Deck 18: The Respiratory System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: The Respiratory System
1
Where does the process of gaseous exchange take place in the body during respiration?
A) between the parietal and visceral pleura
B) in the right primary bronchus
C) in the tracheal passage
D) in the pulmonary capillaries
E) at the nasal conchae
A) between the parietal and visceral pleura
B) in the right primary bronchus
C) in the tracheal passage
D) in the pulmonary capillaries
E) at the nasal conchae
D
2
What is the function of the external intercostal muscles during inspiration?
A) They help decrease alveolar pressure.
B) They increase the pressure within the thoracic cavity.
C) They help increase the volume of the thoracic cavity.
D) They help promote elastic recoil of the chest walls.
E) They elevate the sternum and the upper two ribs.
A) They help decrease alveolar pressure.
B) They increase the pressure within the thoracic cavity.
C) They help increase the volume of the thoracic cavity.
D) They help promote elastic recoil of the chest walls.
E) They elevate the sternum and the upper two ribs.
C
3
Surface tension accounts for
A) the increase in the size of alveoli
B) the maintenance of mucus volume
C) muscular contraction during expiration
D) the attachment of the lungs to the chest wall
E) elastic recoil of the lungs
A) the increase in the size of alveoli
B) the maintenance of mucus volume
C) muscular contraction during expiration
D) the attachment of the lungs to the chest wall
E) elastic recoil of the lungs
E
4
Identify structure A in the image. 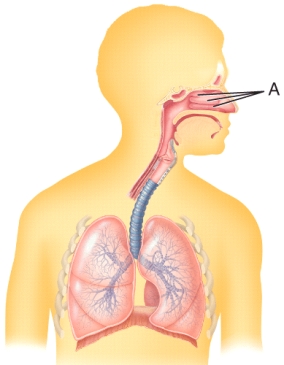
A) nostril
B) sinus
C) olfactory epithelium
D) nasal cavity
E) nasal conchae

A) nostril
B) sinus
C) olfactory epithelium
D) nasal cavity
E) nasal conchae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the function of the cilia in the nose?
A) They move mucus and trapped particles down toward the pharynx.
B) They lubricate the lining of the respiratory tract.
C) They cause the inhaled air to become turbulent.
D) They facilitate the movement of mucus along the respiratory tract.
E) They help increase the total surface area for gaseous exchange.
A) They move mucus and trapped particles down toward the pharynx.
B) They lubricate the lining of the respiratory tract.
C) They cause the inhaled air to become turbulent.
D) They facilitate the movement of mucus along the respiratory tract.
E) They help increase the total surface area for gaseous exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The nose helps make the incoming air warm and humid by
A) stimulating the lubrication of the respiratory tract lining
B) facilitating decreased mucus secretion
C) causing a turbulence of the inhaled air
D) secreting large amounts of periciliary fluid
E) promoting ciliary growth
A) stimulating the lubrication of the respiratory tract lining
B) facilitating decreased mucus secretion
C) causing a turbulence of the inhaled air
D) secreting large amounts of periciliary fluid
E) promoting ciliary growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Flow of air into and out of the lungs can be attributed to
A) a pressure gradient between the atmosphere and the alveoli
B) a pulsating contraction and relaxation movement of the trachea
C) the air turbulence created in the nasal conchae
D) the rigidity of the diaphragm that maintains the pressure in the thorax
E) a change in the volume of the intrapleural fluid
A) a pressure gradient between the atmosphere and the alveoli
B) a pulsating contraction and relaxation movement of the trachea
C) the air turbulence created in the nasal conchae
D) the rigidity of the diaphragm that maintains the pressure in the thorax
E) a change in the volume of the intrapleural fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What causes the alveoli to assume the smallest possible diameter in the lungs?
A) airway resistance
B) surface tension
C) gas pressure
D) capillary action
E) Poiseuille flow
A) airway resistance
B) surface tension
C) gas pressure
D) capillary action
E) Poiseuille flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What happens if the epiglottis fails to function?
A) air humidification and warming does not occur
B) food or liquid substances flow into the airways
C) cilia fail to trap and eliminate foreign particles
D) periciliary fluid volume reduces
E) the cough reflex for foreign material expulsion does not occur
A) air humidification and warming does not occur
B) food or liquid substances flow into the airways
C) cilia fail to trap and eliminate foreign particles
D) periciliary fluid volume reduces
E) the cough reflex for foreign material expulsion does not occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify the group of muscles indicated on the image by the double arrows. 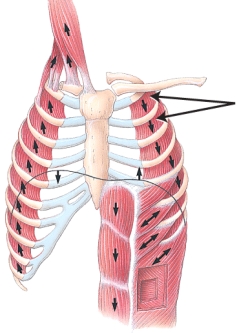
A) deltoideus muscles
B) scalene muscles
C) intercostal muscles
D) rectus abdominis
E) gluteus maximus

A) deltoideus muscles
B) scalene muscles
C) intercostal muscles
D) rectus abdominis
E) gluteus maximus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following occurs during expiration?
A) The external intercostals relax, and the ribs become depressed.
B) Alveolar pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
C) The diaphragm descends at least 1 cm.
D) Intrapleural pressure increases considerably.
E) The abdominal muscles expand and push the ribs upward.
A) The external intercostals relax, and the ribs become depressed.
B) Alveolar pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
C) The diaphragm descends at least 1 cm.
D) Intrapleural pressure increases considerably.
E) The abdominal muscles expand and push the ribs upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the process of respiration, the step in which air flows into and out of the lungs is called
A) systemic circulation
B) inflation reflex
C) ventilation
D) bronchoconstriction
E) perfusion
A) systemic circulation
B) inflation reflex
C) ventilation
D) bronchoconstriction
E) perfusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The collapse of the air sacs shown in this image will have which of the following consequences? 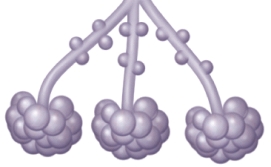
A) the mucus layer will disintegrate
B) lung ventilation will increase
C) ciliary movement will be impaired
D) gas exchange will be impaired
E) expiration of oxygen will occur

A) the mucus layer will disintegrate
B) lung ventilation will increase
C) ciliary movement will be impaired
D) gas exchange will be impaired
E) expiration of oxygen will occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Pleurisy is a condition characterized by
A) thinning of the parietal and visceral pleura
B) inflammation of the pleural membranes
C) diffusion of intrapleural fluid through visceral pleura into the lungs
D) thickening of the intrapleural fluid
E) bacterial infection of the intrapleural fluid
A) thinning of the parietal and visceral pleura
B) inflammation of the pleural membranes
C) diffusion of intrapleural fluid through visceral pleura into the lungs
D) thickening of the intrapleural fluid
E) bacterial infection of the intrapleural fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Exposing the pleural cavity to the atmosphere results in
A) excessive inflation of the lungs
B) negative intrapleural pressure
C) uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall
D) contraction of the chest wall inward
E) elevation of oxygen levels in the blood
A) excessive inflation of the lungs
B) negative intrapleural pressure
C) uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall
D) contraction of the chest wall inward
E) elevation of oxygen levels in the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a function of periciliary fluid?
A) It allows only air, but not food or liquid, into the respiratory tract.
B) It facilitates thickening of the mucus along the respiratory tract.
C) It acts as the site of gas exchange between the air and blood.
D) It causes turbulence in inhaled air in the nasal cavity.
E) It facilitates movement of mucus along the respiratory tract.
A) It allows only air, but not food or liquid, into the respiratory tract.
B) It facilitates thickening of the mucus along the respiratory tract.
C) It acts as the site of gas exchange between the air and blood.
D) It causes turbulence in inhaled air in the nasal cavity.
E) It facilitates movement of mucus along the respiratory tract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The _____ is a funnel-shaped tube that extends from the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx and esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The surfactant in alveolar fluid reduces surface tension by disrupting the cohesive forces between water molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the true statement about the resting phase in a respiratory cycle.
A) During this phase, alveolar pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
B) The resting phase is characterized by a flattened diaphragm.
C) Alveolar pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure in this phase.
D) Alveolar pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure during this phase.
E) The external intercostal muscles remain contracted during this phase.
A) During this phase, alveolar pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
B) The resting phase is characterized by a flattened diaphragm.
C) Alveolar pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure in this phase.
D) Alveolar pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure during this phase.
E) The external intercostal muscles remain contracted during this phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Explain why smokers cough to remove foreign particles from their airways.
A) Deposits of carbon in the epiglottis obstruct expectoration of trapped particles.
B) The cilia are paralyzed by nicotine and are unable to help in the expulsion of trapped particles.
C) The air turbulence created by the act of coughing prevents cilia from trapping the foreign particles.
D) An increase in the periciliary fluid by nicotine causes mucus to thicken.
E) The presence of nicotine causes cilia to entangle and inhibits their ability to trap foreign particles.
A) Deposits of carbon in the epiglottis obstruct expectoration of trapped particles.
B) The cilia are paralyzed by nicotine and are unable to help in the expulsion of trapped particles.
C) The air turbulence created by the act of coughing prevents cilia from trapping the foreign particles.
D) An increase in the periciliary fluid by nicotine causes mucus to thicken.
E) The presence of nicotine causes cilia to entangle and inhibits their ability to trap foreign particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider that the surface tension of an alveolus is 10 and its radius is 2. Using the law of Laplace, calculate the pressure inside the alveolus.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 12
D) 24
E) 18
A) 10
B) 20
C) 12
D) 24
E) 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What do you get when you add inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume?
A) total lung capacity
B) functional residual capacity
C) vital capacity
D) inspiratory capacity
E) expiratory capacity
A) total lung capacity
B) functional residual capacity
C) vital capacity
D) inspiratory capacity
E) expiratory capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A record of lung volumes and lung capacities is known as a/an
A) echogram
B) mammogram
C) sonogram
D) spirogram
E) histogram
A) echogram
B) mammogram
C) sonogram
D) spirogram
E) histogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is an effect of emphysema?
A) surface area for gas exchange increases
B) the rate of O2 diffusion across the respiratory membrane increases
C) lung elastic recoil increases with a loss of elastic fibers
D) size of the chest cage decreases
E) the walls of the alveoli are damaged
A) surface area for gas exchange increases
B) the rate of O2 diffusion across the respiratory membrane increases
C) lung elastic recoil increases with a loss of elastic fibers
D) size of the chest cage decreases
E) the walls of the alveoli are damaged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is tidal volume of the lungs?
A) It is the volume of air inspired or expired during a single breathing cycle under resting conditions.
B) It is the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal inspiration.
C) It is the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a normal expiration.
D) It is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a maximum expiration.
E) It is the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inspiration.
A) It is the volume of air inspired or expired during a single breathing cycle under resting conditions.
B) It is the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal inspiration.
C) It is the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a normal expiration.
D) It is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a maximum expiration.
E) It is the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The process depicted by this image occurs as a result of which of the following scenarios? 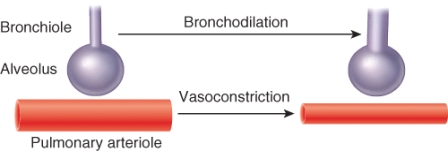
A) atmospheric pressure matches alveolar pressure
B) intrapleural pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure
C) perfusion matches ventilation
D) perfusion exceeds ventilation
E) ventilation exceeds perfusion

A) atmospheric pressure matches alveolar pressure
B) intrapleural pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure
C) perfusion matches ventilation
D) perfusion exceeds ventilation
E) ventilation exceeds perfusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What factors affect lung compliance?
A) rigidity and osmotic pressure
B) Poiseuille flow and gas pressure
C) capillarity and airway resistance
D) elasticity and surface tension
E) osmolality and surface adsorption
A) rigidity and osmotic pressure
B) Poiseuille flow and gas pressure
C) capillarity and airway resistance
D) elasticity and surface tension
E) osmolality and surface adsorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A premature infant is undergoing treatment for respiratory distress syndrome. Identify a true statement in the context of this scenario.
A) The infant has excessive amounts of surfactant in the alveolar fluid.
B) The infant's alveoli are inflating after each expiration.
C) The infant's alveolar surface tension is extremely high.
D) The infant shows signs of reduced work of breathing.
E) The infant shows signs of high lung compliance.
A) The infant has excessive amounts of surfactant in the alveolar fluid.
B) The infant's alveoli are inflating after each expiration.
C) The infant's alveolar surface tension is extremely high.
D) The infant shows signs of reduced work of breathing.
E) The infant shows signs of high lung compliance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
_____ volume is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a maximum expiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A disadvantage of a spirometer is that it cannot be used to
A) measure residual volume
B) measure inspiratory reserve volume
C) determine minute ventilation
D) assess the effect of medication
E) assess the efficiency of autoregulatory mechanisms
A) measure residual volume
B) measure inspiratory reserve volume
C) determine minute ventilation
D) assess the effect of medication
E) assess the efficiency of autoregulatory mechanisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following describes functional residual capacity?
A) the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a normal expiration
B) the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal expiration
C) the volume of air in the lungs at the end of a normal expiration
D) the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal inspiration
E) the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inspiration
A) the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a normal expiration
B) the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal expiration
C) the volume of air in the lungs at the end of a normal expiration
D) the maximum volume of air that can be inspired after a normal inspiration
E) the maximum volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inspiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A long-drawn and deep inspiration followed by a strong expiration that suddenly sends a blast of air through the upper respiratory passages is called
A) laughing
B) crying
C) sneezing
D) coughing
E) hiccupping
A) laughing
B) crying
C) sneezing
D) coughing
E) hiccupping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which action involves a spasmodic contraction of the diaphragm followed by a spasmodic closure of the larynx?
A) coughing
B) yawning
C) sighing
D) sneezing
E) hiccupping
A) coughing
B) yawning
C) sighing
D) sneezing
E) hiccupping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When a person is in a supine position, the force of gravity causes ventilation and perfusion to be less at the base of the lungs than at the apex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How is the inspiratory capacity of the lungs calculated?
A) adding vital capacity and residual volume
B) adding residual volume, expiratory reserve volume, and inspiratory reserve volume
C) adding inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume
D) adding vital capacity and residual volume
E) adding tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume
A) adding vital capacity and residual volume
B) adding residual volume, expiratory reserve volume, and inspiratory reserve volume
C) adding inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume
D) adding vital capacity and residual volume
E) adding tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Explain why oxygen therapy is used in the treatment of a person with emphysema.
A) Reduced lung compliance promotes carbon dioxide absorption by the alveoli.
B) Reduced surface area for gas exchanges leads to lower blood oxygen levels.
C) The individual begins expelling oxygen from the body during expiration.
D) The individual's hemoglobin exhibits increased affinity to carbon monoxide.
E) The amount of air retained in the lung at the end of expiration decreases significantly.
A) Reduced lung compliance promotes carbon dioxide absorption by the alveoli.
B) Reduced surface area for gas exchanges leads to lower blood oxygen levels.
C) The individual begins expelling oxygen from the body during expiration.
D) The individual's hemoglobin exhibits increased affinity to carbon monoxide.
E) The amount of air retained in the lung at the end of expiration decreases significantly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The term used to define the normal pattern of quiet breathing is
A) apnea
B) eupnea
C) hyponea
D) polypnea
E) dyspnea
A) apnea
B) eupnea
C) hyponea
D) polypnea
E) dyspnea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What happens when ventilation exceeds perfusion in the lungs?
A) The CO2 level in the alveolus and surrounding tissue increases.
B) The O2 level in the alveolus decreases.
C) The bronchiolar smooth muscles contract.
D) The pulmonary arteriole constricts.
E) The air flow to the overventilated alveolus increases.
A) The CO2 level in the alveolus and surrounding tissue increases.
B) The O2 level in the alveolus decreases.
C) The bronchiolar smooth muscles contract.
D) The pulmonary arteriole constricts.
E) The air flow to the overventilated alveolus increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does vasodilation help when ventilation exceeds perfusion?
A) It reduces blood flow to the underventilated alveolus.
B) It increases O2 delivery to the overventilated alveolus.
C) It facilitates the expulsion of excess CO2.
D) It decreases the level of CO2 in the alveolus and the surrounding tissues.
E) It enables the dilation of bronchiolar smooth muscle.
A) It reduces blood flow to the underventilated alveolus.
B) It increases O2 delivery to the overventilated alveolus.
C) It facilitates the expulsion of excess CO2.
D) It decreases the level of CO2 in the alveolus and the surrounding tissues.
E) It enables the dilation of bronchiolar smooth muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
By triggering relaxation of bronchiolar smooth muscle, signals from the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) facilitate bronchodilation and decreased resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why does alveolar air have less O2 compared with inhaled air?
A) Reduced surface tension in the alveoli leads to reduced O2 concentration in the alveolar air.
B) The air turbulence in the nasal conchae dissipates most O2 from inhaled air.
C) The O2 concentration in the atmosphere is less than CO2 concentration.
D) Alveolar air is humidified and, therefore, has more water vapor and less O2.
E) Alveolar air is the air in the anatomical dead space that does not participate in the gas exchange.
A) Reduced surface tension in the alveoli leads to reduced O2 concentration in the alveolar air.
B) The air turbulence in the nasal conchae dissipates most O2 from inhaled air.
C) The O2 concentration in the atmosphere is less than CO2 concentration.
D) Alveolar air is humidified and, therefore, has more water vapor and less O2.
E) Alveolar air is the air in the anatomical dead space that does not participate in the gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the difference between pulmonary and systemic gas exchange?
A) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the nasal cavity, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the blood.
B) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the blood vessels, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the lymphatic vessels.
C) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the lungs, while systemic gas exchange occurs throughout the body.
D) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs throughout the body, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the blood.
E) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs throughout the body, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in lungs.
A) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the nasal cavity, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the blood.
B) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the blood vessels, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the lymphatic vessels.
C) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs only in the lungs, while systemic gas exchange occurs throughout the body.
D) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs throughout the body, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in the blood.
E) Pulmonary gas exchange occurs throughout the body, while systemic gas exchange occurs only in lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_____ _____ is a clinical application of Henry's law used to treat diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria, such as those that cause tetanus and gangrene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In an adult, tidal volume of lungs is 600 mL/breath, and respiratory rate is about 14 breaths/min. What is the average minute ventilation?
A) 7400 mL/min
B) 8000 mL/min
C) 6400 mL/min
D) 6000 mL/min
E) 8400 mL/min
A) 7400 mL/min
B) 8000 mL/min
C) 6400 mL/min
D) 6000 mL/min
E) 8400 mL/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
1 mL of O2 is bound to 100 mL of blood. The maximum amount of O2 that can potentially be bound is 1.30 mL per 100 mL of blood. Calculate the percentage saturation of hemoglobin.
A) 86%
B) 77%
C) 95%
D) 93%
E) 74%
A) 86%
B) 77%
C) 95%
D) 93%
E) 74%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How is the percent saturation of hemoglobin calculated?
A) (Amount of O2 that can potentially be bound/ Amount of O2 actually bound) x 100
B) (Amount of O2 actually bound/ Maximum amount of O2 that can potentially be bound) x 100
C) (Number of O2 molecule bound/ Total number of O2 molecules available) x 100
D) (Volume of O2 per mL of blood/ Total volume of blood) x 100
E) (Mass of O2 molecule/ Total mass of blood) x 100
A) (Amount of O2 that can potentially be bound/ Amount of O2 actually bound) x 100
B) (Amount of O2 actually bound/ Maximum amount of O2 that can potentially be bound) x 100
C) (Number of O2 molecule bound/ Total number of O2 molecules available) x 100
D) (Volume of O2 per mL of blood/ Total volume of blood) x 100
E) (Mass of O2 molecule/ Total mass of blood) x 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A characteristic feature of emphysema is damaged alveolar walls. What is a consequence of this condition?
A) decrease in the amount of air retained in the lungs after expiration
B) increase in lung elastic recoil during expiration
C) increase in mucus production and secretion
D) decrease in the rate of pulmonary gas exchange
E) increase in the rate of systemic gas exchange
A) decrease in the amount of air retained in the lungs after expiration
B) increase in lung elastic recoil during expiration
C) increase in mucus production and secretion
D) decrease in the rate of pulmonary gas exchange
E) increase in the rate of systemic gas exchange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to Boyle's law, each gas in a mixture of gases exerts its own pressure as if no other gases are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which is a factor that helps maintain an optimal rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange in our body?
A) minimal functional alveolar surface area for gas exchange
B) greater diffusion distance between the alveoli and blood
C) higher partial pressure difference between alveolar and blood O2
D) low solubility of CO2 in the blood
E) higher molecular weight of O2
A) minimal functional alveolar surface area for gas exchange
B) greater diffusion distance between the alveoli and blood
C) higher partial pressure difference between alveolar and blood O2
D) low solubility of CO2 in the blood
E) higher molecular weight of O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A scuba diver breathing air under high pressure is likely to experience giddiness due to the
A) intrapleural pressure exceeding the atmospheric pressure
B) accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural cavity
C) high partial pressure of O2 under high atmospheric pressure
D) low solubility of O2 in the blood under high pressure
E) dissolution of a considerable amount of nitrogen in the plasma
A) intrapleural pressure exceeding the atmospheric pressure
B) accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural cavity
C) high partial pressure of O2 under high atmospheric pressure
D) low solubility of O2 in the blood under high pressure
E) dissolution of a considerable amount of nitrogen in the plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify the true statement about pulmonary gas exchange.
A) It involves the conversion of deoxygenated blood to oxygenated blood.
B) It facilitates the diffusion of CO2 from the air to blood.
C) It involves the diffusion of O2 from pulmonary capillaries to the alveoli.
D) It takes place in the systemic capillaries and tissue cells.
E) It is dependent on the partial pressures of O2 and CO2 in areas of diffusion.
A) It involves the conversion of deoxygenated blood to oxygenated blood.
B) It facilitates the diffusion of CO2 from the air to blood.
C) It involves the diffusion of O2 from pulmonary capillaries to the alveoli.
D) It takes place in the systemic capillaries and tissue cells.
E) It is dependent on the partial pressures of O2 and CO2 in areas of diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_____ _____ is defined as the volume of air per minute that actually reaches the respiratory zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The pressure of a specific gas in a mixture is called its
A) partial pressure
B) hydrostatic pressure
C) osmotic pressure
D) differential pressure
E) absolute pressure
A) partial pressure
B) hydrostatic pressure
C) osmotic pressure
D) differential pressure
E) absolute pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under what condition does more oxygen combine with hemoglobin?
A) at very high altitudes
B) when the partial pressure of O2 is low
C) when cooperativity between oxygen and hemoglobin is low
D) when the partial pressure of O2 is high
E) in the body's metabolically active sites
A) at very high altitudes
B) when the partial pressure of O2 is low
C) when cooperativity between oxygen and hemoglobin is low
D) when the partial pressure of O2 is high
E) in the body's metabolically active sites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Imagine that the atmosphere is made up of only nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Given that the partial pressures of the three gases is 597.4 mmHg, 158.8 mmHg, and 0.3 mmHg respectively, what is the total atmospheric pressure?
A) 750 mmHg
B) 756.5 mmHg
C) 760 mmHg
D) 765.5 mmHg
E) 770 mmHg
A) 750 mmHg
B) 756.5 mmHg
C) 760 mmHg
D) 765.5 mmHg
E) 770 mmHg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the process indicated by the circle in the figure below. 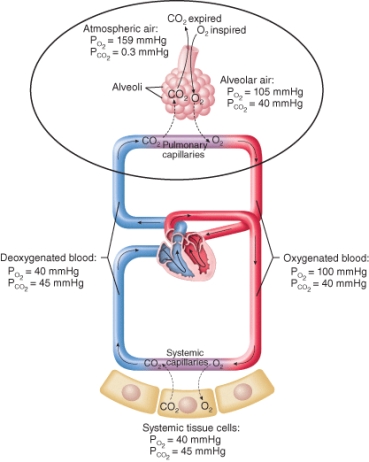
A) anaerobic respiration
B) pulmonary gas exchange
C) systemic gas exchange
D) cellular respiration
E) blood deoxygenation

A) anaerobic respiration
B) pulmonary gas exchange
C) systemic gas exchange
D) cellular respiration
E) blood deoxygenation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How can a scuba diver prevent himself or herself from developing decompression sickness?
A) by ascending rapidly to the sea surface
B) by ascending slowly to the sea surface
C) by using nitrogen-free compressed air for breathing underwater
D) by using compressed gas with high oxygen concentration
E) by ensuring adequate humidification of the compressed air he or she is breathing underwater
A) by ascending rapidly to the sea surface
B) by ascending slowly to the sea surface
C) by using nitrogen-free compressed air for breathing underwater
D) by using compressed gas with high oxygen concentration
E) by ensuring adequate humidification of the compressed air he or she is breathing underwater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Henry's law states:
A) In a mixture of non-reacting gases the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.
B) The quantity of a gas that will dissolve in a liquid is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas and its solubility.
C) At constant temperature the product of the pressure and volume of a given mass of an ideal gas in a closed system is always constant.
D) For a given mass of an ideal gas at constant pressure and in a closed system its volume is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
E) For a given mass and constant volume of an ideal gas the pressure exerted on the sides of its container is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
A) In a mixture of non-reacting gases the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.
B) The quantity of a gas that will dissolve in a liquid is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas and its solubility.
C) At constant temperature the product of the pressure and volume of a given mass of an ideal gas in a closed system is always constant.
D) For a given mass of an ideal gas at constant pressure and in a closed system its volume is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
E) For a given mass and constant volume of an ideal gas the pressure exerted on the sides of its container is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why is CO2 more soluble in blood plasma than O2?
A) it is lighter than O2
B) its partial pressure is lower than that of O2
C) it is highly soluble in water
D) its specific gravity is lesser than that of O2
E) it is a higher affinity to hemoglobin than O2
A) it is lighter than O2
B) its partial pressure is lower than that of O2
C) it is highly soluble in water
D) its specific gravity is lesser than that of O2
E) it is a higher affinity to hemoglobin than O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In an adult, tidal volume measures 500 mL/breath, anatomic dead space is 120 mL/breath, and respiratory rate is about 10 breaths/min. What is the alveolar ventilation?
A) 3.8 L/min
B) 4.0 L/min
C) 3.6 L/min
D) 4.4 L/min
E) 3.0 L/min
A) 3.8 L/min
B) 4.0 L/min
C) 3.6 L/min
D) 4.4 L/min
E) 3.0 L/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify the true statement about regulation of ventilation.
A) A stimulated limbic system decreases the rate and depth of ventilation.
B) A decrease in body temperature decreases respiratory rate.
C) Stretching the anal sphincter muscle decreases the rate of respiration.
D) A prolonged somatic pain decreases respiratory rate.
E) Physical or chemical irritation of the pharynx increases ventilation.
A) A stimulated limbic system decreases the rate and depth of ventilation.
B) A decrease in body temperature decreases respiratory rate.
C) Stretching the anal sphincter muscle decreases the rate of respiration.
D) A prolonged somatic pain decreases respiratory rate.
E) Physical or chemical irritation of the pharynx increases ventilation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Clusters of neurons located in the medulla oblongata and pons of the brain stem send action potentials to the respiratory muscles to alter the size of the thoracic cavity. These clusters together make up the _____ _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following scenarios does label A most likely represent? 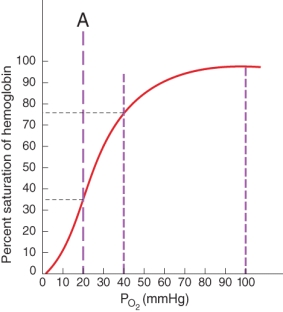
A) oxygenated blood at high altitudes
B) oxygenated blood in systemic arteries
C) deoxygenated blood due to contracting skeletal muscles
D) deoxygenated blood due to high cooperativity between oxygen and hemoglobin
E) deoxygenated blood in systemic veins at rest

A) oxygenated blood at high altitudes
B) oxygenated blood in systemic arteries
C) deoxygenated blood due to contracting skeletal muscles
D) deoxygenated blood due to high cooperativity between oxygen and hemoglobin
E) deoxygenated blood in systemic veins at rest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The amount of O2 binding to hemoglobin is reduced when
A) partial pressure of O2 is 60 mmHg
B) the sites for binding are pulmonary capillaries
C) cooperativity is low
D) inspired air has high humidity
E) skeletal muscles are at rest
A) partial pressure of O2 is 60 mmHg
B) the sites for binding are pulmonary capillaries
C) cooperativity is low
D) inspired air has high humidity
E) skeletal muscles are at rest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify a neural change that causes an abrupt increase in ventilation at the start of an exercise.
A) Sensory information from proprioceptors in muscles is sent to the dorsal respiratory group.
B) Motor information from the primary motor cortex reaches the pontine respiratory center.
C) Deactivation of the limbic system takes place.
D) The pre-Bötzinger complex gets activated.
E) The pre-Bötzinger complex sends action potentials for sternocleidomastoid muscle contraction.
A) Sensory information from proprioceptors in muscles is sent to the dorsal respiratory group.
B) Motor information from the primary motor cortex reaches the pontine respiratory center.
C) Deactivation of the limbic system takes place.
D) The pre-Bötzinger complex gets activated.
E) The pre-Bötzinger complex sends action potentials for sternocleidomastoid muscle contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Identify the true statement about peripheral chemoreceptors.
A) They respond to changes in hydrogen ion concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid.
B) They are sensitive to changes in partial pressure of O2 in the blood.
C) They respond to changes in partial pressure of CO2 in the cerebrospinal fluid.
D) They are insensitive to partial pressure of CO2 in the blood.
E) They are insensitive to changes in hydrogen ion concentration in the blood.
A) They respond to changes in hydrogen ion concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid.
B) They are sensitive to changes in partial pressure of O2 in the blood.
C) They respond to changes in partial pressure of CO2 in the cerebrospinal fluid.
D) They are insensitive to partial pressure of CO2 in the blood.
E) They are insensitive to changes in hydrogen ion concentration in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Gradual increase in ventilation during moderate exercise is due to
A) slightly decreased partial pressure of O2
B) decreased O2 consumption
C) slightly decreased partial pressure of CO2
D) decreased temperature
E) reduced CO2 production
A) slightly decreased partial pressure of O2
B) decreased O2 consumption
C) slightly decreased partial pressure of CO2
D) decreased temperature
E) reduced CO2 production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following occurs when cardiac output rises?
A) The amount of O2 diffusing from alveolar air into the blood decreases.
B) The amount of blood flowing to the lungs increases.
C) The amount of O2 consumed by muscles decreases.
D) The surface area available for O2 diffusion decreases.
E) The amount of CO2 retained by the lungs increases.
A) The amount of O2 diffusing from alveolar air into the blood decreases.
B) The amount of blood flowing to the lungs increases.
C) The amount of O2 consumed by muscles decreases.
D) The surface area available for O2 diffusion decreases.
E) The amount of CO2 retained by the lungs increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What happens in the respiratory center during forced expiration?
A) The inspiratory neurons of the dorsal respiratory group send action potentials for scalene muscle relaxation.
B) The pre-Bötzinger complex sends action potentials for sternocleidomastoid muscle contraction.
C) Neurons in the pontine respiratory center send action potentials to the diaphragm.
D) The inspiratory neurons of the dorsal respiratory group get activated.
E) The expiratory neurons of the ventral respiratory group get activated.
A) The inspiratory neurons of the dorsal respiratory group send action potentials for scalene muscle relaxation.
B) The pre-Bötzinger complex sends action potentials for sternocleidomastoid muscle contraction.
C) Neurons in the pontine respiratory center send action potentials to the diaphragm.
D) The inspiratory neurons of the dorsal respiratory group get activated.
E) The expiratory neurons of the ventral respiratory group get activated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What brings about an immediate cessation of breathing followed by coughing or sneezing?
A) irritation of the airways
B) a drop in blood pressure
C) stretching of the anal sphincter muscle
D) a stimulated limbic system
E) a prolonged somatic pain
A) irritation of the airways
B) a drop in blood pressure
C) stretching of the anal sphincter muscle
D) a stimulated limbic system
E) a prolonged somatic pain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The lower the amount of oxyhemoglobin (Hb-O2), the higher the CO2 carrying capacity of the blood. What is this relationship called?
A) Tyndall effect
B) chronotropic effect
C) Bohr effect
D) Haldane effect
E) inotropic effect
A) Tyndall effect
B) chronotropic effect
C) Bohr effect
D) Haldane effect
E) inotropic effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The figure below shows various components of the respiratory center. Identify the group of neurons indicated by the arrow. 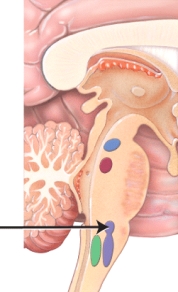
A) pre-Bötzinger complex
B) medulla oblongata
C) dorsal respiratory group
D) apneustic area
E) pneumotaxic area

A) pre-Bötzinger complex
B) medulla oblongata
C) dorsal respiratory group
D) apneustic area
E) pneumotaxic area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The condition in which the partial pressure of CO2 exceeds 40 mmHg is called
A) hyperemia
B) emphysema
C) hypoxia
D) narcosis
E) hypercapnia
A) hyperemia
B) emphysema
C) hypoxia
D) narcosis
E) hypercapnia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Identify the true statement about the affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
A) Presence of carbonic acid in the erythrocytes increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
B) The affinity of hemoglobin for O2 increases with an increase in temperature.
C) A decrease in the partial pressure of CO2 causes the affinity of hemoglobin for O2 to decrease.
D) Presence of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
E) The affinity of hemoglobin for O2 decreases with a decrease in acidity.
A) Presence of carbonic acid in the erythrocytes increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
B) The affinity of hemoglobin for O2 increases with an increase in temperature.
C) A decrease in the partial pressure of CO2 causes the affinity of hemoglobin for O2 to decrease.
D) Presence of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate increases the affinity of hemoglobin for O2.
E) The affinity of hemoglobin for O2 decreases with a decrease in acidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the effect of increased acidity in the blood?
A) It decreases the level of hydrogen ions in the blood.
B) It decreases the O2 available for tissues.
C) It increases hemoglobin's affinity to CO.
D) It facilitates O2 dissociation from hemoglobin.
E) It shifts the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left.
A) It decreases the level of hydrogen ions in the blood.
B) It decreases the O2 available for tissues.
C) It increases hemoglobin's affinity to CO.
D) It facilitates O2 dissociation from hemoglobin.
E) It shifts the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which component of the respiratory center sets the basic rhythm of breathing?
A) dorsal respiratory group
B) apneustic area
C) pneumotaxic area
D) pre-Bötzinger complex
E) peripheral chemoreceptors
A) dorsal respiratory group
B) apneustic area
C) pneumotaxic area
D) pre-Bötzinger complex
E) peripheral chemoreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
How does the respiratory system contribute to homeostasis?
A) It helps the endocrine system regulate pH of body fluids.
B) It assists the urinary system in the process of formation of angiotensin I.
C) It aids return of venous blood to the heart during expiration.
D) It helps adjust pH of body fluids through exhalation of carbon dioxide.
E) It helps facilitate bowel movements in the digestive system.
A) It helps the endocrine system regulate pH of body fluids.
B) It assists the urinary system in the process of formation of angiotensin I.
C) It aids return of venous blood to the heart during expiration.
D) It helps adjust pH of body fluids through exhalation of carbon dioxide.
E) It helps facilitate bowel movements in the digestive system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What happens when partial pressure of CO2 is high in blood?
A) hemoglobin releases O2 more readily
B) acidity of the blood decreases
C) hydrogen ion concentration decreases
D) saturation curve shifts to the right
E) production of lactic acid increases
A) hemoglobin releases O2 more readily
B) acidity of the blood decreases
C) hydrogen ion concentration decreases
D) saturation curve shifts to the right
E) production of lactic acid increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
To which muscle does the dorsal respiratory group send action potential?
A) abdominal muscles
B) external intercostals
C) internal intercostals
D) sternocleidomastoid muscles
E) scalene muscles
A) abdominal muscles
B) external intercostals
C) internal intercostals
D) sternocleidomastoid muscles
E) scalene muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
During the exchange of O2 and CO2 in systemic capillaries, H+ combines with HCO3− inside erythrocytes to form H2CO3. What happens to this H2CO3?
A) it splits into CO2 and H2O
B) it splits into CO2, H2, and O-
C) it reacts with Cl2 to form HCl and CO2
D) it reacts with H+ to form HCO3− and O2
E) it splits into CO and H2O2
A) it splits into CO2 and H2O
B) it splits into CO2, H2, and O-
C) it reacts with Cl2 to form HCl and CO2
D) it reacts with H+ to form HCO3− and O2
E) it splits into CO and H2O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



