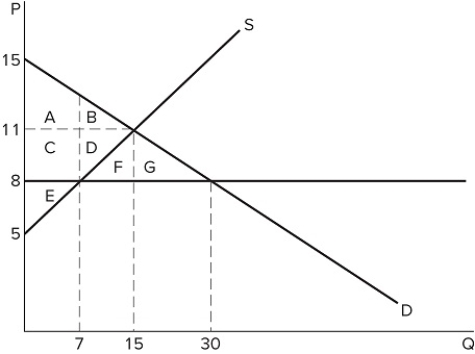 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent deadweight loss?
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent deadweight loss?A) F + G
B) B + D
C) E
D) B + D + F + G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
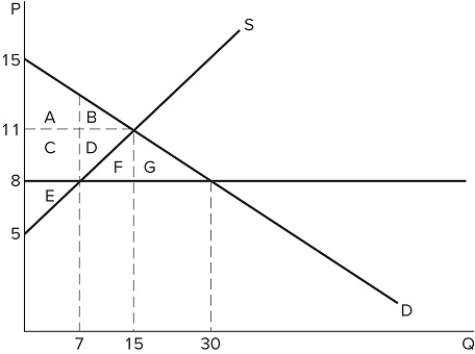 Which action could cause the price ceiling shown in the graph to become non-binding?
Which action could cause the price ceiling shown in the graph to become non-binding?A) An increase in demand (shift to the right)
B) A decrease in supply (shift to the left)
C) An increase in supply (shift to the right)
D) None of these would cause the price ceiling to become non-binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
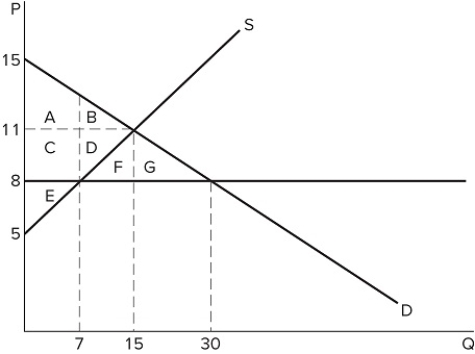 A price ceiling that is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph is:
A price ceiling that is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph is:A) non-binding and would not affect the market.
B) binding and would cause a shortage.
C) binding and would cause excess supply.
D) non-binding and would not prevent the market from reaching equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A price ceiling is non-binding when:
A) it is set above the equilibrium price.
B) it is set below the equilibrium price.
C) it reduces the output in a market.
D) it increases the output in a market.
A) it is set above the equilibrium price.
B) it is set below the equilibrium price.
C) it reduces the output in a market.
D) it increases the output in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
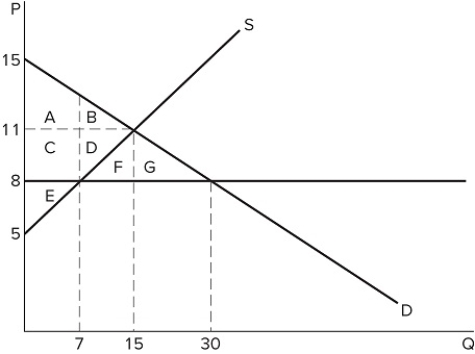 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:A) some surplus will be transferred from consumer to producer.
B) some surplus will be transferred from producer to consumer.
C) all consumers will be better off.
D) all producers will be better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
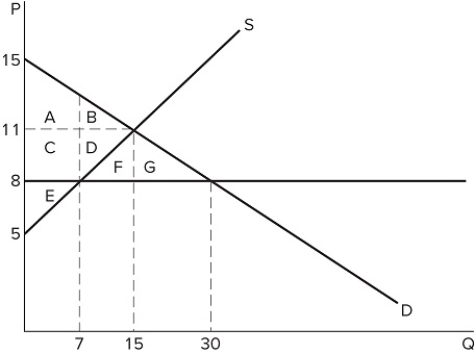 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:A) excess supply of 7 units will occur.
B) excess supply of 15 units will occur.
C) excess supply of 23 units will occur.
D) no excess supply will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
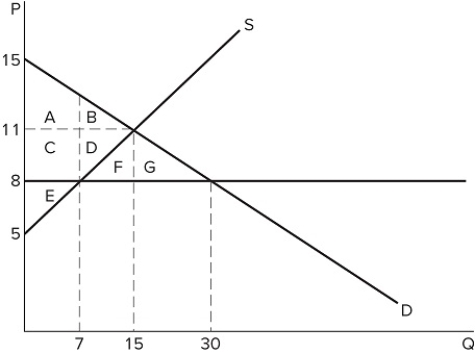 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent consumer surplus?
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent consumer surplus?A) A + C
B) A + B
C) A + B + C
D) A + B + C + D + F + G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
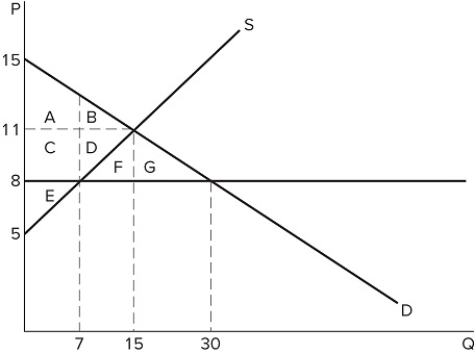 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market in the graph shown:
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market in the graph shown:A) some consumers will benefit because they pay a lower price.
B) producers will lose because they sell at a lower price.
C) the quantity traded in the market will fall.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
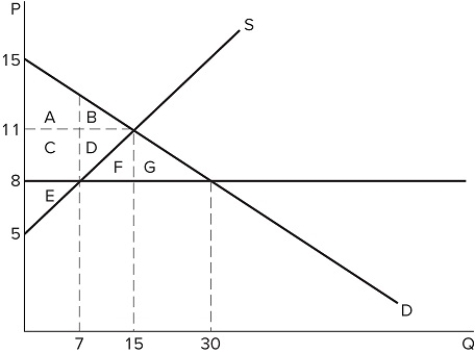 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph:A) a shortage of 7 units will occur.
B) a shortage of 15 units will occur.
C) a shortage of 23 units will occur.
D) a shortage of 8 units will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
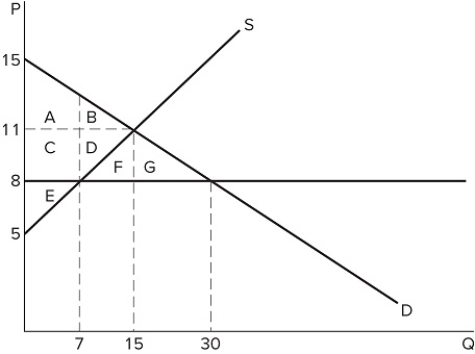 If a binding price ceiling is set in the market shown in the graph:
If a binding price ceiling is set in the market shown in the graph:A) quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied.
B) quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded.
C) the demand curve will have to shift.
D) the supply curve will have to shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
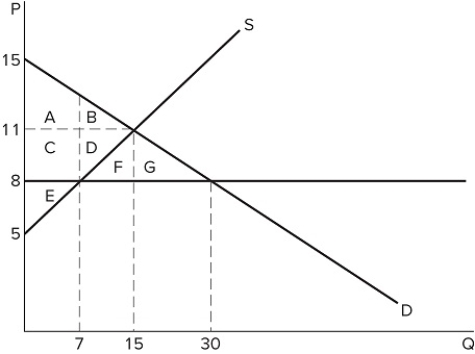 Which action could cause the price ceiling shown in the graph to become non-binding?
Which action could cause the price ceiling shown in the graph to become non-binding?A) An increase in demand (shift to the right)
B) A decrease in demand (shift to the left)
C) A decrease in supply (shift to the left)
D) None of these would cause the price ceiling to become non-binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
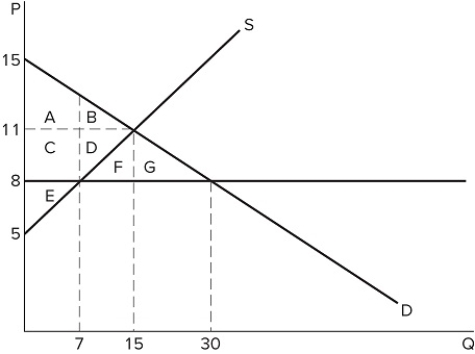 If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent the surplus that is transferred from producers to consumers?
If a price ceiling is set at $8 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent the surplus that is transferred from producers to consumers?A) C + D + F + G
B) C + D
C) F + G
D) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A binding price ceiling:
A) will cause quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
B) will increase total well-being.
C) will set a legal minimum price in a market.
D) will cause quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.
A) will cause quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
B) will increase total well-being.
C) will set a legal minimum price in a market.
D) will cause quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
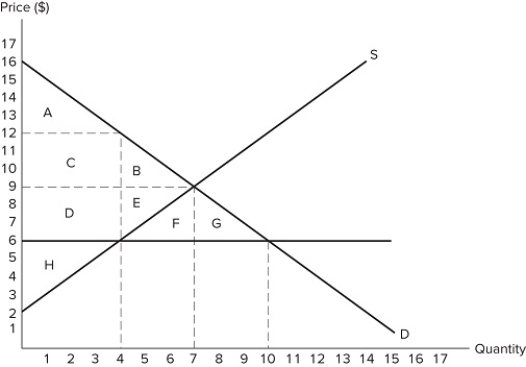 If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, what would positive analysis consider?
If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, what would positive analysis consider?A) Whether the surplus transferred from consumers to producers is greater than the consumer surplus lost.
B) Whether the producer surplus lost to deadweight loss is greater than the producer surplus gained from a higher price.
C) Whether the surplus transferred from producers to consumers is greater than the consumer surplus lost.
D) Whether the producer surplus lost due to lower prices is greater than the producer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
 If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, the policy was:
If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, the policy was:A) effective because consumers gained in surplus overall.
B) ineffective because some consumers lost surplus.
C) ineffective because consumers lost surplus overall.
D) effective because all consumers gained surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is a prominent argument against the use of price ceilings?
A) They are unfair.
B) They lead to an increase in surplus but a waste of society's resources.
C) They lead to a decrease in total surplus.
D) They raise corporate profits.
A) They are unfair.
B) They lead to an increase in surplus but a waste of society's resources.
C) They lead to a decrease in total surplus.
D) They raise corporate profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
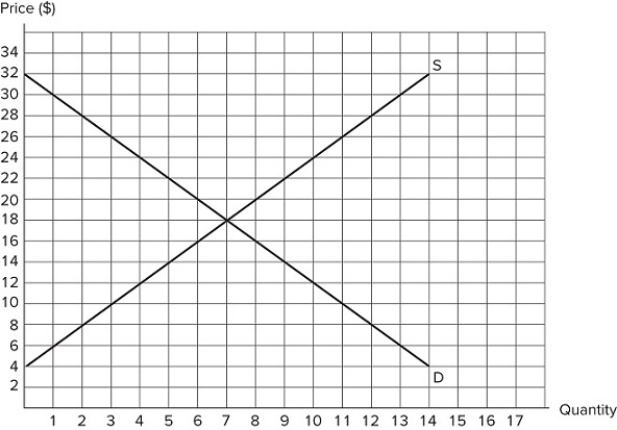 If a price ceiling of $14 is set in the market shown in the graph: QS appears to be incomplete.I. Total surplus will be $90.II. Deadweight loss will be $8.III. Producer surplus will be $25.
If a price ceiling of $14 is set in the market shown in the graph: QS appears to be incomplete.I. Total surplus will be $90.II. Deadweight loss will be $8.III. Producer surplus will be $25.A) I only
B) III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
 The graph shown best represents:
The graph shown best represents:A) a non-binding price ceiling.
B) a non-binding price floor.
C) a missing market.
D) the market for an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is an unintended consequence of price ceilings?
A) The loss of surplus always outweighs the benefits of the policy.
B) Non-price rationing must occur and can lead to bribes.
C) The transfer of surplus from producer to consumer rarely is recognized.
D) Producers will increase the quality of the goods sold.
A) The loss of surplus always outweighs the benefits of the policy.
B) Non-price rationing must occur and can lead to bribes.
C) The transfer of surplus from producer to consumer rarely is recognized.
D) Producers will increase the quality of the goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In order for a price floor to be binding, it must be set _______ the equilibrium price, and it will likely cause _______.
A) above; a shortage
B) below; a shortage
C) above; excess supply
D) below; excess supply
A) above; a shortage
B) below; a shortage
C) above; excess supply
D) below; excess supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
 The graph shown best represents:
The graph shown best represents:A) a non-binding price ceiling.
B) a non-binding price floor.
C) a missing market.
D) the market for an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A price floor is:
A) a legal maximum price.
B) a legal minimum price.
C) a legal maximum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
D) a legal minimum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
A) a legal maximum price.
B) a legal minimum price.
C) a legal maximum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.
D) a legal minimum quantity that can be sold at a particular price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How can one allocate a good that is undersupplied due to a binding price ceiling?
A) Offer it on a first-come, first-served basis.
B) Ration a certain quantity per household.
C) Give the good to the friends and family of the producers.
D) All of these are correct.
A) Offer it on a first-come, first-served basis.
B) Ration a certain quantity per household.
C) Give the good to the friends and family of the producers.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
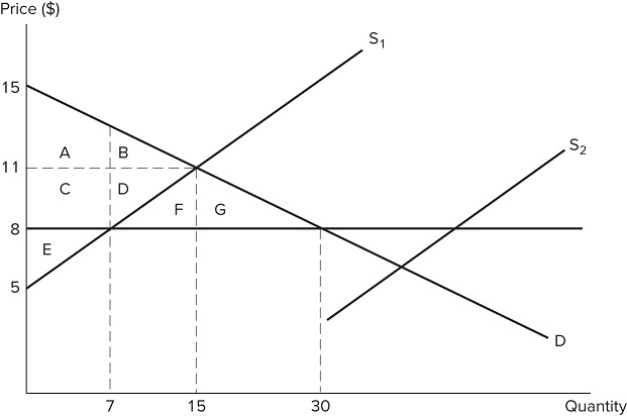 Suppose S1 represents the initial market supply in the graph shown. A price ceiling is then set at $8. If supply shifts from S1 to S2, what will occur?
Suppose S1 represents the initial market supply in the graph shown. A price ceiling is then set at $8. If supply shifts from S1 to S2, what will occur?A) The price ceiling will no longer be binding.
B) The price ceiling will prevent output from changing.
C) The size of the shortage will increase.
D) The market will not reach equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
 If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would conclude that the policy was:
If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would conclude that the policy was:A) effective because the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is greater than the surplus they lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
B) ineffective because the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
C) effective because the surplus lost by producers through lower prices is less than the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices.
D) ineffective because the amount of deadweight loss is greater than the surplus gained by consumers from lower prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
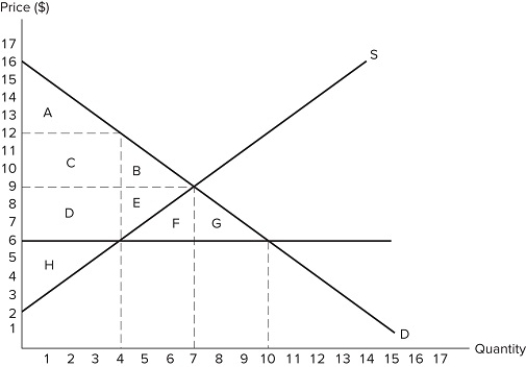 If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would conclude that the policy was:
If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then positive analysis would conclude that the policy was:A) effective because areas A + C are larger than areas B + D.
B) effective because area B is smaller than area D.
C) ineffective because area D is larger than area E.
D) ineffective because areas A + C + D are larger than areas B + E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
%media ch06_42_43. j p g %If a price ceiling of $10 is set in the market shown in the graph, the quantity exchanged will:
A) fall by 4 units.
B) rise by 4 units.
C) rise by 8 units.
D) not change.
A) fall by 4 units.
B) rise by 4 units.
C) rise by 8 units.
D) not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Because a price ceiling causes:
A) a shortage, some form of rationing must occur.
B) excess supply, some form of rationing must occur.
C) a shortage, the outcome will be efficient.
D) excess supply, the outcome will be inefficient.
A) a shortage, some form of rationing must occur.
B) excess supply, some form of rationing must occur.
C) a shortage, the outcome will be efficient.
D) excess supply, the outcome will be inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
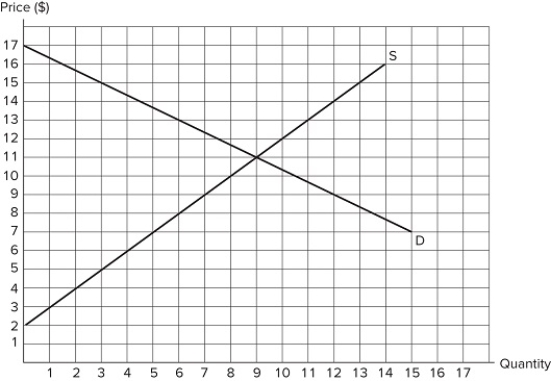 According to the market in the graph shown, at which of the following prices could a binding price ceiling be set?
According to the market in the graph shown, at which of the following prices could a binding price ceiling be set?A) $15
B) $11
C) $8
D) A binding price ceiling could not be set at any of these prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
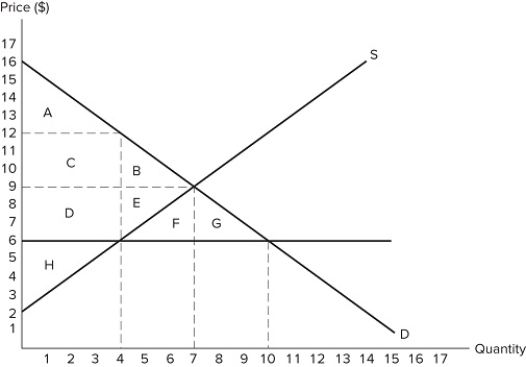 If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then normative analysis would conclude that the policy was:
If the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then normative analysis would conclude that the policy was:A) effective because the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
B) ineffective because the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
C) effective because the surplus lost by producers through lower prices is less than the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices.
D) There is no "right" conclusion to be reached (in a normative sense) because different people will have different opinions concerning what constitutes a better outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A binding price floor:
A) will cause quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.
B) will cause quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
C) will increase total well-being.
D) will set a legal maximum price in a market.
A) will cause quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.
B) will cause quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
C) will increase total well-being.
D) will set a legal maximum price in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
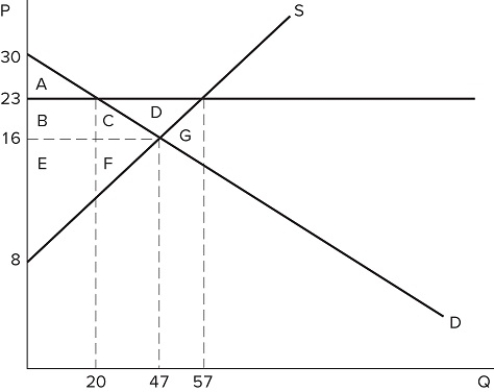 The graph shown best represents:
The graph shown best represents:A) a binding price ceiling.
B) a binding price floor.
C) a missing market.
D) the market for an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
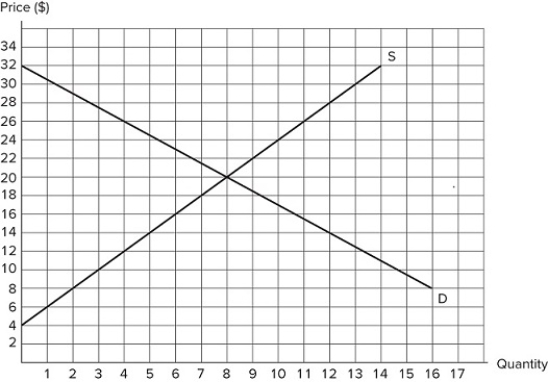 If a price ceiling of $12 is set in the market shown in the graph, what will consumer surplus be?
If a price ceiling of $12 is set in the market shown in the graph, what will consumer surplus be?A) $260
B) $130
C) $88
D) $60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
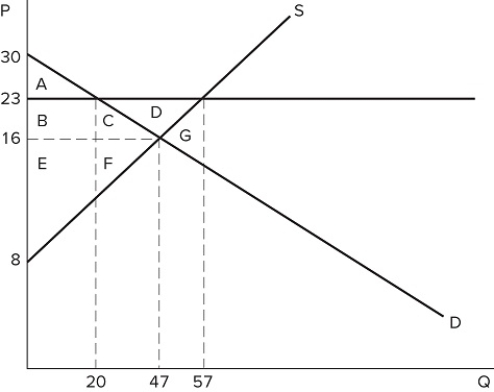
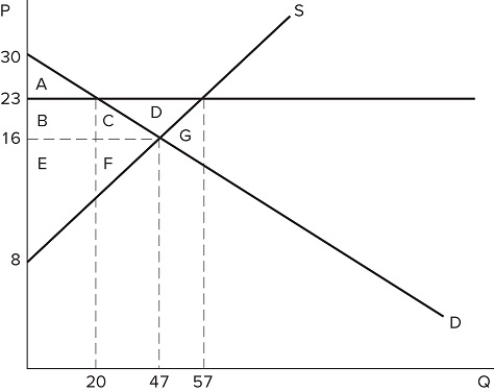 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:A) some surplus will be transferred from consumers to producers.
B) some surplus will be transferred from producers to consumers.
C) all producers will be better off.
D) all consumers will be better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
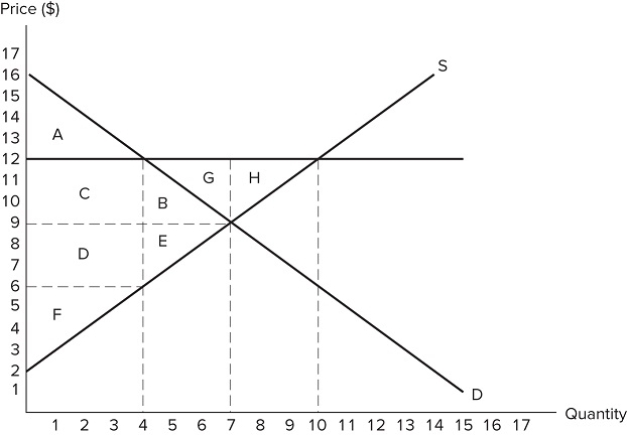 If the intended aim of the price floor set at $12, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then positive analysis would consider the policy to be:
If the intended aim of the price floor set at $12, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then positive analysis would consider the policy to be:A) effective if area C is larger than area E.
B) effective if areas E + B are larger than areas C + D + F.
C) ineffective if area B is larger than area E.
D) ineffective if areas E + B are larger than areas A + C + D + F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
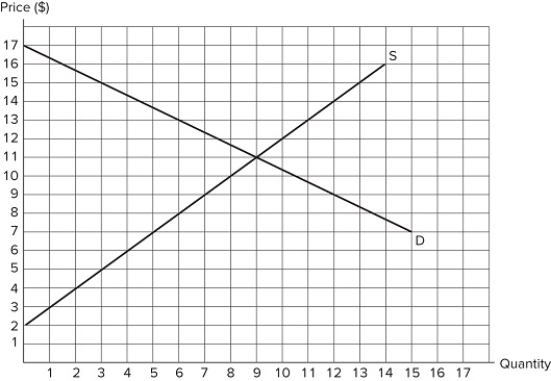 Suppose the market in the graph shown is in equilibrium. If a price floor is set at $13, the total number of units traded:
Suppose the market in the graph shown is in equilibrium. If a price floor is set at $13, the total number of units traded:A) falls by 5.
B) falls by 3.
C) increases by 2.
D) increases by 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
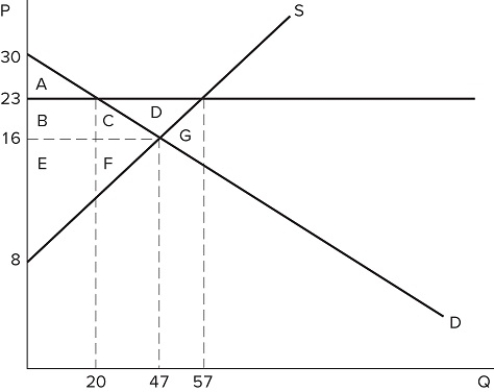 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:A) a shortage of 37 will occur.
B) a shortage of 10 will occur.
C) a shortage of 27 will occur.
D) no shortage will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
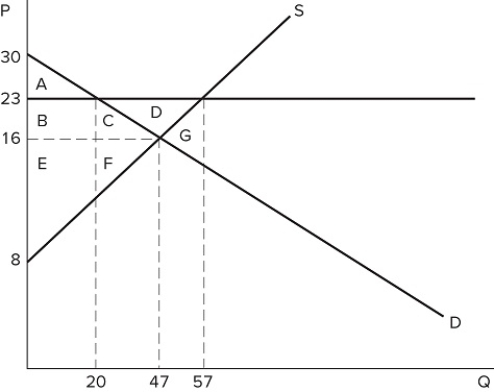 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:A) some consumers would lose because they will pay a higher price.
B) some producers would gain because they will sell at a higher price.
C) the quantity traded in the market would fall.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
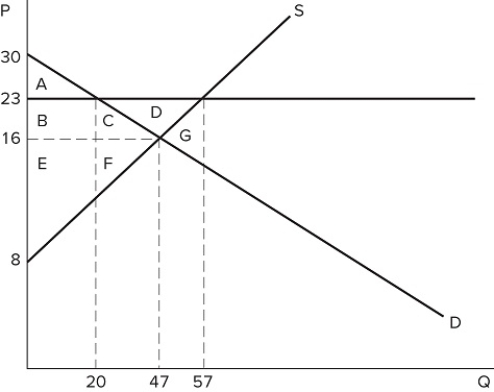 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent total surplus?
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent total surplus?A) A
B) B + C + E + F
C) A + B + E
D) A + B + C + E + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
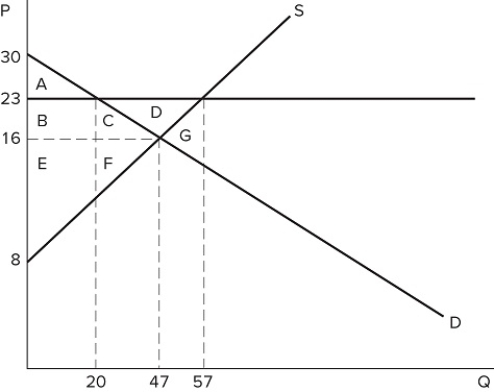 If a binding price floor were placed in the market shown in the graph:
If a binding price floor were placed in the market shown in the graph:A) quantity demanded would exceed quantity supplied.
B) quantity supplied would exceed quantity demanded.
C) the demand curve would have to shift.
D) the supply curve would have to shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
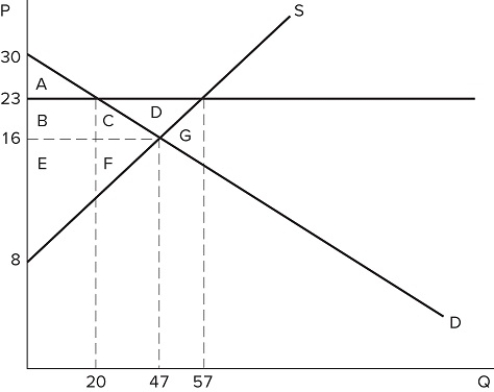 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, the total number of units traded will:
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, the total number of units traded will:A) fall by 20, relative to equilibrium.
B) fall by 27, relative to equilibrium.
C) fall by 37, relative to equilibrium.
D) rise by 10, relative to equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
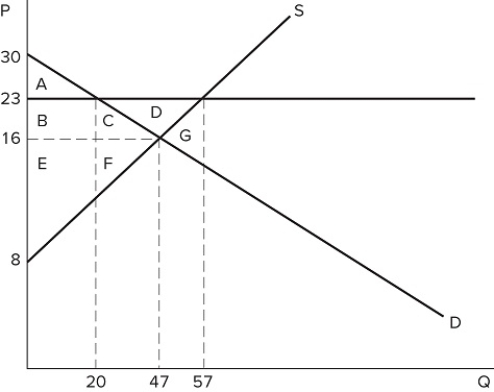 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent consumer surplus?
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent consumer surplus?A) A
B) A + B
C) A + B + C
D) A + B + C + D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
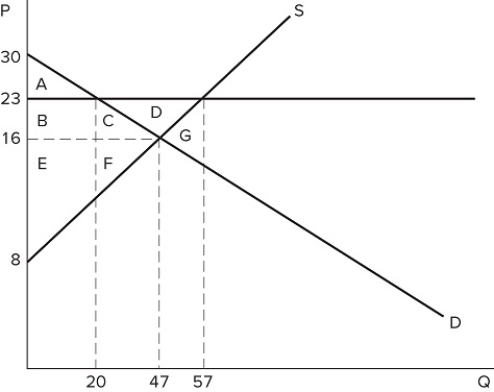 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent the surplus that is transferred from consumers to producers?
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent the surplus that is transferred from consumers to producers?A) B + C + D
B) B + C
C) C
D) B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
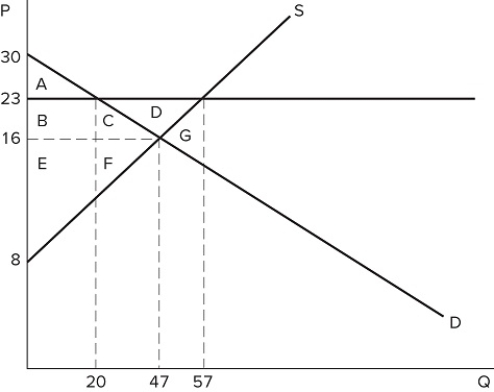 A price floor that is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph is:
A price floor that is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph is:A) binding and would cause a shortage.
B) non-binding and would not affect the market.
C) binding and would cause excess supply.
D) non-binding and would not prevent the market from reaching equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
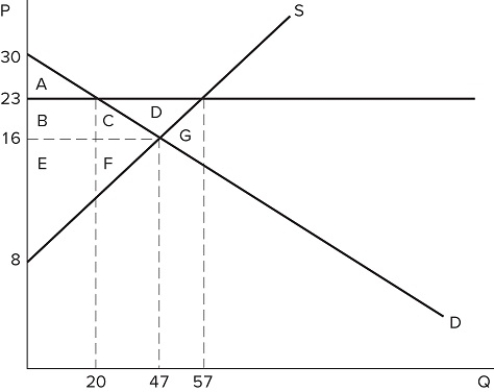 If the intended aim of the price floor set at $23, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then positive analysis would have us consider whether:
If the intended aim of the price floor set at $23, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then positive analysis would have us consider whether:A) the surplus transferred from producers to consumers is greater than the consumer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
B) the surplus transferred from consumers to producers is greater than the consumer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place.
C) the producer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place is greater than the producer surplus gained from a higher price.
D) the producer surplus lost due to lower prices is greater than the producer surplus lost due to fewer transactions taking place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
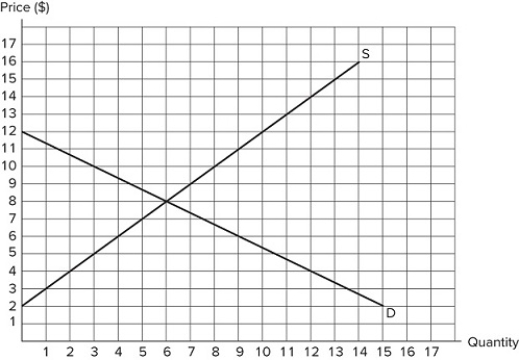 Suppose a price floor is set at $10 in the market shown in the graph. Which of the following statements is true?
Suppose a price floor is set at $10 in the market shown in the graph. Which of the following statements is true?A) A shortage of five units occurs
B) Excess supply of five units occurs
C) Total surplus increases
D) Deadweight loss falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
 According to the market in the graph shown, at which of the following prices could a binding price floor be set?
According to the market in the graph shown, at which of the following prices could a binding price floor be set?A) $10
B) $6
C) $8
D) A binding price floor could not be set at any of these prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
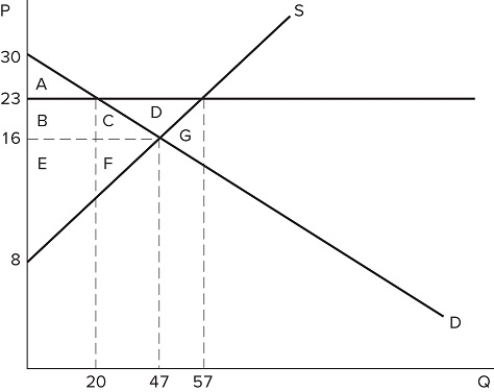 A price floor in the market shown in the graph would be non-binding if it were set at:
A price floor in the market shown in the graph would be non-binding if it were set at:A) $30.
B) $23.
C) $16.
D) Any of these prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
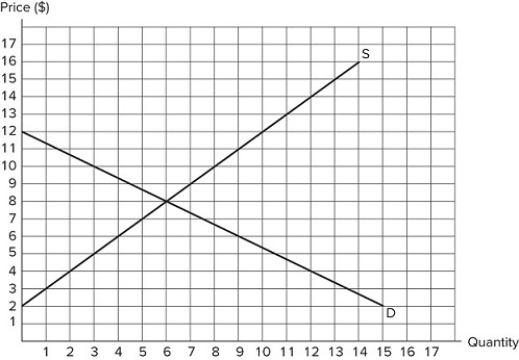 Suppose a price floor is set at $10 in the market shown in the graph. Which of the following statements is true?I. All consumers are worse off due to the higher price.II. All producers are better off, because producer surplus increases.III. The economy as a whole is worse off, because total surplus falls.
Suppose a price floor is set at $10 in the market shown in the graph. Which of the following statements is true?I. All consumers are worse off due to the higher price.II. All producers are better off, because producer surplus increases.III. The economy as a whole is worse off, because total surplus falls.A) II only
B) I and III only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
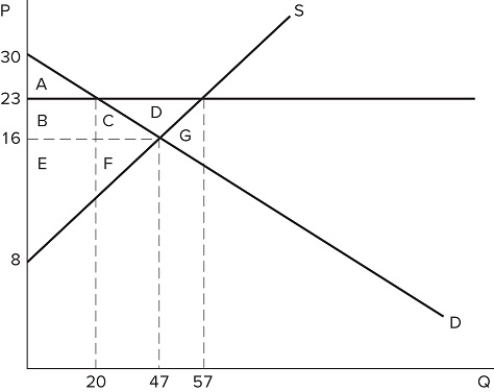 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which areas would represent producer surplus?
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which areas would represent producer surplus?A) B + C + D + F
B) B + E
C) B + C + D
D) B + C + E + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
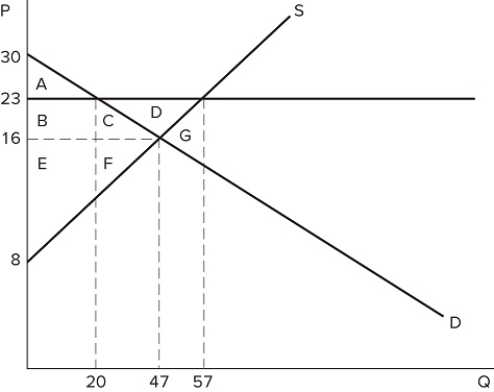 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent deadweight loss?
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph, which area(s) would represent deadweight loss?A) C + F
B) C + D + F
C) G
D) B + C + E + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
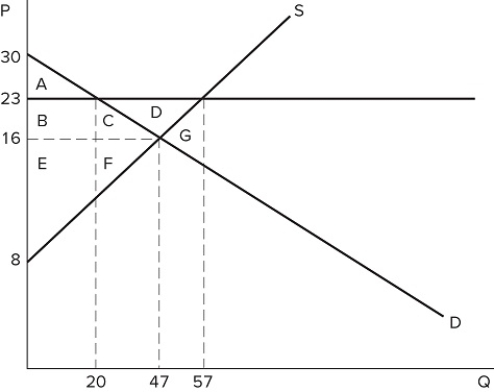 If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:
If a price floor is set at $23 in the market shown in the graph:A) excess supply of 27 will occur.
B) excess supply of 37 will occur.
C) excess supply of 10 will occur.
D) no excess supply will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
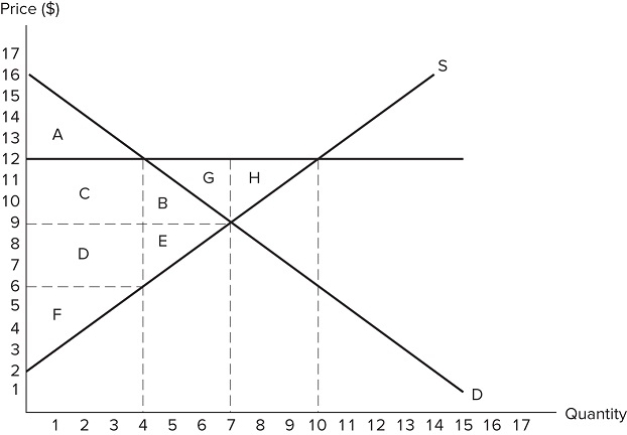 If the intended aim of the price floor set at $12, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then normative analysis would conclude that the policy was:
If the intended aim of the price floor set at $12, as shown in the graph, was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then normative analysis would conclude that the policy was:A) effective because the surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
B) ineffective because the surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
C) effective because the surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus lost by consumers through higher prices.
D) There is no "right" conclusion to be reached in a normative sense, because normative analysis is not based on value judgements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 171 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



