Deck 3: Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/170
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Markets
1
The buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service make up what we call a:
A) market.
B) store.
C) mall.
D) negotiators.
A) market.
B) store.
C) mall.
D) negotiators.
market.
2
Consider the market for tacos. To figure out which buyers and sellers we should include in our description of this market, economists will consider:
A) their physical proximity.
B) the context.
C) their preferences.
D) the income levels.
A) their physical proximity.
B) the context.
C) their preferences.
D) the income levels.
the context.
3
In a _____ economy, private individuals (as opposed to a central planner) make decisions.
A) market
B) government controlled
C) socialist
D) barter
A) market
B) government controlled
C) socialist
D) barter
market
4
Which of the following is the best example of a standardized good?
A) Corn
B) A handbag
C) An autographed baseball
D) Breakfast cereal
A) Corn
B) A handbag
C) An autographed baseball
D) Breakfast cereal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The term market refers to:
A) a physical location where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods for money.
B) the buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service, not to a physical location.
C) a location where buyers go to fulfill their wants and needs.
D) a hypothetical place of exchange.
A) a physical location where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods for money.
B) the buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service, not to a physical location.
C) a location where buyers go to fulfill their wants and needs.
D) a hypothetical place of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A perfectly competitive market is one in which _____ buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service.
A) fully informed, price-taking
B) fully informed, price-making
C) uninformed, price-taking
D) uninformed, price-making
A) fully informed, price-taking
B) fully informed, price-making
C) uninformed, price-taking
D) uninformed, price-making

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What are transaction costs?
A) The costs incurred by buyers and sellers in agreeing to and executing a sale of goods or services.
B) The costs that the government must pay to allow for an exchange.
C) The costs incurred by buyers and sellers in agreeing to and executing a purchase of goods or services, excluding transportation costs.
D) The costs that the government incurs to create a structured market for the exchange of goods and services.
A) The costs incurred by buyers and sellers in agreeing to and executing a sale of goods or services.
B) The costs that the government must pay to allow for an exchange.
C) The costs incurred by buyers and sellers in agreeing to and executing a purchase of goods or services, excluding transportation costs.
D) The costs that the government incurs to create a structured market for the exchange of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For almost all goods, the:
A) lower the price goes, the higher the quantity demanded.
B) higher the price goes, the more luxurious it is.
C) lower the price goes, the higher demand is.
D) higher the price goes, the higher the quantity demanded.
A) lower the price goes, the higher the quantity demanded.
B) higher the price goes, the more luxurious it is.
C) lower the price goes, the higher demand is.
D) higher the price goes, the higher the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The four important characteristics that define a perfectly competitive market are:
A) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
B) standardized information, a finished good, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.
C) a standardized good, the same information for buyers and sellers, low transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
D) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.
A) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
B) standardized information, a finished good, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.
C) a standardized good, the same information for buyers and sellers, low transaction costs, and price-taking participants.
D) a standardized good, full information, no transaction costs, and price-making participants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why is the market for used cars not considered to be perfectly competitive?
A) There is complete information.
B) The buyers are not price takers.
C) The good is standardized.
D) There are always very low transaction costs.
A) There is complete information.
B) The buyers are not price takers.
C) The good is standardized.
D) There are always very low transaction costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In economic terminology, a buyer or seller who cannot affect the market price is called a:
A) price taker.
B) price maker.
C) price setter.
D) price signaler.
A) price taker.
B) price maker.
C) price setter.
D) price signaler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Demand describes how much of something people:
A) are willing and able to buy at alternative prices under certain circumstances.
B) want, but may not necessarily be able, to buy under certain circumstances.
C) are willing and able to sell under certain circumstances.
D) are able to buy, but might not want to buy under certain circumstances.
A) are willing and able to buy at alternative prices under certain circumstances.
B) want, but may not necessarily be able, to buy under certain circumstances.
C) are willing and able to sell under certain circumstances.
D) are able to buy, but might not want to buy under certain circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
We study the simple model of competitive markets because it helps to:
A) provide useful insights to markets that are not perfectly competitive.
B) show how the government controls the economy.
C) indicate whether buyers or sellers matter more.
D) show how poorly the economy actually functions.
A) provide useful insights to markets that are not perfectly competitive.
B) show how the government controls the economy.
C) indicate whether buyers or sellers matter more.
D) show how poorly the economy actually functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A price taker is a buyer or seller who:
A) cannot affect the market price.
B) takes the market price and chooses to increase or decrease it.
C) takes prices in the area and averages them together to set the price for his or her good.
D) can affect the market price only when collaborating with other buyers or sellers.
A) cannot affect the market price.
B) takes the market price and chooses to increase or decrease it.
C) takes prices in the area and averages them together to set the price for his or her good.
D) can affect the market price only when collaborating with other buyers or sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Members who shop at a warehouse store, such as Sam's Club or Costco, pay very low prices on the goods and services they buy. Do these sorts of customers incur transaction costs?
A) Yes, because they must be members to shop at the store.
B) No, because they pay prices that are lower than at any other location.
C) Yes, because they must buy a product in bulk.
D) No, because they can return purchases for any reason.
A) Yes, because they must be members to shop at the store.
B) No, because they pay prices that are lower than at any other location.
C) Yes, because they must buy a product in bulk.
D) No, because they can return purchases for any reason.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The law of demand describes the:
A) inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) direct relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C) inverse relationship between income and quantity demanded.
D) direct relationship between income and quantity demanded.
A) inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) direct relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C) inverse relationship between income and quantity demanded.
D) direct relationship between income and quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The amount of a particular good or service that buyers in a market will purchase at a given price during a specified period is called:
A) quantity demanded.
B) quantity supplied.
C) demand.
D) supply.
A) quantity demanded.
B) quantity supplied.
C) demand.
D) supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements describes a standardized good or service?
A) Any two units have the same features and are interchangeable.
B) Any two units have similar features and could be considered close substitutes.
C) Any two units have different, unique features.
D) Any two units are economically unique with distinguishable characteristics.
A) Any two units have the same features and are interchangeable.
B) Any two units have similar features and could be considered close substitutes.
C) Any two units have different, unique features.
D) Any two units are economically unique with distinguishable characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The best example of a perfectly competitive market would be the market for:
A) grain.
B) shoes.
C) computers.
D) cameras.
A) grain.
B) shoes.
C) computers.
D) cameras.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Perfectly competitive markets are:
A) the most common type of market in our economy.
B) hard to find in a real-world setting.
C) made up principally by consumer goods.
D) typically found in industrial sectors of our economy.
A) the most common type of market in our economy.
B) hard to find in a real-world setting.
C) made up principally by consumer goods.
D) typically found in industrial sectors of our economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
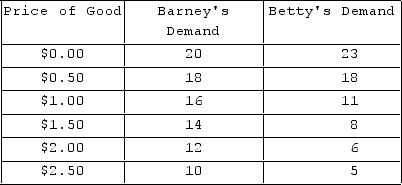 The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. What is the equilibrium price in this market?
The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. What is the equilibrium price in this market?A) $0.50
B) $1.50
C) $2.00
D) The equilibrium price cannot be determined without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ceteris paribus is:
A) the Latin term for "all other things being the same."
B) only necessary for the definition of the law of demand.
C) often used by economists to isolate the effect of a multiple changes that are important.
D) the Latin term for "as things change only consider these changes".
A) the Latin term for "all other things being the same."
B) only necessary for the definition of the law of demand.
C) often used by economists to isolate the effect of a multiple changes that are important.
D) the Latin term for "as things change only consider these changes".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a non-price determinant of demand?
A) Consumer preferences
B) Income of the consumers
C) The number of sellers in the market
D) The prices of related goods
A) Consumer preferences
B) Income of the consumers
C) The number of sellers in the market
D) The prices of related goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When graphing the demand curve:
A) quantity goes on the horizontal axis and price goes on the vertical axis.
B) quantity goes on the vertical axis and price goes on the horizontal axis.
C) both quantity and price go on the horizontal axis.
D) it doesn't matter which axis price and quantity are placed on.
A) quantity goes on the horizontal axis and price goes on the vertical axis.
B) quantity goes on the vertical axis and price goes on the horizontal axis.
C) both quantity and price go on the horizontal axis.
D) it doesn't matter which axis price and quantity are placed on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
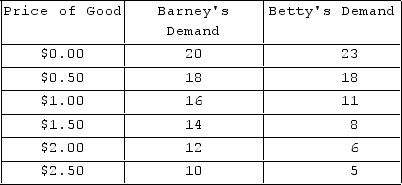 The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. What can be said of Betty and Barney's demands for this good?
The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. What can be said of Betty and Barney's demands for this good?A) Both of their demands follow the law of demand.
B) Barney's demand follows the law of demand, but Betty's does not.
C) Betty's demand follows the law of demand, but Barney's does not.
D) Neither of their demands follows the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The "Made in the USA" campaign was popularized by unions in an effort to influence which determinant of demand?
A) Incomes
B) Consumer preferences
C) Expectations of future prices
D) Prices of related goods
A) Incomes
B) Consumer preferences
C) Expectations of future prices
D) Prices of related goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
On the first day of school, Jackie notices many of her classmates are wearing Converse sneakers. Ever the fashionista, this will likely affect:
A) Jackie's income, as she will now buy Converse sneakers and will have less to spend on other goods.
B) Jackie's preferences for Converse sneakers, since she feels as though she needs them now.
C) Jackie's expectations of future prices, since the price of Converse sneakers will likely increase due to their popularity.
D) the prices of related goods, since other sneakers will be less popular and thus their prices will decrease.
A) Jackie's income, as she will now buy Converse sneakers and will have less to spend on other goods.
B) Jackie's preferences for Converse sneakers, since she feels as though she needs them now.
C) Jackie's expectations of future prices, since the price of Converse sneakers will likely increase due to their popularity.
D) the prices of related goods, since other sneakers will be less popular and thus their prices will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Ren loves to go to the movie theater, and he just learned that he can buy a ticket at a discounted price using his student ID. Ren now sees movies at the theater even more frequently. Which of the following factors of demand caused the change in Ren's behavior?
A) Income
B) Price
C) Consumer preferences
D) Number of buyers
A) Income
B) Price
C) Consumer preferences
D) Number of buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An article about how coffee boosts critical thinking is likely to affect which determinant of demand?
A) Incomes
B) Consumer preferences
C) Number of sellers in the market
D) Price
A) Incomes
B) Consumer preferences
C) Number of sellers in the market
D) Price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The demand schedule assumes that factors other than price:
A) remain the same.
B) must also be in the table.
C) remain separate in the table.
D) change as price changes.
A) remain the same.
B) must also be in the table.
C) remain separate in the table.
D) change as price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A demand schedule is a _____ that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers are willing to purchase at various _____.
A) table; prices
B) graph; prices
C) table; income levels
D) line; prices
A) table; prices
B) graph; prices
C) table; income levels
D) line; prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A non-price determinant of demand refers to something:
A) other than demand that affects the price.
B) other than the price that affects demand.
C) that determines how large a role price plays in the demand decision.
D) that determines how prices are affected by income.
A) other than demand that affects the price.
B) other than the price that affects demand.
C) that determines how large a role price plays in the demand decision.
D) that determines how prices are affected by income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The demand curve:
A) represents consumers' willingness, but not ability, to buy.
B) shows the highest amount consumers are able to pay for a specific quantity.
C) visually displays the demand schedule.
D) represents consumers' ability, but not willingness, to buy.
A) represents consumers' willingness, but not ability, to buy.
B) shows the highest amount consumers are able to pay for a specific quantity.
C) visually displays the demand schedule.
D) represents consumers' ability, but not willingness, to buy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
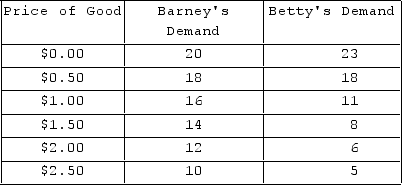 The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. If the price of the good is $0.50, total demand by Betty and Barney will be:
The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. If the price of the good is $0.50, total demand by Betty and Barney will be:A) 18 units.
B) 36 units.
C) 75 units.
D) 47 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
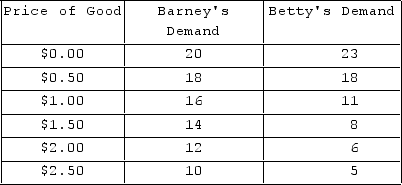 The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. At a price of $1.00, how much of the good will be demanded by Betty?
The table shows individual demand schedules for a market. At a price of $1.00, how much of the good will be demanded by Betty?A) 16
B) 11
C) 46
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The demand curve is a(n) _____ line that reflects the _____ relationship between price and quantity.
A) downward-sloping; inverse
B) upward-sloping; inverse
C) downward-sloping; positive
D) upward-sloping; direct
A) downward-sloping; inverse
B) upward-sloping; inverse
C) downward-sloping; positive
D) upward-sloping; direct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The law of demand states that, all else held equal:
A) quantity demanded rises as price falls.
B) quantity demanded rises as price rises.
C) quantity demanded rises as income rises.
D) demand rises as price falls.
A) quantity demanded rises as price falls.
B) quantity demanded rises as price rises.
C) quantity demanded rises as income rises.
D) demand rises as price falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The demand curve represents the relationship between _____, with everything else held constant.
A) price and quantity demanded
B) income and quantity demanded
C) consumer preferences and quantity demanded
D) income and price demanded
A) price and quantity demanded
B) income and quantity demanded
C) consumer preferences and quantity demanded
D) income and price demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A demand curve is a graph that:
A) visually displays the demand schedule.
B) depicts various price-quantity combinations of a good for a seller.
C) shows the quantities demanded by consumers of a particular good or service at various incomes.
D) shows the quantities demanded by consumers of a particular good or service at one price.
A) visually displays the demand schedule.
B) depicts various price-quantity combinations of a good for a seller.
C) shows the quantities demanded by consumers of a particular good or service at various incomes.
D) shows the quantities demanded by consumers of a particular good or service at one price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers are willing to purchase at various prices is known as a:
A) demand schedule.
B) demand figure.
C) demand curve.
D) demand graph.
A) demand schedule.
B) demand figure.
C) demand curve.
D) demand graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A decrease in the price of spaghetti noodles is likely to cause a(n) _____ in the demand for penne pasta, due to a change in the price of a _____.
A) increase; complementary good
B) increase; substitute good
C) decrease; complementary good
D) decrease; substitute good
A) increase; complementary good
B) increase; substitute good
C) decrease; complementary good
D) decrease; substitute good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Demand for Shell gasoline will increase if the price of:
A) motor vehicles increases.
B) BP gasoline increases.
C) BP gasoline decreases.
D) Shell gasoline decreases.
A) motor vehicles increases.
B) BP gasoline increases.
C) BP gasoline decreases.
D) Shell gasoline decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The city of Provincetown is a very popular spot for tourism during the summer months. What would we expect to occur in this town?
A) The demand for normal goods would increase each summer.
B) The demand for normal goods would decrease each summer.
C) The prices of all normal goods would decrease each summer.
D) The demand curve for normal goods would shift to the left.
A) The demand for normal goods would increase each summer.
B) The demand for normal goods would decrease each summer.
C) The prices of all normal goods would decrease each summer.
D) The demand curve for normal goods would shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in the price of Heinz ketchup is likely to cause a(n) _____ in the demand for Hunt's ketchup, due to a change in _____.
A) increase; consumer preferences
B) increase; the price of a substitute good
C) decrease; consumer preferences
D) increase; the price of a complementary good
A) increase; consumer preferences
B) increase; the price of a substitute good
C) decrease; consumer preferences
D) increase; the price of a complementary good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
We say that goods are substitutes when they:
A) serve similar-enough purposes that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other.
B) are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make a consumer more likely to purchase the other.
C) can replace something consumers typically purchase at a significantly lower price.
D) change a consumer's preferences for a good or service.
A) serve similar-enough purposes that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other.
B) are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make a consumer more likely to purchase the other.
C) can replace something consumers typically purchase at a significantly lower price.
D) change a consumer's preferences for a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Junie is shopping for dinner. She notices that hamburgers are on sale, so she puts the hamburgers in her cart instead of the hot dogs she originally came to the store to buy. She then heads over to the bread aisle to pick up hamburger buns. The change in Junie's demand for hamburger buns is due to a change in:
A) the price of related goods.
B) Junie's income.
C) Junie's preferences.
D) Junie's expectation of future prices.
A) the price of related goods.
B) Junie's income.
C) Junie's preferences.
D) Junie's expectation of future prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The most likely complementary good for cereal would be:
A) a bagel.
B) milk.
C) pizza.
D) a sub sandwich.
A) a bagel.
B) milk.
C) pizza.
D) a sub sandwich.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The city of Burlington experiences very high temperatures each summer and very low temperatures each winter. We would expect the demand for ice cream to:
A) increase constantly.
B) decrease each summer and increase each winter.
C) increase each summer and decrease each winter.
D) decrease constantly.
A) increase constantly.
B) decrease each summer and increase each winter.
C) increase each summer and decrease each winter.
D) decrease constantly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The most likely substitute good for cereal would be:
A) a bagel.
B) milk.
C) pizza.
D) a hot dog.
A) a bagel.
B) milk.
C) pizza.
D) a hot dog.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A decrease in the price of ice cream is likely to cause a(n) _____ in the demand for ice cream cones, due to a change in _____.
A) increase; the price of a complementary good
B) increase; the price of a substitute good
C) increase; consumer preferences
D) decrease; the price of a related good
A) increase; the price of a complementary good
B) increase; the price of a substitute good
C) increase; consumer preferences
D) decrease; the price of a related good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The demand for Snickers candy bars will decrease if:
A) the price of Snickers candy bars decreases.
B) a news story claims 95 percent of all geniuses eat at least one Snickers candy bar a day.
C) the price of Milky Way candy bars (a substitute) decreases.
D) the price of Milky Way candy bars (a substitute) increases.
A) the price of Snickers candy bars decreases.
B) a news story claims 95 percent of all geniuses eat at least one Snickers candy bar a day.
C) the price of Milky Way candy bars (a substitute) decreases.
D) the price of Milky Way candy bars (a substitute) increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Oliver just brought home a new kitten. We could expect Oliver's demand for:
A) cat toys, a complementary good, to increase.
B) cat toys, a complementary good, to decrease.
C) dog toys, a substitute good, to increase.
D) dog toys, a substitute good, to decrease.
A) cat toys, a complementary good, to increase.
B) cat toys, a complementary good, to decrease.
C) dog toys, a substitute good, to increase.
D) dog toys, a substitute good, to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Bob just got laid off from his job and now has no income. What can we assume about his demand?
A) His demand for normal goods will increase.
B) His demand for inferior goods will increase.
C) His demand for inferior goods will decrease.
D) His demand for normal goods will stay the same.
A) His demand for normal goods will increase.
B) His demand for inferior goods will increase.
C) His demand for inferior goods will decrease.
D) His demand for normal goods will stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The most likely complementary good for hot dogs would be:
A) ketchup.
B) burgers.
C) tacos.
D) pizza.
A) ketchup.
B) burgers.
C) tacos.
D) pizza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose John just won the Mega Millions lottery jackpot. What can we assume about his demand?
A) His demand for normal goods will increase.
B) His demand for inferior goods will increase.
C) His demand for normal goods will decrease.
D) His demand for normal goods will stay the same.
A) His demand for normal goods will increase.
B) His demand for inferior goods will increase.
C) His demand for normal goods will decrease.
D) His demand for normal goods will stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
After getting a raise at work, Tiana now regularly buys steak instead of hamburger. Based on this behavior, what can we assume about these goods for Tiana?
A) Steak is a normal good and hamburger is an inferior good.
B) Steak is an inferior good and hamburger is a normal good.
C) Steak and hamburger are complementary goods.
D) Steak and hamburger are normal goods.
A) Steak is a normal good and hamburger is an inferior good.
B) Steak is an inferior good and hamburger is a normal good.
C) Steak and hamburger are complementary goods.
D) Steak and hamburger are normal goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An increase in the price of butter is likely to cause the demand for:
A) olive oil to increase.
B) olive oil to decrease.
C) butter to increase.
D) butter to decrease.
A) olive oil to increase.
B) olive oil to decrease.
C) butter to increase.
D) butter to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Jan heads to the store to buy burgers for dinner. Seeing a sale on hot dogs, she buys those instead. The change in her demand for burgers is due to which factor?
A) Consumer preferences
B) Income
C) Prices of related goods
D) Number of buyers
A) Consumer preferences
B) Income
C) Prices of related goods
D) Number of buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
We say that goods are complements when they:
A) serve similar-enough purposes that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other.
B) are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make a consumer more likely to purchase the other.
C) can replace something consumers typically purchase at a significantly lower price.
D) change a consumer's preferences for a good or service.
A) serve similar-enough purposes that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other.
B) are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make a consumer more likely to purchase the other.
C) can replace something consumers typically purchase at a significantly lower price.
D) change a consumer's preferences for a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The most likely substitute good for hot dogs would be:
A) ketchup.
B) burgers.
C) potato chips.
D) a plate.
A) ketchup.
B) burgers.
C) potato chips.
D) a plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
With the baby boomer generation hitting the retirement age, waiting lists to get into nursing homes are on the rise. In this situation, we could reasonably expect the demand for geriatric care to:
A) increase due to the number of buyers increasing.
B) decrease due to the number of buyers increasing.
C) increase due to expectations of future prices.
D) decrease due to expectations of future prices.
A) increase due to the number of buyers increasing.
B) decrease due to the number of buyers increasing.
C) increase due to expectations of future prices.
D) decrease due to expectations of future prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following would not affect an individual's demand?
A) Prices of related goods
B) The individual's preferences
C) The individual's income
D) The costs of inputs
A) Prices of related goods
B) The individual's preferences
C) The individual's income
D) The costs of inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose the demand for socks has decreased. This change can be shown graphically as a:
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A news report states that the housing market is making a comeback and that house prices are on the rise. This information is likely to:
A) increase the demand for houses due to a change in expectations of future prices.
B) decrease the demand for houses due to a change in expectations of future prices.
C) have no effect on the current housing market, but will increase the demand for houses in the future.
D) have no effect on the demand for houses, but it will decrease the supply.
A) increase the demand for houses due to a change in expectations of future prices.
B) decrease the demand for houses due to a change in expectations of future prices.
C) have no effect on the current housing market, but will increase the demand for houses in the future.
D) have no effect on the demand for houses, but it will decrease the supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose the demand for chicken has increased. This change can be shown graphically as a:
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Ray's company just announced that all employees will be receiving a 5 percent pay cut in order to avoid the company shutting down. Ray's demand for coffee, a normal good, will likely _____ and his demand curve will _____.
A) decrease; shift to the right
B) decrease; shift to the left
C) increase; shift to the right
D) increase; shift to the left
A) decrease; shift to the right
B) decrease; shift to the left
C) increase; shift to the right
D) increase; shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose the price of dog collars has decreased and all other variables have remained constant. This change can be shown graphically as a:
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
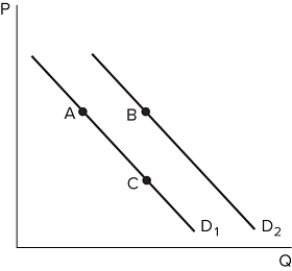 Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A shift from A to B might be caused by:
Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A shift from A to B might be caused by:A) an increase in price.
B) a decrease in price.
C) an increase in income.
D) a decrease in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
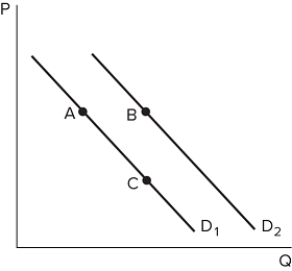 Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A movement from A to C might be caused by:
Suppose the graph shown depicts the demand for a normal good. A movement from A to C might be caused by:A) an increase in price.
B) a decrease in price.
C) an increase in income.
D) a decrease in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A decrease in the price of spaghetti is likely to cause:
A) a movement to the right along the demand curve for spaghetti.
B) an inward shift of the demand curve for spaghetti.
C) an outward shift of the demand curve for spaghetti.
D) a movement to the left along the demand curve for spaghetti.
A) a movement to the right along the demand curve for spaghetti.
B) an inward shift of the demand curve for spaghetti.
C) an outward shift of the demand curve for spaghetti.
D) a movement to the left along the demand curve for spaghetti.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A department store announces that its annual tent sale is happening next week. What affect will this have on your current demand for a coat from that department store?
A) Your demand will increase because of an income constraint.
B) Your demand will increase because of your expectations about the price of the coat next week.
C) Your demand will decrease because of an income constraint.
D) Your demand will decrease because of your expectations about the price of the coat next week.
A) Your demand will increase because of an income constraint.
B) Your demand will increase because of your expectations about the price of the coat next week.
C) Your demand will decrease because of an income constraint.
D) Your demand will decrease because of your expectations about the price of the coat next week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
As part of recent cutbacks at his company, Paul just accepted a 10percent cut in pay. Now he brews coffee at home instead of stopping at Starbucks every day. Based on this behavior, what can we assume about these goods for Paul?
A) Home-brewed coffee is a normal good and Starbucks coffee is an inferior good.
B) Home-brewed coffee and Starbucks coffee are normal goods.
C) Home-brewed coffee will become a normal good over time.
D) Home-brewed coffee is an inferior good and Starbucks coffee is a normal good.
A) Home-brewed coffee is a normal good and Starbucks coffee is an inferior good.
B) Home-brewed coffee and Starbucks coffee are normal goods.
C) Home-brewed coffee will become a normal good over time.
D) Home-brewed coffee is an inferior good and Starbucks coffee is a normal good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An expectation that the price of a good will increase in the future is likely to:
A) increase current demand.
B) decrease current demand.
C) have no impact on current demand.
D) only affect the seller's decisions.
A) increase current demand.
B) decrease current demand.
C) have no impact on current demand.
D) only affect the seller's decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
After getting a raise at work, Gustavo now regularly buys steak instead of chicken. Which factor of demand has influenced Gustavo's demand for steak?
A) Price of a substitute good
B) Price of a complementary good
C) Income
D) Preferences
A) Price of a substitute good
B) Price of a complementary good
C) Income
D) Preferences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose the price of house paint, a normal good, has increased. This change can be shown graphically as a:
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.
A) shift in the demand curve to the right.
B) shift in the demand curve to the left.
C) movement along the demand curve to the right.
D) movement along the demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Yang just got a big promotion at work, which includes a sizable pay increase. Yang's demand for ramen noodles, an inferior good, will likely _____ and his demand curve will _____.
A) decrease; shift to the right
B) decrease; shift to the left
C) increase; shift to the right
D) decrease; not move, although there will be movement along the curve
A) decrease; shift to the right
B) decrease; shift to the left
C) increase; shift to the right
D) decrease; not move, although there will be movement along the curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A change in a non-price factor of demand will cause:
A) a movement along the demand curve.
B) a shift of the demand curve.
C) the demand curve to rotate inward.
D) the demand curve to rotate outward.
A) a movement along the demand curve.
B) a shift of the demand curve.
C) the demand curve to rotate inward.
D) the demand curve to rotate outward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An increase in the price of ice cream is likely to cause:
A) a movement to the left along the demand curve for ice cream.
B) an inward shift of the demand curve for ice cream.
C) an outward shift of the demand curve for ice cream.
D) a movement to the right along the demand curve for ice cream.
A) a movement to the left along the demand curve for ice cream.
B) an inward shift of the demand curve for ice cream.
C) an outward shift of the demand curve for ice cream.
D) a movement to the right along the demand curve for ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Upon Apple's announcement that the newest iPhone model will be released in the next six months, we could reasonably expect that demand for the current iPhone model will _____ due to a change in _____.
A) decrease; expectations of future prices
B) increase; expectations of future prices
C) increase; the supply of the current model
D) decrease; the price of a substitute good
A) decrease; expectations of future prices
B) increase; expectations of future prices
C) increase; the supply of the current model
D) decrease; the price of a substitute good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What happens to the demand curve when a non-price determinant of demand changes?
A) The demand curve shifts to the left or to the right.
B) There is a movement along the demand curve.
C) The consumer moves to a different price point.
D) The demand curve does not change when a non-price determinant of demand changes.
A) The demand curve shifts to the left or to the right.
B) There is a movement along the demand curve.
C) The consumer moves to a different price point.
D) The demand curve does not change when a non-price determinant of demand changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



