Deck 4: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Carbohydrates
1
Dietary fiber
A) raises blood cholesterol levels.
B) speeds up transit time for food through the digestive tract.
C) causes diverticulosis.
D) causes constipation.
A) raises blood cholesterol levels.
B) speeds up transit time for food through the digestive tract.
C) causes diverticulosis.
D) causes constipation.
The soluble dietary fiber found in foodstuffs such as fruits, oats, and beans can bind to cholesterol when in the gut, thereby reducing its absorption. This reduces the blood cholesterol levels.
Diverticulosis is the condition in which pouches are formed that protrude out from the wall of the cecum. Lack of dietary fiber is believed to be one of the causes of diverticulosis.
The insoluble type of dietary fiber can absorb large amounts of water without dissolving in it. If adequate water is not provided for the fiber to soak, it can become hard, making the feces difficult to pass, thereby causing constipation. The lack of adequate fluid intake leads to constipation.
Hence, options 'a', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect.
The insoluble type of dietary fiber found in foods such as rice, potato, and wheat bran, cannot dissolve in water. However, it can absorb water. When it absorbs the water in the food, it adds bulk to the feces. This shortens the transit time for the food through the digestive tract.
Therefore, the correct option is option
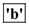 .
.
Diverticulosis is the condition in which pouches are formed that protrude out from the wall of the cecum. Lack of dietary fiber is believed to be one of the causes of diverticulosis.
The insoluble type of dietary fiber can absorb large amounts of water without dissolving in it. If adequate water is not provided for the fiber to soak, it can become hard, making the feces difficult to pass, thereby causing constipation. The lack of adequate fluid intake leads to constipation.
Hence, options 'a', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect.
The insoluble type of dietary fiber found in foods such as rice, potato, and wheat bran, cannot dissolve in water. However, it can absorb water. When it absorbs the water in the food, it adds bulk to the feces. This shortens the transit time for the food through the digestive tract.
Therefore, the correct option is option
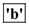 .
. 2
Why do we need carbohydrates in the diet
Food consumed by animals provides macronutrients, namely, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Carbohydrates comprise of fiber, starch, and sugar. Together they are responsible for providing energy to the body and performing several important functions.
Metabolism of starch and sugars results in the release of energy, which is used for basal metabolism, physical activity, thermic effect and thermogenesis. In general, every gram of carbohydrate provides 4 kcal of energy. Though energy is also obtained from the other macronutrients, glucose is the simplest form of sugar and thus can be utilized very rapidly compared to any other source of energy. it is also vital for cellular respiration. Starch is a concentrated source of sugar. It too is broken down like the sugars. When the starch and sugar is not utilized immediately by the body, it is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
The dietary fibers, which are also a form of carbohydrates, do not provide any energy. However, they perform several other critical functions. The fibers that are soluble can bind to the cholesterol in the gut of the intestine and reduce their levels in the blood. They also are responsible to maintain the health of the gut. The other type of fibers that are not soluble, do not dissolve in the water ingested in through the foods and fluids, but soak in it. This makes them bulky, which in turn reduces the transit time of food in the digestive tract. Due to these critical functions performed by them and their energy-yielding capabilities, we need carbohydrates in the diet.
Metabolism of starch and sugars results in the release of energy, which is used for basal metabolism, physical activity, thermic effect and thermogenesis. In general, every gram of carbohydrate provides 4 kcal of energy. Though energy is also obtained from the other macronutrients, glucose is the simplest form of sugar and thus can be utilized very rapidly compared to any other source of energy. it is also vital for cellular respiration. Starch is a concentrated source of sugar. It too is broken down like the sugars. When the starch and sugar is not utilized immediately by the body, it is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
The dietary fibers, which are also a form of carbohydrates, do not provide any energy. However, they perform several other critical functions. The fibers that are soluble can bind to the cholesterol in the gut of the intestine and reduce their levels in the blood. They also are responsible to maintain the health of the gut. The other type of fibers that are not soluble, do not dissolve in the water ingested in through the foods and fluids, but soak in it. This makes them bulky, which in turn reduces the transit time of food in the digestive tract. Due to these critical functions performed by them and their energy-yielding capabilities, we need carbohydrates in the diet.
3
When the pancreas detects excess glucose, it releases the
A) enzyme amylase.
B) monosaccharide glucose.
C) hormone insulin.
D) hormone glucagon.
A) enzyme amylase.
B) monosaccharide glucose.
C) hormone insulin.
D) hormone glucagon.
Enzymes and hormones are substances secreted by the cells of the body having specific biochemical action. Amylase is an enzyme that specializes in breaking down the macronutrients consumed in the food. It is also present in the saliva, apart form the pancreas.
Glucagon is a hormone produced in the alpha cells of the pancreas. The pancreas secretes it when the blood glucose levels in the body decrease. Glucagon converts the glycogen stored in the liver to monosaccharide glucose, thereby increasing the levels of blood glucose in the body.
Hence, options 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect.
The pancreas also produce the hormone insulin. When the blood glucose levels increase, the pancreas secrete insulin. This insulin binds to the sugar molecules flowing in the blood and transports them to the cells that absorb glucose. When the blood sugar level comes within the normal blood sugar range, the secretion of insulin subsides.
Therefore, the correct option is option
 .
.
Glucagon is a hormone produced in the alpha cells of the pancreas. The pancreas secretes it when the blood glucose levels in the body decrease. Glucagon converts the glycogen stored in the liver to monosaccharide glucose, thereby increasing the levels of blood glucose in the body.
Hence, options 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect.
The pancreas also produce the hormone insulin. When the blood glucose levels increase, the pancreas secrete insulin. This insulin binds to the sugar molecules flowing in the blood and transports them to the cells that absorb glucose. When the blood sugar level comes within the normal blood sugar range, the secretion of insulin subsides.
Therefore, the correct option is option
 .
. 4
What are the three major monosaccharides and the three major disaccharides Describe how each plays a part in the human diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Cellulose is a(n)
A) indigestible fiber.
B) simple carbohydrate.
C) energy-yielding nutrient.
D) animal polysaccharide.
A) indigestible fiber.
B) simple carbohydrate.
C) energy-yielding nutrient.
D) animal polysaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why are some foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as cookies and fat-free milk, not considered to be concentrated sources of carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Digested white sugar is broken into _____ and _____.
A) glucose, lactose
B) glucose, fructose
C) sucrose, maltose
D) fructose, sucrose
A) glucose, lactose
B) glucose, fructose
C) sucrose, maltose
D) fructose, sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Describe the digestion of the various types of carbohydrates in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Starch is a
A) complex carbohydrate.
B) fiber.
C) simple carbohydrate.
D) gluten.
A) complex carbohydrate.
B) fiber.
C) simple carbohydrate.
D) gluten.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe the reason why some people are unable to tolerate high intakes of milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Fiber content of the diet can be increased by adding
A) fresh fruits.
B) fish and poultry.
C) eggs.
D) whole grains and cereals.
E) Both a and d.
A) fresh fruits.
B) fish and poultry.
C) eggs.
D) whole grains and cereals.
E) Both a and d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
List three alternatives to simple sugars for adding sweetness to the diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which form of diabetes is most common
A) type 1
B) type 2
C) type 3
D) gestational
A) type 1
B) type 2
C) type 3
D) gestational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Outline the basic steps in blood glucose regulation, including the roles of insulin and glucagon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The recommended daily intake for fiber is approximately _____ grams.
A) 5
B) 30
C) 100
D) 450
A) 5
B) 30
C) 100
D) 450

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What are the important roles that fiber plays in the diet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Lactose intolerance is the result of
A) drinking high-fat milk.
B) eating a large amount of yogurt.
C) low lactase activity.
D) a high-fiber diet.
A) drinking high-fat milk.
B) eating a large amount of yogurt.
C) low lactase activity.
D) a high-fiber diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Summarize current carbohydrate intake recommendations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One of the components of metabolic syndrome is
A) high body weight.
B) high waist circumference.
C) low blood sugar.
D) low blood pressure.
A) high body weight.
B) high waist circumference.
C) low blood sugar.
D) low blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What, if any, are the proven ill effects of sugar in the diet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why are carbohydrates considered our most valuable energy source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are the names and definitions of the monosaccharides and disaccharides, and what happens to them when they are digested and absorbed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is a polysaccharide and what are the differences between the plant polysaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are the name and locations of the storage form of glucose in the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What makes fiber a very different kind of carbohydrate, and what is the difference between nonfermentable, viscous, and functional fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which food groups are the primary sources of carbohydrates in our diets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What specific foods contain the highest percentage of calories from carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What are the common nutritive sweeteners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which alternative sweeteners are approved for use in food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In what form are carbohydrates absorbed, and what happens to these compounds after absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are the names and locations of the enzymes that digest carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why do some individuals feel discomfort after they consume large amounts of lactose How can they avoid these symptoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What are the beneficial effects of fiber in the intestinal tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the primary role of carbohydrates in the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How does the body respond when too little carbohydrate is consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What are the mechanisms by which blood glucose levels are maintained within a narrow range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How can the glycemic index be applied in meal planning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What are some of the important functions of fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the recommended intake of total carbohydrate per day, and how do typical dietary intakes compare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How much fiber is recommended each day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How can we reduce our consumption of added sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the link between sugar and oral health

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



