Deck 39: Emission Control Devices Operation and Diagnosis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 39: Emission Control Devices Operation and Diagnosis
1
Two technicians are discussing clogged EGR passages. Technician A says clogged EGR passages can cause excessive NOx exhaust emission. Technician B says that clogged EGR passages can cause the engine to ping (spark knock or detonation). Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is an emission control system that lowers the amount of nitrogen oxides
 formed during combustion. Excessive nitrogen oxide
formed during combustion. Excessive nitrogen oxide
 is caused due to the clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages. The clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages may cause the engine to ping in other sense, spark knock, or detonation.
is caused due to the clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages. The clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages may cause the engine to ping in other sense, spark knock, or detonation.
So, according to the above mentioned context, both technicians (technician A and technician B) are correct.
Therefore, the correct option is
 .
.
 formed during combustion. Excessive nitrogen oxide
formed during combustion. Excessive nitrogen oxide  is caused due to the clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages. The clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages may cause the engine to ping in other sense, spark knock, or detonation.
is caused due to the clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages. The clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) passages may cause the engine to ping in other sense, spark knock, or detonation.So, according to the above mentioned context, both technicians (technician A and technician B) are correct.
Therefore, the correct option is
 .
. 2
How does the use of exhaust gas recirculation reduce NOx exhaust emission?
The use of the EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) to reduce oxides of nitrogen
 exhaust emission can be explained as follows:
exhaust emission can be explained as follows:
The EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) is an emission control system that lowers the amount of oxides of nitrogen
 formed during combustion. During the combustion process, nitrogen
formed during combustion. During the combustion process, nitrogen
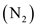 and oxygen
and oxygen
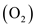 molecules are separated into individual atoms of nitrogen and oxygen.
molecules are separated into individual atoms of nitrogen and oxygen.
These molecules then combine to form oxides of nitrogen
 . It can be carried out by the recirculation of a little amount (percentage) of the exhaust gases back into the intake. The process results in reduced combustion temperatures. The exhaust gases don not enter into the combustion process as they are chemically inert. This results into a lower peak combustion temperature and when the combustion temperature is lowered, the production of oxides of nitrogen is reduced.
. It can be carried out by the recirculation of a little amount (percentage) of the exhaust gases back into the intake. The process results in reduced combustion temperatures. The exhaust gases don not enter into the combustion process as they are chemically inert. This results into a lower peak combustion temperature and when the combustion temperature is lowered, the production of oxides of nitrogen is reduced.
When the EGR valve is opened, the exhaust gases flow through the valve and into the passages in the intake manifolds. The process can be clearly understood by figure shown below:
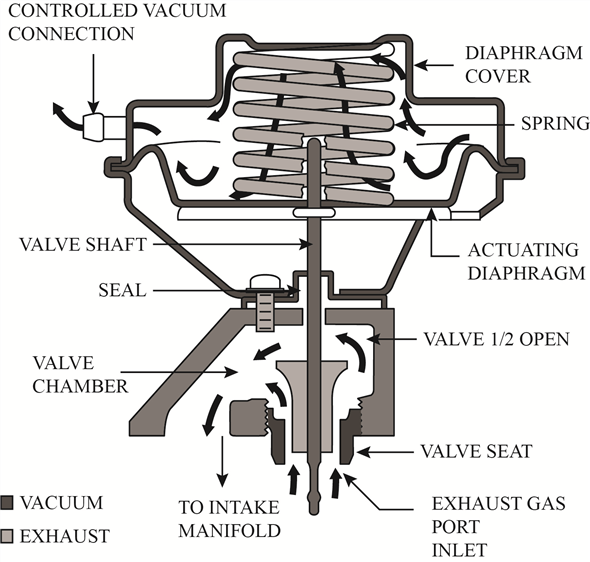 Figure 1
Figure 1
 exhaust emission can be explained as follows:
exhaust emission can be explained as follows:The EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) is an emission control system that lowers the amount of oxides of nitrogen
 formed during combustion. During the combustion process, nitrogen
formed during combustion. During the combustion process, nitrogen 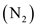 and oxygen
and oxygen 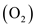 molecules are separated into individual atoms of nitrogen and oxygen.
molecules are separated into individual atoms of nitrogen and oxygen.These molecules then combine to form oxides of nitrogen
 . It can be carried out by the recirculation of a little amount (percentage) of the exhaust gases back into the intake. The process results in reduced combustion temperatures. The exhaust gases don not enter into the combustion process as they are chemically inert. This results into a lower peak combustion temperature and when the combustion temperature is lowered, the production of oxides of nitrogen is reduced.
. It can be carried out by the recirculation of a little amount (percentage) of the exhaust gases back into the intake. The process results in reduced combustion temperatures. The exhaust gases don not enter into the combustion process as they are chemically inert. This results into a lower peak combustion temperature and when the combustion temperature is lowered, the production of oxides of nitrogen is reduced.When the EGR valve is opened, the exhaust gases flow through the valve and into the passages in the intake manifolds. The process can be clearly understood by figure shown below:
 Figure 1
Figure 1 3
An EGR valve that is partially stuck open would most likely cause what condition?
A) Rough idle/stalling
B) Excessive NOx exhaust emissions
C) Ping (spark knock or detonation)
D) Missing at highway speed
A) Rough idle/stalling
B) Excessive NOx exhaust emissions
C) Ping (spark knock or detonation)
D) Missing at highway speed
The exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) valve when partially struck open would most likely cause the following condition:
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is an emission control system that reduces the amount of nitrogen oxide
 formed during the process of combustion. For the specified condition when the EGR valve is partially struck open will cause the condition of rough idle or stalling.
formed during the process of combustion. For the specified condition when the EGR valve is partially struck open will cause the condition of rough idle or stalling.
Therefore, the correct option is
 .
.
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is an emission control system that reduces the amount of nitrogen oxide
 formed during the process of combustion. For the specified condition when the EGR valve is partially struck open will cause the condition of rough idle or stalling.
formed during the process of combustion. For the specified condition when the EGR valve is partially struck open will cause the condition of rough idle or stalling.Therefore, the correct option is
 .
. 4
How does the DPFE sensor work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How much air flows through the PCV system when the engine is at idle speed?
A) 1% to 3%
B) 5% to 10%
C) 10% to 20%
D) Up to 30%
A) 1% to 3%
B) 5% to 10%
C) 10% to 20%
D) Up to 30%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What exhaust emissions does the PCV valve and SAI system control?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Technician A says that if a PCV valve rattles, then it is okay and does not need to be replaced. Technician B says that if a PCV valve does not rattle, it should be replaced. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How does a catalytic converter reduce NOx to nitrogen and oxygen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The switching valves on the AIR pump have failed several times. Technician A says that a defective exhaust check valve could be the cause. Technician B says that a leaking exhaust system at the muffler could be the cause. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How does the computer monitor catalytic converter performance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two technicians are discussing testing a catalytic converter. Technician A says that a vacuum gauge can be used and observed to see if the vacuum drops with the engine at 2,500 RPM for 60 seconds. Technician B says that a pressure gauge can be used to check for backpressure. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At about what temperature does oxygen combine with the nitrogen in the air to form NOx?
a. 500°F (260°C)
b. 750°F (400°C)
c. 1,500°F (815°C)
d. 2,500°F (1,370°C)
a. 500°F (260°C)
b. 750°F (400°C)
c. 1,500°F (815°C)
d. 2,500°F (1,370°C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A P0401 is being discussed. Technician A says that a stuck-closed EGR valve could be the cause. Technician B says that clogged EGR ports could be the cause. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B
A) Technician A only
B) Technician B only
C) Both Technicians A and B
D) Neither Technician A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which EVAP valve(s) is(are) normally closed?
A) Canister purge valve
B) Canister vent valve
C) Both canister purge and canister vent valves
D) Neither canister purge nor canister vent valve
A) Canister purge valve
B) Canister vent valve
C) Both canister purge and canister vent valves
D) Neither canister purge nor canister vent valve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Before an evaporative emission monitor will run, the fuel level must be where?
A) At least 75% full
B) Over 25%
C) Between 15% and 85%
D) The level of the fuel in the tank is not needed to run [1]the monitor test
A) At least 75% full
B) Over 25%
C) Between 15% and 85%
D) The level of the fuel in the tank is not needed to run [1]the monitor test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



