Deck 12: Compensation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Compensation
1
Employers computing taxable income receive a deduction for reasonable salary and wages paid to employees.
True
2
Employees complete a Form W-2 to specify their income tax withholding.
False
3
The date on which stock options are no longer subject to forfeiture is called the vesting date.
True
4
A section 83(b)election freezes the value of restricted stock for compensation purposes on the vesting date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Employer's expense for stock options is typically recognized earlier for book than tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An employee's income with respect to restricted stock is the fair market value on the vesting date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Employers receive a deduction for compensation paid to and employment taxes paid on behalf of employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Employers computing taxable income under the accrual method to unrelated taxpayers may deduct wages accrued as compensation expense in one year and paid in the subsequent year, as long as the company makes the payment within two and a half months after the employer's year-end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Without an election, the income from an employee's restricted stock is measured on the grant date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Employees will always prefer to receive incentive stock options over nonqualified stock options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Employers always prefer to award incentive stock options rather than nonqualified stock options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The use of restricted stock is increasing relative to the use of stock options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Stock options will always provide employees with future compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The date on which stock options are given to the employee is called the exercise date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An employee can indicate whether they want an additional amount withheld for payroll taxes on the Form W-4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One purpose of Form W-4 is to determine an employee's withholding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When stock options are exercised, they are converted into actual employer stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An employer always receives a deduction for total compensation paid to a CEO.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
On Form W-4, an employee can change their withholding through claiming dependents, other adjustments for non-wage income or deductions, and choosing extra withholding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One primary purpose of equity compensation is to motivate employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Employers cannot discriminate between highly and non-highly compensated employees when providing taxable fringe benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Employees may exclude from income items such as occasional theater tickets, T-shirts, or a Thanksgiving turkey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A cafeteria plan provides employees discounted meals at a company-sponsored dining room.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Up to $10,000 of dependent care expenses can be excluded from an employee's compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Group-term life insurance is a fringe benefit that can be partially taxable and partially tax-free.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Cornhusker Bank reimburses employees for dues to the local banker's association. The reimbursement is includible in the employee's income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Qualified employee discounts allow employees to purchase employer goods at a discount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Hotel employees can receive free lodging on a space-available basis without incurring compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A section 83(i)election freezes the value of restricted stock for compensation purposes on the vesting date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements regarding compensation is false?
A)Wages are usually paid by the hour.
B)Salary is usually a form of fixed compensation.
C)Bonuses are a form of compensation obtained if certain criteria are met.
D)Bonuses paid within two and a half months of year-end are included in employee's compensation in the year they were earned.
A)Wages are usually paid by the hour.
B)Salary is usually a form of fixed compensation.
C)Bonuses are a form of compensation obtained if certain criteria are met.
D)Bonuses paid within two and a half months of year-end are included in employee's compensation in the year they were earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Up to $5,250 of educational benefits can be excluded from an employee's compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following items is not included on an employee's Form W-2?
A)Taxable wages, tips, and compensation
B)Social Security withholding
C)Value of stock options granted during the year
D)Federal and state income tax withholding
A)Taxable wages, tips, and compensation
B)Social Security withholding
C)Value of stock options granted during the year
D)Federal and state income tax withholding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Flexible spending accounts allow employees to set aside before-tax dollars for medical and dependent care expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Health insurance is an example of a nontaxable fringe benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Fringe benefits are generally a form of noncash compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If certain conditions are met, an apartment manager can exclude the fair market value of free rent from his or her income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For 2020, up to $300 of transportation fringe benefits can be excluded from income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Employers sometimes pay a "gross-up" to employees to cover taxes associated with taxable fringe benefits they provide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Taxable fringe benefits include automobile allowances, gym memberships, and personal-use tickets to the theater or sporting events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following isn't reported on the Form W-2?
A)The employee's taxable salary and wages
B)Annual federal and state withholding information
C)Indication as to whether an employee had more than one employer during the year
D)Annual amount of Social Security and Medicare tax withholding information
A)The employee's taxable salary and wages
B)Annual federal and state withholding information
C)Indication as to whether an employee had more than one employer during the year
D)Annual amount of Social Security and Medicare tax withholding information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements is true regarding the $1,000,000 limit on covered employees for publicly traded companies?
A)The limitation applies to all employees.
B)The limitation applies to all officers.
C)The limitation applies only to the CEO and three other highest compensated officers.
D)The limitation applies only to the CEO, CFO, three other highest compensated officers, and all covered employees from previous years.
A)The limitation applies to all employees.
B)The limitation applies to all officers.
C)The limitation applies only to the CEO and three other highest compensated officers.
D)The limitation applies only to the CEO, CFO, three other highest compensated officers, and all covered employees from previous years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Maren received 10 NQOs (each option gives her the right to purchase 10 shares of stock for $8 per share)at the time she started working when the stock price was $6 per share. When the share price was $15 per share, she exercised all of her options. Eighteen months later she sold all of the shares for $20 per share. What is the amount of Maren's bargain element?
A)$0
B)$700
C)$900
D)$1,500
E)None of the choices are correct.
A)$0
B)$700
C)$900
D)$1,500
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements regarding restricted stock is false?
A)Like stock options, restricted stock has to vest before it can be sold.
B)Like nonqualified stock options, the employee's income inclusion for restricted stock is the bargain element.
C)Even if the value of restricted stock decreases from the price on the grant date, it retains some value to the employee.
D)There are no effective tax planning elections for restricted stock.
A)Like stock options, restricted stock has to vest before it can be sold.
B)Like nonqualified stock options, the employee's income inclusion for restricted stock is the bargain element.
C)Even if the value of restricted stock decreases from the price on the grant date, it retains some value to the employee.
D)There are no effective tax planning elections for restricted stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following regarding the Form W-4 is incorrect?
A)It determines an employee's income tax withholding.
B)Employees can claim dependents.
C)Employees can specify additional amounts to be withheld each month.
D)The form can only be adjusted at the beginning of the year or start of employment.
A)It determines an employee's income tax withholding.
B)Employees can claim dependents.
C)Employees can specify additional amounts to be withheld each month.
D)The form can only be adjusted at the beginning of the year or start of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Bad Brad received 20 NQOs (each option gives him the right to purchase 30 shares of stock for $12 per share)from his employer. At the time he started working, the stock price was $11 per share. Now that the share price is $25 per share, he exercises all of the options. Two years later Bad Brad sells the stock for $27 per share. What is Bad Brad's basis in his stock for purposes of calculating the gain or loss at the time of the sale?
A)$7,200
B)$7,800
C)$15,000
D)$16,200
A)$7,200
B)$7,800
C)$15,000
D)$16,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following pairs of items is not needed to calculate the after-tax proceeds for a same-day sale?
A)Strike price and market price on exercise date
B)Strike price and market price on grant date
C)Market price on sale date and market price on exercise date
D)Market price on sale date and marginal tax rate
A)Strike price and market price on exercise date
B)Strike price and market price on grant date
C)Market price on sale date and market price on exercise date
D)Market price on sale date and marginal tax rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Maren received 11 NQOs (each option gives her the right to purchase 14 shares of stock for $10 per share)at the time she started working when the stock price was $7 per share. When the share price was $16 per share, she exercised all of her options. Eighteen months later she sold all of the shares for $21 per share. What is the amount of Maren's bargain element?
A)$0
B)$924
C)$1,386
D)$2,464
E)None of the choices are correct.
A)$0
B)$924
C)$1,386
D)$2,464
E)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Aharon exercises 10 stock options awarded several years ago. The following information pertains to the options: (1)each option gives the employee the right to buy 10 shares, (2)the market price on the grant date was $7, (3)the strike price is $10, and (4)the market price on the exercise date was $15. How much will it cost Aharon to purchase the options on the exercise date?
A)$90
B)$500
C)$700
D)$1,000
A)$90
B)$500
C)$700
D)$1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is true regarding stock options?
A)A loss is realized when stock options lapse.
B)There is typically no tax effect on the grant date.
C)Income recognized on the exercise date is greater for incentive stock options than nonqualified options.
D)The bargain element on a nonqualified option is taxed to employees at capital gain rates.
A)A loss is realized when stock options lapse.
B)There is typically no tax effect on the grant date.
C)Income recognized on the exercise date is greater for incentive stock options than nonqualified options.
D)The bargain element on a nonqualified option is taxed to employees at capital gain rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following refers to the date stock options are awarded to an employee?
A)Grant date
B)Exercise date
C)Lapse date
D)Vesting date
A)Grant date
B)Exercise date
C)Lapse date
D)Vesting date

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Maren received 12 NQOs (each option gives her the right to purchase 7 shares of stock for $10 per share)at the time she started working when the stock price was $8 per share. When the share price was $20 per share, she exercised all of her options. Eighteen months later she sold all of the shares for $23 per share. How much gain will Maren recognize on the sale of the shares and how much tax will she pay assuming her marginal tax rate is 37 percent?
A)$0 gain and $0 tax
B)$252 gain and $50 tax
C)$252 gain and $93 tax
D)$1,092 gain and $218 tax
A)$0 gain and $0 tax
B)$252 gain and $50 tax
C)$252 gain and $93 tax
D)$1,092 gain and $218 tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Stevie recently received 1,000 shares of restricted stock from her employer, Nicks Corporation, when the share price was $8 per share. Stevie's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $11. Stevie held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $16. What is the amount of Stevie's ordinary income with respect to the restricted stock?
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$8,000
D)$11,000
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$8,000
D)$11,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Maren received 10 NQOs (each option gives her the right to purchase 10 shares of stock for $8 per share)at the time she started working when the stock price was $6 per share. When the share price was $15 per share, she exercised all of her options. Eighteen months later she sold all of the shares for $20 per share. How much gain will Maren recognize on the sale of the shares and how much tax will she pay assuming her marginal tax rate is 37 percent?
A)$0 gain and $0 tax
B)$500 gain and $100 tax
C)$500 gain and $185 tax
D)$1,200 gain and $240 tax
A)$0 gain and $0 tax
B)$500 gain and $100 tax
C)$500 gain and $185 tax
D)$1,200 gain and $240 tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For compensation plans adopted by a publicly traded company in the current year, when a CEO's salary exceeds $1,000,000, the employee ______ taxed on the entire amount, and the employer ______ allowed a deduction on the entire amount.
A)is; is
B)is; is not
C)is not; is
D)is not; is not
A)is; is
B)is; is not
C)is not; is
D)is not; is not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Tom recently received 2,000 shares of restricted stock from his employer, Independence Corporation, when the share price was $10 per share. Tom's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $14. Tom held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $20. What is the amount of Tom's income or loss on the vesting date?
A)$0
B)$10,000
C)$20,000
D)$28,000
A)$0
B)$10,000
C)$20,000
D)$28,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Tom recently received 2,000 shares of restricted stock from his employer, Independence Corporation, when the share price was $10 per share. Tom's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $14. Tom held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $12. What is the amount of Tom's income or loss on the sale?
A)$0
B)$2,000 loss
C)$4,000 gain
D)$4,000 loss
A)$0
B)$2,000 loss
C)$4,000 gain
D)$4,000 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Tom recently received 2,110 shares of restricted stock from his employer, Independence Corporation, when the share price was $12 per share. Tom's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $16. Tom held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $14. What is the amount of Tom's income or loss on the sale?
A)$0
B)$2,110 loss
C)$4,220 gain
D)$4,220 loss
A)$0
B)$2,110 loss
C)$4,220 gain
D)$4,220 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not a purpose of equity-based compensation?
A)Provides both risk and incentives to employees
B)Motivates employees by aligning employee and employer incentives
C)Avoids compensation limits for certain publicly traded company executives
D)Provides a low- or no-cost form of compensation
A)Provides both risk and incentives to employees
B)Motivates employees by aligning employee and employer incentives
C)Avoids compensation limits for certain publicly traded company executives
D)Provides a low- or no-cost form of compensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How is the bargain element for a stock option calculated?
A)The difference between the strike price and the market price on the date of grant
B)The difference between the market price on the exercise date and the market price on the date of grant
C)The difference between the market price on the exercise date and the strike price
D)The difference between the market price on the sale date and the strike price
A)The difference between the strike price and the market price on the date of grant
B)The difference between the market price on the exercise date and the market price on the date of grant
C)The difference between the market price on the exercise date and the strike price
D)The difference between the market price on the sale date and the strike price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is false regarding a section 83(b)election?
A)The election freezes the value of the employee's compensation as of the grant date.
B)The election is an important tax-planning tool if the stock is expected to increase in value.
C)The election must be made within 30 days of the grant date.
D)If an employee leaves before the vesting date, any loss is limited to $3,000.
A)The election freezes the value of the employee's compensation as of the grant date.
B)The election is an important tax-planning tool if the stock is expected to increase in value.
C)The election must be made within 30 days of the grant date.
D)If an employee leaves before the vesting date, any loss is limited to $3,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Kevin is the financial manager of Levingston BMW. The shop allows employees to purchase up to two vehiclesper year at a discount. Levingston's average gross profit percentage is 15 percent. This year Kevin purchased a 530 model and a new M3. 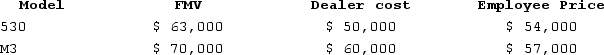 What amount must Kevin include in income?
What amount must Kevin include in income?
A)$0
B)$2,500
C)$2,950
D)$22,000
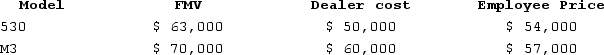 What amount must Kevin include in income?
What amount must Kevin include in income?A)$0
B)$2,500
C)$2,950
D)$22,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements regarding employer-provided educational benefits is true?
A)All undergraduate tuition expenses can be excluded.
B)Only educational benefits from public universities can be excluded.
C)Up to $5,250 in tuition benefits can be excluded.
D)All graduate tuition expenses are included.
A)All undergraduate tuition expenses can be excluded.
B)Only educational benefits from public universities can be excluded.
C)Up to $5,250 in tuition benefits can be excluded.
D)All graduate tuition expenses are included.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Francis works for a local fly-fishing shop. The shop allows employees to purchase two fly rods per year at a discount. This year, Francis purchased one rod. The rod normally retails for $300, was purchased for $225, was sold to Francis for $250, and the employer's average gross profit percentage is 30 percent. What amount of the discount must be included in Francis's income?
A)$0
B)$25
C)$40
D)Some other amount
A)$0
B)$25
C)$40
D)Some other amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Grace's employer is now offering group-term life insurance. The company will provide each employee with $200,000 of group-term life insurance. It costs Grace's employer $700 to provide this amount of insurance to Grace each year. Assuming that Grace is 43 years old, use the table to determine the monthly premium that Grace must include in income as a result of receiving the group-term life benefit. Uniform Premiums for $1,000 of Group-Term Life Insurance Protection: 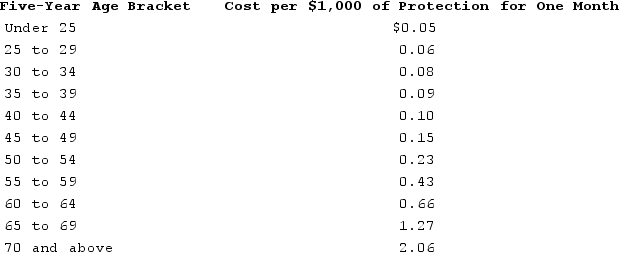
A)$0
B)$15.00
C)$22.00
D)$58.33

A)$0
B)$15.00
C)$22.00
D)$58.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Rachel receives employer-provided health insurance. The employer's cost of the health insurance is $6,400 annually. What is her employer's after-tax cost of providing the health insurance, assuming that the employer's marginal tax rate is 21 percent andthe employer is profitable?
A)$0
B)$1,344
C)$5,056
D)$6,400
A)$0
B)$1,344
C)$5,056
D)$6,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Tasha receives reimbursement from her employer for dependent-care expenses for up to $8,000. Tasha applies for and receives reimbursement of $6,000 for her 10-year-old son. How much, if any, is includible in her income?
A)$0
B)$1,000
C)$3,000
D)$6,000
A)$0
B)$1,000
C)$3,000
D)$6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following benefits cannot be excluded as a no-additional-cost service fringe benefit?
A)Free tax return preparation from a client
B)Complimentary dry cleaning for employees at a laundry company
C)A car wash at an automobile dealership
D)Free local phone service for phone company employees
A)Free tax return preparation from a client
B)Complimentary dry cleaning for employees at a laundry company
C)A car wash at an automobile dealership
D)Free local phone service for phone company employees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is false regarding a section 83(i)election?
A)The election allows employees of any corporation to defer income tax liability.
B)The election is an important tax-planning tool for illiquid equity grants.
C)The election must be made within 30 days of the grant date.
D)The election may terminate on the date the employer stock becomes publicly traded.
A)The election allows employees of any corporation to defer income tax liability.
B)The election is an important tax-planning tool for illiquid equity grants.
C)The election must be made within 30 days of the grant date.
D)The election may terminate on the date the employer stock becomes publicly traded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Tanya's employer offers a cafeteria plan that allows employees to choose among a number of benefits. Each employee is allowed $6,000 in benefits. For 2020, Tanya selected $3,480 ($290 per month)of parking, $1,720 in 401(k)contributions, and $800 of cash. How much must Tanya include in taxable income?
A)$0
B)$1,040
C)$3,480
D)$4,280
A)$0
B)$1,040
C)$3,480
D)$4,280

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements concerning cafeteria plans is true?
A)Allows employees to choose from a menu of fringe benefits or to choose cash.
B)Most of the menu choices are nontaxable fringe benefits.
C)Any receipt of cash option that is elected is treated as taxable compensation.
D)All of the statements are true.
A)Allows employees to choose from a menu of fringe benefits or to choose cash.
B)Most of the menu choices are nontaxable fringe benefits.
C)Any receipt of cash option that is elected is treated as taxable compensation.
D)All of the statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Stevie recently received 1,080 shares of restricted stock from her employer, Nicks Corporation, when the share price was $9 per share. Stevie's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $12. Stevie held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $15. Assuming Stevie made a section 83(b)election, what is the amount of Stevie's ordinary income with respect to the restricted stock?
A)$0
B)$3,240
C)$9,720
D)$12,960
A)$0
B)$3,240
C)$9,720
D)$12,960

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is not a requirement of a "qualified employee discount"?
A)The discount relates to goods or services of the employer.
B)The discount on services doesn't exceed 20 percent of the price offered to customers.
C)The discount can be elected up to five times annually.
D)The employee discount on goods is not greater than employer's average gross profit.
A)The discount relates to goods or services of the employer.
B)The discount on services doesn't exceed 20 percent of the price offered to customers.
C)The discount can be elected up to five times annually.
D)The employee discount on goods is not greater than employer's average gross profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is false regarding dependent-care expenses?
A)Up to $5,000 of reimbursed expenses can qualify.
B)Employers may discriminate among employees.
C)Dependent children under 13 qualify.
D)Spouses who are physically or mentally unable to care for themselves qualify.
A)Up to $5,000 of reimbursed expenses can qualify.
B)Employers may discriminate among employees.
C)Dependent children under 13 qualify.
D)Spouses who are physically or mentally unable to care for themselves qualify.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not an example of a nontaxable fringe benefit?
A)Monthly employer-provided transit benefit of $100
B)Group-term life insurance policy providing $100,000 of coverage
C)Employer-provided parking of $100 per month
D)Qualified employee discounts
A)Monthly employer-provided transit benefit of $100
B)Group-term life insurance policy providing $100,000 of coverage
C)Employer-provided parking of $100 per month
D)Qualified employee discounts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Kevin is the financial manager of Levingston BMW. The shop allows employees to purchase up to two vehiclesper year at a discount. Levingston's average gross profit percentage is 15 percent. This year Kevin purchased a 530 model and a new M3. 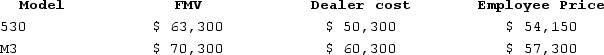 What amount must Kevin include in income?
What amount must Kevin include in income?
A)$0
B)$2,455
C)$2,950
D)$22,000
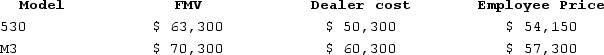 What amount must Kevin include in income?
What amount must Kevin include in income?A)$0
B)$2,455
C)$2,950
D)$22,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not an example of a taxable fringe benefit?
A)Personal use of corporate jet
B)$1,000,000 group-term life insurance policy
C)$225 of monthly employer-provided parking
D)Automobile allowance
A)Personal use of corporate jet
B)$1,000,000 group-term life insurance policy
C)$225 of monthly employer-provided parking
D)Automobile allowance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Rachel receives employer-provided health insurance. The employer's cost of the health insurance is $6,000 annually. What is her employer's after-tax cost of providing the health insurance, assuming that the employer's marginal tax rate is 21 percent and the employer is profitable?
A)$0
B)$1,260
C)$4,740
D)$6,000
A)$0
B)$1,260
C)$4,740
D)$6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Stevie recently received 1,000 shares of restricted stock from her employer, Nicks Corporation, when the share price was $8 per share. Stevie's restricted shares vested three years later when the market price was $11. Stevie held the shares for a little more than a year and sold them when the market price was $16. Assuming Stevie made a section 83(b)election, what is the amount of Stevie's ordinary income with respect to the restricted stock?
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$8,000
D)$11,000
A)$0
B)$5,000
C)$8,000
D)$11,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Bonnie's employer provides her with an annual dinner club membership costing $5,000. Her marginal tax rate is 24 percent. Her employer has a marginal tax rate of 21 percent. What is Bonnie's after-tax benefit?
A)$0
B)$1,200
C)$3,800
D)$5,000
A)$0
B)$1,200
C)$3,800
D)$5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Grace's employer is now offering group-term life insurance. The company will provide each employee with $155,000 of group-term life insurance. It costs Grace's employer $785 to provide this amount of insurance to Grace each year. Assuming that Grace is 43 years old, use the table to determine the monthly premium that Grace must include in income as a result of receiving the group-term life benefit. Uniform Premiums for $1,000 of Group-Term Life Insurance Protection:
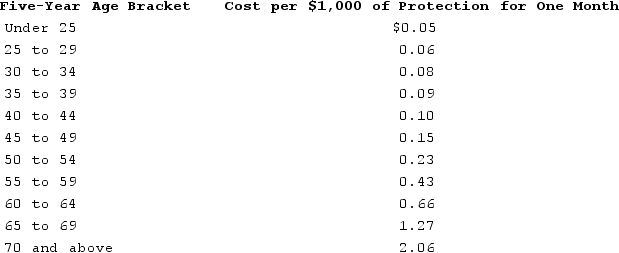
A)$0
B)$10.50
C)$19.50
D)$57.63

A)$0
B)$10.50
C)$19.50
D)$57.63

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



