Deck 15: Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/223
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation
1
Because of the existence of a large number of similar but not identical substitutes in most communities, the market for financial planners is best considered to be:
A)a monopoly.
B)an oligopoly.
C)a perfect competition.
D)monopolistically competitive.
A)a monopoly.
B)an oligopoly.
C)a perfect competition.
D)monopolistically competitive.
D
2
Monopolistic competition describes an industry characterized by a ________ number of firms producing products with for firms.
A)small; identical; barriers to entry
B)small; similar; relatively easy entry .C.large; similar; relatively easy entry .D.large; identical; relatively easy entry
A)small; identical; barriers to entry
B)small; similar; relatively easy entry .C.large; similar; relatively easy entry .D.large; identical; relatively easy entry
C
3
A monopolistically competitive industry is characterized by a:
A)small number of firms producing identical products, with barriers to entry for firms.
B)small number of firms producing similar products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
C)large number of firms producing similar products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
D)large number of firms producing identical products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
A)small number of firms producing identical products, with barriers to entry for firms.
B)small number of firms producing similar products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
C)large number of firms producing similar products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
D)large number of firms producing identical products, with relatively easy entry for firms.
C
4
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition? product differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following industries is most likely to be monopolistically competitive?
A)automobile production
B)fresh bagel shops
C)corn farming
D)electric utility production
A)automobile production
B)fresh bagel shops
C)corn farming
D)electric utility production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A market structure characterized by many competitors, each producing identical products, with free entry and exit into the industry, is described as a(n):
A)monopolistically competitive industry.
B)oligopoly.
C)perfectly competitive industry.
D)monopoly.
A)monopolistically competitive industry.
B)oligopoly.
C)perfectly competitive industry.
D)monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In monopolistic competition:
A)there is free entry and exit in the long run.
B)each firm produces a standardized product.
C)there are few producers.
D)there are barriers to entry.
A)there is free entry and exit in the long run.
B)each firm produces a standardized product.
C)there are few producers.
D)there are barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An industry characterized by many firms producing similar but differentiated products in a market with easy entry and exit is called:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopoly.
C)monopolistic competition.
D)oligopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopoly.
C)monopolistic competition.
D)oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Monopolistic competition is an industry structure characterized by:
A)a product with no close substitutes.
B)a horizontal demand curve.
C)a large number of firms.
D)barriers to entry and exit.
A)a product with no close substitutes.
B)a horizontal demand curve.
C)a large number of firms.
D)barriers to entry and exit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In monopolistic competition, each firm:
A)is a price-taker.
B)has some ability to set the price of its differentiated good.
C)will set price equal to marginal cost.
D)has marginal revenue that is greater than price.
A)is a price-taker.
B)has some ability to set the price of its differentiated good.
C)will set price equal to marginal cost.
D)has marginal revenue that is greater than price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Monopolistic competition is similar to perfect competition because firms in both market structures:
A)are price-takers.
B)produce goods that are perfect substitutes.
C)find it beneficial to advertise.
D)do not face any barriers to entry into the industry in the long run.
A)are price-takers.
B)produce goods that are perfect substitutes.
C)find it beneficial to advertise.
D)do not face any barriers to entry into the industry in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A feature of monopolistic competition that makes it different from monopoly is the:
A)fact that firms in monopolistically competitive industries follow the marginal decision rule, while monopolies do not.
B)downward-sloping demand curve.
C)downward-sloping marginal revenue curve.
D)number of firms in the industry.
A)fact that firms in monopolistically competitive industries follow the marginal decision rule, while monopolies do not.
B)downward-sloping demand curve.
C)downward-sloping marginal revenue curve.
D)number of firms in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A monopolistically competitive industry, such as corn snack chips, and a perfectly competitive industry, like wheat farming, are alike in that:
A)firms in both types of industries produce identical products.
B)firms in both types of industries produce similar but not identical products.
C)barriers to entry in both industries are large.
D)there are many firms in each industry.
A)firms in both types of industries produce identical products.
B)firms in both types of industries produce similar but not identical products.
C)barriers to entry in both industries are large.
D)there are many firms in each industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The wedding dress industry is monopolistically competitive.As a result, which of the following conditions applies to this industry?
A)There are thousands of dress suppliers, all selling identical products.
B)Dresses tend to be differentiated among the many sellers serving this market.
C)There is freedom of entry but not exit in this industry.
D)Prices tend to be lower than if the dress industry approximated perfect competition.
A)There are thousands of dress suppliers, all selling identical products.
B)Dresses tend to be differentiated among the many sellers serving this market.
C)There is freedom of entry but not exit in this industry.
D)Prices tend to be lower than if the dress industry approximated perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Because of the existence of a large number of similar but not identical substitutes in most communities, the market for chiropractors is best considered to be:
A)an oligopoly.
B)a perfect competition.
C)monopolistically competitive.
D)a monopoly.
A)an oligopoly.
B)a perfect competition.
C)monopolistically competitive.
D)a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following describes a feature shared by both monopolistic competition and perfect competition?
A)few firms competing in the industry
B)no barriers to entry or exit in the long run
C)absolute market power
D)standardized products
A)few firms competing in the industry
B)no barriers to entry or exit in the long run
C)absolute market power
D)standardized products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In large shopping malls, the retail market is most illustrative of:
A)monopolistic competition.
B)monopoly.
C)perfect competition.
D)perfect oligopoly.
A)monopolistic competition.
B)monopoly.
C)perfect competition.
D)perfect oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The downward-sloping demand curve for a monopolistically competitive firm:
A)reflects product differentiation.
B)eventually will become perfectly elastic as more firms enter.
C)indicates collusion among firms in the industry.
D)ensures that the firm will produce at minimum average cost in the long run.
A)reflects product differentiation.
B)eventually will become perfectly elastic as more firms enter.
C)indicates collusion among firms in the industry.
D)ensures that the firm will produce at minimum average cost in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An industry with a large number of relatively small firms producing differentiated products in a market with easy entry and exit of firms is:
A)a monopoly.
B)a duopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)monopolistically competitive.
A)a monopoly.
B)a duopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)monopolistically competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For the monopolistically competitive wild-caught seafood market, the demand curve for any individual firm is , and there are producers of seafood.
A)downward sloping; few .B.upward sloping; many .C.vertical; few
D)downward sloping; many
A)downward sloping; few .B.upward sloping; many .C.vertical; few
D)downward sloping; many

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The sources of product differentiation do not include:
A)differences in location.
B)differences in quality.
C)the perception by consumers that products are different, even if they are physically identical.
D)consumers' value in uniformity.
A)differences in location.
B)differences in quality.
C)the perception by consumers that products are different, even if they are physically identical.
D)consumers' value in uniformity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The profit-maximizing rule MC = MR is followed by firms operating within:
A)monopolistic competition but not perfect competition.
B)perfect competition but not monopolistic competition.
C)either monopolistic competition or perfect competition, depending on the costs of production.
D)both monopolistic competition and perfect competition.
A)monopolistic competition but not perfect competition.
B)perfect competition but not monopolistic competition.
C)either monopolistic competition or perfect competition, depending on the costs of production.
D)both monopolistic competition and perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Product differentiation under monopolistic competition means that each firm:
A)charges slightly different prices.
B)has a pure monopoly.
C)maximizes profit where MC = P.
D)faces a horizontal demand curve.
A)charges slightly different prices.
B)has a pure monopoly.
C)maximizes profit where MC = P.
D)faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the toothpaste market is monopolistically competitive, product differentiation will take place in which of the following ways?
A)the production of different varieties of toothpaste, including those with whitening agents
B)differentiation in the locations where certain toothpastes are available
C)quality differences among the various brands
D)the production of different varieties of toothpaste, including those with whitening agents, differentiation in the locations where certain toothpastes are available, and quality differences among the various brands
A)the production of different varieties of toothpaste, including those with whitening agents
B)differentiation in the locations where certain toothpastes are available
C)quality differences among the various brands
D)the production of different varieties of toothpaste, including those with whitening agents, differentiation in the locations where certain toothpastes are available, and quality differences among the various brands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The demand curve for a firm operating within a monopolistically competitive industry is:
A)U-shaped.
B)upward sloping.
C)downward sloping.
D)vertical.
A)U-shaped.
B)upward sloping.
C)downward sloping.
D)vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Monopolistic competition describes an industry characterized by which of the following?
A)a product with many close substitutes
B)a horizontal demand curve
C)a small number of firms .D.barriers to entry and exit
A)a product with many close substitutes
B)a horizontal demand curve
C)a small number of firms .D.barriers to entry and exit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Because of the lack of substitutes, the market for newly developed brand-name prescription drugs is best considered to be:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a monopolistically competitive industry:
A)a firm maximizes profits when MR = MC yet P > MC.
B)people would be better off if output were reduced.
C)output could be increased without an increase in total cost.
D)to maximize profits, firms set MR = MC, and people would be better off if output were reduced.
A)a firm maximizes profits when MR = MC yet P > MC.
B)people would be better off if output were reduced.
C)output could be increased without an increase in total cost.
D)to maximize profits, firms set MR = MC, and people would be better off if output were reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The market for grade A large eggs in the state of California is best considered to be:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Product differentiation under monopolistic competition means that each firm:
A)charges the same price.
B)maximizes profit where MC = P.
C)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)receives economic profits.
A)charges the same price.
B)maximizes profit where MC = P.
C)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)receives economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An industry with a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes and which is protected by barriers to entry is:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
Perfect competition.monopolistic competition.oligopoly.
Monopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
Perfect competition.monopolistic competition.oligopoly.
Monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Since a monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product, its price will be:
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)less than marginal revenue.
C)greater than marginal revenue.
D)equal to total revenue.
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)less than marginal revenue.
C)greater than marginal revenue.
D)equal to total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A monopolistically competitive firm has a downward-sloping demand curve for its product, primarily because:
A)there exist no barriers to entry or exit in the long run.
B)there are many sellers in the industry.
C)the firm sells a product distinct from products sold by competing firms.
D)the price is greater than the marginal revenue.
A)there exist no barriers to entry or exit in the long run.
B)there are many sellers in the industry.
C)the firm sells a product distinct from products sold by competing firms.
D)the price is greater than the marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An industry with a large number of small firms producing a standardized product in a market with easy entry and exit of firms is:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Many customers will walk right past a diner that serves coffee and go to Starbucks, where they pay more for a cup of coffee.For these customers, cups of coffee are differentiated by:
A)style.
B)location.
C)quality.
D)type.
A)style.
B)location.
C)quality.
D)type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The demand curve for a firm under monopolistic competition is:
A)downward sloping, unlike the horizontal demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)horizontal, unlike the downward-sloping demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
C)horizontal, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm.
D)downward sloping, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm.
A)downward sloping, unlike the horizontal demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)horizontal, unlike the downward-sloping demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
C)horizontal, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm.
D)downward sloping, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Monopolistic competition is different from monopoly because of which one of the following features?
A)firms with some power to set prices
B)downward-sloping demand curve
C)firms facing some competition
D)downward-sloping marginal revenue curve
A)firms with some power to set prices
B)downward-sloping demand curve
C)firms facing some competition
D)downward-sloping marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The market for dentists in most communities can be considered a because there are a large number of similar but not identical substitutes in the market.
A)monopolistic competition .B.a monopoly
C)perfect competition .D.an oligopoly
A)monopolistic competition .B.a monopoly
C)perfect competition .D.an oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In many cities you can stay at a Holiday Inn in the downtown area, in a suburban community, or near the airport.These Holiday Inn establishments are examples of product differentiation by:
A)type.
B)location.
C)quality.
D)style.
A)type.
B)location.
C)quality.
D)style.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An industry with a few interdependent firms is best described as:
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm can increase its profits by decreasing its output.Then it must be the case that at the current output:
A)marginal revenue is less than zero.
B)price is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
D)price is less than average total cost.
A)marginal revenue is less than zero.
B)price is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
D)price is less than average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A monopolistically competitive firm is operating in the short run at the optimal level of output and is earning negative economic profits.Which of the following must be true?
A)ATC > P > MR = MC.
B)ATC = P > MR = MC.
C)ATC > P = MR = MC.
D)ATC > P > MR > MC.
A)ATC > P > MR = MC.
B)ATC = P > MR = MC.
C)ATC > P = MR = MC.
D)ATC > P > MR > MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces at the optimal level of output and is earning positive economic profits.Which of the following must be true for this firm?
A)MR = MC and P = ATC.
B)MR = MC and P > ATC.
C)MR > MC and P = ATC.
D)P = MR = MC > ATC.
A)MR = MC and P = ATC.
B)MR = MC and P > ATC.
C)MR > MC and P = ATC.
D)P = MR = MC > ATC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure: Monopolistic Competition  (Figure: Monopolistic Competition) The monopolistic competitor in the figure Monopolistic Competition is producing at the output level that maximizes profits (minimizes losses).The shaded rectangle depicts the level of:
(Figure: Monopolistic Competition) The monopolistic competitor in the figure Monopolistic Competition is producing at the output level that maximizes profits (minimizes losses).The shaded rectangle depicts the level of:
A)profit.
B)loss.
C)fixed cost.
D)variable cost.
 (Figure: Monopolistic Competition) The monopolistic competitor in the figure Monopolistic Competition is producing at the output level that maximizes profits (minimizes losses).The shaded rectangle depicts the level of:
(Figure: Monopolistic Competition) The monopolistic competitor in the figure Monopolistic Competition is producing at the output level that maximizes profits (minimizes losses).The shaded rectangle depicts the level of:A)profit.
B)loss.
C)fixed cost.
D)variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a firm operating within monopolistic competition is producing a quantity that generates MC = MR, then the marginal decision rule tells us that profit:
A)is maximized.
B)can be increased by decreasing production.
C)can be increased by decreasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.
A)is maximized.
B)can be increased by decreasing production.
C)can be increased by decreasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
To maximize profit, a monopolistically competitive firm should produce the level of output at which:
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)price equals marginal cost.
C)price equals total cost.
D)marginal revenue equals price.
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)price equals marginal cost.
C)price equals total cost.
D)marginal revenue equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The _________ demand curve for a firm operating in a monopolistically competitive market _.
A)downward-sloping; is the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)downward-sloping; differs from the horizontal demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
C)horizontal; differs from the downward-sloping demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
D)horizontal; is the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
A)downward-sloping; is the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)downward-sloping; differs from the horizontal demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
C)horizontal; differs from the downward-sloping demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
D)horizontal; is the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, then price _.
A)equals marginal revenue.
B)equals average total cost.
C)is greater than average total cost.
D)equals marginal cost.
A)equals marginal revenue.
B)equals average total cost.
C)is greater than average total cost.
D)equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose Susan owns a business that operates in a market characterized by monopolistic competition.Susan's profit-maximizing price is $12, her profit-maximizing output is 900 units per week, and her profits are $1,800 per week.Susan decides that she needs more profits and therefore raises her price to $15.At the new price of $15:
A)profits will increase.
B)profits will remain at $1,800.
C)marginal revenue will be greater than marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue will be less than marginal cost.
A)profits will increase.
B)profits will remain at $1,800.
C)marginal revenue will be greater than marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue will be less than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If a firm operating in monopolistic competition is producing a quantity at which MC < MR, then profit can be ________ by _.
A)increased; decreasing production
B)increased; increasing production
C)increased; increasing the price
D)maximized; decreasing production
A)increased; decreasing production
B)increased; increasing production
C)increased; increasing the price
D)maximized; decreasing production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In order to maximize profits, a firm in monopolistic competition will likely produce:
A)at the output level at which marginal cost equals average total cost.
B)at the output level at which marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
C)at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
D)at the output level at which marginal cost equals price.
A)at the output level at which marginal cost equals average total cost.
B)at the output level at which marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
C)at the output level at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
D)at the output level at which marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms:
A)produce output at the level that minimizes average total cost.
B)set marginal revenue equal to price.
C)cannot earn an economic profit.
D)produce so that marginal cost equals price.
A)produce output at the level that minimizes average total cost.
B)set marginal revenue equal to price.
C)cannot earn an economic profit.
D)produce so that marginal cost equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The demand curve for a firm operating in a monopolistically competitive market is best described as:
A)U-shaped.
B)upward sloping.
C)downward sloping.D.horizontal.
A)U-shaped.
B)upward sloping.
C)downward sloping.D.horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If a firm operating within monopolistic competition is producing a quantity that generates MC < MR, then the marginal decision rule tells us that profit:
A)can be increased by increasing production.
B)can be increased by decreasing production.
C)can be increased by increasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.
A)can be increased by increasing production.
B)can be increased by decreasing production.
C)can be increased by increasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The price for a firm under monopolistic competition is:
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)greater than marginal revenue.
C)less than marginal revenue.
D)greater than total revenue.
A)equal to marginal revenue.
B)greater than marginal revenue.
C)less than marginal revenue.
D)greater than total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm is making a profit but it can increase its profits by increasing output.Then it must be the case that at the current level of output:
A)marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
B)price is less than marginal cost.
C)price is less than average total cost.
D)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
A)marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
B)price is less than marginal cost.
C)price is less than average total cost.
D)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium.Then:
A)price equals average total cost.
B)price equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals price.
D)price is greater than average total cost.
A)price equals average total cost.
B)price equals marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue equals price.
D)price is greater than average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a firm operating in monopolistic competition is producing a quantity at which , then the marginal decision rule tells us that profit _.
A)MC > MR; can be increased by increasing production
B)MC < MR; can be increased by decreasing production
C)MC < MR; can be increased by increasing production
D)MC > MR; is maximized
A)MC > MR; can be increased by increasing production
B)MC < MR; can be increased by decreasing production
C)MC < MR; can be increased by increasing production
D)MC > MR; is maximized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A firm operating in a monopolistically competitive market is producing a quantity at which MC = MR.Profit:
A)can be increased by increasing production.
B)is maximized.
C)can be increased by decreasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.
A)can be increased by increasing production.
B)is maximized.
C)can be increased by decreasing the price.
D)is maximized only if MC = P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A gas station operates in a monopolistically competitive market and is in short-run equilibrium.Suppose that a fixed cost for this firm decreases.As a result, the firm's price will ________, the firm's output will , and the firm's economic profit will ________.
A)increase; increase;
B)increase increase; increase; decrease
C)stay the same; stay the same; increase
D)decrease; stay the same; increase
A)increase; increase;
B)increase increase; increase; decrease
C)stay the same; stay the same; increase
D)decrease; stay the same; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms always experience high economic profits.
B)In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms tend to experience zero economic profits.
C)In the long run, it is likely that monopolistically competitive firms experience negative economic profits.
D)In the long run, it is likely that monopolistically competitive firms experience substantial economic losses.
A)In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms always experience high economic profits.
B)In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms tend to experience zero economic profits.
C)In the long run, it is likely that monopolistically competitive firms experience negative economic profits.
D)In the long run, it is likely that monopolistically competitive firms experience substantial economic losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If monopolistically competitive firms are earning positive economic profits in the short run, then in the long run:
A)firms will leave the industry.
B)the demand curves faced by existing firms will move to the right.
C)economic profits will increase.
D)economic profits will be reduced to zero.
A)firms will leave the industry.
B)the demand curves faced by existing firms will move to the right.
C)economic profits will increase.
D)economic profits will be reduced to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The model of monopolistic competition can characterize the market for plumbing services in a city.This market is initially in long-run equilibrium, but then there is an increase in demand for plumbing services.We expect that in the long run:
A)firms will leave the plumbing market.
B)there will be a short-run increase in the number of firms, but then the number will return to the original level.
C)new firms will enter the plumbing market.
D)firms will shut down, but they will not leave the industry.
A)firms will leave the plumbing market.
B)there will be a short-run increase in the number of firms, but then the number will return to the original level.
C)new firms will enter the plumbing market.
D)firms will shut down, but they will not leave the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
General Snacks is a typical firm in a market characterized by the model of monopolistic competition.If the market is in long-run equilibrium, then the price General Snacks charges for its snack goods would:
A)equal average total cost.
B)exceed average total cost.
C)be less than average total cost.
D)be greater than the average for all other firms in the market.
A)equal average total cost.
B)exceed average total cost.
C)be less than average total cost.
D)be greater than the average for all other firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms tend to experience:
A)high economic profits.
B)zero economic profits.
C)negative economic profits.
D)substantial economic losses.
A)high economic profits.
B)zero economic profits.
C)negative economic profits.
D)substantial economic losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
General Snacks is a typical firm in a market characterized by the model of monopolistic competition.Initially, the market is initially in long-run equilibrium, and then there is an increase in demand for snacks.In the long run, the economic profits of typical firms in the industry will be:
A)typical of those earned by monopoly firms.
B)positive but less than the level typically earned by monopoly firms.
C)zero.
D)negative.
A)typical of those earned by monopoly firms.
B)positive but less than the level typically earned by monopoly firms.
C)zero.
D)negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition 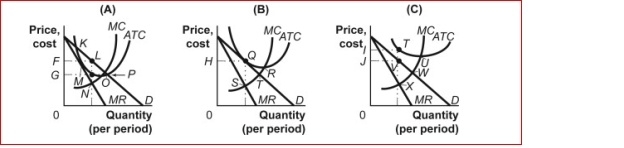 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing
Quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
A)Q.
B)R.
C)S.
D)T.
 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizingQuantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
A)Q.
B)R.
C)S.
D)T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces at the optimal level of output and is earning positive economic profits.Which of the following describes how this firm will adjust in the long run?
A)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves leftward, decreasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
B)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves leftward, decreasing the firm's level of output and increasing the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
C)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's marginal cost and average cost curves downward, decreasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
D)The exit of firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves rightward, increasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
A)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves leftward, decreasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
B)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves leftward, decreasing the firm's level of output and increasing the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
C)The entry of new firms shifts the firm's marginal cost and average cost curves downward, decreasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.
D)The exit of firms shifts the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves rightward, increasing the firm's level of output and the price the firm can charge until price equals average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition 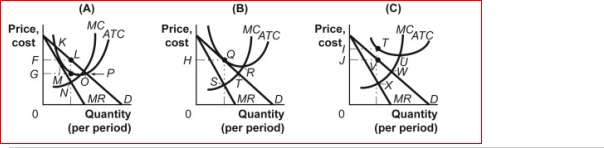 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic profit per unit is:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic profit per unit is:
A)KL.
B)LM.
C)MN.
D)NO.
 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic profit per unit is:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic profit per unit is:A)KL.
B)LM.
C)MN.
D)NO.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Toby operates a small deli downtown.The deli industry is monopolistically competitive.If some delis leave the industry, Toby's ________ curve will shift to the _.
A)marginal cost; left
B)marginal cost; right .C.demand; left
D)demand; right
A)marginal cost; left
B)marginal cost; right .C.demand; left
D)demand; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition 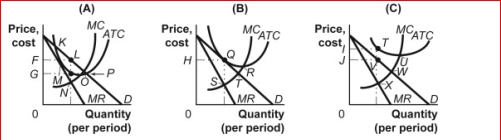
 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
A)U.
B)V.
C)W.
D)X.

 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:A)U.
B)V.
C)W.
D)X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition 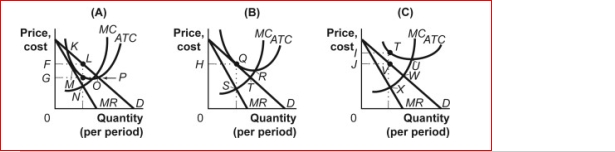 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
A)K.
B)P.
C)N.
D)O.
 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel A of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection at point:A)K.
B)P.
C)N.
D)O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In a long-run equilibrium, firms in a monopolistically competitive industry sell at a price:
A)equal to marginal cost.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)greater than marginal cost.
D)less than marginal revenue.
A)equal to marginal cost.
B)less than marginal cost.
C)greater than marginal cost.
D)less than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Monopolistically competitive firms have zero economic profits in the long run because of:
A)excess capacity.
B)price wars among firms.
C)easy entry and exit.
D)excessive advertising.
A)excess capacity.
B)price wars among firms.
C)easy entry and exit.
D)excessive advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The model of monopolistic competition can characterize the market for plumbing services in a city.Suppose that the market is in long-run equilibrium.For a typical plumbing firm, price:
A)equals average total cost.
B)exceeds average total cost.
C)is less than average total cost.
D)is greater than the average for all other firms in the market.
A)equals average total cost.
B)exceeds average total cost.
C)is less than average total cost.
D)is greater than the average for all other firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose the dry-cleaning market is monopolistically competitive and economically profitable this year.In the long run, the demand for any one firm's dry-cleaning services will ________ as more firms enter the industry, causing profits to _.
A)decrease; become economic losses .B.decrease; fall to zero
C)not change; fall
D)increase; increase
A)decrease; become economic losses .B.decrease; fall to zero
C)not change; fall
D)increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In monopolistic competition:
A)firms advertise to increase demand for their product.
B)entry of new firms shifts the demand curve for existing firms to the right.
C)when some firms exit, the demand curve for the firms that remain in the industry shifts to the left.
D)firms earn large economic profits in the long run.
A)firms advertise to increase demand for their product.
B)entry of new firms shifts the demand curve for existing firms to the right.
C)when some firms exit, the demand curve for the firms that remain in the industry shifts to the left.
D)firms earn large economic profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Toby operates a small deli downtown.The deli industry is monopolistically competitive.In the long run, Toby will produce where:
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)price equals minimum average total cost.
C)price equals marginal cost.
D)price equals marginal revenue.
A)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)price equals minimum average total cost.
C)price equals marginal cost.
D)price equals marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition 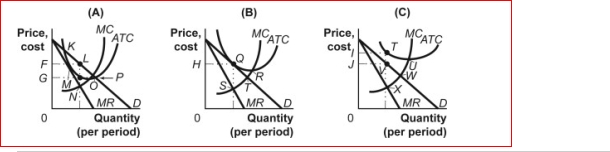 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic loss per unit is:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic loss per unit is:
A)XT.
B)UW.
C)VW.
D)VT.
 (Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic loss per unit is:
(Figure: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C of the figure Firms in Monopolistic Competition, economic loss per unit is:A)XT.
B)UW.
C)VW.
D)VT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a monopolistically competitive firm is making zero economic profits, it is producing at the output level at which the average total cost curve is tangent to the demand curve faced by the firm.At this output:
A)the firm is maximizing profits, and marginal cost must equal marginal revenue.
B)the firm is not maximizing profits, and a slight increase or decrease in output will lead to positive profits.
C)since economic profits are equal to zero, the condition that marginal revenue equals marginal cost is irrelevant and need not hold.
D)the condition that marginal revenue equals marginal cost continues to be relevant, but the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves need not intersect directly below the point of tangency between the average total cost curve and the demand curve faced by the firm.
A)the firm is maximizing profits, and marginal cost must equal marginal revenue.
B)the firm is not maximizing profits, and a slight increase or decrease in output will lead to positive profits.
C)since economic profits are equal to zero, the condition that marginal revenue equals marginal cost is irrelevant and need not hold.
D)the condition that marginal revenue equals marginal cost continues to be relevant, but the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves need not intersect directly below the point of tangency between the average total cost curve and the demand curve faced by the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 223 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



