Deck 35: Financial Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Financial Economics
1
Suppose that the city of New York issues bonds to raise money to pay for a new tunnel linking New Jersey and Manhattan. An investor named Susan buys one of the bonds on the same day that the city of New York pays a contractor for completing the first stage of construction. Is Susan making an economic or a financial investment? What about the city of New York?
The investments that are used to fuel to deveof the economy are known as economic investment. In other words, economic investment is when investor is investing in capital (produced means of further production).
Financial investment is an asset that an investor put money into it with the hope that it will grow. In other words, financial investment is putting money into businesses rather than another form of involvement of the business.
In this case, City-NY is making an economic investment by issues bonds to raise money to pay for a new tunnel linking New Jersey and Manhattan because it refers to paying for the new addition to capital
An investor named-SU buys one of the bonds on the same day that the city of New York pays a contactor for completing the first stage of construction. Investor is making a financial investment because it involves purchase of a financial asset to finance the project for the City-NY.
Financial investment is an asset that an investor put money into it with the hope that it will grow. In other words, financial investment is putting money into businesses rather than another form of involvement of the business.
In this case, City-NY is making an economic investment by issues bonds to raise money to pay for a new tunnel linking New Jersey and Manhattan because it refers to paying for the new addition to capital
An investor named-SU buys one of the bonds on the same day that the city of New York pays a contactor for completing the first stage of construction. Investor is making a financial investment because it involves purchase of a financial asset to finance the project for the City-NY.
2
Suppose that you invest $ 100 today in a risk-free investment and let the 4 percent annual interest rate compound. Rounded to full dollars, what will be the value of your investment 4 years from now?
Remember that the formula for compound interest is:
 .
.
We are given that we have $100 today, and the interest rate is 4 percent
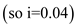 . We want to find out how much this $100 would be in
. We want to find out how much this $100 would be in
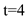 years. Substituting into the expression, we have:
years. Substituting into the expression, we have:
 In other words,
In other words,
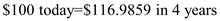 Rounded to the nearest full dollar, we have $100 today is equal to $117 dollars in 4 years.
Rounded to the nearest full dollar, we have $100 today is equal to $117 dollars in 4 years.
 .
.We are given that we have $100 today, and the interest rate is 4 percent
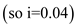 . We want to find out how much this $100 would be in
. We want to find out how much this $100 would be in 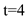 years. Substituting into the expression, we have:
years. Substituting into the expression, we have: In other words,
In other words,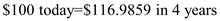 Rounded to the nearest full dollar, we have $100 today is equal to $117 dollars in 4 years.
Rounded to the nearest full dollar, we have $100 today is equal to $117 dollars in 4 years. 3
Identify each of the folinvestments as either an economic investment or a financial investment.
a. A company builds a new factory.
b. A pension plan buys some Google stock.
c. A mining company sets up a new gold mine.
d. A woman buys a 100-year-old farmhouse in the countryside.
e. A man buys a newly built home in the city.
f. A company buys an old factory.
a. A company builds a new factory.
b. A pension plan buys some Google stock.
c. A mining company sets up a new gold mine.
d. A woman buys a 100-year-old farmhouse in the countryside.
e. A man buys a newly built home in the city.
f. A company buys an old factory.
Economic investment:
Economic investment is the purchase of assets that would generate income. Financial investment:
Financial investment is the purchase of an existing asset that would grow or appreciate the value of asset.
a. Building a new factory:
Building new factory leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to increase the production and generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
b. Buying 'G' stock:
People are buying an existing 'G' stock with the intention that in the future the value of this asset would increase. Thus, it is a financial investment.
c. Setting up of new gold mine:
Setting up of new gold mine leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to increase the production and generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
d. Buying 100 years old farm house:
A person buying a 100 year old farm house is a purchase of existing assets with the intention that in the future the value of this asset would increase. Thus, it is a financial investment.
e. Buying new home:
Buying new home leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
f. Buying old factory:
Purchase of existing factory does not increase the capital stock rather the intention of a person is to get financial gains through increases in the value of asset in the future. Thus, it is a financial investment.
Economic investment is the purchase of assets that would generate income. Financial investment:
Financial investment is the purchase of an existing asset that would grow or appreciate the value of asset.
a. Building a new factory:
Building new factory leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to increase the production and generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
b. Buying 'G' stock:
People are buying an existing 'G' stock with the intention that in the future the value of this asset would increase. Thus, it is a financial investment.
c. Setting up of new gold mine:
Setting up of new gold mine leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to increase the production and generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
d. Buying 100 years old farm house:
A person buying a 100 year old farm house is a purchase of existing assets with the intention that in the future the value of this asset would increase. Thus, it is a financial investment.
e. Buying new home:
Buying new home leads to increase in the capital stock that helps to generates more income. Thus, it is an economic investment.
f. Buying old factory:
Purchase of existing factory does not increase the capital stock rather the intention of a person is to get financial gains through increases in the value of asset in the future. Thus, it is a financial investment.
4
What is compound interest? How does it relate to the formula X t = (1 + i ) t X 0 ? What is present value? How does it relate to the formula X t /(1 + i ) t = X 0 ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose that you desire to get a lump sum payment of $100,000 two years from now. Rounded to full dollars, how many current dollars will you have to invest today at a 10 percent interest to accomplish your goal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
It is a fact that  . Knowing that to be true, what is the present value of $140 received in three years if the annual interest rate is 12 percent?
. Knowing that to be true, what is the present value of $140 received in three years if the annual interest rate is 12 percent?
A) $1.40.
B) $12.
C) $100.
D) $112.
 . Knowing that to be true, what is the present value of $140 received in three years if the annual interest rate is 12 percent?
. Knowing that to be true, what is the present value of $140 received in three years if the annual interest rate is 12 percent?A) $1.40.
B) $12.
C) $100.
D) $112.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How do stocks and bonds differ in terms of the future payments that they are expected to make? Which type of investment (stocks or bonds) is considered to be more risky? Given what you know, which investment (stocks or bonds) do you think commonly goes by the nickname "fixed income"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that a risk-free investment will make three future payments of $100 in one year, $100 in two years, and $100 in three years. If the Federal Reserve has set the risk-free interest rate at 8 percent, what is the proper current price of this investment? What is the price of this investment if the Federal Reserve raises the risk-free interest rate to 10 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Asset X is expected to deliver 3 future payments. They have present values of, respectively, $1,000, $2,000, and $7,000. Asset Y is expected to deliver 10 future payments, each having a present value of $1,000. Which of the folstatements correctly describes the relationship between the current price of Asset X and the current price of Asset Y?
A) Asset X and Asset Y should have the same current price.
B) Asset X should have a higher current price than Asset Y.
C) Asset X should have a current price than Asset Y.
A) Asset X and Asset Y should have the same current price.
B) Asset X should have a higher current price than Asset Y.
C) Asset X should have a current price than Asset Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What are mutual funds? What different types of mutual funds are there? And why do you think they are so popular with investors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider an asset that costs $120 today. You are going to hold it for 1year and then sell it. Suppose that there is a 25 percent chance that it will be worth $100 in a year, a 25 percent chance that it will be worth $115 in a year, and a 50 percent chance that it will be worth $140 in a year. What is its average expected rate of return? Next, figure out what the investment's average expected rate of return would be if its current price were $130 today. Does the increase in the current price increase or decrease the asset's average expected rate of return? At what price would the asset have a zero average expected rate of return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Tammy can buy an asset this year for $1,000. She is expecting to sell it next year for $1,050. What is the asset's anticipated percentage rate of return?
A) 0 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 15 percent.
A) 0 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 10 percent.
D) 15 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Corporations often distribute profits to their shareholders in the form of dividends, which are simply checks mailed out to shareholders. Suppose that you have the chance to buy a share in a fashion company called Rogue Designs for $35 and that the company will pay dividends of $2 per year on that share every year. What is the annual percentage rate of return? Next, suppose that you and other investors could get a 12 percent per year rate of return by owning the stocks of other very similar fashion companies. If investors care only about rates of return, what should happen to the share price of Rogue Designs? (Hint: This is an arbitrage situation.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose initially that two assets, A and B, will each make a single guaranteed payment of $100 in 1year. But asset A has a current price of $80 while asset B has a current price of $90.
a. What are the rates of return of assets A and B at their ,current prices? Given these rates of return, which asset should investors buy and which asset should they sell?
b. Assume that arbitrage continues until A and B have the same expected rate of return. When arbitrage ends, will A and B have the same price?
Next, consider another pair of assets, C and D. Asset C will make asingle payment of $150 in one year, while D will make a single payment of $200 in one year. Assume that the current price of C is $120 and that the current price of D is $180.
c. What are the rates of return of assets C and D at their current prices? Given these rates of return, which asset should investors buy and which asset should they sell?
d. Assume that arbitrage continues until C and D have the same expected rate of return. When arbitrage ends, will C and D have the same price?
Compare your answers to questions a through d before answering question e. e. We know that arbitrage will equalize rates of return. Does it also guarantee to equalize prices? In what simations will it equalize prices?
a. What are the rates of return of assets A and B at their ,current prices? Given these rates of return, which asset should investors buy and which asset should they sell?
b. Assume that arbitrage continues until A and B have the same expected rate of return. When arbitrage ends, will A and B have the same price?
Next, consider another pair of assets, C and D. Asset C will make asingle payment of $150 in one year, while D will make a single payment of $200 in one year. Assume that the current price of C is $120 and that the current price of D is $180.
c. What are the rates of return of assets C and D at their current prices? Given these rates of return, which asset should investors buy and which asset should they sell?
d. Assume that arbitrage continues until C and D have the same expected rate of return. When arbitrage ends, will C and D have the same price?
Compare your answers to questions a through d before answering question e. e. We know that arbitrage will equalize rates of return. Does it also guarantee to equalize prices? In what simations will it equalize prices?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Sammy buys stock in a suntan-maker and also stock in an umbrella maker. One stock does well when the weather is good; the other does well when the weather is bad. Sammy's portfolio indicates that "weather risk" is a __________risk.
A) Diversifiable.
B) Non-diversifiable.
C) Automatic.
A) Diversifiable.
B) Non-diversifiable.
C) Automatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why is it reasonable to ignore diversifiable risk and care only about nondiversifiable risk? What about investors who put all their money into only a single risky stock? Can they properly ignore diversifiable risk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
ADVANCED ANALYSIS Suppose that the equation for the SML is Y = 0.05 + 0.04X, where Y is the average expected rate of return, 0.05 is the vertical intercept, 0.04 is the sand X is the risk level as measured by beta. What is the risk free interest rate for this SML? What is the average expected rate of return at a beta of 1.5? What is the value of beta at an average expected rate of return of 7 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
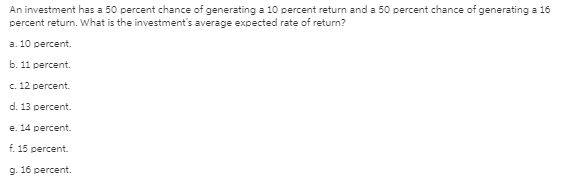

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If we compare the betas of various investment opportunities, why do the assets that have higher betas also have higher average expected rates of return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If an investment has 35 percent more non-diversifiable risk than the market portfolio, its beta will be:
A) 35.
B) 1.35.
C) 0.35.
A) 35.
B) 1.35.
C) 0.35.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In this chapter we discussed short-term U.S. government bonds. But the U.S. government also issues bonds with horizons of up to 30 years. Why do 20-year bonds issued by the U.S. government have rates of return than 20-year bonds issued by corporations? And which would you consider more likely, that term U.S. government bonds have a higher interest rate than short-term U.S. government bonds, or vice versa? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The interest rate on short-term U.S. government bonds is 4 percent. The risk premium for any asset with a beta 5 1.0 is 6 percent. What is the average expected rate of return on the market portfolio?
A) 0 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 6 percent.
D) 10 percent.
A) 0 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 6 percent.
D) 10 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What determines the vertical intercept of the Security Market Line (SML)? What determines its sAnd what will happen to an asset's price if it initially ponto a point above the SML?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that an SML indicates that assets with a beta 5 1.15 should have an average expected rate of return of 12 percent per year. If a particular stock with a beta 5 1.15 currently has an average expected rate of return of 15 percent, what should we expect to happen to its price?
A) Rise.
B) Fall.
C) Stay the same.
A) Rise.
B) Fall.
C) Stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that the Federal Reserve thinks that a stock market bubble is occurring and wants to reduce stock prices. What should it do to interest rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the Fed increases interest rates, the SML will shift__________ and asset prices will __________.
A) Down; rise.
B) Down; fall.
C) Up; rise.
D) Up; fall.
A) Down; rise.
B) Down; fall.
C) Up; rise.
D) Up; fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider another situation involving the SML. Suppose that the risk-free interest rate stays the same, but that investors' dislike of risk grows more intense. Given this change, will average expected rates of return rise or fall? Next, compare what will happen to the rates of return on and high-risk investments. Which will have a larger increase in average expected rates of return, investments with high betas or investments with betas? And will high-beta or investments show larger percentage changes in their prices?.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
LAST WORD Why is it so hard for actively managed funds to generate higher rates of return than passively managed index funds having similar levels of risk? Is there a simple way for an actively managed fund to increase its average expected rate of return?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



