Deck 20: Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Nuclear Chemistry
1
Uranium-235 decays by alpha emission. What isotope is also produced by this transformation?
A) Pa-234
B) Th-237
C) Pu-237
D) Th-231
E) Pu-239
A) Pa-234
B) Th-237
C) Pu-237
D) Th-231
E) Pu-239
Th-231
2
What is the name for spontaneous emission of particles or electromagnetic radiation by certain nuclei?
A) Protons
B) Isotopes
C) Radioactivity
D) Neutrons
E) Electrons
A) Protons
B) Isotopes
C) Radioactivity
D) Neutrons
E) Electrons
Radioactivity
3
Beta particles are identical to
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
electrons.
4
What is the missing symbol in this plutonium fission reaction? 
A)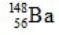
B)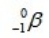
C)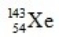
D)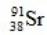
E)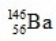

A)
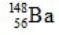
B)
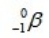
C)
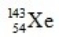
D)
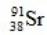
E)
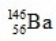

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When atoms of beryllium-9 are bombarded with alpha particles, neutrons are produced. What new isotope is also formed? 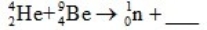
A)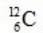
B)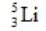
C)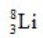
D)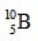
E)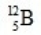
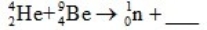
A)
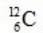
B)
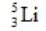
C)
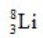
D)
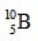
E)
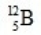

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The only stable isotope of aluminum is aluminum-27. What type of radioactive decay should be expected from 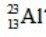 ?
?
A)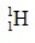
B)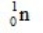
C)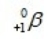
D)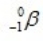
E)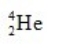
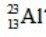 ?
?A)
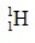
B)
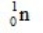
C)
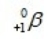
D)
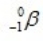
E)
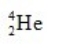

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which equation correctly represents positron decay of 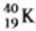 ?
?
A)
B)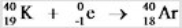
C)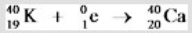
D)
E)
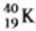 ?
?A)

B)
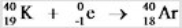
C)
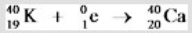
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Alpha particles are identical to
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.
A) protons.
B) helium atoms.
C) hydrogen atoms.
D) helium nuclei.
E) electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the equation below, what particle or type of radiation needs to be included to balance the equation? 208Pb → ? + 204Hg
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Proton
D) Beta particle
E) Positron
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Proton
D) Beta particle
E) Positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As a result of beta decay, the product nucleus is
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.
A) one atomic number lower than the original element.
B) two atomic numbers higher than the original element.
C) one atomic number higher than the original element.
D) two atomic numbers lower than the original element.
E) four atomic numbers lower than the original element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What other particle is emitted when a neutron is converted to a proton in a nucleus?
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Positron
D) Beta particle
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Positron
D) Beta particle
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which is an incorrect representation of the indicated particle or nucleus?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the equation below, what particle or type of radiation needs to be included to balance the equation? 234Th → ? + beta particle
A) Ac-234
B) Pa-234
C) Ac-235
D) Pa-235
E) Ac-233
A) Ac-234
B) Pa-234
C) Ac-235
D) Pa-235
E) Ac-233

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the equation below, what particle or type of radiation needs to be included to balance the equation? 208Po → ? + 208At
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Proton
D) Beta particle
E) Positron
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Proton
D) Beta particle
E) Positron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A typical radius of an atomic nucleus is about
A) 100 µm.
B) 5000 mm.
C) 100 nm.
D) 5 × 10-3 pm.
E) 500 pm.
A) 100 µm.
B) 5000 mm.
C) 100 nm.
D) 5 × 10-3 pm.
E) 500 pm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Select the nuclide that completes the following nuclear reaction 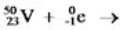 ?
?
A)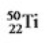
B)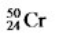
C)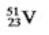
D)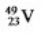
E) None of these choices is correct.
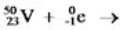 ?
?A)
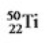
B)
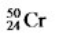
C)
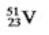
D)
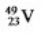
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the name given to the nuclear process that results from the bombardment of nuclei by neutrons, protons, or other nuclei?
A) Nuclear transmutation
B) Protonation
C) Nucleation
D) Nuclear condensation
E) Radioactivity
A) Nuclear transmutation
B) Protonation
C) Nucleation
D) Nuclear condensation
E) Radioactivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which equation correctly represents electron capture by the 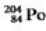 nucleus?
nucleus?
A)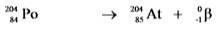
B)
C)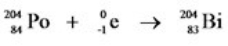
D)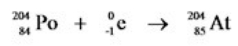
E)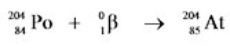
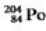 nucleus?
nucleus?A)
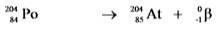
B)

C)
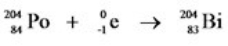
D)
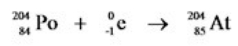
E)
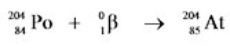

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the equation below, what particle or type of radiation needs to be included to balance the equation? 220Rn → ? + alpha particle
A) Ra-224
B) Rn-224
C) Rn-216
D) At-220
E) Po-216
A) Ra-224
B) Rn-224
C) Rn-216
D) At-220
E) Po-216

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When atoms of aluminum-27 are bombarded with alpha particles, a neutron and an element are produced. Which particular isotope of this element is formed? 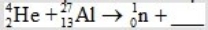
A)
B)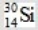
C)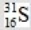
D)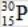
E)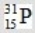
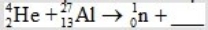
A)

B)
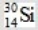
C)
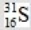
D)
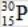
E)
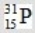

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Charcoal found under a stone at Stonehenge, England, has a carbon-14 activity that is 0.60 that of new wood. How old is the charcoal? (The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years.)
A) Less than 5730 yr
B) Between 5730 and 11,460 yr
C) Between 11,460 and 17,190 yr
D) More than 17,190 yr
A) Less than 5730 yr
B) Between 5730 and 11,460 yr
C) Between 11,460 and 17,190 yr
D) More than 17,190 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The radiochemist, Will I. Glow, studied thorium-232 and found that 2.82 × 10-7 moles emitted 8.42 × 106 α particles in one year. What is the decay constant for thorium-232?
A) 3.35 × 10-14 yr-1
B) 4.96 × 10-11 yr-1
C) 1.40 × 1010 yr-1
D) 2.99 × 1013 yr-1
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) 3.35 × 10-14 yr-1
B) 4.96 × 10-11 yr-1
C) 1.40 × 1010 yr-1
D) 2.99 × 1013 yr-1
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A mass of 6.02 × 1026 amu is equivalent to
A) 1 J.
B) 1 kg.
C) 1 g.
D) 1 mol.
E) 1 mg.
A) 1 J.
B) 1 kg.
C) 1 g.
D) 1 mol.
E) 1 mg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Polonium-208 is an alpha emitter with a half-life of 2.90 years. How many milligrams of polonium from an original sample of 2.00 mg will remain after 8.00 years?
A) 0.147 mg
B) 0.296 mg
C) 0.725 mg
D) 6.77 mg
E) 1.90 mg
A) 0.147 mg
B) 0.296 mg
C) 0.725 mg
D) 6.77 mg
E) 1.90 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon for 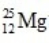 ? (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu;
? (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu;
C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
Particle Mass (amu)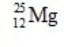 24.985839
24.985839 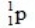 1.007276
1.007276 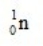 1.008665
1.008665
A) 0.214 J/nucleon
B) 3.20 × 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 1.28 × 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 0.999 J/nucleon
E) 7.35 × 10-11 J/nucleon
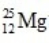 ? (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu;
? (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu;C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
Particle Mass (amu)
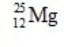 24.985839
24.985839 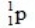 1.007276
1.007276 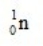 1.008665
1.008665A) 0.214 J/nucleon
B) 3.20 × 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 1.28 × 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 0.999 J/nucleon
E) 7.35 × 10-11 J/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Calculate the energy released in joules when one mole of polonium-214 decays according to the following equation. 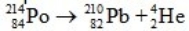
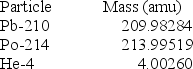 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 8.78 × 1014 J/mol
B) 7.2 × 1014 J/mol
C) 8.76 × 1011 J/mol
D) -9.75 × 10-3 J/mol
E) 1.46 × 10-9 J/mol
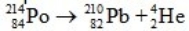
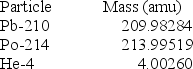 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 8.78 × 1014 J/mol
B) 7.2 × 1014 J/mol
C) 8.76 × 1011 J/mol
D) -9.75 × 10-3 J/mol
E) 1.46 × 10-9 J/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Iodine-131, t1/2 = 8.0 days, is used in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid gland diseases. If a laboratory sample of iodine-131 initially emits 9.95 × 1018 β particles per day, how long will it take for the activity to drop to 6.22 × 1017 β particles per day?
A) 2.0 days
B) 16 days
C) 32 days
D) 128 days
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) 2.0 days
B) 16 days
C) 32 days
D) 128 days
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon of uranium-234? ![<strong>What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon of uranium-234? [1 kg = 6.022 × 10<sup>26</sup> amu; N<sub>A</sub> = 6.022 × 10<sup>23</sup> mol<sup>-1</sup>; c = 2.99792458 × 10<sup>8</sup> m/s]</strong> A) 2.75 × 10<sup>-10</sup> J/nucleon B) 3.04 × 10<sup>-10</sup> J/nucleon C) 1.38 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon D) 1.27 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon E) 1.18 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a2c_afc3_8d9d_d3bdda18c1b7_TB8482_00.jpg) [1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1; c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s]
[1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1; c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s]
A) 2.75 × 10-10 J/nucleon
B) 3.04 × 10-10 J/nucleon
C) 1.38 × 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 1.27 × 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 1.18 × 10-12 J/nucleon
![<strong>What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon of uranium-234? [1 kg = 6.022 × 10<sup>26</sup> amu; N<sub>A</sub> = 6.022 × 10<sup>23</sup> mol<sup>-1</sup>; c = 2.99792458 × 10<sup>8</sup> m/s]</strong> A) 2.75 × 10<sup>-10</sup> J/nucleon B) 3.04 × 10<sup>-10</sup> J/nucleon C) 1.38 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon D) 1.27 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon E) 1.18 × 10<sup>-12</sup> J/nucleon](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/11eb6c5c_3a2c_afc3_8d9d_d3bdda18c1b7_TB8482_00.jpg) [1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1; c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s]
[1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1; c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s]A) 2.75 × 10-10 J/nucleon
B) 3.04 × 10-10 J/nucleon
C) 1.38 × 10-12 J/nucleon
D) 1.27 × 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 1.18 × 10-12 J/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The nuclear binding energy per nucleon is defined by which of the following?
A)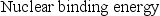
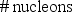
B) (Nuclear binding energy)2 × (# nucleons)
C)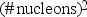
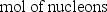
D) (# nucleons)2 × (mol of nucleons)
E) None of the answers is correct.
A)
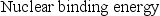
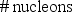
B) (Nuclear binding energy)2 × (# nucleons)
C)
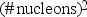
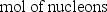
D) (# nucleons)2 × (mol of nucleons)
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An isotope with a high value of N/Z will tend to decay through
A) α decay.
B) β decay.
C) positron decay.
D) electron capture.
E) γ decay.
A) α decay.
B) β decay.
C) positron decay.
D) electron capture.
E) γ decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What fraction of radioactive atoms remains in a sample after six half-lives?
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) zero
B) 1/6
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Cesium-134 is a β emitter with a half-life of 2.0 years. How much of a 2.50-g sample of cesium-134 will remain after 10 years?
A) 0.0024 g
B) 0.078 g
C) 0.25 g
D) 0.50 g
E) 80.0 g
A) 0.0024 g
B) 0.078 g
C) 0.25 g
D) 0.50 g
E) 80.0 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the energy equivalent of 1 amu? (c = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 5.0 × 10-19 J
B) 5.4 × 1043 J
C) 6.6 × 109 J
D) 1.5 × 10-10 J
A) 5.0 × 10-19 J
B) 5.4 × 1043 J
C) 6.6 × 109 J
D) 1.5 × 10-10 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the name for the difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons?
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Mass difference
D) Beta particle
E) Mass defect
A) Gamma particle
B) Alpha particle
C) Mass difference
D) Beta particle
E) Mass defect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A rock contains 0.37 mg of Pb-206 and 0.95 mg of U-238. Approximately how many U-238 atoms were in the rock when it was formed billions of years ago? (The half life for 238U → 206Pb is 4.51 × 109 yr.)
A) 1.32 atoms
B) 5.8 × 10-6 atoms
C) 2.4 × 1018 atoms
D) 3.3 × 1018 atoms
E) 3.5 × 1021 atoms
A) 1.32 atoms
B) 5.8 × 10-6 atoms
C) 2.4 × 1018 atoms
D) 3.3 × 1018 atoms
E) 3.5 × 1021 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The 14C activity of some ancient Peruvian corn was found to be 10 disintegrations per minute per gram of carbon. If present-day plant life shows 15 dpm/g, how old is the Peruvian corn? (The half-life of 14C is 5730 yr.)
A) 1460 yr
B) 1910 yr
C) 3350 yr
D) 3820 yr
E) 9080 yr
A) 1460 yr
B) 1910 yr
C) 3350 yr
D) 3820 yr
E) 9080 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cobalt-60 is a beta emitter with a half-life of 5.3 years. Approximately what fraction of cobalt-60 atoms will remain in a particular sample after 26.5 years?
A) 1/5
B) 1/16
C) 1/26
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
A) 1/5
B) 1/16
C) 1/26
D) 1/32
E) 1/64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Determine how much energy is released when thorium-230 decays according to the following equation. 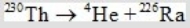
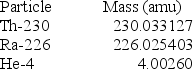 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 3.98 × 109 kJ/mol
B) 4.61 × 108 kJ/mol
C) 7.20 × 1011 kJ/mol
D) 4.90 × 109 kJ/mol
E) 7.15 × 1011 kJ/mol
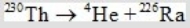
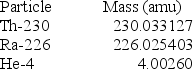 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 3.98 × 109 kJ/mol
B) 4.61 × 108 kJ/mol
C) 7.20 × 1011 kJ/mol
D) 4.90 × 109 kJ/mol
E) 7.15 × 1011 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
1 joule equals ________.
A) 1 kg • m
B) 1 g • m2 • s2
C) 1 kg • m2/s
D) 1 g • m2/s
E) 1 kg • m2/s2
A) 1 kg • m
B) 1 g • m2 • s2
C) 1 kg • m2/s
D) 1 g • m2/s
E) 1 kg • m2/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the nuclear binding energy per nucleon of potassium-40? 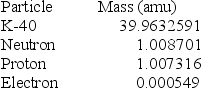 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 1.33 × 10-12 J/nucleon
B) 5.33 × 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 5.64 × 10-11 J/nucleon
D) 1.41 × 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 2.97 × 10-12 J/nucleon
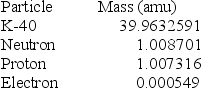 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 1.33 × 10-12 J/nucleon
B) 5.33 × 10-11 J/nucleon
C) 5.64 × 10-11 J/nucleon
D) 1.41 × 10-12 J/nucleon
E) 2.97 × 10-12 J/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The radioisotope potassium-40 decays to argon-40 by positron emission with a half-life of 1.3 × 109 yr. A sample of moon rock was found to contain 78 argon-40 atoms for every 22 potassium-40 atoms. The age of the rock is
A) 8.1 × 10-10 yr.
B) 2.4 × 109 yr.
C) 2.8 × 109 yr.
D) 4.6 × 109 yr.
E) 6.8 × 109 yr.
A) 8.1 × 10-10 yr.
B) 2.4 × 109 yr.
C) 2.8 × 109 yr.
D) 4.6 × 109 yr.
E) 6.8 × 109 yr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the following reaction, identify X. 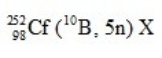
A)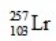
B)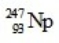
C)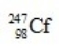
D)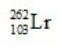
E)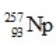
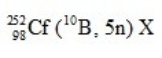
A)
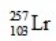
B)
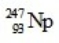
C)
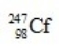
D)
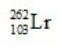
E)
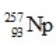

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The half-life of 14C is 5730 yr. Assuming some charcoal from a campfire 29,000 years old was found, what fraction of the original C-14 would remain today?
A) 3.0 × 10-2
B) 0.20
C) 3.5
D) 0.33
E) 0.29
A) 3.0 × 10-2
B) 0.20
C) 3.5
D) 0.33
E) 0.29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Petroleum is a fossil fuel containing many different carbon compounds. If the carbon atoms in petroleum have been in the ground for 100 million years, what fraction of the initial 14C atoms is still there? (t1/2 = 5730 yr)
A) 0
B) 1 × 10-10
C) 5.7 × 10-5
D) 1.0 × 10-3
E) 5.7 × 10-1
A) 0
B) 1 × 10-10
C) 5.7 × 10-5
D) 1.0 × 10-3
E) 5.7 × 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which isotope, when bombarded with nitrogen-15, yields four neutrons and the artificial isotope dubnium-260?
A) Californium-245
B) Thorium-257
C) Nobelium-245
D) Californium-249
E) Dubnium-249
A) Californium-245
B) Thorium-257
C) Nobelium-245
D) Californium-249
E) Dubnium-249

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Identify the missing species in the following nuclear transmutation. 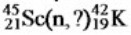
A)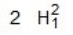
B)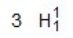
C)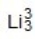
D)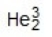
E)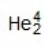
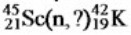
A)
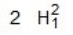
B)
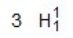
C)
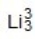
D)
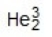
E)
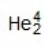

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify the missing species in the following nuclear transmutation. U-238 + ? → 1 neutron + Fm-249
A)
B)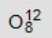
C)
D)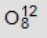
E)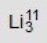
A)

B)
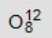
C)

D)
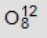
E)
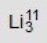

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A pure sample of tritium, 3H, was prepared and sealed in a container for a number of years. Tritium undergoes β decay with a half-life of 12.32 years. How long has the container been sealed if analysis of the contents shows there are 5.25 mol of 3H and 6.35 mol of 3He present?
A) 2.34 yr
B) 3.38 yr
C) 9.77 yr
D) 14.1 yr
E) 25.6 yr
A) 2.34 yr
B) 3.38 yr
C) 9.77 yr
D) 14.1 yr
E) 25.6 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A patient's thyroid gland is to be exposed to an average of 5.5 µCi for 16 days as an ingested sample of iodine-131 decays. If the energy of the β radiation is 9.7 × 10-14 J and the mass of the thyroid is 32.0 g, what is the dose received by the patient? (1 rad = 1 × 10-5 J/g; 1 Ci = 3.7 × 1010 disintegrations/s)
A) 0.027 rads
B) 85 rads
C) 37 rads
D) 23 rads
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) 0.027 rads
B) 85 rads
C) 37 rads
D) 23 rads
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the following reaction, identify X. 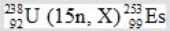
A) 7β
B) 3α
C) 4n
D)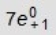
E) 15p
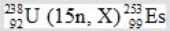
A) 7β
B) 3α
C) 4n
D)
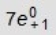
E) 15p

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A sample of a radioisotope shows an activity of 999 disintegrations per minute due to beta decay. If after 1.10 years the activity is 952 disintegrations per minute, what is the half-life of this radioisotope?
A) 4.38 × 10-2 yr
B) 11.4 yr
C) 0.25 yr
D) 15.8 yr
E) 9.1 yr
A) 4.38 × 10-2 yr
B) 11.4 yr
C) 0.25 yr
D) 15.8 yr
E) 9.1 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The carbon-14 activity of some ancient Indian corn was found to be 7.0 disintegrations per minute (dpm) per gram of carbon. If present-day plant life has 16 dpm per gram of carbon, how old is the Indian corn? (t1/2 = 5730 yr)
A) 6800 yr
B) 2500 yr
C) 4700 yr
D) 10,000 yr
E) 7200 yr
A) 6800 yr
B) 2500 yr
C) 4700 yr
D) 10,000 yr
E) 7200 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Rubidium-87 decays by beta decay with a half-life of 4.9 × 1010 yr. How many 87Rb atoms are in a moon rock sample that has a rubidium decay rate of 3500 disintegrations per hour?
A) 9.0 × 1016 atoms
B) 4.3 × 10-4 atoms
C) 2.2 × 1018 atoms
D) 2.5 × 1014 atoms
E) 1.7 × 1014 atoms
A) 9.0 × 1016 atoms
B) 4.3 × 10-4 atoms
C) 2.2 × 1018 atoms
D) 2.5 × 1014 atoms
E) 1.7 × 1014 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An 85-kg person exposed to barium-141 receives 2.5 × 105 β particles, each with an energy of 5.2 × 10-13 J. How many rads does the person receive? (1 rad = 1 × 10-5 J/g)
A) 2.4 × 10-20 rads
B) 1.5 × 10-7 rads
C) 1.8 × 10-16 rads
D) 6.1 × 10-15 rads
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) 2.4 × 10-20 rads
B) 1.5 × 10-7 rads
C) 1.8 × 10-16 rads
D) 6.1 × 10-15 rads
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Identify the missing species in the following nuclear transmutation. 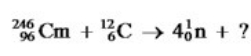
A)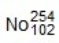
B)
C)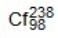
D)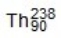
E) None of the answers is correct.
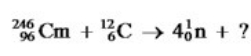
A)
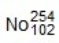
B)

C)
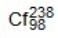
D)
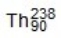
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the missing species in the following nuclear transmutation. 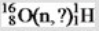
A)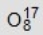
B)
C)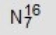
D)
E)
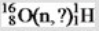
A)
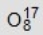
B)

C)
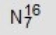
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Present-day plant life has a carbon-14 decay rate of 16 disintegrations per minute (dpm) per gram of carbon. If a contemporary wooden chair were preserved for the next 3900 years, what 14C decay rate should be expected from the wood used to make the chair? (t1/2 = 5730 yr)
A) 26 dpm
B) 12 dpm
C) 11 dpm
D) 10 dpm
E) 8 dpm
A) 26 dpm
B) 12 dpm
C) 11 dpm
D) 10 dpm
E) 8 dpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How many 14C atoms are in a charcoal sample that has a decay rate of 3500 disintegrations per min? (For 14C, t1/2 = 5730 yr.)
A) 2.9 × 107 atoms
B) 8.0 × 10-7 atoms
C) 1.4 × 1014 atoms
D) 1.5 × 1013 atoms
E) 6.02 × 1020 atoms
A) 2.9 × 107 atoms
B) 8.0 × 10-7 atoms
C) 1.4 × 1014 atoms
D) 1.5 × 1013 atoms
E) 6.02 × 1020 atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Estimate the age of a bottled wine that has a tritium, 3H, content 60% that of freshly bottled wine. Tritium decays by beta decay and has a half-life of 12.3 yr. 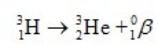
A) 0.029 yr
B) 7.4 yr
C) 9.1 yr
D) 16 yr
E) 35 yr
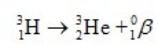
A) 0.029 yr
B) 7.4 yr
C) 9.1 yr
D) 16 yr
E) 35 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which isotope, when bombarded with bismuth-209, would yield two neutrons and an isotope with atomic number 121 and mass number 299?
A) Pb-211
B) Po-209
C) Sr-92
D) Rn-38
E) Sr-38
A) Pb-211
B) Po-209
C) Sr-92
D) Rn-38
E) Sr-38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The energy released by the sun is the result of
A) natural radioactivity.
B) nuclear fusion.
C) combustion of hydrogen.
D) photosynthesis.
E) nuclear fission.
A) natural radioactivity.
B) nuclear fusion.
C) combustion of hydrogen.
D) photosynthesis.
E) nuclear fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What role does cadmium metal (Cd) play in a nuclear reactor?
A) Slows down the fission neutrons (moderator)
B) Transfers heat from the reactor to the heat exchanger (primary coolant)
C) Controls chain reaction (control rods)
D) Transfers heat from the condenser to the environment (cooling tower)
E) Undergoes fission (fuel rods)
A) Slows down the fission neutrons (moderator)
B) Transfers heat from the reactor to the heat exchanger (primary coolant)
C) Controls chain reaction (control rods)
D) Transfers heat from the condenser to the environment (cooling tower)
E) Undergoes fission (fuel rods)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In passing through matter, alpha particles lose energy chiefly by causing
A) fermentation.
B) neutralization.
C) ionization.
D) condensation.
E) carbonation.
A) fermentation.
B) neutralization.
C) ionization.
D) condensation.
E) carbonation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exposure to 10 nCi for 10 minutes is more hazardous for a child than for an adult because
A) the child's cells are dividing more rapidly than the adult's and are, therefore, more susceptible to the radiation.
B) the child's smaller body size makes the effective dose larger for the child than for the adult.
C) the child's immune system is not developed well enough to resist damage.
D) the child's skin is not as thick as an adult's and cannot block as much radiation.
E) None of these reasons is correct.
A) the child's cells are dividing more rapidly than the adult's and are, therefore, more susceptible to the radiation.
B) the child's smaller body size makes the effective dose larger for the child than for the adult.
C) the child's immune system is not developed well enough to resist damage.
D) the child's skin is not as thick as an adult's and cannot block as much radiation.
E) None of these reasons is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the nuclear process called where small nuclei are combined into larger ones?
A) Photonuclear reactions
B) Nuclear fission
C) Thermal conductivity
D) Nuclear combination
E) Nuclear fusion
A) Photonuclear reactions
B) Nuclear fission
C) Thermal conductivity
D) Nuclear combination
E) Nuclear fusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A particle accelerator uses which of the following to increase the kinetic energy of charged species so that a reaction will occur?
A) Electromagnetic fields
B) Fission reaction
C) Gravitational field
D) Fusion reaction
E) Combustion reaction
A) Electromagnetic fields
B) Fission reaction
C) Gravitational field
D) Fusion reaction
E) Combustion reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
It is believed that two carbon-12 nuclei can react in the core of a supergiant star to form sodium-23 and hydrogen-1. Calculate the energy released from this reaction for each mole of hydrogen formed. 
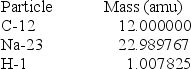 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 2.16 × 1014 kJ
B) 2.16 × 1011 kJ
C) 2.16 × 108 kJ
D) 2.16 × 105 kJ
E) None of the answers is correct.

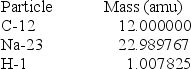 (1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;
(1 kg = 6.022 × 1026 amu; NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1;C = 2.99792458 × 108 m/s)
A) 2.16 × 1014 kJ
B) 2.16 × 1011 kJ
C) 2.16 × 108 kJ
D) 2.16 × 105 kJ
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which type of nuclear process requires an extremely high temperature (millions of degrees)?
A) Beta decay
B) Fission reaction
C) Fusion reaction
D) Alpha decay
E) Positron emission
A) Beta decay
B) Fission reaction
C) Fusion reaction
D) Alpha decay
E) Positron emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following materials is put into a nuclear reactor to slow the chain reaction?
A) Heavy water
B) Moderators
C) Control rods
D) Reflectors
E) Chlorine
A) Heavy water
B) Moderators
C) Control rods
D) Reflectors
E) Chlorine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What causes the radiation damage to matter when gamma rays damages it?
A) Another isotope
B) Oxidation
C) Reduction
D) Free radicals and ions
E) Corrosion
A) Another isotope
B) Oxidation
C) Reduction
D) Free radicals and ions
E) Corrosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The dose unit of ionizing radiation is called the rad. The rad is defined in terms of
A) the half-life of a radioisotope.
B) the energy deposited per gram of an object.
C) the biological damage produced.
D) the accumulation of fission products.
E) the number of ions per centimeter.
A) the half-life of a radioisotope.
B) the energy deposited per gram of an object.
C) the biological damage produced.
D) the accumulation of fission products.
E) the number of ions per centimeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which statement is false?
A) Fission occurs among the heaviest isotopes, whereas fusion occurs more readily for light isotopes.
B) The mass defect (Δm) for a fission reaction is negative, whereas Δm for fusion is positive.
C) In order for fusion reactions to occur, temperatures must be in the millions of degrees.
D) The fission of Pu-239 atoms produces isotopes of many different elements.
E) Neutron-induced fission processes can occur at room temperature, rather than at millions of degrees.
A) Fission occurs among the heaviest isotopes, whereas fusion occurs more readily for light isotopes.
B) The mass defect (Δm) for a fission reaction is negative, whereas Δm for fusion is positive.
C) In order for fusion reactions to occur, temperatures must be in the millions of degrees.
D) The fission of Pu-239 atoms produces isotopes of many different elements.
E) Neutron-induced fission processes can occur at room temperature, rather than at millions of degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A 30.0-kg child receives 2.65 × 107 β particles, each with an energy of 4.60 × 10-13 J. If the RBE = 0.78, how many millirem did the child receive?
A) 3.2 × 10-7 millirem
B) 5.2 × 10-7 millirem
C) 5.2 × 10-4 millirem
D) 3.2 × 10-2 millirem
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 3.2 × 10-7 millirem
B) 5.2 × 10-7 millirem
C) 5.2 × 10-4 millirem
D) 3.2 × 10-2 millirem
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What element is the stable end-product of the uranium radioactive decay series?
A) Th
B) Pu
C) Ra
D) Au
E) Pb
A) Th
B) Pu
C) Ra
D) Au
E) Pb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Sodium-21 will emit positrons, each having an energy of 4.0 × 10-13 J. What is this energy in MeV? (1 MeV = 1.602 × 10-13 J)
A) 4.0 × 10-7 MeV
B) 2.5 MeV
C) 40 MeV
D) 2.5 × 106 MeV
E) 2.5 × 10-6 MeV
A) 4.0 × 10-7 MeV
B) 2.5 MeV
C) 40 MeV
D) 2.5 × 106 MeV
E) 2.5 × 10-6 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which type of radiation is the least dangerous to humans?
A) Positrons
B) Neutrons
C) Alpha
D) Beta
E) Gamma
A) Positrons
B) Neutrons
C) Alpha
D) Beta
E) Gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Calcium-39 undergoes positron decay. Each positron carries 5.49 MeV of energy. How much energy will be emitted when 0.00250 mol of calcium-39 decays? (1 MeV = 1.602 × 10-13 J)
A) 13.2 kJ
B) 1.32 × 104 kJ
C) 1.32 × 106 kJ
D) 1.32 × 109 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 13.2 kJ
B) 1.32 × 104 kJ
C) 1.32 × 106 kJ
D) 1.32 × 109 kJ
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A 55-kg person exposed to thorium-234 receives 7.5 × 104 β particles, each with an energy of 1.6 × 10-14 J. How many rads does the person receive?
A) 2.1 × 10-19 rads
B) 1.2 × 10-17 rads
C) 2.2 × 10-9 rads
D) 1.2 × 10-9 rads
E) None of these choices is correct.
A) 2.1 × 10-19 rads
B) 1.2 × 10-17 rads
C) 2.2 × 10-9 rads
D) 1.2 × 10-9 rads
E) None of these choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is an advantage of nuclear power plants over coal-burning plants? Nuclear power plants
A) form numerous radioactive fission products.
B) do not pollute the air with SO2, soot, and fly-ash.
C) produce more thermal pollution than coal plants.
D) use more fuel.
A) form numerous radioactive fission products.
B) do not pollute the air with SO2, soot, and fly-ash.
C) produce more thermal pollution than coal plants.
D) use more fuel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which type of radiation is the most dangerous to humans?
A) Protons
B) Neutrons
C) Alpha
D) Beta
E) Gamma
A) Protons
B) Neutrons
C) Alpha
D) Beta
E) Gamma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



