Deck 21: The Digestive System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: The Digestive System
1
The single-unit smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract consists of two types of cells. They are
A) autorhythmic fibers and contractile fibers
B) oxidative fibers and glycolytic fibers
C) elastic fibers and collagenous fibers
D) reticular fibers and autorhythmic fibers
E) contractile fibers and spindle fibers
A) autorhythmic fibers and contractile fibers
B) oxidative fibers and glycolytic fibers
C) elastic fibers and collagenous fibers
D) reticular fibers and autorhythmic fibers
E) contractile fibers and spindle fibers
A
2
What is a function of the parts labeled A and B in the image below? 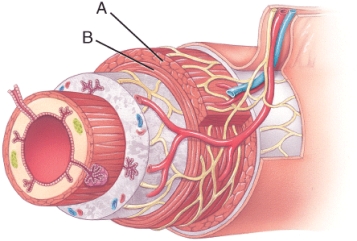
A) They help propel food along the gastrointestinal tract.
B) They secrete enzymes into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract that digest ingested food substances.
C) They secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
D) They facilitate the transfer of absorbed nutrients to the blood.
E) They hold the digestive system in place.

A) They help propel food along the gastrointestinal tract.
B) They secrete enzymes into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract that digest ingested food substances.
C) They secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
D) They facilitate the transfer of absorbed nutrients to the blood.
E) They hold the digestive system in place.
A
3
Identify the structure that is incorrectly paired with its respective function.
A) lips: keeps food between the upper and lower teeth
B) soft palate: elevates during swallowing to close off the pharynx
C) tongue: facilitates simultaneous chewing and breathing
D) salivary glands: secrete saliva that lubricates and dissolves food
A) lips: keeps food between the upper and lower teeth
B) soft palate: elevates during swallowing to close off the pharynx
C) tongue: facilitates simultaneous chewing and breathing
D) salivary glands: secrete saliva that lubricates and dissolves food
C
4
Identify the organ of the gastrointestinal tract indicated in the image. 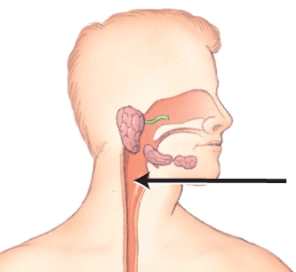
A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) larynx
D) tongue
E) epiglottis

A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) larynx
D) tongue
E) epiglottis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the gastrointestinal reflex pathway is confined entirely within the gastrointestinal tract wall, then it is called a/an _____ _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The sympathetic nerves that supply the gastrointestinal tract enhance gastrointestinal secretion and motility by inhibiting the neurons of the enteric nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The capability of the gastrointestinal tract to mix and move material along its length is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the structure indicated in the image below. 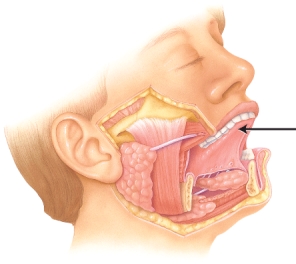
A) uvula
B) tongue
C) teeth
D) lips
E) cheek

A) uvula
B) tongue
C) teeth
D) lips
E) cheek

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In addition to being the outermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract, the _____ is also part of the peritoneum that lines the abdominal cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify an organ that is part of the gastrointestinal tract.
A) larynx
B) gallbladder
C) esophagus
D) pancreas
E) liver
A) larynx
B) gallbladder
C) esophagus
D) pancreas
E) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, the epithelial cells that secrete hormones into the blood stream are collectively known as
A) exocrine cells
B) enteroendocrine cells
C) absorptive cells
D) intercalated cells
E) receptor cells
A) exocrine cells
B) enteroendocrine cells
C) absorptive cells
D) intercalated cells
E) receptor cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
_____ in the saliva lubricates food so it can be moved around easily in the mouth, formed into a ball, and swallowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the function of the soft palate and the uvula?
A) They facilitate changes in the shape and size of the tongue for swallowing.
B) They keep food in the mouth between the upper and lower teeth.
C) They prevent the entry of food and liquid substances into the nasal cavity.
D) They facilitate the movement of the food to the back of the mouth for swallowing.
E) They propel the food along the gastrointestinal tract.
A) They facilitate changes in the shape and size of the tongue for swallowing.
B) They keep food in the mouth between the upper and lower teeth.
C) They prevent the entry of food and liquid substances into the nasal cavity.
D) They facilitate the movement of the food to the back of the mouth for swallowing.
E) They propel the food along the gastrointestinal tract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the tissue that is correctly matched with its appropriate function.
A) lamina propria: provides passage for nutrients absorbed by the GI tract to enter the blood
B) muscularis mucosae: facilitates voluntary swallowing
C) submucosa: lines the abdominal cavity and covers the organs within that cavity
D) muscularis externa: provides the GI tract with distensibility and elasticity
E) peritoneum: increases surface area for digestion and absorption
A) lamina propria: provides passage for nutrients absorbed by the GI tract to enter the blood
B) muscularis mucosae: facilitates voluntary swallowing
C) submucosa: lines the abdominal cavity and covers the organs within that cavity
D) muscularis externa: provides the GI tract with distensibility and elasticity
E) peritoneum: increases surface area for digestion and absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Muscular contractions of the accessory organs of the digestive system stimulate the physical breakdown of the food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The process of _____ refers to alternating muscular contractions that mix luminal contents in the small intestine in response to distension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the digestive process indicated by the green arrow in the image below. 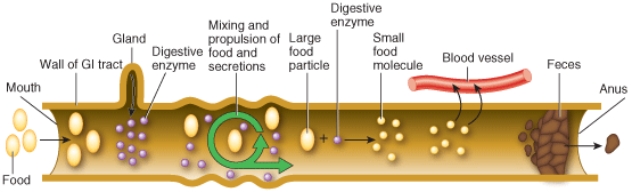
A) ingestion
B) absorption
C) digestion
D) motility
E) secretion

A) ingestion
B) absorption
C) digestion
D) motility
E) secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify a function of the myenteric plexus.
A) increasing gastrointestinal surface area
B) regulating gastrointestinal secretion
C) regulating gastrointestinal tract motility
D) promoting nutrient absorption from the gastrointestinal tract
E) inhibiting secretion of hormones into the bloodstream
A) increasing gastrointestinal surface area
B) regulating gastrointestinal secretion
C) regulating gastrointestinal tract motility
D) promoting nutrient absorption from the gastrointestinal tract
E) inhibiting secretion of hormones into the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The teeth is protected from wear and tear by the
A) mucus
B) enamel
C) teniae coli
D) haustra
E) uvula
A) mucus
B) enamel
C) teniae coli
D) haustra
E) uvula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the process depicted in the image. 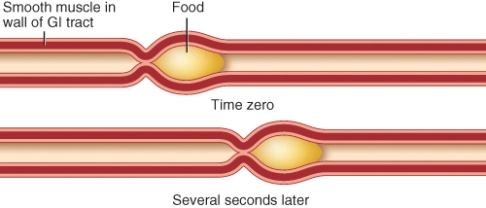
A) peristalsis
B) segmentation
C) inspiration
D) expiration
E) distension

A) peristalsis
B) segmentation
C) inspiration
D) expiration
E) distension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following actions constitutes the voluntary stage of swallowing?
A) The tongue forces the bolus to move into the pharynx.
B) The entry of the bolus triggers the chemoreceptors in the pharynx.
C) The action potentials from the deglutination center trigger the elevation of the soft palate and the uvula.
D) The epiglottis closes to prevent the passage of the bolus into the larynx.
E) The upper esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow the entry of the bolus into the esophagus.
A) The tongue forces the bolus to move into the pharynx.
B) The entry of the bolus triggers the chemoreceptors in the pharynx.
C) The action potentials from the deglutination center trigger the elevation of the soft palate and the uvula.
D) The epiglottis closes to prevent the passage of the bolus into the larynx.
E) The upper esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow the entry of the bolus into the esophagus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which enzyme breaks down dietary triglycerides in the stomach?
A) salivary amylase
B) carbonic anhydrase
C) pepsin
D) lingual lipase
E) chymotrypsin
A) salivary amylase
B) carbonic anhydrase
C) pepsin
D) lingual lipase
E) chymotrypsin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The soupy liquid obtained as a result of repeated propulsion and retropulsion is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify the ion that the proton pump transports into the parietal cells.
A) HCO3-
B) K+
C) Cl-
D) H+
E) O2-
A) HCO3-
B) K+
C) Cl-
D) H+
E) O2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The secretion of saliva is stimulated by the action potentials returning from the superior and inferior salivatory nuclei along parasympathetic fibers of the
A) hypoglossal and abducens nerves
B) facial and glossopharyngeal nerves
C) palatine and nasopalatine nerves
D) thoracic and lumbar splanchnic nerves
E) vagus and pelvic splanchnic nerves
A) hypoglossal and abducens nerves
B) facial and glossopharyngeal nerves
C) palatine and nasopalatine nerves
D) thoracic and lumbar splanchnic nerves
E) vagus and pelvic splanchnic nerves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The cells in the stomach that produce the intrinsic factor needed for absorption of vitamin B12 are
A) chief cells
B) S cells
C) mucous neck cells
D) G cells
E) parietal cells
A) chief cells
B) S cells
C) mucous neck cells
D) G cells
E) parietal cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify the labeled regions of the stomach where gastric emptying occurs? 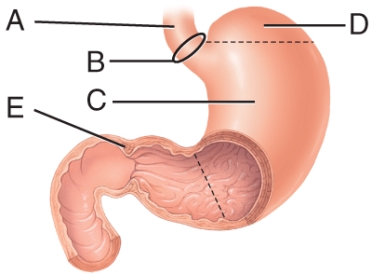
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How does mastication help in the digestion process?
A) It enables the breakdown of dietary triglycerides into fatty acids and diglycerides.
B) It facilitates the digestion of starches in the ingested food.
C) It reduces food to a soft, flexible, and easily swallowed mass.
D) It prevents wear and tear of the teeth by buffering acids present in the ingested food.
E) It prevents the development of achalasia.
A) It enables the breakdown of dietary triglycerides into fatty acids and diglycerides.
B) It facilitates the digestion of starches in the ingested food.
C) It reduces food to a soft, flexible, and easily swallowed mass.
D) It prevents wear and tear of the teeth by buffering acids present in the ingested food.
E) It prevents the development of achalasia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The presence of which layer of the muscularis externa enhances gastric motility in the stomach?
A) oblique layer
B) longitudinal layer
C) mucosal layer
D) submucosal layer
E) circular layer
A) oblique layer
B) longitudinal layer
C) mucosal layer
D) submucosal layer
E) circular layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which enzyme is inactivated when chyme mixes with acidic gastric juice?
A) lingual lipase
B) salivary amylase
C) carbonic anhydrase
D) gastric lipase
E) pancreatic amylase
A) lingual lipase
B) salivary amylase
C) carbonic anhydrase
D) gastric lipase
E) pancreatic amylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Imagine that you have just finished a meal. A few minutes later, you regurgitate everything you had eaten. In addition to this, you experience a burning sensation near your heart. Which is a likely explanation for your symptoms?
A) gastroesophageal reflux disease
B) pulmonary edema
C) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
D) aneurysm
E) cardiogenic shock
A) gastroesophageal reflux disease
B) pulmonary edema
C) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
D) aneurysm
E) cardiogenic shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify the function of the epiglottis in coordination with organs A and B in the image. 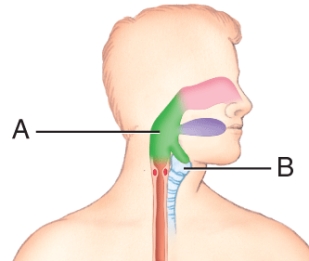 v
v
A) It hinders the passage of air from B to A.
B) Its movements help create air turbulence in A and B.
C) It prevents blood circulation between A and B.
D) It prevents the passage of food from A to B.
E) Its movements facilitate the humidification of air in A and B.
 v
vA) It hinders the passage of air from B to A.
B) Its movements help create air turbulence in A and B.
C) It prevents blood circulation between A and B.
D) It prevents the passage of food from A to B.
E) Its movements facilitate the humidification of air in A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which cells are primarily concerned with the secretion of pepsinogen and gastric lipase?
A) parietal cells
B) mucous neck cells
C) chief cells
D) surface mucous cells
E) mast cells
A) parietal cells
B) mucous neck cells
C) chief cells
D) surface mucous cells
E) mast cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the statement that correctly describes premolars.
A) One-cusped to tear and shred food
B) Three-cusped that crush and grind food
C) Chisel-shaped to cut into food
D) Two-cusped that crush and grind food
A) One-cusped to tear and shred food
B) Three-cusped that crush and grind food
C) Chisel-shaped to cut into food
D) Two-cusped that crush and grind food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
_____, or swallowing, is the movement of food from the mouth into the stomach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify a step involved in the esophageal stage of swallowing.
A) The epiglottis covers the opening of the larynx.
B) Peristalsis facilitates the movement of the bolus to the stomach.
C) The soft palate and the uvula become elevated to block the nasal cavity.
D) The deglutination center in the brain stem gets activated.
E) Deglutination enables the bolus to enter the pharynx.
A) The epiglottis covers the opening of the larynx.
B) Peristalsis facilitates the movement of the bolus to the stomach.
C) The soft palate and the uvula become elevated to block the nasal cavity.
D) The deglutination center in the brain stem gets activated.
E) Deglutination enables the bolus to enter the pharynx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is most likely to happen if the parts labeled A in the image fail to relax? 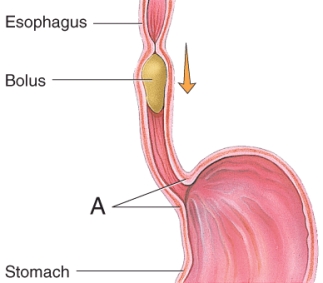
A) narcosis
B) edema
C) pleurisy
D) atelectasis
E) achalasia

A) narcosis
B) edema
C) pleurisy
D) atelectasis
E) achalasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Retropulsion occurs because
A) the fundus prevents the chyme from passing into the narrow pyloric sphincter
B) mostly the large food particles slow down the peristaltic movement in the fundus
C) the chemoreceptors and the stomach receptors are inactivated in the presence of food particles
D) the peristaltic waves of the body of the stomach constrict the antrum
E) most food particles in the stomach initially are too large to fit through the narrow pyloric sphincter
A) the fundus prevents the chyme from passing into the narrow pyloric sphincter
B) mostly the large food particles slow down the peristaltic movement in the fundus
C) the chemoreceptors and the stomach receptors are inactivated in the presence of food particles
D) the peristaltic waves of the body of the stomach constrict the antrum
E) most food particles in the stomach initially are too large to fit through the narrow pyloric sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The _____ _____ extends and develops into the upper esophageal sphincter (UES) and the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Propulsion is the movement of gastric contents from the body of the stomach to the antrum. This movement is brought about by
A) elastic recoil
B) diffusion
C) opsonization
D) segmentation
E) peristalsis
A) elastic recoil
B) diffusion
C) opsonization
D) segmentation
E) peristalsis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The bile is yellow-green in color primarily due to the pigment _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
One of the reactions involved in the carbohydrate metabolism in the liver is the
A) conversion of ammonia to urea
B) synthesis of plasma proteins
C) conversion of glycogen to glucose
D) breakdown of fatty acids
E) synthesis of bile salts from cholesterol
A) conversion of ammonia to urea
B) synthesis of plasma proteins
C) conversion of glycogen to glucose
D) breakdown of fatty acids
E) synthesis of bile salts from cholesterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify a function of the gallbladder.
A) detoxifying alcohol
B) excreting feces
C) activating vitamin D
D) storing bile
E) secreting insulin and glucagon
A) detoxifying alcohol
B) excreting feces
C) activating vitamin D
D) storing bile
E) secreting insulin and glucagon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which is the only protein-digesting enzyme present in the stomach?
A) trypsin
B) chymotrypsin
C) elastase
D) pepsin
E) carboxypeptidase
A) trypsin
B) chymotrypsin
C) elastase
D) pepsin
E) carboxypeptidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An individual suffering from peptic ulcer disease is treated with histamine blockers when the peptic ulcer disease is caused due to
A) hyperactivity of the enzyme gastric lipase
B) incomplete conversion of pepsinogen
C) hyposecretion of NaCl
D) hypersecretion of HCl
E) the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
A) hyperactivity of the enzyme gastric lipase
B) incomplete conversion of pepsinogen
C) hyposecretion of NaCl
D) hypersecretion of HCl
E) the bacterium Helicobacter pylori

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How do the acinar cells of the pancreas assist in the digestion process?
A) They secrete the enzymatic component of the pancreatic juice.
B) They secrete a fluid rich in bicarbonate ions.
C) They secrete the inactive form of pepsin.
D) They synthesize the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
E) They synthesize a substance that causes the breakdown of fatty acids.
A) They secrete the enzymatic component of the pancreatic juice.
B) They secrete a fluid rich in bicarbonate ions.
C) They secrete the inactive form of pepsin.
D) They synthesize the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
E) They synthesize a substance that causes the breakdown of fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How does the product of parietal cells help in the digestion process in the stomach?
A) It prevents the splitting of short-chain triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
B) It stimulates the secretion of hormones that promote the flow of bile and pancreatic juice.
C) It inhibits the breakdown of protein chains into smaller peptide fragments.
D) It facilitates the deactivation of the enzyme pepsin.
E) It provides a suitable environment for the production of pepsinogen from the G cells.
A) It prevents the splitting of short-chain triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
B) It stimulates the secretion of hormones that promote the flow of bile and pancreatic juice.
C) It inhibits the breakdown of protein chains into smaller peptide fragments.
D) It facilitates the deactivation of the enzyme pepsin.
E) It provides a suitable environment for the production of pepsinogen from the G cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Mastication involves forcibly expelling the contents of the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The longest portion of the small intestine is separated from the large intestine by the
A) pyloric sphincter
B) sphincter of Oddi
C) ileocecal sphincter
D) lower esophageal sphincter
E) upper esophageal sphincter
A) pyloric sphincter
B) sphincter of Oddi
C) ileocecal sphincter
D) lower esophageal sphincter
E) upper esophageal sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify the cells that secrete the hormones insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin.
A) acini
B) islets of Langerhans
C) parietal cells
D) mucous neck cells
E) interstitial cells of Cajal
A) acini
B) islets of Langerhans
C) parietal cells
D) mucous neck cells
E) interstitial cells of Cajal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the process of _____, bile salts facilitate the breakdown of large lipid globules into a suspension of small lipid globules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following enzymes split short-chain triglycerides?
A) gastric lipase
B) salivary amylase
C) pepsin
D) enterokinase
A) gastric lipase
B) salivary amylase
C) pepsin
D) enterokinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Parietal cells generate a product that aids in digestion. Identify the name of the product that should replace the area with the question mark on the figure below. 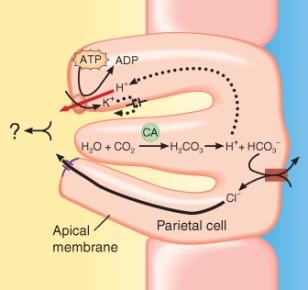
A) carbonic acid
B) hypochlorous acid
C) hydrochloric acid
D) lactic acid
E) ribonucleic acid

A) carbonic acid
B) hypochlorous acid
C) hydrochloric acid
D) lactic acid
E) ribonucleic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Identify the fluid that flows through structure A. 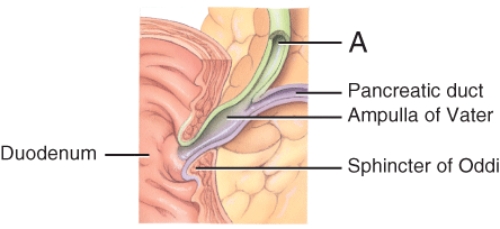
A) pancreatic juice
B) bile
C) chyme
D) intestinal juicev
E) bolus

A) pancreatic juice
B) bile
C) chyme
D) intestinal juicev
E) bolus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The image details the parts of a liver lobule. Identify one of the functions of the cell indicated by the arrow. 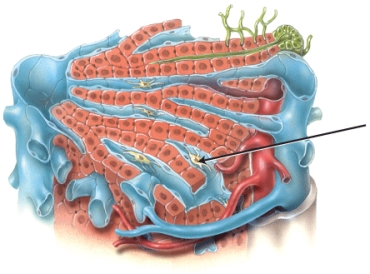
A) destroying foreign particles in the venous blood from the gastrointestinal tract
B) providing surface area for exchange of gases and substances between blood and liver cells
C) collecting bile produced by the specialized epithelial cells of the liver lobule
D) producing enzymes that activate other inactive precursors
E) regulating the bile content in the small intestine

A) destroying foreign particles in the venous blood from the gastrointestinal tract
B) providing surface area for exchange of gases and substances between blood and liver cells
C) collecting bile produced by the specialized epithelial cells of the liver lobule
D) producing enzymes that activate other inactive precursors
E) regulating the bile content in the small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The brush-border enzyme plays a key role in activating precursors such as chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase to produce their active enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why is an individual who regularly consumes alcohol more likely to suffer from hepatic jaundice?
A) In such individuals, passage of blood through the liver is limited, and this causes the liver to lose its functional abilities.
B) Such individuals have an excess of liver flukes in their livers that obstruct bile excretion and contribute to bilirubin build-up in the body.
C) In such individuals, the liver loses its ability to prevent bilirubin conjugation with glucuronic acid.
D) Necrosis of the liver cells in such individuals reduces the liver's ability to metabolize and excrete bilirubin.
E) In the livers of such individuals, conversion of alcohol to acetaldehyde increases the production of high-density cholesterol that inhibits the synthesis of bile salts.
A) In such individuals, passage of blood through the liver is limited, and this causes the liver to lose its functional abilities.
B) Such individuals have an excess of liver flukes in their livers that obstruct bile excretion and contribute to bilirubin build-up in the body.
C) In such individuals, the liver loses its ability to prevent bilirubin conjugation with glucuronic acid.
D) Necrosis of the liver cells in such individuals reduces the liver's ability to metabolize and excrete bilirubin.
E) In the livers of such individuals, conversion of alcohol to acetaldehyde increases the production of high-density cholesterol that inhibits the synthesis of bile salts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The duct that helps to transport the pancreatic juice from the pancreatic duct to the lumen of the duodenum is
A) acinus
B) ampulla of Vater
C) cystic duct
D) gallbladder
E) common hepatic duct
A) acinus
B) ampulla of Vater
C) cystic duct
D) gallbladder
E) common hepatic duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Each liver lobule consists of specialized epithelial cells called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Identify the structures labeled as A in the image. 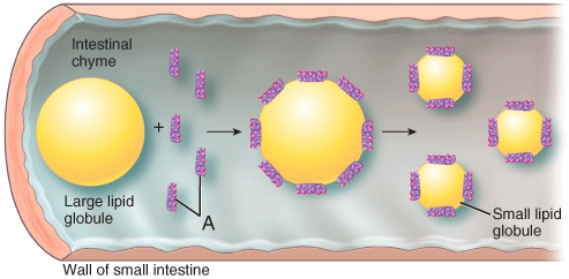
A) Kupffer cells
B) bile salts
C) beta globulins
D) parietal cells
E) glycogen

A) Kupffer cells
B) bile salts
C) beta globulins
D) parietal cells
E) glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The migrating motility complex that occurs in the small intestine is a type of
A) segmentation
B) peristalsis
C) emulsification
D) autoregulation
E) mastication
A) segmentation
B) peristalsis
C) emulsification
D) autoregulation
E) mastication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The digestion of which of the following gives nitrogenous bases, pentose sugars, and phosphates as products?
A) triglycerides
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) proteins
E) starch
A) triglycerides
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) proteins
E) starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Identify the enzyme that yields maltose as its end product.
A) lingual lipase
B) α-dextrinase
C) pancreatic amylase
D) lipoprotein lipase
A) lingual lipase
B) α-dextrinase
C) pancreatic amylase
D) lipoprotein lipase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain the role of bacteria during chemical digestion in the large intestine.
A) They ferment a small amount of carbohydrates and release flatus.
B) They facilitate the dissolution of vitamins and release flatus.
C) They cause the breakdown of stercobilin to release bilirubin in the feces.
D) They initiate the lysis of fatty acids into simpler molecules.
E) They cause inflammation of the appendix in response to foreign pathogens.
A) They ferment a small amount of carbohydrates and release flatus.
B) They facilitate the dissolution of vitamins and release flatus.
C) They cause the breakdown of stercobilin to release bilirubin in the feces.
D) They initiate the lysis of fatty acids into simpler molecules.
E) They cause inflammation of the appendix in response to foreign pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A person experiences bloating, gas, abdominal cramps, and episodes of diarrhea after consuming dairy products. How can these symptoms be prevented in this individual?
A) by stimulating bile salt production by the hepatocytes for rapid emulsification of dairy products
B) by triggering the liver to synthesize the active form of vitamin D
C) by inhibiting synthesis of excess lactase by the goblet cells of the small intestine
D) by inhibiting lactase production by the acinar cells of the pancreas
E) by stimulating adequate secretion of lactase by the absorptive cells of the small intestine
A) by stimulating bile salt production by the hepatocytes for rapid emulsification of dairy products
B) by triggering the liver to synthesize the active form of vitamin D
C) by inhibiting synthesis of excess lactase by the goblet cells of the small intestine
D) by inhibiting lactase production by the acinar cells of the pancreas
E) by stimulating adequate secretion of lactase by the absorptive cells of the small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following mechanisms describes the way in which the structure labeled C leaves the absorptive cell? 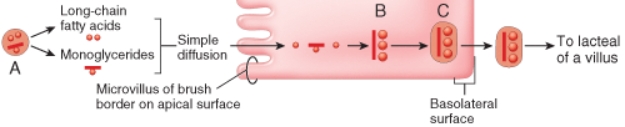
A) simple diffusion
B) exocytosis
C) secondary active transport
D) exosmosis
E) facilitated diffusion v

A) simple diffusion
B) exocytosis
C) secondary active transport
D) exosmosis
E) facilitated diffusion v

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the two ways by which monosaccharides are absorbed by the absorptive cells?
A) bulk flow and facilitated diffusion
B) simple diffusion and osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion and active transport
D) osmosis and migrating motility complex
E) active transport and osmosis
A) bulk flow and facilitated diffusion
B) simple diffusion and osmosis
C) facilitated diffusion and active transport
D) osmosis and migrating motility complex
E) active transport and osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Identify the cell that is correctly paired with its associated function.
A) absorptive cells: secrete intestinal juice
B) goblet cells: secrete lysozyme
C) paneth cells: secrete mucus
D) K cells: secrete glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide
A) absorptive cells: secrete intestinal juice
B) goblet cells: secrete lysozyme
C) paneth cells: secrete mucus
D) K cells: secrete glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Identify the brush-border enzymes involved in the process of carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine.
A) aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase
B) salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase
C) sucrase and lactase
D) lingual lipase and gastric lipase
E) trypsin and elastase
A) aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase
B) salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase
C) sucrase and lactase
D) lingual lipase and gastric lipase
E) trypsin and elastase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The hormone _____ causes contraction of the wall of the gallbladder to release the stored bile out of the gallbladder into the cystic duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is a function that a micelle shares with a symporter?
A) They both attach to unstable molecules in the blood capillaries and cleave them to stabilize them.
B) They both attach to substances in the stomach for the purpose of digestion.
C) They both help to transport substances from the absorptive cells to the blood capillaries in the small intestine.
D) They both help to transport substances from the lumen to the absorptive cells in the small intestine.
E) They both cleave inactive precursors to form active enzymes in the small intestine.
A) They both attach to unstable molecules in the blood capillaries and cleave them to stabilize them.
B) They both attach to substances in the stomach for the purpose of digestion.
C) They both help to transport substances from the absorptive cells to the blood capillaries in the small intestine.
D) They both help to transport substances from the lumen to the absorptive cells in the small intestine.
E) They both cleave inactive precursors to form active enzymes in the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify a movement that is unique to the large intestine.
A) active transport
B) enterohepatic circulation
C) peristalsis
D) segmentation
E) haustral churning
A) active transport
B) enterohepatic circulation
C) peristalsis
D) segmentation
E) haustral churning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The enzyme primarily responsible for lipid digestion in the small intestine is
A) pancreatic lipase
B) carboxypeptidase
C) lingual lipase
D) α-dextrin
E) ribonuclease
A) pancreatic lipase
B) carboxypeptidase
C) lingual lipase
D) α-dextrin
E) ribonuclease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Brush-border enzymes are synthesized by the paneth cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Imagine you suffer from a mild case of delayed gastric emptying. If you consume alcohol in this scenario, which of these will be observed after a short duration?
A) negligible alcohol absorption in the stomach
B) low blood alcohol level
C) low Na+ concentration in the blood
D) high water content in the urine
E) presence of alcohol in the stomach for a short time period
A) negligible alcohol absorption in the stomach
B) low blood alcohol level
C) low Na+ concentration in the blood
D) high water content in the urine
E) presence of alcohol in the stomach for a short time period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following helps to transport long-chain fatty acids from the interior of the small intestinal lumen to the absorptive cells?
A) chylomicrons
B) micelles
C) villi
D) bile salts
E) symporters
A) chylomicrons
B) micelles
C) villi
D) bile salts
E) symporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Identify a factor that contributes to low absorption rates in the large intestine when compared with the small intestine.
A) absence of the lymphoid nodule
B) presence of the tenia coli
C) absence of paneth cells in the crypts of Lieberkühn
D) absence of circular folds
E) presence of microvilli
A) absence of the lymphoid nodule
B) presence of the tenia coli
C) absence of paneth cells in the crypts of Lieberkühn
D) absence of circular folds
E) presence of microvilli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
_____ _____ is a clear yellow and slightly alkaline fluid secreted by the crypts of Lieberkühn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The cycle of bile salt secretion by hepatocytes into bile, absorption by the ileum, and resecretion into bile is called the _____ _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase are known as exopeptidases because they
A) remove amino acids from the ends of a peptide
B) remove nucleic acids from the ends of a nucleotide
C) remove fatty acids from the ends of a peptide
D) cause the breakdown of proteins into dipeptides and tripeptides
E) cleave peptide bonds within the interior of a protein
A) remove amino acids from the ends of a peptide
B) remove nucleic acids from the ends of a nucleotide
C) remove fatty acids from the ends of a peptide
D) cause the breakdown of proteins into dipeptides and tripeptides
E) cleave peptide bonds within the interior of a protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



