Deck 16: Organic Polymer Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Organic Polymer Chemistry
1
Which polymers will be strongest?
A) PET 0% crystallinity
B) PET 20% crystallinity
C) PET 35% crystallinity
D) PET 55% crystallinity
A) PET 0% crystallinity
B) PET 20% crystallinity
C) PET 35% crystallinity
D) PET 55% crystallinity
PET 55% crystallinity
2
Which polymers will be brittle at 0° C?
I. PVC, Tg = 83° C
II. PVA, Tg = 200° C
III. teflon, Tg = -80° C
IV. polypropylene, Tg = -100° C
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) II, IV
I. PVC, Tg = 83° C
II. PVA, Tg = 200° C
III. teflon, Tg = -80° C
IV. polypropylene, Tg = -100° C
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) II, IV
I, II
3
What is characteristic of the process of Step-Growth Polymerization?
I. In the beginning of the polymerization process, there are many oligomers (an oligomer is made from a few monomers, its chain length is short).
II. High macromolecular weights are only reached at the very end of the polymerization process.
III. If two bifunctional monomers (e.g. diamine and dicarboxylic acid) are used, slight deviations from 1:1 stoichiometry will prevent high macromolecular weights at the end of the polymerization process.
IV. Polymer chains can grow individually to high macromolecular weight at any time during the polymerization process.
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I, II and III
D) II and IV
I. In the beginning of the polymerization process, there are many oligomers (an oligomer is made from a few monomers, its chain length is short).
II. High macromolecular weights are only reached at the very end of the polymerization process.
III. If two bifunctional monomers (e.g. diamine and dicarboxylic acid) are used, slight deviations from 1:1 stoichiometry will prevent high macromolecular weights at the end of the polymerization process.
IV. Polymer chains can grow individually to high macromolecular weight at any time during the polymerization process.
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I, II and III
D) II and IV
I, II and III
4
Which polymers are correctly classified? 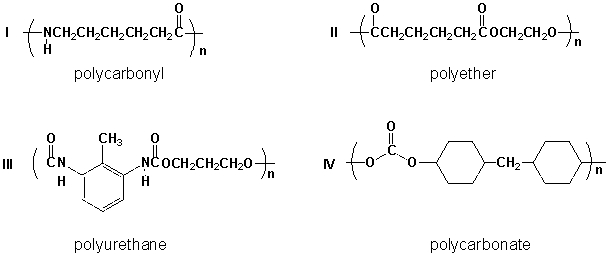
A) I, III
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) II, IV

A) I, III
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which characteristics are found in polymers with low degrees of crystallinity?
I. large molecular side groups
II. high Tm
III. strong intermolecular forces
IV. elasticity
A) I, III
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) I, IV
I. large molecular side groups
II. high Tm
III. strong intermolecular forces
IV. elasticity
A) I, III
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) I, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What small molecules can be released during Step-Growth-Polymerization?
I. H2O
II. NH3
III. methanol
IV. none
A) I
B) II, III
C) I, III
D) IV
I. H2O
II. NH3
III. methanol
IV. none
A) I
B) II, III
C) I, III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are typical polymer architectures?
I. linear
II. tetrahedral
III. star
IV. ladder
V. forked
A) II, III, IV
B) III, IV, V
C) I, III, IV
D) I, II, IV
I. linear
II. tetrahedral
III. star
IV. ladder
V. forked
A) II, III, IV
B) III, IV, V
C) I, III, IV
D) I, II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which characteristics are found in polymers with high degrees of crystallinity?
I. regular, compact structures
II. high Tm
III. weak intermolecular forces
IV. elasticity
A) I, III
B) I, II
C) III, IV
D) II, IV
I. regular, compact structures
II. high Tm
III. weak intermolecular forces
IV. elasticity
A) I, III
B) I, II
C) III, IV
D) II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which pair of compounds would react to form the polymer shown? 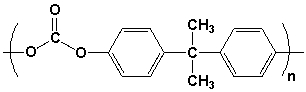

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which polymers are step-growth polymers?
I. Polyamides (e.g.Kevlar)
II. Polyesters (e.g.Mylar)
III. PVC
IV. PMMA (e.g. Lucite)
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV
I. Polyamides (e.g.Kevlar)
II. Polyesters (e.g.Mylar)
III. PVC
IV. PMMA (e.g. Lucite)
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which terms are matched correctly with their definitions?
I. Crystalline domain - order regions in the solid state of a polymer.
II. Amorphous domain - disordered regions in the solid state of a polymer.
III. Melt transition temperature - temperature at which a polymer undergoes the transition from
Hard to rubbery state.
IV. Glass transition temperature - temperature at which glass polymers melt.
A) II, III
B) III, IV
C) I, IV
D) I, II
I. Crystalline domain - order regions in the solid state of a polymer.
II. Amorphous domain - disordered regions in the solid state of a polymer.
III. Melt transition temperature - temperature at which a polymer undergoes the transition from
Hard to rubbery state.
IV. Glass transition temperature - temperature at which glass polymers melt.
A) II, III
B) III, IV
C) I, IV
D) I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which pair of compounds would react to form the polymer shown? 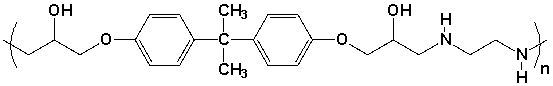
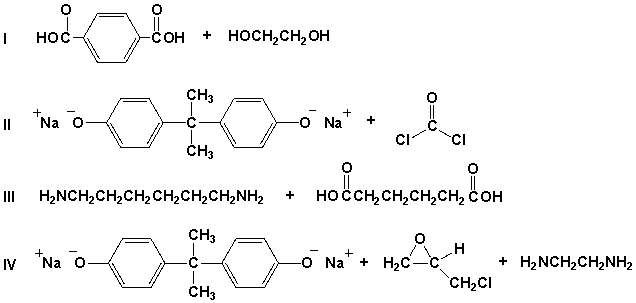
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which classification best describes the mechanism of the synthesis of polyamides via step growth polymerization?
A) nucleophilic acyl addition
B) nucleophilic acyl substitution
C) electrophilic addition
D) radical substitution
A) nucleophilic acyl addition
B) nucleophilic acyl substitution
C) electrophilic addition
D) radical substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which pair of compounds would react to form the polymer shown under appropriate reaction conditions? 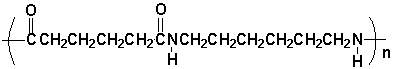
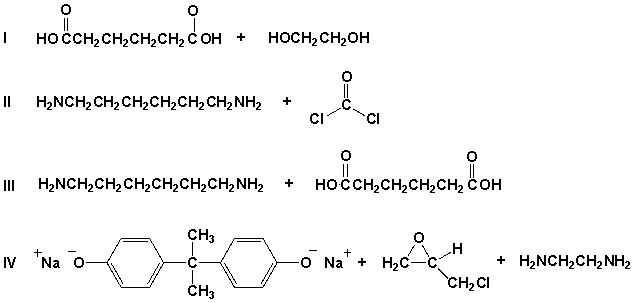
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
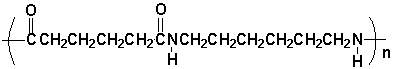

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which polymers are correctly classified? 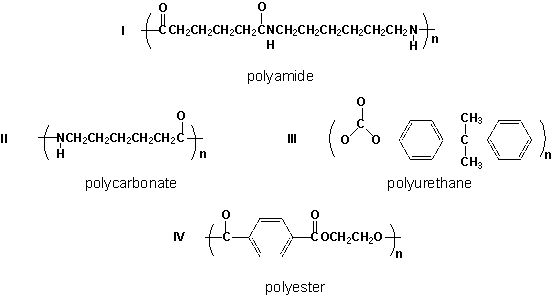
A) II, III
B) III, IV
C) I, IV
D) I, II

A) II, III
B) III, IV
C) I, IV
D) I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which terms are correctly matched to their definitions?
I. Plastic - a long chain molecule synthesized by linking together many single parts.
II. Polymer - can be molded when hot and retains its shape when cooled.
III. Thermoplastic - can be molded when hot and retains its shape when cooled.
IV. Thermosetting plastic - can be molded when first prepared, but hardens irreversibly when
Cooled.
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) I, IV
I. Plastic - a long chain molecule synthesized by linking together many single parts.
II. Polymer - can be molded when hot and retains its shape when cooled.
III. Thermoplastic - can be molded when hot and retains its shape when cooled.
IV. Thermosetting plastic - can be molded when first prepared, but hardens irreversibly when
Cooled.
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) I, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why can any nylon-polymer not be used as an insulator in lead/sulfuric acid batteries?
A) PbO2 would oxidize the polymer.
B) Aqueous H2SO4 would hydrolyze the amide-bonds.
C) Aqueous H2SO4 would dissolve the polymer.
D) Pb would reduce nylon to a polyamine.
A) PbO2 would oxidize the polymer.
B) Aqueous H2SO4 would hydrolyze the amide-bonds.
C) Aqueous H2SO4 would dissolve the polymer.
D) Pb would reduce nylon to a polyamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which polymers will be the most elastic?
A) PET 0% crystallinity
B) PET 20% crystallinity
C) PET 35% crystallinity
D) PET 55% crystallinity
A) PET 0% crystallinity
B) PET 20% crystallinity
C) PET 35% crystallinity
D) PET 55% crystallinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which polymers will be elastic at 0° C?
I. PVC, Tg = 83° C
II. PVA, Tg = 200° C
III. teflon, Tg = -80° C
IV. polypropylene, Tg = -100° C
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) II, IV
I. PVC, Tg = 83° C
II. PVA, Tg = 200° C
III. teflon, Tg = -80° C
IV. polypropylene, Tg = -100° C
A) III, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II
D) II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which polymers are step-growth polymers?
I. nylon
II. HDPE
III. Teflon
IV. PET
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV
I. nylon
II. HDPE
III. Teflon
IV. PET
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which polymers are correctly matched to their primary use?
I. Kevlar and containers
II. Polymethylmethacrylate and Plexiglas
III. Polytetrafluoroethylene and nonstick coatings
IV. PET and bulletproof vests
A) I, III
B) II, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV
I. Kevlar and containers
II. Polymethylmethacrylate and Plexiglas
III. Polytetrafluoroethylene and nonstick coatings
IV. PET and bulletproof vests
A) I, III
B) II, III
C) II, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Before recycling, plastics are sorted according to their resin identification code, which was developed by the Society of the Plastics Industry in 1988. Presorting is necessary, because of the following physical and chemical characteristics of polymers:
I. Polymers have a tendency to phase-separate when molten.
II. Different polymers have very different decomposition temperatures.
III. Polymers featuring very high melting temperatures decompose into smaller molecules at high temperatures rather than melt.
IV. Molten polymers mix easily.
A) I, II, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II, III
D) all of the above
I. Polymers have a tendency to phase-separate when molten.
II. Different polymers have very different decomposition temperatures.
III. Polymers featuring very high melting temperatures decompose into smaller molecules at high temperatures rather than melt.
IV. Molten polymers mix easily.
A) I, II, IV
B) II, III
C) I, II, III
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Keratins are a family of tough and insoluble proteins that are able to form fibers. They form the hard but unmineralized (not bony) structures in amphibians, mammals and reptiles/birds. Keratin, a byproduct from the poultry industry, has recently sparked interest. Keratins are made from a high proportion of the amino acid glycine (R=H), followed by the amino acid alanine (R=-CH3). Two neighboring strands of keratin are shown below.
To what class of polymers is Keratin quite similar?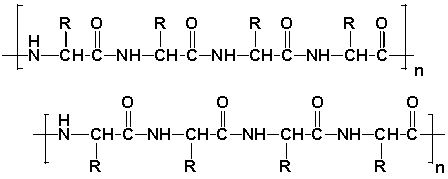
A) polyesters, such as PET
B) polyamides, such as nylon
C) polyalkenes, such as polyacrylate
D) polyurethanes
To what class of polymers is Keratin quite similar?

A) polyesters, such as PET
B) polyamides, such as nylon
C) polyalkenes, such as polyacrylate
D) polyurethanes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The polymer (PEN) synthesized from the following monomers 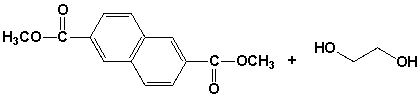
is

is


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A carbonate, which forms the backbone of polycarbonates, has the following structure, 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What small molecules can be released during Chain-Growth-Polymerization?
A) H2O
B) NH3
C) methanol
D) none
A) H2O
B) NH3
C) methanol
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Determine the repeat unit for the following polymer. 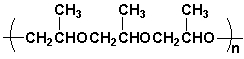
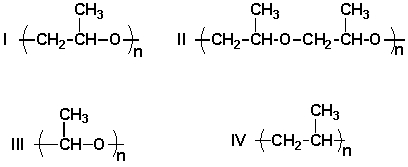
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
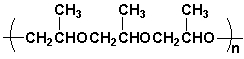

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is characteristic of the process of Chain-Growth Polymerization
I. In the beginning of the polymerization process, there are many oligomers (an oligomer is made from a few monomers, its chain length is short).
II. High macromolecular weights are only reached at the very end of the polymerization process.
III. The macromolecular weight of the polymer chains grows approximately linear during the time required for the polymerization process.
IV. Polymer chains grow by addition of monomers to the polymer.
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) II, IV
I. In the beginning of the polymerization process, there are many oligomers (an oligomer is made from a few monomers, its chain length is short).
II. High macromolecular weights are only reached at the very end of the polymerization process.
III. The macromolecular weight of the polymer chains grows approximately linear during the time required for the polymerization process.
IV. Polymer chains grow by addition of monomers to the polymer.
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) II, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The structure of the polymer (Nylon 6,12), synthesized from the following monomers, 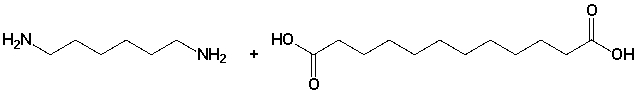
is

is


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which polymers are chain-growth polymers?
I. Polyamides (e.g. Kevlar)
II. Polyesters (e.g.Mylar)
III. PVC
IV. PMMA(e.g. Lucite)
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV
I. Polyamides (e.g. Kevlar)
II. Polyesters (e.g.Mylar)
III. PVC
IV. PMMA(e.g. Lucite)
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A diepoxide, which forms the backbone of epoxy resins, has the following structure, 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which polymers are chain-growth polymers?
I. nylon
II. HDPE
III. Teflon
IV. PET
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV
I. nylon
II. HDPE
III. Teflon
IV. PET
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, IV
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Principally, the anhydrous depolymerization of Chain-Growth polymers into their monomers would/will have the following advantages, compared to hydrous pyrolysis of plastics?
I. The yield of alkene-monomers, that can be repolymerized, would be higher.
II. If several monomers are formed, they can be separated by distillation.
III. The use of polymerization/depolymerization catalysts permits lower process temperatures than during the hydrous pyrolysis, in which the heat is supplied by superheated water.
IV. A greater variety of small organic compounds will be formed.
A) I, II
B) I, II, III
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV
I. The yield of alkene-monomers, that can be repolymerized, would be higher.
II. If several monomers are formed, they can be separated by distillation.
III. The use of polymerization/depolymerization catalysts permits lower process temperatures than during the hydrous pyrolysis, in which the heat is supplied by superheated water.
IV. A greater variety of small organic compounds will be formed.
A) I, II
B) I, II, III
C) II, III, IV
D) I, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Kapton is a polyimide developed by DuPont which has an excellent stability in the temperature range of 0K to 673K). Therefore, it is widely used in the aircraft and space industry although its resistance to mechanical wear is inferior to that of other polymers, such as Mylar (polyethylene terephthalate). Which of the following molecules can be either starting materials or intermediates in the synthesis of Kapton? 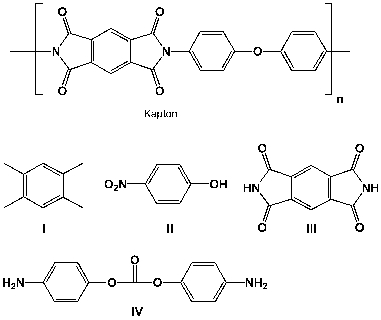
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, III
D) III, IV

A) I, II
B) II, III
C) I, III
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which is not a step in the mechanism of a chain growth polymerization?
A) initiation
B) propagation
C) proliferation
D) termination
A) initiation
B) propagation
C) proliferation
D) termination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statements are true describing the Ziegler-Natta process?
I. the process yields low density polyethylene
II. the process involves radicals
III. the original process used an alkytitanium catalyst
IV. the process yields polyethylene 3 to 10 times stronger than other methods
A) I, II
B) II, IV
C) II, III
D) III, IV
I. the process yields low density polyethylene
II. the process involves radicals
III. the original process used an alkytitanium catalyst
IV. the process yields polyethylene 3 to 10 times stronger than other methods
A) I, II
B) II, IV
C) II, III
D) III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Determine the repeat unit for the following polymer. 
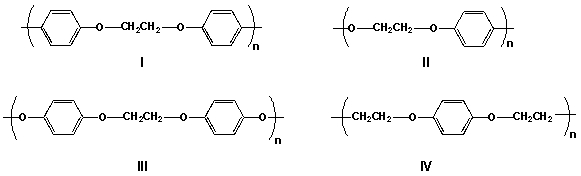
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The monomers used to synthesize Nomex are 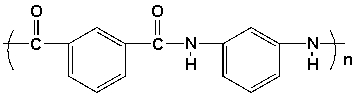



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How can one distinguish between polyethylene-terephthalate and polystyrene during the process of recycling?
I. the IR-spectra are different
II. different glass temperatures
III. different crystallinity
IV. different polymer density
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) I, IV
I. the IR-spectra are different
II. different glass temperatures
III. different crystallinity
IV. different polymer density
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) I, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which compound would react to form the polymer shown? 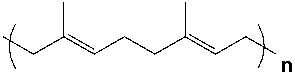
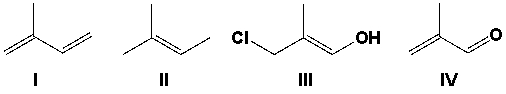
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The opacity of a crystalline polymer correlates to the Tm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The repeat unit of polyacrylonitrile is 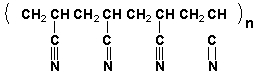




Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The label of the following step of radical chain polymerization is __________________________. 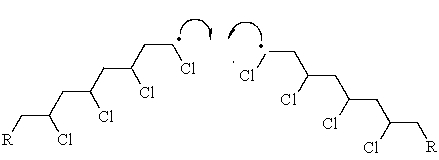


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An elastomer with a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 25° C will lose its elasticity below 25° C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The monomers used to synthesize the following polyurethane are, 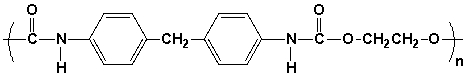



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Branching of polyethylene, due to a chain transfer reaction, produces low-density polyethylene (LDPE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Poly-3- hydroxybutanoic acid is a biodegradable polymer. Complete the reaction scheme shown below, which leads to the synthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. 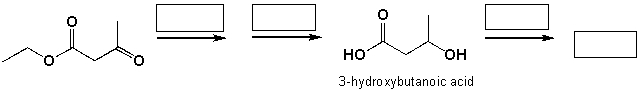


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Complete the mechanism of the ring-opening and subsequent polymerization of caprolactam. This reaction proceeds at higher temperatures (> 150oC). 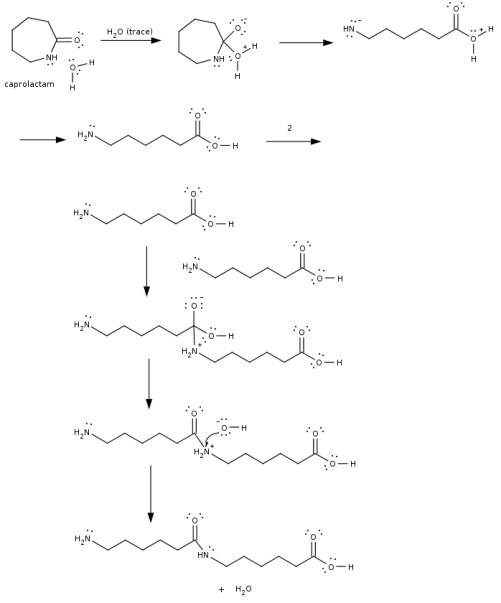


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A polymer synthesized from the following monomers could have the form 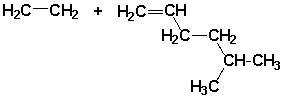
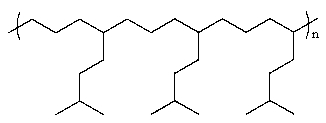
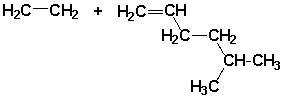


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A polymer with a melt transition temperature (Tm) of 200° C is stronger than a polymer with a Tm of 150° C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A polymer synthesized from the following monomers could have the form 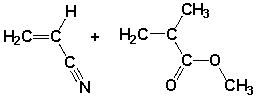
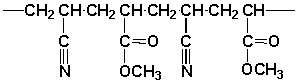
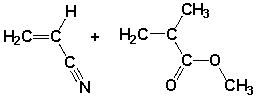
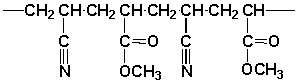

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The glass transition temperature (Tg) must be low for an elastomer to maintain its properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Zeigler-Natta process yields low-density polyethylene (LDPE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Radical chain growth polymers tend to form head to head bonds between carbon one of one monomer and carbon one of another monomer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The polymer synthesized from the following monomer is 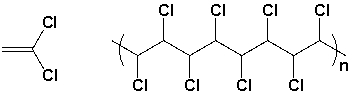


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The repeat unit of polymethylacrylate is, 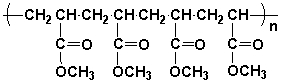

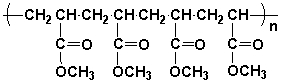


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Complete the mechanism for radical chain propagation begun below. 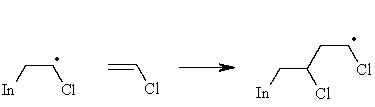


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Poly-amino-levulinic acid is a biodegradable polymer. Complete the reaction scheme shown below, which leads to the synthesis of poly-amino-levulinic acid: 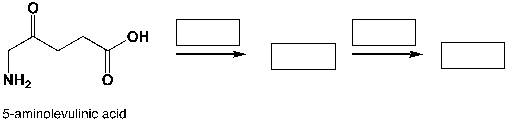


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



