Deck 8: Aggregate Demand and the Powerful Consumer
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Aggregate Demand and the Powerful Consumer
1
Explain the difference between investment as the term is used by most people and investment as defined by an economist.
Meaning of Investment
According to an economist, investment refers to the total amount invested today to generate revenue in the future. It is the amount that firms and individuals spend on the purchase of new physical assets like purchase of machinery, software, new house, etc. The level of investment is determined by the rate of interest. Level of investment is negatively determined by the rate of interest rate. That is, when the rate of interest increases, level of investment decreases and vice versa.
On the other hand, common people tend to define investment in a different manner. According to them, investment is made in the stock market, bank account, etc. But in general, this kind of investment is just swapping of one form of financial asset into the other.
According to an economist, investment refers to the total amount invested today to generate revenue in the future. It is the amount that firms and individuals spend on the purchase of new physical assets like purchase of machinery, software, new house, etc. The level of investment is determined by the rate of interest. Level of investment is negatively determined by the rate of interest rate. That is, when the rate of interest increases, level of investment decreases and vice versa.
On the other hand, common people tend to define investment in a different manner. According to them, investment is made in the stock market, bank account, etc. But in general, this kind of investment is just swapping of one form of financial asset into the other.
2
What are the four main components of aggregate demand? Which is the largest? Which is the smallest?
Components of Aggregate Demand
The components of aggregate demand are as follows:
• Consumption can be simply defined as spending to purchase goods and services. Consumption depends on size of income and the marginal propensity to consume. Consumption depends positively on disposable income: the amount of income after all taxes have been paid. The higher the disposable income, the greater the consumption.
• Investment The addition of capital to the existing capital to enhance the productivity. It includes addition of machinery, payment for the additional labor, and addition of stock capital, and so on.
• Government expenditure It consists of government purchases of goods and services in an economy at a given point of time. It is denoted as G.
• Net exports It is the difference between imports and exports. When exports are greater than the imports, the money value of net exports is more and vice versa.
The equation for aggregate demand can be written as follows:
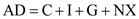 ……(1)
……(1)
Where,
AD = Aggregate demand
C = Consumption expenditure
G = Government expenditure
NX= Net exports
Equation (1) states that aggregate demand is the sum of consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Largest and smallest component of aggregate demand
The largest component of aggregate demand is consumption expenditure because it constitutes more than two-third of the total expenditure.
The smallest component of aggregate demand is Net exports because it is the difference between exports and imports. Although the value of exports and imports are high, the difference in the value of these two components would be smaller.
The components of aggregate demand are as follows:
• Consumption can be simply defined as spending to purchase goods and services. Consumption depends on size of income and the marginal propensity to consume. Consumption depends positively on disposable income: the amount of income after all taxes have been paid. The higher the disposable income, the greater the consumption.
• Investment The addition of capital to the existing capital to enhance the productivity. It includes addition of machinery, payment for the additional labor, and addition of stock capital, and so on.
• Government expenditure It consists of government purchases of goods and services in an economy at a given point of time. It is denoted as G.
• Net exports It is the difference between imports and exports. When exports are greater than the imports, the money value of net exports is more and vice versa.
The equation for aggregate demand can be written as follows:
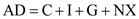 ……(1)
……(1)Where,
AD = Aggregate demand
C = Consumption expenditure
G = Government expenditure
NX= Net exports
Equation (1) states that aggregate demand is the sum of consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Largest and smallest component of aggregate demand
The largest component of aggregate demand is consumption expenditure because it constitutes more than two-third of the total expenditure.
The smallest component of aggregate demand is Net exports because it is the difference between exports and imports. Although the value of exports and imports are high, the difference in the value of these two components would be smaller.
3
What would the circular flow diagram (Figure 1) look like in an economy with no government? Draw one for yourself.
Graphical representation
The following diagram represents the circular flow of income without government interference.
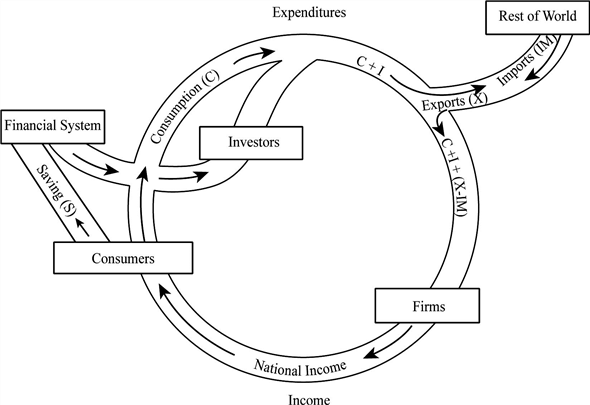 In the above diagram, the economic system is explained through a circular flow diagram where there is no government interference.
In the above diagram, the economic system is explained through a circular flow diagram where there is no government interference.
To explain this circular flow diagram better, start with consumers. Consumers either spend their disposable income on consumption of goods and services or they save their disposable income. The savings flows to the financial system and the expenditure on consumption flows to the firms. The first injection of the funds is done by investors, which consist of business firms and individuals; this expenditure is a part of investment and not consumption. At this point, total spending in an economy increases to
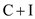 .
.
At the final stage, the rest of the world comes into picture where the spending on exports enters the system and spending on imports leaks out of the system. The impact of net exports depends on whether the values of net exports are positive or negative
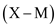 . Finally, by adding up these three components, we derive aggregate demand without government interference. This can be written as
. Finally, by adding up these three components, we derive aggregate demand without government interference. This can be written as
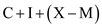 .
.
The following diagram represents the circular flow of income without government interference.
 In the above diagram, the economic system is explained through a circular flow diagram where there is no government interference.
In the above diagram, the economic system is explained through a circular flow diagram where there is no government interference.To explain this circular flow diagram better, start with consumers. Consumers either spend their disposable income on consumption of goods and services or they save their disposable income. The savings flows to the financial system and the expenditure on consumption flows to the firms. The first injection of the funds is done by investors, which consist of business firms and individuals; this expenditure is a part of investment and not consumption. At this point, total spending in an economy increases to
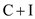 .
.At the final stage, the rest of the world comes into picture where the spending on exports enters the system and spending on imports leaks out of the system. The impact of net exports depends on whether the values of net exports are positive or negative
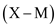 . Finally, by adding up these three components, we derive aggregate demand without government interference. This can be written as
. Finally, by adding up these three components, we derive aggregate demand without government interference. This can be written as 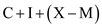 .
. 4
Which of the following acts constitute investment according to the economist's definition of that term?
a. Pfizer builds a new factory in the United States to manufacture pharmaceuticals.
b. You buy 100 shares of Pfizer stock.
c. A small drugmaker goes bankrupt, and Pfizer purchases its factory and equipment.
d. Your family buys a newly constructed home from a developer.
e. Your family buys an older home from another family. ( Hint: Are any new products demanded by this action?)
a. Pfizer builds a new factory in the United States to manufacture pharmaceuticals.
b. You buy 100 shares of Pfizer stock.
c. A small drugmaker goes bankrupt, and Pfizer purchases its factory and equipment.
d. Your family buys a newly constructed home from a developer.
e. Your family buys an older home from another family. ( Hint: Are any new products demanded by this action?)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) for the United States as a whole is roughly 0.90. Explain in words what this means. What is your personal MPC at this stage in your life? How might that change by the time you are your parents' age?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
On a piece of graph paper, construct a consumption function from the data given here and determine the MPC.
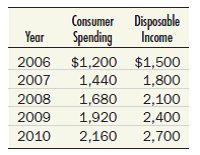
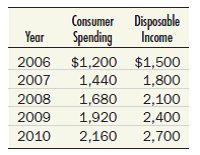

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Look at the scatter diagram in Figure 3. What does it tell you about what was going on in this country in the years 1942 to 1945?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which direction will the consumption function shift if the price level rises? Show this on your graph from the previous question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is a consumption function, and why is it a useful device for government economists planning a tax cut?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Explain why permanent tax cuts are likely to lead to bigger increases in consumer spending than temporary tax cuts do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In 2001 and again in 2003, Congress enacted changes in the tax law designed to promote saving. If such saving incentives had been successful, how would the consumption function have shifted?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
(More difficult) Between 2008 and 2009, real disposable income (in 2005 dollars) barely increased at all, owing to a recession. (It rose from $10,043 billion to $10,100 billion.) Use the data on real consumption expenditures given on the inside back cover of this book to compare the change in C to this $57 billion change in DI. Explain why dividing the two does not give a good estimate of the marginal propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Explain the difference between final goods and intermediate goods. Why is it sometimes difficult to apply this distinction in practice? In this regard, why is the concept of value added useful?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following transactions are included in the gross domestic product, and by how much does each raise GDP?
a. You buy a new Toyota, made in the United States, paying $25,000.
b. You buy a new Toyota, imported from Japan, paying $25,000.
c. You buy a used Cadillac, paying $12,000.
d. Google spends $500 million to increase its Internet capacity.
e. Your grandmother receives a Social Security check for $1,500.
f. Chrysler manufactures 1,000 automobiles at a cost of $15,000 each. Unable to sell them, the company holds the cars as inventories.
g. Mr. Black and Mr. Blue, each out for a Sunday drive, have a collision in which their cars are destroyed. Black and Blue each hire a lawyer to sue the other, paying the lawyers $5,000 each for services rendered. The judge throws the case out of court.
h. You sell a used computer to your friend for $100.
a. You buy a new Toyota, made in the United States, paying $25,000.
b. You buy a new Toyota, imported from Japan, paying $25,000.
c. You buy a used Cadillac, paying $12,000.
d. Google spends $500 million to increase its Internet capacity.
e. Your grandmother receives a Social Security check for $1,500.
f. Chrysler manufactures 1,000 automobiles at a cost of $15,000 each. Unable to sell them, the company holds the cars as inventories.
g. Mr. Black and Mr. Blue, each out for a Sunday drive, have a collision in which their cars are destroyed. Black and Blue each hire a lawyer to sue the other, paying the lawyers $5,000 each for services rendered. The judge throws the case out of court.
h. You sell a used computer to your friend for $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Explain the difference between government spending and government purchases of goods and services ( G ). Which is larger?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following outline provides a complete description of all economic activity in Trivialand for 2010. Draw up versions of Tables 3 and 4 for Trivialand showing GDP computed in two different ways. 10
i. There are thousands of farmers but only two big business firms in Trivialand: Specific Motors (an auto company) and Super Duper (a chain of food markets). There is no government and no depreciation
ii.Specific Motors produced 1,000 small cars, which it sold at $6,000 each, and 100 trucks, which it sold at $8,000 each. Consumers bought 800 of the cars, and the remaining 200 cars were exported to the United States. Super Duper bought all the trucks.
iii. Sales at Super Duper markets amounted to $14 million, all of it sold to consumers.
iv. All farmers in Trivialand are self-employed and sell all of their wares to Super Duper.
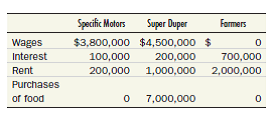
v. The costs incurred by all of Trivialand's businesses were as follows:
i. There are thousands of farmers but only two big business firms in Trivialand: Specific Motors (an auto company) and Super Duper (a chain of food markets). There is no government and no depreciation
ii.Specific Motors produced 1,000 small cars, which it sold at $6,000 each, and 100 trucks, which it sold at $8,000 each. Consumers bought 800 of the cars, and the remaining 200 cars were exported to the United States. Super Duper bought all the trucks.
iii. Sales at Super Duper markets amounted to $14 million, all of it sold to consumers.
iv. All farmers in Trivialand are self-employed and sell all of their wares to Super Duper.
v. The costs incurred by all of Trivialand's businesses were as follows:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Explain why national income and gross domestic product would be essentially equal if there were no depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
(More difficult) Now complicate Trivialand in the following ways and answer the same questions. In addition, calculate national income and disposable income. 11
a. The government bought 50 cars, leaving only 150 cars for export. In addition, the government spent $800,000 on wages and made $1,200,000 in transfer payments.
b. Depreciation for the year amounted to $600,000 for Specific Motors and $200,000 for Super Duper. (The farmers had no depreciation.)
c. The government levied sales taxes amounting to $500,000 on Specific Motors and $200,000 on Super Duper (but none on farmers). In addition, the government levied a 10 percent income tax on all wages, interest, and rental income.
d. In addition to the food and cars mentioned in Test Yourself Question 2, consumers in Trivialand imported 500 computers from the United States at $2,000 each.
a. The government bought 50 cars, leaving only 150 cars for export. In addition, the government spent $800,000 on wages and made $1,200,000 in transfer payments.
b. Depreciation for the year amounted to $600,000 for Specific Motors and $200,000 for Super Duper. (The farmers had no depreciation.)
c. The government levied sales taxes amounting to $500,000 on Specific Motors and $200,000 on Super Duper (but none on farmers). In addition, the government levied a 10 percent income tax on all wages, interest, and rental income.
d. In addition to the food and cars mentioned in Test Yourself Question 2, consumers in Trivialand imported 500 computers from the United States at $2,000 each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



