Deck 22: Health Care
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Health Care
1
Why would increased spending as a percentage of GDP on, say, household appliances or education in a particular economy be regarded as economically desirable Why, then, is there so much concern about rising expenditures as a percentage of GDP on health care
Increasing expenditures on goods such as household appliances or education is regarded as desirable because production is expanding under relatively competitive market conditions. Thus, not only are output and employment expanding, but presumably these are happening because of allocative efficiency. Consumers are choosing to buy appliances or education because they are willing to pay the price for these goods.
There is concern about the same rising expenditures in the health care industry because of the unique factors that characterize the market for health care services. On the demand side, there is imperfect competition in that buyers do not have good information about the services needed or the fees that will be charged for the services; doctors control much of this information and, in fact, order the services for the consumer in most cases. Third-party insurance companies pay the direct costs of most health care on a fee-for-service basis, and therefore the consumer pays less than the full price at the time of consumption, leading to overconsumption; overconsumption by the insured may also be encouraged by the "moral hazard" problem. On the supply side, technology is encouraged without much regard for its cost by insurance providers; doctors also control much of the provision of health care in an imperfectly competitive supply structure, since they really don't compete on the basis of price. In other words, many of the unique factors of the health care market lead economists to believe that overconsumption is occurring and that society is losing because resources are not being allocated efficiently in a way that maximizes society's welfare.
There is concern about the same rising expenditures in the health care industry because of the unique factors that characterize the market for health care services. On the demand side, there is imperfect competition in that buyers do not have good information about the services needed or the fees that will be charged for the services; doctors control much of this information and, in fact, order the services for the consumer in most cases. Third-party insurance companies pay the direct costs of most health care on a fee-for-service basis, and therefore the consumer pays less than the full price at the time of consumption, leading to overconsumption; overconsumption by the insured may also be encouraged by the "moral hazard" problem. On the supply side, technology is encouraged without much regard for its cost by insurance providers; doctors also control much of the provision of health care in an imperfectly competitive supply structure, since they really don't compete on the basis of price. In other words, many of the unique factors of the health care market lead economists to believe that overconsumption is occurring and that society is losing because resources are not being allocated efficiently in a way that maximizes society's welfare.
2
Suppose that the price elasticity for hip replacement surgeries is 0.2. Further suppose that hip replacement surgeries are originally not covered by health insurance and that at a price of $50,000 each, 10,000 such surgeries are demanded each year.
a. Suppose that health insurance begins to cover hip replacement surgeries and that everyone interested in getting a hip replacement has health insurance. If insurance covers 50 percent of the cost of the surgery, by what percentage would you expect the quantity demanded of hip replacements to increase What if insurance covered 90 percent of the price (Hint: Do not bother to calculate the percentage changes using the midpoint formula given in Chapter 6. If insurance covers 50 percent of the bill, just assume that the price paid by consumers falls 50 percent.)
b. Suppose that with insurance companies covering 90 percent of the price, the increase in demand leads to a jump in the price per hip surgery from $50,000 to $100,000. How much will each insured patient now pay for a hip replacement surgery Compared to the original situation, where hip replacements cost $50,000 each but people had no insurance to help subsidize the cost, will the quantity demanded increase or decrease By how much
a. Suppose that health insurance begins to cover hip replacement surgeries and that everyone interested in getting a hip replacement has health insurance. If insurance covers 50 percent of the cost of the surgery, by what percentage would you expect the quantity demanded of hip replacements to increase What if insurance covered 90 percent of the price (Hint: Do not bother to calculate the percentage changes using the midpoint formula given in Chapter 6. If insurance covers 50 percent of the bill, just assume that the price paid by consumers falls 50 percent.)
b. Suppose that with insurance companies covering 90 percent of the price, the increase in demand leads to a jump in the price per hip surgery from $50,000 to $100,000. How much will each insured patient now pay for a hip replacement surgery Compared to the original situation, where hip replacements cost $50,000 each but people had no insurance to help subsidize the cost, will the quantity demanded increase or decrease By how much
a)Insurance covers only 50% :
Price or cost of a hip replacement surgery = $50,000
Percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 50%
Fall in price due to insurance cover =
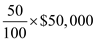 = $25,000
= $25,000
Price elasticity for hip replacement surgery = 0.2
To recall, price elasticity =
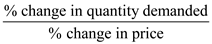 Therefore,
Therefore,
0.2 =
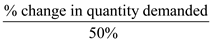 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×50% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×50% =
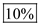
 Now if the percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 90%
Now if the percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 90%
So, 0.2 =
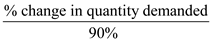 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×90% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×90% =
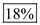
 ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
(b)If insurance companies cover 90% of the surgery;
New price of hip replacement surgery due to increased demand = $100,000
90% coverage by insurance = $90,000
Price to be paid by patient = $10,000
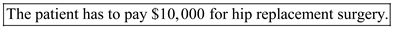 In payment terms, % of new price with actual price=
In payment terms, % of new price with actual price=
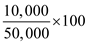 = 20%
= 20%
Percentage change in price (from $50,000 to $10,000) = 80%
Therefore,
0.2 =
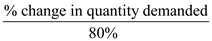 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×80% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×80% =
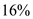 Number of surgeries demanded in a year = 10,000
Number of surgeries demanded in a year = 10,000
Therefore, the quantity of surgeries demanded increases =
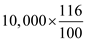 =
=
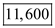 Change in quantity demanded for surgeries = 11,600 - 10,000 =
Change in quantity demanded for surgeries = 11,600 - 10,000 =
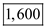
Price or cost of a hip replacement surgery = $50,000
Percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 50%
Fall in price due to insurance cover =
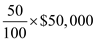 = $25,000
= $25,000Price elasticity for hip replacement surgery = 0.2
To recall, price elasticity =
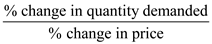 Therefore,
Therefore,0.2 =
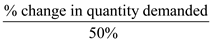 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×50% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×50% = 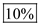
 Now if the percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 90%
Now if the percentage cost of the surgery covered by insurance = 90%So, 0.2 =
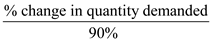 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×90% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×90% = 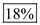
 ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________(b)If insurance companies cover 90% of the surgery;
New price of hip replacement surgery due to increased demand = $100,000
90% coverage by insurance = $90,000
Price to be paid by patient = $10,000
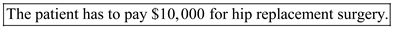 In payment terms, % of new price with actual price=
In payment terms, % of new price with actual price= 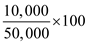 = 20%
= 20%Percentage change in price (from $50,000 to $10,000) = 80%
Therefore,
0.2 =
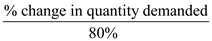 % change in quantity demanded = 0.2×80% =
% change in quantity demanded = 0.2×80% = 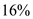 Number of surgeries demanded in a year = 10,000
Number of surgeries demanded in a year = 10,000Therefore, the quantity of surgeries demanded increases =
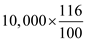 =
= 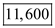 Change in quantity demanded for surgeries = 11,600 - 10,000 =
Change in quantity demanded for surgeries = 11,600 - 10,000 = 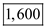
3
Which of the following best describes the United States' level of health care spending as compared to that of other nations
A) The lowest of all nations.
B) A bit lower than average.
C) Average.
D) A bit higher than average.
E) The highest of all nations.
A) The lowest of all nations.
B) A bit lower than average.
C) Average.
D) A bit higher than average.
E) The highest of all nations.
Health care spending of U.S.:
The U.S. spends more amount of money for the health care to its gross domestic product than other countries spending amount for the health care to their countries gross domestic product in the world.
Hence, options 'e' is correct.
The U.S. spends more amount of money for the health care to its gross domestic product than other countries spending amount for the health care to their countries gross domestic product in the world.
Hence, options 'e' is correct.
4
What are the "twin problems" of the health care industry as viewed by society How are they related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The federal tax code allows businesses but not individuals to deduct the cost of health insurance premiums from their taxable income. Consider a company named HeadBook that could either spend $5,000 on an insurance policy for an employee named Vanessa or increase her annual salary by $5,000 instead.
a. As far as the tax code is concerned, HeadBook will increase its expenses by $5,000 in either case. If it pays for the policy, it incurs a $5,000 health care expense. If it raises Vanessa's salary by $5,000, it incurs $5,000 of salary expense. If HeadBook is profitable and pays corporate profit taxes at a marginal 35 percent rate, by how much will HeadBook's tax liability be reduced in either case
b. Suppose that Vanessa pays personal income tax at a marginal 20 percent rate. If HeadBook increases her salary by $5,000, how much of that increase will she have after paying taxes on that raise If Vanessa can only devote what remains after paying taxes on the $5,000 to purchasing health insurance, how much will she be able to spend on health insurance for herself
c. If HeadBook spends the $5,000 on a health insurance policy for Vanessa instead of giving it to her as a raise, how many more dollars will HeadBook be able to spend on Vanessa's health insurance than if she had to purchase it herself after being given a $5,000 raise and paying taxes on that raise
d. Would Vanessa prefer to have the raise or to have HeadBook purchase insurance for her Would HeadBook have any profit motive for denying Vanessa her preference
e. Suppose the government changes the tax law so that individuals can now deduct the cost of health insurance from their personal incomes. If Vanessa gets the $5,000 raise and then spends all of it on health insurance, how much will her tax liability change How much will she be able to spend on health insurance Will she now have a preference for HeadBook to buy insurance on her behalf
a. As far as the tax code is concerned, HeadBook will increase its expenses by $5,000 in either case. If it pays for the policy, it incurs a $5,000 health care expense. If it raises Vanessa's salary by $5,000, it incurs $5,000 of salary expense. If HeadBook is profitable and pays corporate profit taxes at a marginal 35 percent rate, by how much will HeadBook's tax liability be reduced in either case
b. Suppose that Vanessa pays personal income tax at a marginal 20 percent rate. If HeadBook increases her salary by $5,000, how much of that increase will she have after paying taxes on that raise If Vanessa can only devote what remains after paying taxes on the $5,000 to purchasing health insurance, how much will she be able to spend on health insurance for herself
c. If HeadBook spends the $5,000 on a health insurance policy for Vanessa instead of giving it to her as a raise, how many more dollars will HeadBook be able to spend on Vanessa's health insurance than if she had to purchase it herself after being given a $5,000 raise and paying taxes on that raise
d. Would Vanessa prefer to have the raise or to have HeadBook purchase insurance for her Would HeadBook have any profit motive for denying Vanessa her preference
e. Suppose the government changes the tax law so that individuals can now deduct the cost of health insurance from their personal incomes. If Vanessa gets the $5,000 raise and then spends all of it on health insurance, how much will her tax liability change How much will she be able to spend on health insurance Will she now have a preference for HeadBook to buy insurance on her behalf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following make a person less likely to have health insurance
Select one or more answers from the choices shown.
A) Working for a larger firm.
B) Being a low-wage worker.
C) Being employed.
D) Having excellent health.
E) Being chronically ill.
Select one or more answers from the choices shown.
A) Working for a larger firm.
B) Being a low-wage worker.
C) Being employed.
D) Having excellent health.
E) Being chronically ill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Briefly describe the main features of Medicare and Medicaid, indicating how each is financed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Preventive care is not always cost-effective. Suppose that it costs $100 per person to administer a screening exam for a particular disease. Also suppose that if the screening exam finds the disease, the early detection given by the exam will avert $1,000 of costly future treatment.
a. Imagine giving the screening test to 100 people. How much will it cost to give those 100 tests Imagine a case in which 15 percent of those receiving the screening exam test positive. How much in future costly treatments will be averted How much is saved by setting up a screening system
b. Imagine that everything is the same as in part a except that now only 5 percent of those receiving the screening exam test positive. In this case, how much in future costly treatments will be averted How much is lost by setting up a screening system
a. Imagine giving the screening test to 100 people. How much will it cost to give those 100 tests Imagine a case in which 15 percent of those receiving the screening exam test positive. How much in future costly treatments will be averted How much is saved by setting up a screening system
b. Imagine that everything is the same as in part a except that now only 5 percent of those receiving the screening exam test positive. In this case, how much in future costly treatments will be averted How much is lost by setting up a screening system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A patient named Jen visits Dr. Jan. Dr. Jan is nearly certain that Jen only has a cold. But because Dr. Jan is afraid of malpractice lawsuits, she orders an extensive battery of tests just to make sure that Jen can never claim-if she turns out to have something more severe-that Dr. Jan shirked her duties as a medical professional. Dr. Jan's behavior is an example of:
A) Asymmetric information.
B) Fee-for-service.
C) Defensive medicine.
D) Positive externalities.
A) Asymmetric information.
B) Fee-for-service.
C) Defensive medicine.
D) Positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What are the implications of rapidly rising health care prices and spending for ( a ) the growth of real wage rates, ( b ) government budgets, and ( c ) offshoring of U.S. jobs Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
All MegaCorp employees who stay on the job for more than three years are rewarded with a 10 percent pay increase and coverage under a private health insurance plan that MegaCorp pays for. Tina just passed three years as a MegaCorp employee and reacts to having health insurance by taking up several dangerous sports because now she knows that the insurance plan will pay for any injuries that she may sustain. This change in Tina's behavior is known as:
A) Defensive medicine.
B) Asymmetric information.
C) The moral hazard problem.
D) The personal mandate.
A) Defensive medicine.
B) Asymmetric information.
C) The moral hazard problem.
D) The personal mandate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What are the main groups without health insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
By increasing demand, health insurance creates:
A) A deadweight loss related to overconsumption.
B) A deadweight loss related to underconsumption.
C) Neither of the above.
A) A deadweight loss related to overconsumption.
B) A deadweight loss related to underconsumption.
C) Neither of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
List the special characteristics of the U.S. health care market and specify how each affects health care problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ralph will consume any health care service just as long as its MB exceeds the money he must pay out of pocket. His insurance policy has a zero deductible and a 10 percent copay, so Ralph only has to pay 10 percent of the price charged for any medical procedure. Which of the following procedures will Ralph choose to consume
A) An $800 eye exam that has an MB of $100 to Ralph.
B) A $90 hearing test that has an MB of $5 to Ralph.
C) A $35,000 knee surgery that has an MB of $3,000 to Ralph.
D) A $10,000 baldness treatment that has an MB of $16,000 to Ralph.
A) An $800 eye exam that has an MB of $100 to Ralph.
B) A $90 hearing test that has an MB of $5 to Ralph.
C) A $35,000 knee surgery that has an MB of $3,000 to Ralph.
D) A $10,000 baldness treatment that has an MB of $16,000 to Ralph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What are the estimated income and price elasticities of demand for health care How does each relate to rising health care costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
True or False. Under the PPACA, Americans are free to decide for themselves whether or not they should have health insurance coverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Briefly discuss the demand and supply factors that contribute to rising health costs. Specify how ( a ) asymmetric information, ( b ) fee-for-service payments, ( c ) defensive medicine, and ( d ) medical ethics might cause health care costs to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How do advances in medical technology and health insurance interact to drive up the cost of medical care

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Using the concepts in Chapter 7's discussion of consumer behavior, explain how health care insurance results in an overallocation of resources to the health care industry. Use a demand and supply diagram to specify the resulting efficiency loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How is the moral hazard problem relevant to the health care market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the rationale for exempting a firm's contribution to its workers' health insurance from taxation as worker income What is the impact of this exemption on allocative efficiency in the health care industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are ( a ) preferred provider organizations and ( b ) health maintenance organizations In your answer, explain how each is designed to alleviate the overconsumption of health care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What are health savings accounts (HSAs) How might they reduce the overconsumption of health care resulting from traditional insurance How might they introduce an element of price competition into the health care system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why is the PPACA's attempt to extend insurance coverage to all Americans so costly How does the PPACA attempt to obtain the funds needed to extend insurance coverage to all Americans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How does the PPACA attempt to ensure affordable health insurance for the poor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What were the objections made by opponents of the PPACA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
LAST WORD What are the three major cost-reducing features of the Singapore health care system Which one do you think has the largest effect on holding down the price of medical care in Singapore What element of the Singapore system is shared by the Whole Foods and State of Indiana systems What elements are missing How difficult do you think it would be to implement those missing elements in the United States Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



