Deck 14: Chemical Kinetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Chemical Kinetics
1
The reaction A + 2B → Products has the rate law, rate = k[A][B]3. If the concentration of B is doubled while that of A is unchanged, by what factor will the rate of reaction increase?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9
8
2
For the reaction BrO3- + 5Br- + 6H+ → 3Br2 + 3H2O at a particular time, -Δ[BrO3-]/Δt = 1.5 × 10-2 M/s. What is -Δ[Br-]/Δt at the same instant?
A) 13 M/s
B) 7.5 × 10-2 M/s
C) 1.5 × 10-2 M/s
D) 3.0 × 10-3 M/s
E) 330 M/s
A) 13 M/s
B) 7.5 × 10-2 M/s
C) 1.5 × 10-2 M/s
D) 3.0 × 10-3 M/s
E) 330 M/s
7.5 × 10-2 M/s
3
Which equation best describes the average rate for the reaction shown? A(aq) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(aq)
A)![<strong>Which equation best describes the average rate for the reaction shown? A(aq) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(aq)</strong> A) B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a94_4abc_8d9d_31bf26bbd7a7_TB8482_11.jpg)
B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt
C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt
D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt
E)![<strong>Which equation best describes the average rate for the reaction shown? A(aq) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(aq)</strong> A) B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a94_71cd_8d9d_6df9722a0467_TB8482_11.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Which equation best describes the average rate for the reaction shown? A(aq) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(aq)</strong> A) B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a94_4abc_8d9d_31bf26bbd7a7_TB8482_11.jpg)
B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt
C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt
D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt
E)
![<strong>Which equation best describes the average rate for the reaction shown? A(aq) + B(aq) → C(aq) + D(aq)</strong> A) B) rate = +Δ[B]/Δt C) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt D) rate = -Δ[A]/Δt E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a94_71cd_8d9d_6df9722a0467_TB8482_11.jpg)
rate = -Δ[A]/Δt
4
What are possible units for the rate of a reaction?
A) L • mol-1 • s-1
B) L2 • mol-2 • s-1
C) s-1
D) s-2
E) mol • L-1 • s-1
A) L • mol-1 • s-1
B) L2 • mol-2 • s-1
C) s-1
D) s-2
E) mol • L-1 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g)
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.![<strong>For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A) Rate = k[A][B] B) Rate = k[A][B]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k[A]<sup>3</sup>[B]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[A]<sup>1.5</sup>[B] E) Rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a95_f86f_8d9d_d7268e63c91a_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[A][B]
B) Rate = k[A][B]2
C) Rate = k[A]3[B]2
D) Rate = k[A]1.5[B]
E) Rate = k[A]2[B]
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A) Rate = k[A][B] B) Rate = k[A][B]<sup>2</sup> C) Rate = k[A]<sup>3</sup>[B]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[A]<sup>1.5</sup>[B] E) Rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a95_f86f_8d9d_d7268e63c91a_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[A][B]
B) Rate = k[A][B]2
C) Rate = k[A]3[B]2
D) Rate = k[A]1.5[B]
E) Rate = k[A]2[B]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the name given for the study of how fast reactions take place?
A) Reaction rate
B) Activation energy
C) Chemical kinetics
D) Reactivity
E) Half-life
A) Reaction rate
B) Activation energy
C) Chemical kinetics
D) Reactivity
E) Half-life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the following reaction 8A(g) + 5B(g) → 8C(g) + 6D(g)
If [C] is increasing at the rate of 4.0 mol L-1 • s-1, at what rate is [B] changing?
A) -0.40 mol L-1• s-1
B) -2.5 mol L-1• s-1
C) -4.0 mol L-1• s-1
D) -5.0 mol L-1• s-1
E) -6.4 mol L-1• s-1
If [C] is increasing at the rate of 4.0 mol L-1 • s-1, at what rate is [B] changing?
A) -0.40 mol L-1• s-1
B) -2.5 mol L-1• s-1
C) -4.0 mol L-1• s-1
D) -5.0 mol L-1• s-1
E) -6.4 mol L-1• s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The reaction A + 2B → Products was found to follow the rate law: rate = k[A]2[B]. Predict by what factor the rate of reaction will increase when the concentration of A is doubled, the concentration of B is tripled, and the temperature remains constant.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 12
D) 18
E) None of these
A) 5
B) 6
C) 12
D) 18
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the general reaction 5Br-(aq) + BrO3-(aq) + 6H+(aq) → 3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(aq)
For this reaction, which is equal to Δ[Br2]/Δt?
A) -Δ[H2O]/Δt
B) 3Δ[BrO3-]/Δt
C) -5Δ[Br-]/Δt
D) -0.6Δ[Br-]/Δt
E) None of these choices is correct.
For this reaction, which is equal to Δ[Br2]/Δt?
A) -Δ[H2O]/Δt
B) 3Δ[BrO3-]/Δt
C) -5Δ[Br-]/Δt
D) -0.6Δ[Br-]/Δt
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For the reaction A + 2B → C, which expression is correct?
A) Δ[C]/Δt = Δ[A]/Δt
B) Δ[C]/Δt = 2Δ[B]/Δt
C) Δ[C]/Δt = -2Δ[B]/Δt
D) Δ[C]/Δt = -½Δ[B]/Δt
E) Δ[C]/Δt = -½Δ[A]/Δt
A) Δ[C]/Δt = Δ[A]/Δt
B) Δ[C]/Δt = 2Δ[B]/Δt
C) Δ[C]/Δt = -2Δ[B]/Δt
D) Δ[C]/Δt = -½Δ[B]/Δt
E) Δ[C]/Δt = -½Δ[A]/Δt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The reaction A + 2B → Products has been found to have the rate law, rate = k[A][B]2. While holding the concentration of A constant, the concentration of B is increased to three times its initial value. By what factor does the rate of reaction increase?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 27
E) 30
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 27
E) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For the overall chemical reaction shown below, which one of the following statements can be rightly assumed? 2H2S(g) + O2(g) → 2S(s) + 2H2O(l)
A) The reaction is third-order overall.
B) The reaction is second-order overall.
C) The rate law is: rate = k[H2S]2 [O2].
D) The rate law is: rate = k[H2S] [O2].
E) The rate law cannot be determined from the information given.
A) The reaction is third-order overall.
B) The reaction is second-order overall.
C) The rate law is: rate = k[H2S]2 [O2].
D) The rate law is: rate = k[H2S] [O2].
E) The rate law cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For the reaction C6H14(g) → C6H6(g) + 4H2(g), ΔP(H2)/Δt was found to be 2.5 × 10-2 atm/s, where ΔP(H2) is the change in pressure of hydrogen. Determine ΔP(C6H14)/Δt for this reaction at the same time.
A) 2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
B) -6.3 × 10-3 atm/s
C) -2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
D) 0.10 atm/s
E) 6.3 × 10-3 atm/s
A) 2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
B) -6.3 × 10-3 atm/s
C) -2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
D) 0.10 atm/s
E) 6.3 × 10-3 atm/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the hypothetical reaction A + 3B → 2C, the rate should be expressed as
A) rate = Δ[A]/Δt.
B) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt.
C) rate = -3(Δ[B]/Δt).
D) rate = (1/2)(Δ[C]/Δt).
E) rate = (1/3)(Δ[B]/Δt).
A) rate = Δ[A]/Δt.
B) rate = -Δ[C]/Δt.
C) rate = -3(Δ[B]/Δt).
D) rate = (1/2)(Δ[C]/Δt).
E) rate = (1/3)(Δ[B]/Δt).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g)
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A) Rate = k[A][B] B) Rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B] C) Rate = k[A][B]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[A] E) Rate = k[A]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a96_1f80_8d9d_0fc18890c605_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[A][B]
B) Rate = k[A]2[B]
C) Rate = k[A][B]2
D) Rate = k[A]
E) Rate = k[A]3
The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction.
![<strong>For the reaction A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g) + 2D(g) The following data were collected at constant temperature. Determine the correct rate law for this reaction. </strong> A) Rate = k[A][B] B) Rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B] C) Rate = k[A][B]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[A] E) Rate = k[A]<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a96_1f80_8d9d_0fc18890c605_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k[A][B]
B) Rate = k[A]2[B]
C) Rate = k[A][B]2
D) Rate = k[A]
E) Rate = k[A]3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the rate expression for the production of X, which is a gas, at constant volume?
A) rate = PgVΔ[X]/RΔt
B) rate = -TΔ[X]/PgVΔt
C) rate = -PgV(Δ[X]/TΔt)
D) rate = (1/RT)(ΔPX/Δt)
E) rate = (1/RΔPX)(VT/Δt)
A) rate = PgVΔ[X]/RΔt
B) rate = -TΔ[X]/PgVΔt
C) rate = -PgV(Δ[X]/TΔt)
D) rate = (1/RT)(ΔPX/Δt)
E) rate = (1/RΔPX)(VT/Δt)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The reaction A + 2B → Products was found to have the rate law, rate = k[A][B]2. Predict by what factor the rate of reaction will increase when the concentration of A is doubled and the concentration of B is also doubled.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For the following reaction, ΔP(C6H14)/Δt was found to be -6.2 × 10-3 atm/s. C6H14(g) → C6H6(g) + 4H2(g)
Determine ΔP(H2)/Δt for this reaction at the same time.
A) 6.2 × 10-3 atm/s
B) 1.6 × 10-3 atm/s
C) 2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
D) -1.6 × 10-3 atm/s
E) -2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
Determine ΔP(H2)/Δt for this reaction at the same time.
A) 6.2 × 10-3 atm/s
B) 1.6 × 10-3 atm/s
C) 2.5 × 10-2 atm/s
D) -1.6 × 10-3 atm/s
E) -2.5 × 10-2 atm/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The compound RX3 decomposes according to the equation 3RX3 → R + R2X3 + 3X2
In an experiment the following data were collected for the decomposition at 100°C. What is the average rate of change of RX3 over the entire experiment?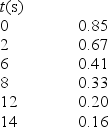
A) -0.011 mol • L-1 • s-1
B) -0.019 mol • L-1 • s-1
C) -0.044 mol • L-1 • s-1
D) -0.049 mol • L-1 • s-1
E) -0.069 mol • L-1 • s-1
In an experiment the following data were collected for the decomposition at 100°C. What is the average rate of change of RX3 over the entire experiment?

A) -0.011 mol • L-1 • s-1
B) -0.019 mol • L-1 • s-1
C) -0.044 mol • L-1 • s-1
D) -0.049 mol • L-1 • s-1
E) -0.069 mol • L-1 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the reaction 2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3H2(g)
If the rate Δ[H2]/Δt is 0.030 mol L-1 • s-1, what is Δ[NH3]/Δt?
A) -0.045 mol L-1• s-1
B) -0.030 mol L-1• s-1
C) -0.020 mol L-1• s-1
D) -0.010 mol L-1• s-1
E) None of these choices is correct.
If the rate Δ[H2]/Δt is 0.030 mol L-1 • s-1, what is Δ[NH3]/Δt?
A) -0.045 mol L-1• s-1
B) -0.030 mol L-1• s-1
C) -0.020 mol L-1• s-1
D) -0.010 mol L-1• s-1
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is the correct unit for a first-order rate constant?
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M -1 • s-1
E) M -2 • s-1
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M -1 • s-1
E) M -2 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The data below were determined for the reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3I-(aq) → 2SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq). ![<strong>The data below were determined for the reaction S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq) + 3I<sup>-</sup>(aq) → 2SO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq) + I<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq). Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2- </sup>][I <sup>-</sup>]<sup>3</sup> B) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>] C) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>]<sup>2</sup>[I <sup>-</sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k[I <sup>-</sup>] E) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>][I <sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a98_b792_8d9d_71e62401d279_TB8482_00.jpg) Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?
Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?
A) rate = k[S2O82- ][I -]3
B) rate = k[S2O82-]
C) rate = k[S2O82-]2[I -]2
D) rate = k[I -]
E) rate = k[S2O82-][I -]
![<strong>The data below were determined for the reaction S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq) + 3I<sup>-</sup>(aq) → 2SO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq) + I<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq). Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2- </sup>][I <sup>-</sup>]<sup>3</sup> B) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>] C) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>]<sup>2</sup>[I <sup>-</sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k[I <sup>-</sup>] E) rate = k[S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>8</sub><sup>2-</sup>][I <sup>-</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a98_b792_8d9d_71e62401d279_TB8482_00.jpg) Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?
Which rate law is consistent with the experimental data for this reaction?A) rate = k[S2O82- ][I -]3
B) rate = k[S2O82-]
C) rate = k[S2O82-]2[I -]2
D) rate = k[I -]
E) rate = k[S2O82-][I -]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The following initial rate data apply to the reaction F2(g) + 2Cl2O(g) → 2FClO2(g) + Cl2(g). ![<strong>The following initial rate data apply to the reaction F<sub>2</sub>(g) + 2Cl<sub>2</sub>O(g) → 2FClO<sub>2</sub>(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g). Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>4</sup> B) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O] C) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>][Cl<sub>2</sub>O] D) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>][Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> E) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a98_dea3_8d9d_750469a6f3fa_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
A) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]4
B) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]
C) rate = k[F2][Cl2O]
D) rate = k[F2][Cl2O]2
E) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]2
![<strong>The following initial rate data apply to the reaction F<sub>2</sub>(g) + 2Cl<sub>2</sub>O(g) → 2FClO<sub>2</sub>(g) + Cl<sub>2</sub>(g). Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>4</sup> B) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O] C) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>][Cl<sub>2</sub>O] D) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>][Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> E) rate = k[F<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a98_dea3_8d9d_750469a6f3fa_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?A) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]4
B) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]
C) rate = k[F2][Cl2O]
D) rate = k[F2][Cl2O]2
E) rate = k[F2]2[Cl2O]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Ammonium ion (NH4+) reacts with nitrite ion (NO2-) to yield nitrogen gas and liquid water. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reactant concentrations. ![<strong>Ammonium ion (NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>) reacts with nitrite ion (NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>) to yield nitrogen gas and liquid water. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reactant concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>4</sup> B) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] C) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>]<sup>2</sup> [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>]<sup>1/2</sup> [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_2cc4_8d9d_11c51da72048_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?
A) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]4
B) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]
C) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]2
D) rate = k [NH4+]2 [NO2-]
E) rate = k [NH4+]1/2 [NO2-]1/4
![<strong>Ammonium ion (NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>) reacts with nitrite ion (NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>) to yield nitrogen gas and liquid water. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reactant concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>4</sup> B) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] C) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>]<sup>2</sup> [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) rate = k [NH<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>]<sup>1/2</sup> [NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>]<sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_2cc4_8d9d_11c51da72048_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law (rate equation) for this reaction?A) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]4
B) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]
C) rate = k [NH4+] [NO2-]2
D) rate = k [NH4+]2 [NO2-]
E) rate = k [NH4+]1/2 [NO2-]1/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What statement below best describes the graph representing the integrated first-order rate law?
A) A plot of [A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
B) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to k.
C) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to -k.
D) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
E) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to k.
A) A plot of [A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
B) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to k.
C) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to -k.
D) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
E) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to k.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is the correct unit for a second-order rate constant?
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M -1 • s-1
E) M -2 • s-1
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M -1 • s-1
E) M -2 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A certain reaction A → products is second order in A. If this reaction is 85% complete in 12 minutes, how long would it take for the reaction to be 15% complete?
A) 110 s
B) 27 s
C) 62 s
D) 130 s
E) 22 s
A) 110 s
B) 27 s
C) 62 s
D) 130 s
E) 22 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A certain first-order reaction A → B is 25% complete in 42 min at 25°C. What is its rate constant?
A) 6.8 × 10-3 min-1
B) 8.3 × 10-3 min-1
C) 3.3 × 10-2 min-1
D) -3.3 × 10-2 min-1
E) 11 min-1
A) 6.8 × 10-3 min-1
B) 8.3 × 10-3 min-1
C) 3.3 × 10-2 min-1
D) -3.3 × 10-2 min-1
E) 11 min-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which is the correct unit for a zeroth-order rate constant?
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M-1 • s-1
E) M-2 • s-1
A) s-1
B) M • s-1
C) M • s
D) M-1 • s-1
E) M-2 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the reaction A → B + C is studied, a plot of ln[A]t vs. time gives a straight line with a negative slope. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the order.
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A certain first-order reaction A → B is 25% complete in 42 min at 25°C. What is the half-life of the reaction?
A) 21 min
B) 42 min
C) 84 min
D) 120 min
E) 101 min
A) 21 min
B) 42 min
C) 84 min
D) 120 min
E) 101 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sulfuryl chloride, SO2Cl2(g), decomposes at high temperature to form SO2(g) and Cl2(g). The rate constant at a certain temperature is 4.68 × 10-5 s-1. What is the order of the reaction?
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the overall order.
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the overall order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The first-order reaction SO2Cl2→ SO2 + Cl2 is 10% complete in 80. min. How long would it take for the reaction to be 95% complete?
A) 1.8 min
B) 104 min
C) 530 min
D) 2300 min
E) 990 min
A) 1.8 min
B) 104 min
C) 530 min
D) 2300 min
E) 990 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 3.00 × 10-3 s-1. The time required for the reaction to be 75.0% complete is
A) 95.8 s.
B) 462 s.
C) 231 s.
D) 201 s.
E) 41.7 s.
A) 95.8 s.
B) 462 s.
C) 231 s.
D) 201 s.
E) 41.7 s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
At 25°C the rate constant for the first-order decomposition of a pesticide solution is 6.40 × 10-3 min-1. If the starting concentration of pesticide is 0.0314 M, what concentration will remain after 62.0 min at 25°C?
A) 1.14 × 10-1 M
B) 47.4 M
C) 1.25 ×10-2 M
D) 2.11 × 10-2 M
E) 2.68 × 10-2 M
A) 1.14 × 10-1 M
B) 47.4 M
C) 1.25 ×10-2 M
D) 2.11 × 10-2 M
E) 2.68 × 10-2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What statement below best describes the graph representing the integrated second-order rate law?
A) A plot of [A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
B) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to k.
C) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to -k.
D) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
E) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to k.
A) A plot of [A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
B) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to k.
C) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to -k.
D) A plot of ln[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a negative slope equal to -k.
E) A plot of 1/[A]t vs. t yields a straight line with a positive slope equal to k.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The rate constant for a reaction is 4.65 L • mol-1 • s-1. What is the overall order of the reaction?
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the overall order.
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the overall order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 7.5 × 10-3 s-1. The time required for the reaction to be 60% complete is
A) 3.8 × 10-3 s.
B) 6.9 × 10-3 s.
C) 68 s.
D) 120 s.
E) 130 s.
A) 3.8 × 10-3 s.
B) 6.9 × 10-3 s.
C) 68 s.
D) 120 s.
E) 130 s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E
The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. What is the correct rate law for this reaction?![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. What is the correct rate law for this reaction? </strong> A) Rate = k [A][B][C] B) Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>[B][C] C) Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>[B][C]<sup>-1</sup> D) Rate = k [A][B]<sup>2</sup>[C]<sup>-1</sup> E) None of these choices is correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a96_1f81_8d9d_c36580df38d7_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k [A][B][C]
B) Rate = k [A]2[B][C]
C) Rate = k [A]2[B][C]-1
D) Rate = k [A][B]2[C]-1
E) None of these choices is correct.
The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. What is the correct rate law for this reaction?
![<strong>For the reaction 2A + B + 2C → D + E The following initial rate data were collected at constant temperature. What is the correct rate law for this reaction? </strong> A) Rate = k [A][B][C] B) Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>[B][C] C) Rate = k [A]<sup>2</sup>[B][C]<sup>-1</sup> D) Rate = k [A][B]<sup>2</sup>[C]<sup>-1</sup> E) None of these choices is correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a96_1f81_8d9d_c36580df38d7_TB8482_00.jpg)
A) Rate = k [A][B][C]
B) Rate = k [A]2[B][C]
C) Rate = k [A]2[B][C]-1
D) Rate = k [A][B]2[C]-1
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
It takes 42.0 min for the concentration of a reactant in a first-order reaction to drop from 0.45 M to 0.32 M at 25°C. How long will it take for the reaction to be 90% complete?
A) 13.0 min
B) 86.0 min
C) 137 min
D) 222 min
E) 284 min
A) 13.0 min
B) 86.0 min
C) 137 min
D) 222 min
E) 284 min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For the reaction X + Y → Z, the reaction rate is found to depend only upon the concentration of X. A plot of 1/X versus time gives a straight line. ![<strong>For the reaction X + Y → Z, the reaction rate is found to depend only upon the concentration of X. A plot of 1/X versus time gives a straight line. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k [X] B) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup> C) rate = k [X][Y] D) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup>[Y] E) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup>/[Y]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9a_8c59_8d9d_050991b4d202_TB8482_00.jpg) What is the rate law for this reaction?
What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) rate = k [X]
B) rate = k [X]2
C) rate = k [X][Y]
D) rate = k [X]2[Y]
E) rate = k [X]2/[Y]
![<strong>For the reaction X + Y → Z, the reaction rate is found to depend only upon the concentration of X. A plot of 1/X versus time gives a straight line. What is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k [X] B) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup> C) rate = k [X][Y] D) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup>[Y] E) rate = k [X]<sup>2</sup>/[Y]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9a_8c59_8d9d_050991b4d202_TB8482_00.jpg) What is the rate law for this reaction?
What is the rate law for this reaction?A) rate = k [X]
B) rate = k [X]2
C) rate = k [X][Y]
D) rate = k [X]2[Y]
E) rate = k [X]2/[Y]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For the chemical reaction A → B + C, a plot of [A]t versus time is found to give a straight line with a negative slope. What is the order of reaction with respect to A?
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) Such a plot cannot reveal the order of the reaction.
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) Such a plot cannot reveal the order of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Nitric oxide gas (NO) reacts with chlorine gas according to the equation NO + ![<strong>Nitric oxide gas (NO) reacts with chlorine gas according to the equation NO + Cl<sub>2 </sub>→ NOCl. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[NO] B) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_a1f5_8d9d_e52df022ee8d_TB8482_11.jpg) Cl2 → NOCl.
Cl2 → NOCl.
The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations.![<strong>Nitric oxide gas (NO) reacts with chlorine gas according to the equation NO + Cl<sub>2 </sub>→ NOCl. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[NO] B) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_a1f6_8d9d_575afc64634b_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
A) rate = k[NO]
B) rate = k[NO][Cl2]1/2
C) rate = k[NO][Cl2]
D) rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
E) rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]2
![<strong>Nitric oxide gas (NO) reacts with chlorine gas according to the equation NO + Cl<sub>2 </sub>→ NOCl. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[NO] B) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_a1f5_8d9d_e52df022ee8d_TB8482_11.jpg) Cl2 → NOCl.
Cl2 → NOCl.The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations.
![<strong>Nitric oxide gas (NO) reacts with chlorine gas according to the equation NO + Cl<sub>2 </sub>→ NOCl. The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reagent concentrations. Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[NO] B) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup> C) rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>] D) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a99_a1f6_8d9d_575afc64634b_TB8482_00.jpg) Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?A) rate = k[NO]
B) rate = k[NO][Cl2]1/2
C) rate = k[NO][Cl2]
D) rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
E) rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4, can be converted to octafluorocyclobutane, which can be used as a refrigerant or an aerosol propellant. A plot of 1/[C2F4] vs. time gives a straight line with a slope of 0.0448 L •mol-1 • s-1. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = 0.0448 (L • mol-1 • s-1)[C2F4]
B) Rate = 22.3 (mol • L-1 • s)[C2F4]
C) Rate = 0.0448 (L • mol-1 • s-1)[C2F4]2
D) Rate = 22.3 (mol • L-1 • s)[C2F4]2
E) Rate = 0.0448 s-1 [C2F4]
A) Rate = 0.0448 (L • mol-1 • s-1)[C2F4]
B) Rate = 22.3 (mol • L-1 • s)[C2F4]
C) Rate = 0.0448 (L • mol-1 • s-1)[C2F4]2
D) Rate = 22.3 (mol • L-1 • s)[C2F4]2
E) Rate = 0.0448 s-1 [C2F4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For the chemical reaction A → C, a plot of 1/[A]t versus time was found to give a straight line with a positive slope. What is the order of reaction?
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) Such a plot cannot reveal the order of the reaction.
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) Such a plot cannot reveal the order of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Cyclopropane is converted to propene in a first-order process. The rate constant is 5.4 × 10-2 h-1. If the initial concentration of cyclopropane is 0.150 M, what will its concentration be after 22.0 hours?
A) 0.046 M
B) 0.11 M
C) 0.13 M
D) 0.49 M
E) 0.054 M
A) 0.046 M
B) 0.11 M
C) 0.13 M
D) 0.49 M
E) 0.054 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For a zeroth-order reaction, if the concentration of reactant A is plotted vs. time, which corresponds to the slope of this plot?
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The thermal decomposition of acetaldehyde, CH3CHO → CH4 + CO, is a second-order reaction. The following data were obtained at 518°C.  Calculate the rate constant for the decomposition of acetaldehyde from the above data.
Calculate the rate constant for the decomposition of acetaldehyde from the above data.
A) 2.2 × 10-3 s-1
B) 0.70 mmHg • s-1
C) 2.2 × 10-3 /mmHg • s-1
D) 6.7 × 10-6 /mmHg • s-1
E) 5.2 × 10-5 /mmHg • s-1
 Calculate the rate constant for the decomposition of acetaldehyde from the above data.
Calculate the rate constant for the decomposition of acetaldehyde from the above data.A) 2.2 × 10-3 s-1
B) 0.70 mmHg • s-1
C) 2.2 × 10-3 /mmHg • s-1
D) 6.7 × 10-6 /mmHg • s-1
E) 5.2 × 10-5 /mmHg • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sucrose decomposes to fructose and glucose in acid solution. When ln [sucrose] is plotted vs. time, a straight line with slope of -0.208 h-1 results. What is the rate law for the reaction?
A) Rate = (0.208 h-1)[sucrose]2
B) Rate = (0.208 h-1)[sucrose]
C) Rate = (0.0433 h)[sucrose]2
D) Rate = (0.0433 h)[sucrose]
E) Rate = (0.208 mol L-1 • h-1)[sucrose]0
A) Rate = (0.208 h-1)[sucrose]2
B) Rate = (0.208 h-1)[sucrose]
C) Rate = (0.0433 h)[sucrose]2
D) Rate = (0.0433 h)[sucrose]
E) Rate = (0.208 mol L-1 • h-1)[sucrose]0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the reaction 2NOBr(g) → 2NO(g) + Br2(g). The initial rate of the reaction was measured for three different concentrations of NOBr, given below.  Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
A) 0.0360 L • mol-1 • s-1
B) 0.800 L • mol-1 • s-1
C) 1.25 L • mol-1 • s-1
D) 27.8 L • mol-1 • s-1
E) 0.0360 s-1
 Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?
Based on the initial rate data above, what is the value of the rate constant?A) 0.0360 L • mol-1 • s-1
B) 0.800 L • mol-1 • s-1
C) 1.25 L • mol-1 • s-1
D) 27.8 L • mol-1 • s-1
E) 0.0360 s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction?
A) Collision energy
B) Effective collision energy
C) Reaction energy
D) Activation energy
E) Rate energy
A) Collision energy
B) Effective collision energy
C) Reaction energy
D) Activation energy
E) Rate energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A study of the decomposition reaction 3RX2 → 3R + 6X yields the following initial rates. 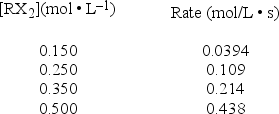 What is the rate constant for the reaction?
What is the rate constant for the reaction?
A) 0.0103 L • mol-1 • s-1
B) 0.263 L • mol-1 • s-1
C) 0.571 L • mol-1 • s-1
D) 1.17 L • mol-1 • s-1
E) 1.75 L • mol-1 • s-1
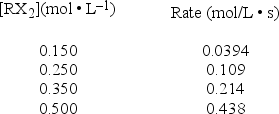 What is the rate constant for the reaction?
What is the rate constant for the reaction?A) 0.0103 L • mol-1 • s-1
B) 0.263 L • mol-1 • s-1
C) 0.571 L • mol-1 • s-1
D) 1.17 L • mol-1 • s-1
E) 1.75 L • mol-1 • s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the activation energy for a reaction if k = 1.89 × 10-8 s-1 at 540. K and k = 2.45 × 10-7 s-1 at 601 K?
A) 113 kJ/mol
B) 83 kJ/mol
C) 410 kJ/mol
D) 280 kJ/mol
E) 580 kJ/mol
A) 113 kJ/mol
B) 83 kJ/mol
C) 410 kJ/mol
D) 280 kJ/mol
E) 580 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
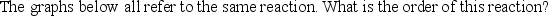
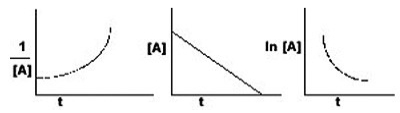
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) Such a plot cannot reveal the order of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The rate law for the rearrangement of CH3NC to CH3CN at 800 K is rate = (1300 s-1)[CH3NC]. What is the half-life for this reaction?
A) 7.69 × 10-4 s
B) 5.3 × 10-4 s
C) 1.9 × 10-3 s
D) 520 s
E) 1920 s
A) 7.69 × 10-4 s
B) 5.3 × 10-4 s
C) 1.9 × 10-3 s
D) 520 s
E) 1920 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A reaction has the following rate law: rate = k[A][B]2
In experiment 1, the concentrations of A and B are both 0.10 mol • L-1; in experiment 2, the concentrations are both 0.30 mol • L-1. If the temperature stays constant, what is the value of the ratio, rate(2)/rate(1)?
A) 3.0
B) 6.0
C) 9.0
D) 18
E) 27
In experiment 1, the concentrations of A and B are both 0.10 mol • L-1; in experiment 2, the concentrations are both 0.30 mol • L-1. If the temperature stays constant, what is the value of the ratio, rate(2)/rate(1)?
A) 3.0
B) 6.0
C) 9.0
D) 18
E) 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The reaction 2NO2(g) → 2NO(g) + O2(g) is suspected to be second order in NO2. Which of the following kinetic plots would be the most useful to confirm whether or not the reaction is second order?
A) A plot of [NO2]-1 vs. t
B) A plot of ln [NO2] vs. t
C) A plot of [NO2] vs. t
D) A plot of ln [NO2]-1 vs. t
E) A plot of [NO2]2 vs. t
A) A plot of [NO2]-1 vs. t
B) A plot of ln [NO2] vs. t
C) A plot of [NO2] vs. t
D) A plot of ln [NO2]-1 vs. t
E) A plot of [NO2]2 vs. t

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The rate law for the reaction 3A → 2B is rate = k[A] with a rate constant of 0.0447 h-1. What is the half-life of the reaction?
A) 0.0224 h
B) 0.0645 h
C) 15.5 h
D) 22.4 h
E) 44.7 h
A) 0.0224 h
B) 0.0645 h
C) 15.5 h
D) 22.4 h
E) 44.7 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Ammonium cyanate (NH4CNO) reacts to form urea (NH2CONH2). At 65°C the rate constant, k, is 3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1. What is the rate law for this reaction?
A) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]
B) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]2
C) Rate = (0.28 mol • L-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]
D) Rate = (0.28 mol • L-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]2
E) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH2CONH2]-1
A) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]
B) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]2
C) Rate = (0.28 mol • L-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]
D) Rate = (0.28 mol • L-1 • s-1)[NH4CNO]2
E) Rate = (3.60 L • mol-1 • s-1)[NH2CONH2]-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the reaction A → B + C is studied, a plot 1/[A]t vs. time gives a straight line with a positive slope. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the order.
A) Zero
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) More information is needed to determine the order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the half-life for a first-order reaction?
A)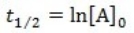
B)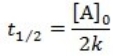
C)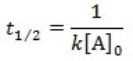
D)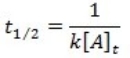
E)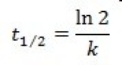
A)
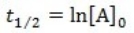
B)
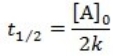
C)
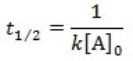
D)
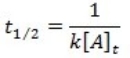
E)
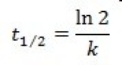

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the half-life for a first-order reaction?
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The rate constant for the reaction 3A → 4B is 6.00 × 10-3 L • mol-1 • min-1. How long will it take the concentration of A to drop from 0.75 M to 0.25 M?
A) 2.2 × 10-3 min
B) 5.5 × 10-3 min
C) 180 min
D) 440 min
E) 5.0 × 102min
A) 2.2 × 10-3 min
B) 5.5 × 10-3 min
C) 180 min
D) 440 min
E) 5.0 × 102min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For a zeroth-order reaction, if the concentration of reactant A is plotted vs. time, which corresponds to the slope of this plot?
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope which decays with a half-life of 5730 years. What is the first-order rate constant for its decay?
A) 5.25 × 10-5 yr-1
B) 1.21 × 10-4 yr-1
C) 1.75 × 10-4 yr-1
D) 3.49 × 10-4 yr-1
E) 3.97 × 103 yr-1
A) 5.25 × 10-5 yr-1
B) 1.21 × 10-4 yr-1
C) 1.75 × 10-4 yr-1
D) 3.49 × 10-4 yr-1
E) 3.97 × 103 yr-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?
A) rate = k[A]t
B)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dcd_8d9d_f720f2473073_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dce_8d9d_ef43d32ff7fa_TB8482_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dcf_8d9d_639aff5467fa_TB8482_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dd0_8d9d_5d68d99334d4_TB8482_11.jpg)
A) rate = k[A]t
B)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dcd_8d9d_f720f2473073_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dce_8d9d_ef43d32ff7fa_TB8482_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dcf_8d9d_639aff5467fa_TB8482_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a zeroth-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_9dd0_8d9d_5d68d99334d4_TB8482_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the half-life for a second-order reaction?
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the half-life for a zeroth-order reaction?
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k
A) t1/2 = k
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o
C) t1/2 = 0.693/k[A]o
D) t1/2 = [A]o/2k
E) t1/2 = 0.693/k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the half-life for a second-order reaction?
A)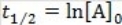
B)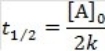
C)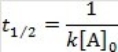
D)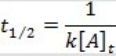
E)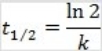
A)
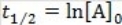
B)
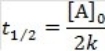
C)
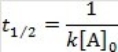
D)
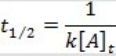
E)
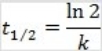

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Butadiene, C4H6 (used to make synthetic rubber and latex paints), dimerizes to C8H12 with a rate law of rate = 0.014 L/mol• s [C4H6]2. What will be the concentration of C4H6 after 3.0 hours if the initial concentration is 0.025 M?
A) 0.0052 M
B) 0.024 M
C) 43 M
D) 190 M
E) 0.0000 M
A) 0.0052 M
B) 0.024 M
C) 43 M
D) 190 M
E) 0.0000 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The reaction CH3NC(g) → CH3CN(g) is first order with respect to methyl isocyanide, CH3NC. If it takes 10.3 minutes for exactly one quarter of the initial amount of methyl isocyanide to react, what is the rate constant in units of min-1?
A) -0.135 min-1
B) 0.0279 min-1
C) 0.089 min-1
D) 0.135 min-1
E) 35.8 min-1
A) -0.135 min-1
B) 0.0279 min-1
C) 0.089 min-1
D) 0.135 min-1
E) 35.8 min-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The rate law for the reaction 3A → C is rate = 4.36 × 10-2 L• mol-1 • h-1[A]2. What is the half-life for the reaction if the initial concentration of A is 0.250 M?
A) 0.0109 h
B) 0.0629 h
C) 15.9 h
D) 23.9 h
E) 91.7 h
A) 0.0109 h
B) 0.0629 h
C) 15.9 h
D) 23.9 h
E) 91.7 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For a second-order reaction, if [A]-1 is plotted vs. time, which corresponds to the slope of this plot?
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k
A) 1/[A]
B) k
C) 1/k
D) ln[A]
E) -k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The activation energy for the following reaction is 60. kJ/mol. Sn2+ + 2Co3+ → Sn4+ + 2Co2+
By what factor will the rate constant increase when the temperature is raised from 10°C to 28°C? (R = 8.314 J/mol• K)
A) 1.002
B) 4.6
C) 5.6
D) 2.8
E) 696
By what factor will the rate constant increase when the temperature is raised from 10°C to 28°C? (R = 8.314 J/mol• K)
A) 1.002
B) 4.6
C) 5.6
D) 2.8
E) 696

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the slope of a plot of ln k vs. 1/T for the Arrhenius equation k = Ae-(Ea/RT)?
A) A
B) -k
C) -Ea/R
D) k
E) Ea
A) A
B) -k
C) -Ea/R
D) k
E) Ea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?
A) rate = k[A]t
B)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1305_8d9d_2d71d97c483e_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1306_8d9d_7fd60eec1204_TB8482_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1307_8d9d_4b6b826937d1_TB8482_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_3a18_8d9d_75c9eceb191a_TB8482_11.jpg)
A) rate = k[A]t
B)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1305_8d9d_2d71d97c483e_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1306_8d9d_7fd60eec1204_TB8482_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_1307_8d9d_4b6b826937d1_TB8482_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a second-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9c_3a18_8d9d_75c9eceb191a_TB8482_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The radioactive isotope tritium decays with a first-order rate constant k of 0.056 yr-1. What fraction of the tritium initially in a sample is still present 30. years later?
A) 0.19
B) 0.60
C) 0.15
D) 2.8 × 10-38
E) 0.81
A) 0.19
B) 0.60
C) 0.15
D) 2.8 × 10-38
E) 0.81

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A reactant R is being consumed in a first-order reaction. What fraction of the initial R is consumed in 4.0 half-lives?
A) 0.94
B) 0.88
C) 0.75
D) 0.13
E) 0.063
A) 0.94
B) 0.88
C) 0.75
D) 0.13
E) 0.063

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What rate constant can be determined from only the half-life of a reaction?
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) The rate constant cannot be determined using only a rate constant for any reaction.
A) Zeroth
B) First
C) Second
D) Third
E) The rate constant cannot be determined using only a rate constant for any reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?
A) rate = k[A]t
B)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_c4e1_8d9d_219787ec7cdb_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_c4e2_8d9d_81654e300a54_TB8482_00.jpg)
D)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_ebf3_8d9d_6dfab365a2f4_TB8482_00.jpg)
E)![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_ebf4_8d9d_1d06a64f3177_TB8482_11.jpg)
A) rate = k[A]t
B)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_c4e1_8d9d_219787ec7cdb_TB8482_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_c4e2_8d9d_81654e300a54_TB8482_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_ebf3_8d9d_6dfab365a2f4_TB8482_00.jpg)
E)
![<strong>What is the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?</strong> A) rate = k[A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a9b_ebf4_8d9d_1d06a64f3177_TB8482_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



