Deck 2: The Simple Regression Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Simple Regression Model
1
In a regression equation, changing the units of measurement of only the independent variable does not affect the _____.
A)dependent variable
B)slope
C)intercept
D)error term
A)dependent variable
B)slope
C)intercept
D)error term
C
2
Simple regression is an analysis of correlation between two variables.
True
3
If a change in variable x causes a change in variable y, variable x is called the _____.
A)dependent variable
B)explained variable
C)explanatory variable
D)response variable
A)dependent variable
B)explained variable
C)explanatory variable
D)response variable
C
4
Consider the following regression model: y =  0 +
0 + 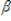 1x1 + u. Which of the following is a property of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates of this model and their associated statistics?
1x1 + u. Which of the following is a property of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates of this model and their associated statistics?
A)The sum, and therefore the sample average of the OLS residuals, is positive.
B)The sum of the OLS residuals is negative.
C)The sample covariance between the regressors and the OLS residuals is positive.
D)The point (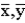 ) always lies on the OLS regression line.
) always lies on the OLS regression line.
 0 +
0 + 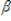 1x1 + u. Which of the following is a property of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates of this model and their associated statistics?
1x1 + u. Which of the following is a property of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates of this model and their associated statistics?A)The sum, and therefore the sample average of the OLS residuals, is positive.
B)The sum of the OLS residuals is negative.
C)The sample covariance between the regressors and the OLS residuals is positive.
D)The point (
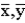 ) always lies on the OLS regression line.
) always lies on the OLS regression line.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If xi and yi are positively correlated in the sample then the estimated slope is _____.
A)less than zero
B)greater than zero
C)equal to zero
D)equal to one
A)less than zero
B)greater than zero
C)equal to zero
D)equal to one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The error term in a regression equation is said to exhibit homoskedasticty if _____.
A)it has zero conditional mean
B)it has the same variance for all values of the explanatory variable
C)it has the same value for all values of the explanatory variable
D)if the error term has a value of one given any value of the explanatory variable
A)it has zero conditional mean
B)it has the same variance for all values of the explanatory variable
C)it has the same value for all values of the explanatory variable
D)if the error term has a value of one given any value of the explanatory variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the equation 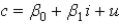 , c denotes consumption and i denotes income. What is the residual for the 5th observation if
, c denotes consumption and i denotes income. What is the residual for the 5th observation if 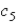 =$500 and
=$500 and 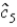 =$475?
=$475?
A)$975
B)$300
C)$25
D)$50
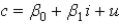 , c denotes consumption and i denotes income. What is the residual for the 5th observation if
, c denotes consumption and i denotes income. What is the residual for the 5th observation if 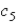 =$500 and
=$500 and 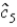 =$475?
=$475?A)$975
B)$300
C)$25
D)$50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What does the equation 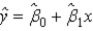 denote if the regression equation is
denote if the regression equation is 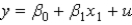 ?
?
A)The explained sum of squares
B)The total sum of squares
C)The sample regression function
D)The population regression function
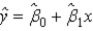 denote if the regression equation is
denote if the regression equation is 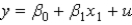 ?
?A)The explained sum of squares
B)The total sum of squares
C)The sample regression function
D)The population regression function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the residual sum of squares (SSR) in a regression analysis is 66 and the total sum of squares (SST) is equal to 90, what is the value of the coefficient of determination?
A)0.73
B)0.55
C)0.27
D)1.2
A)0.73
B)0.55
C)0.27
D)1.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A dependent variable is also known as a(n) _____.
A)explanatory variable
B)control variable
C)predictor variable
D)response variable
A)explanatory variable
B)control variable
C)predictor variable
D)response variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The sample correlation between xi and yi is denoted by _____.
A)
B)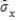
C)
D)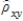
A)

B)
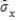
C)

D)
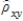

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the regression of y on x, the error term exhibits heteroskedasticity if _____.
A)it has a constant variance
B)Var(y|x) is a function of x
C)x is a function of y
D)y is a function of x
A)it has a constant variance
B)Var(y|x) is a function of x
C)x is a function of y
D)y is a function of x

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is assumed for establishing the unbiasedness of Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates?
A)The error term has an expected value of 1 given any value of the explanatory variable.
B)The regression equation is linear in the explained and explanatory variables.
C)The sample outcomes on the explanatory variable are all the same value.
D)The error term has the same variance given any value of the explanatory variable.
A)The error term has an expected value of 1 given any value of the explanatory variable.
B)The regression equation is linear in the explained and explanatory variables.
C)The sample outcomes on the explanatory variable are all the same value.
D)The error term has the same variance given any value of the explanatory variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the total sum of squares (SST) in a regression equation is 81, and the residual sum of squares (SSR) is 25, what is the explained sum of squares (SSE)?
A)64
B)56
C)32
D)18
A)64
B)56
C)32
D)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A natural measure of the association between two random variables is the correlation coefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The explained sum of squares for the regression function, 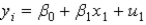 , is defined as _____.
, is defined as _____.
A)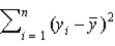
B)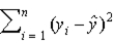
C)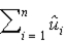
D)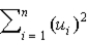
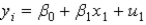 , is defined as _____.
, is defined as _____.A)
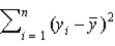
B)
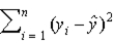
C)
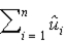
D)
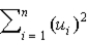

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the equation 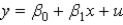 , what is the estimated value of
, what is the estimated value of 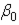 ?
?
A)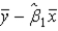
B)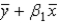
C)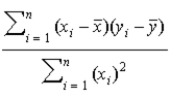
D)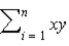
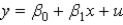 , what is the estimated value of
, what is the estimated value of 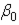 ?
?A)
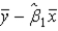
B)
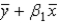
C)
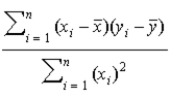
D)
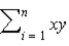

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the estimated value of the slope parameter when the regression equation, y =  0 +
0 + 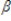 1x1 + u passes through the origin?
1x1 + u passes through the origin?
A)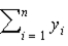
B)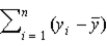
C)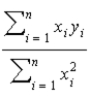
D)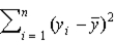
 0 +
0 + 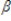 1x1 + u passes through the origin?
1x1 + u passes through the origin?A)
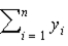
B)
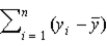
C)
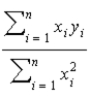
D)
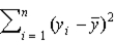

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a nonlinear regression model?
A)y = 0 +
0 + 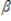 1x1/2 + u
1x1/2 + u
B)log y = 0 +
0 + 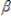 1log x +u
1log x +u
C)y = 1 / ( 0 +
0 + 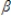 1x) + u
1x) + u
D)y = 0 +
0 + 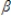 1x + u
1x + u
A)y =
 0 +
0 + 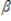 1x1/2 + u
1x1/2 + uB)log y =
 0 +
0 + 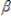 1log x +u
1log x +uC)y = 1 / (
 0 +
0 + 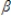 1x) + u
1x) + uD)y =
 0 +
0 + 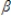 1x + u
1x + u
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the equation y = 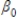 +
+ 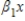 + u,
+ u, 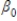 is the _____.
is the _____.
A)dependent variable
B)independent variable
C)slope parameter
D)intercept parameter
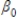 +
+ 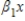 + u,
+ u, 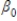 is the _____.
is the _____.A)dependent variable
B)independent variable
C)slope parameter
D)intercept parameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
R2 is the ratio of the explained variation compared to the total variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a simple linear regression model, wage = 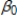 +
+ 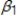 male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise), is the difference in the average wage between males and non-males.
male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise), is the difference in the average wage between males and non-males.
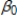 +
+ 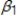 male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise), is the difference in the average wage between males and non-males.
male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise), is the difference in the average wage between males and non-males.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In general, the constant that produces the smallest sum of squared deviations is always the sample average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is an example of a dummy variable?
A)A person's hourly wage
B)The number of years of education someone has
C)The number of years of work experience someone has
D)Whether or not someone has a college degree
A)A person's hourly wage
B)The number of years of education someone has
C)The number of years of work experience someone has
D)Whether or not someone has a college degree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The variance of the slope estimator increases as the error variance decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The sample covariance between the regressors and the Ordinary Least Square (OLS) residuals is always positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider a simple linear regression model, wage = 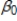 +
+ 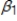 male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise). Now suppose that we know being a male means there is a lower probability of attaining higher education, another factor that is also expected to affect wage. Which of the key assumptions made to establish unbiasedness of OLS estimates do not hold?
male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise). Now suppose that we know being a male means there is a lower probability of attaining higher education, another factor that is also expected to affect wage. Which of the key assumptions made to establish unbiasedness of OLS estimates do not hold?
A)Linear in parameters
B)Random sampling
C)Sample variation in the explanatory variable
D)Zero conditional mean
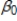 +
+ 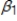 male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise). Now suppose that we know being a male means there is a lower probability of attaining higher education, another factor that is also expected to affect wage. Which of the key assumptions made to establish unbiasedness of OLS estimates do not hold?
male + u, where male is a binary variable (1 if a person is male, and 0 otherwise). Now suppose that we know being a male means there is a lower probability of attaining higher education, another factor that is also expected to affect wage. Which of the key assumptions made to establish unbiasedness of OLS estimates do not hold?A)Linear in parameters
B)Random sampling
C)Sample variation in the explanatory variable
D)Zero conditional mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
There are n-1 degrees of freedom in Ordinary Least Square residuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider a simple linear regression model, y = β0+ β1x + u, . What does the zero conditional mean assumption imply?
A)The expected value of the error term, u , is zero, regardless of what the value of the explanatory variable, x, is.
B)The estimated average value of β1 is zero.
C)The expected value of the explained variable, y , is zero, regardless of what the value of the explanatory variable, x , is.
D)The estimated average value of β0 is zero.
A)The expected value of the error term, u , is zero, regardless of what the value of the explanatory variable, x, is.
B)The estimated average value of β1 is zero.
C)The expected value of the explained variable, y , is zero, regardless of what the value of the explanatory variable, x , is.
D)The estimated average value of β0 is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following will cause Ordinary Least Square (OLS) estimates of a simple regression model, y = 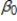 +
+ 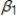 x + u to be biased?
x + u to be biased?
A)Every individual in the population has the same probability of being observed in the sample.
B)The observed values of span a wide range.
C)The constant,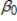 is greater than the coefficient,
is greater than the coefficient, 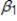 .
.
D)The constant, is greater than the coefficient, x .
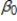 +
+ 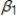 x + u to be biased?
x + u to be biased?A)Every individual in the population has the same probability of being observed in the sample.
B)The observed values of span a wide range.
C)The constant,
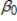 is greater than the coefficient,
is greater than the coefficient, 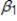 .
.D)The constant, is greater than the coefficient, x .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



