Deck 3: Benefits and Costs, Supply and Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Benefits and Costs, Supply and Demand
1
In the following figure, the marginal willingness to pay for the 10th unit of the good is ________.
A) $12
B) $20
C) $160
D) $200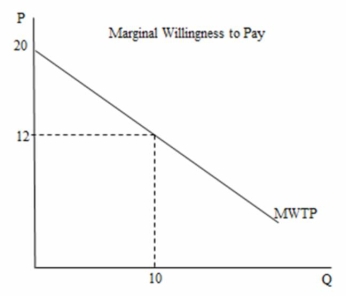
A) $12
B) $20
C) $160
D) $200

A
2
Marginal willingness to pay ____________.
A) is the consumer's additional willingness to pay for one more unit of the good
B) is the consumer's additional ability to pay for one more unit of the good
C) is the consumer's ability to pay for consumption of all units of the good
D) is the consumer's willingness to pay for consumption of all units of the good
A) is the consumer's additional willingness to pay for one more unit of the good
B) is the consumer's additional ability to pay for one more unit of the good
C) is the consumer's ability to pay for consumption of all units of the good
D) is the consumer's willingness to pay for consumption of all units of the good
A
3
As long as marginal willingness is _________, total willingness will _________.
A) declining; stay the same
B) increasing; decrease
C) positive; increase
D) decreasing; decrease
A) declining; stay the same
B) increasing; decrease
C) positive; increase
D) decreasing; decrease
C
4
The determination of how much an individual is willing to pay for a good or service is comprised of both _________ and ________________.
A) current environmental quality; potential environmental impact
B) individual values; ability to pay
C) collective values; unemployment rate
D) societal values; consumer price index
A) current environmental quality; potential environmental impact
B) individual values; ability to pay
C) collective values; unemployment rate
D) societal values; consumer price index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Private costs are ____________, while social costs are ____________.
A) costs experienced by the consumer making the decision; all of the costs of the action
B) costs experience by the private sector; costs experience by the public sector
C) costs that are charged by the private sector; costs that are charged by the public sector
D) all of the costs of a transaction including social costs; only the costs represent damage to the environment
A) costs experienced by the consumer making the decision; all of the costs of the action
B) costs experience by the private sector; costs experience by the public sector
C) costs that are charged by the private sector; costs that are charged by the public sector
D) all of the costs of a transaction including social costs; only the costs represent damage to the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The value of a good or service is measured by _______________.
A) the willingness to pay
B) the sacrifice a person experiences in terms of other goods
C) the sacrifice a consumer experiences in generalized purchasing power
D) all of the above
A) the willingness to pay
B) the sacrifice a person experiences in terms of other goods
C) the sacrifice a consumer experiences in generalized purchasing power
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One criterion for evaluating environmental policies is whether or not they generate ________ for individuals, firms and industries to engage in ________.
A) disincentives; expansion activities
B) incentives; expansion activities
C) disincentives; abatement activities
D) incentives; R&D activities
A) disincentives; expansion activities
B) incentives; expansion activities
C) disincentives; abatement activities
D) incentives; R&D activities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The notion of diminishing willingness to pay reveals that as____________.
A) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units increases
B) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units stays the same
C) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units decreases
D) ability to pay increases, the number of units consumed increases
A) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units increases
B) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units stays the same
C) units consumed increases, willingness to pay for additional units decreases
D) ability to pay increases, the number of units consumed increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Willingness to pay is graphed __________________.
A) as a curve that slopes downward as quantity increases
B) as a curve that slopes upward as quantity increases
C) as a horizontal line
D) as a stepwise function that cannot be translated into a curve
A) as a curve that slopes downward as quantity increases
B) as a curve that slopes upward as quantity increases
C) as a horizontal line
D) as a stepwise function that cannot be translated into a curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following figure shows the impact of technological change on the marginal cost of producing a certain good. Producing Q* units with the new technology reduces total cost by an amount equal to ________.
A) area a
B) area b
C) area c
D) areas a + b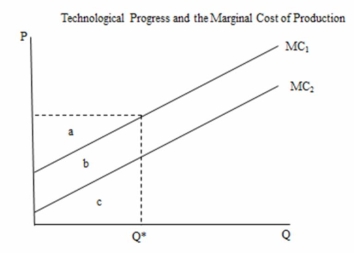
A) area a
B) area b
C) area c
D) areas a + b


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Total willingness to pay ____________.
A) is the consumer's additional willingness to pay for one more unit of the good
B) is the consumer's additional ability to pay for one more unit of the good
C) is the consumer's ability to pay for consumption of all units of the good
D) is the consumer's willingness to pay for consumption of all units of the good
A) is the consumer's additional willingness to pay for one more unit of the good
B) is the consumer's additional ability to pay for one more unit of the good
C) is the consumer's ability to pay for consumption of all units of the good
D) is the consumer's willingness to pay for consumption of all units of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Opportunity cost _______________.
A) is represented by the area under the marginal cost curve
B) is an upward sloping curve that intersects with the demand curve
C) represents the maximum value of other outputs that could have been produced with the same resources
D) all of the above
A) is represented by the area under the marginal cost curve
B) is an upward sloping curve that intersects with the demand curve
C) represents the maximum value of other outputs that could have been produced with the same resources
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the following figure, the total willingness to pay for the 10th unit of the good is _______.
A) $12
B) $20
C) $160
D) $200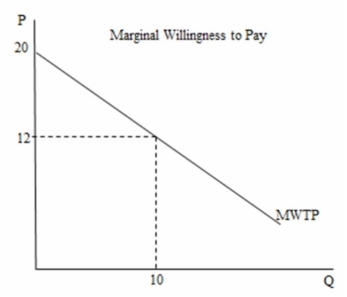
A) $12
B) $20
C) $160
D) $200


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Aggregate demand curves are _________________.
A) not of interest in environmental economics because it is a microeconomic field
B) unrelated to individual demand curves
C) a summation of individual demand curves
D) not related to individual or aggregate willingness to pay
A) not of interest in environmental economics because it is a microeconomic field
B) unrelated to individual demand curves
C) a summation of individual demand curves
D) not related to individual or aggregate willingness to pay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The marginal cost curve is affected by _____.
A) time
B) the price of inputs
C) technology
D) all of the above
A) time
B) the price of inputs
C) technology
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the following figure the marginal cost of producing the 500th unit of output is ________.
A) $500
B) $550
C) $150,000
D) $212,500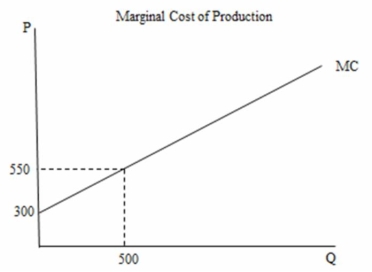
A) $500
B) $550
C) $150,000
D) $212,500


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following figure shows the impact of technological change on the marginal cost of producing a certain good. With MC1 the total cost of producing Q* units is equal to _______.
A) areas a + b + c
B) areas b + c
C) area b
D) area c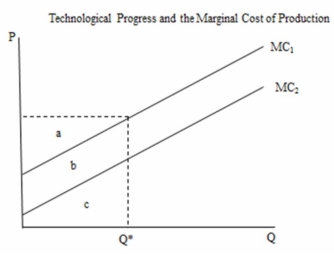
A) areas a + b + c
B) areas b + c
C) area b
D) area c


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following are difficulties with using demand curves to estimate environmental benefits, except
A) demand curves are constructed based on ability to pay.
B) consumers are sometimes unaware of the benefits of environmental quality.
C) downward sloping demand curves inaccurately imply declining benefits.
D) benefits are often difficult to measure when it concerns environmental questions.
A) demand curves are constructed based on ability to pay.
B) consumers are sometimes unaware of the benefits of environmental quality.
C) downward sloping demand curves inaccurately imply declining benefits.
D) benefits are often difficult to measure when it concerns environmental questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the following figure the total cost of producing the 500th unit of output is ________.
A) $550
B) $150,000
C) $212,500
D) $275,000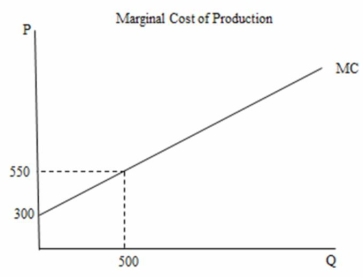
A) $550
B) $150,000
C) $212,500
D) $275,000


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The benefit a consumer acquires from consuming a unit of a good is equal to ________.
A) the willingness to pay minus the cost of production
B) the price that a consumer is willing to pay
C) the profit associated with the good
D) the area above the demand curve
A) the willingness to pay minus the cost of production
B) the price that a consumer is willing to pay
C) the profit associated with the good
D) the area above the demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The equimarginal principle addresses
A) equality
B) efficiency
C) willingness to pay
D) aggregate benefits
Refer to the following table for Dina's marginal willingness-to-pay for scooter rentals. (approximately 10 minutes per rental). Note the MWTP to go from 0 to 5 rentals per week is $10.

A) equality
B) efficiency
C) willingness to pay
D) aggregate benefits
Refer to the following table for Dina's marginal willingness-to-pay for scooter rentals. (approximately 10 minutes per rental). Note the MWTP to go from 0 to 5 rentals per week is $10.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Refer to Table 3.1. According to the equimarginal principle, in order to minimize the cost of producing 100 units, how would we distribute production between plants A and B?
A) 0 units at plant A; 100 units at plant B
B) 20 units at plant A; 80 units at plant B
C) 38 units at plant A; 62 units at plant B
D) 50 units at plan A; 50 units at plant B
A) 0 units at plant A; 100 units at plant B
B) 20 units at plant A; 80 units at plant B
C) 38 units at plant A; 62 units at plant B
D) 50 units at plan A; 50 units at plant B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Total costs are found by ________.
A) the intersection of the marginal cost and marginal benefits curve
B) the area under the marginal willingness to pay curve
C) multiplying the marginal cost by the number of units
D) the sum of the marginal cost for each unit
A) the intersection of the marginal cost and marginal benefits curve
B) the area under the marginal willingness to pay curve
C) multiplying the marginal cost by the number of units
D) the sum of the marginal cost for each unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The marginal cost curve of a firm ________.
A) represents the firm's production function
B) represents the firm's supply curve
C) represents the industry supply curve
D) none of the above
A) represents the firm's production function
B) represents the firm's supply curve
C) represents the industry supply curve
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to Table 3.2. At a market price of $4.00, what is industry supply?
A) 0
B) 48 units
C) $ 192.00
D) Indeterminate. The table does reveal aggregate supply.
A) 0
B) 48 units
C) $ 192.00
D) Indeterminate. The table does reveal aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One important characteristic of all marginal cost curves is that ________.
A) they all intersect the Y axis
B) although they may initially decline, they eventually increase
C) they all eventually decline
D) they are stepwise functions with lumpy investment features
A) they all intersect the Y axis
B) although they may initially decline, they eventually increase
C) they all eventually decline
D) they are stepwise functions with lumpy investment features

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Dina's willingness to pay for a scooter rental depends on her
A) alternatives
B) ability to pay
C) wealth
D) all the above
A) alternatives
B) ability to pay
C) wealth
D) all the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to Table 3.0. What is the total willingness to pay for 4 cups of coffee?
A) $3.50
B) $14.00
C) $21.25
D) $15.75
A) $3.50
B) $14.00
C) $21.25
D) $15.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When market price is $16, aggregate demand is __________.
A) 7 units
B) 44 units
C) $112
D) indeterminate. The table does reveal aggregate demand.
A) 7 units
B) 44 units
C) $112
D) indeterminate. The table does reveal aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Dina's total willingness to pay for 15 rides is
A) 7
B) 10
C) 16
D) 26
A) 7
B) 10
C) 16
D) 26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to Table 3.0. What are the total benefits of consuming 3 cups of coffee?
A) $3.75
B) $17.75
C) $ 5.75
D) Indeterminate. The table does allow the calculation of benefits.
A) $3.75
B) $17.75
C) $ 5.75
D) Indeterminate. The table does allow the calculation of benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Technological progress _______________.
A) results in a downward shift of the marginal cost curve
B) results in an upward shift of the marginal cost curve
C) results in an upward shift of the willingness to pay curve
D) results in a downward shift of the willingness to pay curve
A) results in a downward shift of the marginal cost curve
B) results in an upward shift of the marginal cost curve
C) results in an upward shift of the willingness to pay curve
D) results in a downward shift of the willingness to pay curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When technological changes are adopted, marginal abatement cost usually
A) increases
B) decreases
C) not changed
D) cannot be determined
A) increases
B) decreases
C) not changed
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the price for a 10-ride pass is $6, how many rides would Dina desire?
A) 20
B) 15
C) 5
D) zero
A) 20
B) 15
C) 5
D) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to Table 3.0. At a price of $3.00, how many cups of coffee would this individual consume?
A) 2
B) 6
C) 4
D) There is not enough information in the table to determine the answer.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 4
D) There is not enough information in the table to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



