Deck 6: Multiple Regression Analysis Further Issues
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/27
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Multiple Regression Analysis Further Issues
1
Two equations form a nonnested model when:
A)one is logarithmic and the other is quadratic.
B)neither equation is a special case of the other.
C)each equation has the same independent variables.
D)there is only one independent variable in both equations.
A)one is logarithmic and the other is quadratic.
B)neither equation is a special case of the other.
C)each equation has the same independent variables.
D)there is only one independent variable in both equations.
B
2
An independent variable can be included in a regression model:
A)when it affects y and is uncorrelated with all of the independent variables of interest.
B)when it does not affect y and is uncorrelated with all of the independent variables of interest.
C)when it affects y and is correlated with all of the independent variables of interest.
D)when it does not affect y and is correlated with all of the independent variables of interest.
A)when it affects y and is uncorrelated with all of the independent variables of interest.
B)when it does not affect y and is uncorrelated with all of the independent variables of interest.
C)when it affects y and is correlated with all of the independent variables of interest.
D)when it does not affect y and is correlated with all of the independent variables of interest.
A
3
Residual analysis refers to the process of:
A)examining individual observations to see whether the actual value of a dependent variable differs from the predicted value.
B)calculating the squared sum of residuals to draw inferences for the consistency of estimates.
C)transforming models with variables in level to logarithmic functions so as to understand the effect of percentage changes in the independent variable on the dependent variable.
D)sampling and collection of data in such a way to minimize the squared sum of residuals.
A)examining individual observations to see whether the actual value of a dependent variable differs from the predicted value.
B)calculating the squared sum of residuals to draw inferences for the consistency of estimates.
C)transforming models with variables in level to logarithmic functions so as to understand the effect of percentage changes in the independent variable on the dependent variable.
D)sampling and collection of data in such a way to minimize the squared sum of residuals.
A
4
Which of the following models is used quite often to capture decreasing or increasing marginal effects of a variable?
A)Models with logarithmic functions
B)Models with quadratic functions
C)Models with variables in level
D)Models with interaction terms
A)Models with logarithmic functions
B)Models with quadratic functions
C)Models with variables in level
D)Models with interaction terms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Beta coefficients are always greater than standardized coefficients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If we use 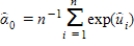 to estimate
to estimate 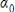 , then the residual for predicting yi is:
, then the residual for predicting yi is:
A)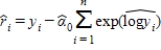
B)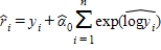
C)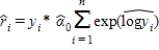
D)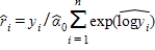
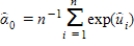 to estimate
to estimate 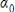 , then the residual for predicting yi is:
, then the residual for predicting yi is:A)
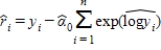
B)
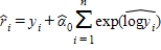
C)
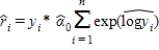
D)
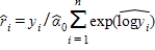

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following correctly identifies a limitation of logarithmic transformation of variables?
A)Taking log of variables make OLS estimates more sensitive to extreme values in comparison to variables taken in level.
B)Logarithmic transformations cannot be used if a variable takes on zero or negative values.
C)Logarithmic transformations of variables are likely to lead to heteroskedasticity.
D)Taking log of a variable often expands its range which can cause inefficient estimates.
A)Taking log of variables make OLS estimates more sensitive to extreme values in comparison to variables taken in level.
B)Logarithmic transformations cannot be used if a variable takes on zero or negative values.
C)Logarithmic transformations of variables are likely to lead to heteroskedasticity.
D)Taking log of a variable often expands its range which can cause inefficient estimates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Changing the unit of measurement of any independent variable, where log of the dependent variable appears in the regression:
A)affects only the intercept coefficient.
B)affects only the slope coefficient.
C)affects both the slope and intercept coefficients.
D)affects neither the slope nor the intercept coefficient.
A)affects only the intercept coefficient.
B)affects only the slope coefficient.
C)affects both the slope and intercept coefficients.
D)affects neither the slope nor the intercept coefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A change in the unit of measurement of the dependent variable in a model does not lead to a change in:
A)the standard error of the regression.
B)the sum of squared residuals of the regression.
C)the goodness-of-fit of the regression.
D)the confidence intervals of the regression.
A)the standard error of the regression.
B)the sum of squared residuals of the regression.
C)the goodness-of-fit of the regression.
D)the confidence intervals of the regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a regression equation has only one explanatory variable, say x1, its standardized coefficient must lie in the range:
A)-2 to 0.
B)-1 to 1.
C)0 to 1.
D)0 to 2.
A)-2 to 0.
B)-1 to 1.
C)0 to 1.
D)0 to 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The centering of explanatory variables about their sample averages before creating quadratics or interactions forces the coefficient on the levels to be average partial effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A variable is standardized in the sample:
A)by multiplying by its mean.
B)by subtracting off its mean and multiplying by its standard deviation.
C)by subtracting off its mean and dividing by its standard deviation.
D)by multiplying by its standard deviation.
A)by multiplying by its mean.
B)by subtracting off its mean and multiplying by its standard deviation.
C)by subtracting off its mean and dividing by its standard deviation.
D)by multiplying by its standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the following equation, gdp refers to gross domestic product, and FDI refers to foreign direct investment.
Log(gdp) = 2.65 + 0.527log(bankcredit) + 0.222FDI
(0)13) (0.022) (0.017)
Which of the following statements is then true?
A)If gdp increases by 1%, bank credit increases by 0.527%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
B)If bank credit increases by 1%, gdp increases by 0.527%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
C)If gdp increases by 1%, bank credit increases by log(0.527)%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
D)If bank credit increases by 1%, gdp increases by log(0.527)%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
Log(gdp) = 2.65 + 0.527log(bankcredit) + 0.222FDI
(0)13) (0.022) (0.017)
Which of the following statements is then true?
A)If gdp increases by 1%, bank credit increases by 0.527%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
B)If bank credit increases by 1%, gdp increases by 0.527%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
C)If gdp increases by 1%, bank credit increases by log(0.527)%, the level of FDI remaining constant.
D)If bank credit increases by 1%, gdp increases by log(0.527)%, the level of FDI remaining constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R2?
A)![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_a7fb_bf83_77c593bc03e0_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
B)![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_a7fc_bf83_ddd70bdfd570_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
C)![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_cf0d_bf83_35c52503c9e1_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)]
D)![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_cf0e_bf83_471d7c2c9879_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]
= 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]
A)
![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_a7fb_bf83_77c593bc03e0_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)]B)
![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_a7fc_bf83_ddd70bdfd570_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)]C)
![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_cf0d_bf83_35c52503c9e1_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)]
= 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)]D)
![<strong>Which of the following correctly represents the equation for adjusted R<sup>2</sup>?</strong> A) = 1 - [SSR/(n -1)]/[SST/(n+1)] B) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n+1)] C) = 1 - [SSR/(n -k - 1)]/[SST/(n - 1)] D) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/11eb6b8a_02be_cf0e_bf83_471d7c2c9879_TB8272_11.jpg) = 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]
= 1 - [SSR]/[SST/(n - 1)]
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Standardized coefficients are also referred to as:
A)beta coefficients.
B)y coefficients.
C)alpha coefficients.
D)j coefficients.
A)beta coefficients.
B)y coefficients.
C)alpha coefficients.
D)j coefficients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A predicted value of a dependent variable:
A)represents the difference between the expected value of the dependent variable and its actual value.
B)is always equal to the actual value of the dependent variable.
C)is independent of explanatory variables and can be estimated on the basis of the residual error term only.
D)represents the expected value of the dependent variable given particular values for the explanatory variables.
A)represents the difference between the expected value of the dependent variable and its actual value.
B)is always equal to the actual value of the dependent variable.
C)is independent of explanatory variables and can be estimated on the basis of the residual error term only.
D)represents the expected value of the dependent variable given particular values for the explanatory variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is true when the dependent variable, y > 0?
A)Taking log of a variable often expands its range.
B)Models using log(y) as the dependent variable will satisfy CLM assumptions more closely than models using the level of y.
C)Taking log of variables make OLS estimates more sensitive to extreme values.
D)Taking logarithmic form of variables make the slope coefficients more responsive to rescaling.
A)Taking log of a variable often expands its range.
B)Models using log(y) as the dependent variable will satisfy CLM assumptions more closely than models using the level of y.
C)Taking log of variables make OLS estimates more sensitive to extreme values.
D)Taking logarithmic form of variables make the slope coefficients more responsive to rescaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
One popular measure to describe the relationship between the dependent variable y and each explanatory variable is the:
A)standardized effect.
B)interaction effect.
C)average partial effect.
D)partial effect.
A)standardized effect.
B)interaction effect.
C)average partial effect.
D)partial effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the following equation, gdp refers to gross domestic product, and FDI refers to foreign direct investment. log(gdp) = 2.65 + 0.527log(bankcredit) + 0.222FDI
(0)13) (0.022) (0.017)
Which of the following statements is then true?
A)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 22.2%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
B)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 26.5%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
C)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 24.8%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
D)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 52.7%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
(0)13) (0.022) (0.017)
Which of the following statements is then true?
A)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 22.2%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
B)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 26.5%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
C)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 24.8%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.
D)If FDI increases by 1%, gdp increases by approximately 52.7%, the amount of bank credit remaining constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following correctly identifies an advantage of using adjusted R2 over R2?
A)Adjusted R2 corrects the bias in R2.
B)Adjusted R2 is easier to calculate than R2.
C)The penalty of adding new independent variables is better understood through adjusted R2 than R2.
D)The adjusted R2 can be calculated for models having logarithmic functions while R2 cannot be calculated for such models.
A)Adjusted R2 corrects the bias in R2.
B)Adjusted R2 is easier to calculate than R2.
C)The penalty of adding new independent variables is better understood through adjusted R2 than R2.
D)The adjusted R2 can be calculated for models having logarithmic functions while R2 cannot be calculated for such models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Let 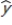 be the estimated average value of the dependent variable given the particular values for the explanatory variables ,
be the estimated average value of the dependent variable given the particular values for the explanatory variables ,  , t = 1, …, k; and let
, t = 1, …, k; and let 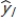 be the estimated expected value of a specific unit given the same particular values for the explanatory variables
be the estimated expected value of a specific unit given the same particular values for the explanatory variables 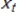 , t = 1, …, k.
, t = 1, …, k.
Then, the standard error for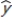 is greater than the standard error for
is greater than the standard error for 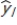
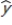 be the estimated average value of the dependent variable given the particular values for the explanatory variables ,
be the estimated average value of the dependent variable given the particular values for the explanatory variables ,  , t = 1, …, k; and let
, t = 1, …, k; and let 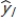 be the estimated expected value of a specific unit given the same particular values for the explanatory variables
be the estimated expected value of a specific unit given the same particular values for the explanatory variables 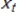 , t = 1, …, k.
, t = 1, …, k.Then, the standard error for
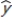 is greater than the standard error for
is greater than the standard error for 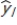

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
F statistic can be used to test nonnested models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To make predictions of logarithmic dependent variables, they first have to be converted to their level forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the R-squared value is low, then using OLS equation is very easy to predict individual future outcomes on y given a set of values for the explanatory variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Predictions of a dependent variable are subject to sampling variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the following equation, govrev represents total government revenue in a given year, and taxrate represents the tax rate, which can take on a value ranging from 0 to 1. govrev = 0.31 + 0.42 taxrate - 0.71 taxrate At what taxrate is govrev maximized?
A)0.59
B)0.30
C)0.15
D)0.37
A)0.59
B)0.30
C)0.15
D)0.37

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a new independent variable is added to a regression equation, the adjusted R2 increases only if the absolute value of the t statistic of the new variable is greater than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



