Deck 15: Investments and Fair Value Accounting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Investments and Fair Value Accounting
1
A Bond investment transactions
Journalize the entries to record the following selected bond investment transactions for Hall Trust:
a. Purchased for cash $300,000 of Oates City 4% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $3,000.
b. Received first semiannual interest payment.
c. Sold $150,000 of the bonds at 97 plus accrued interest of $500.
B Bond investment transactions
Journalize the entries to record the following selected bond investment transactions for Starks Products:
a. Purchased for cash $120,000 of Iceline, Inc. 5% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $1,000.
b. Received first semiannual interest payment.
c. Sold $60,000 of the bonds at 101 plus accrued interest of $500.'
Journalize the entries to record the following selected bond investment transactions for Hall Trust:
a. Purchased for cash $300,000 of Oates City 4% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $3,000.
b. Received first semiannual interest payment.
c. Sold $150,000 of the bonds at 97 plus accrued interest of $500.
B Bond investment transactions
Journalize the entries to record the following selected bond investment transactions for Starks Products:
a. Purchased for cash $120,000 of Iceline, Inc. 5% bonds at 100 plus accrued interest of $1,000.
b. Received first semiannual interest payment.
c. Sold $60,000 of the bonds at 101 plus accrued interest of $500.'
A. Bond investment transaction:
Journal Entries:
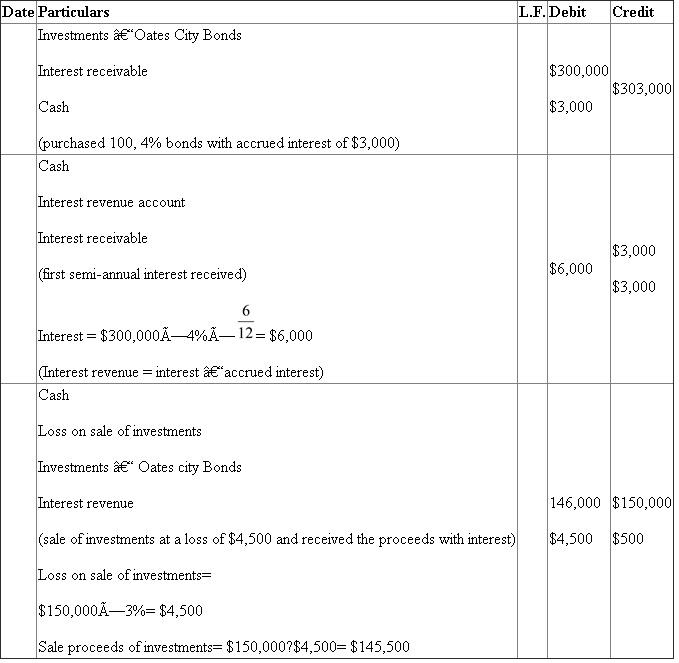 a. investments and accrued interest are purchased, hence they are debited and cash is paid, hence it is credited.
a. investments and accrued interest are purchased, hence they are debited and cash is paid, hence it is credited.
b. semi-annual interest is received in the form of cash, hence cash is debited. Interest revenue is an income, hence it is credited. Interest receivable is credited to cancel the debit in the previous entry.
Cash is received on sale of investments, hence it is debited and investments are surrendering, hence they are credited. Any loss is to be debited; hence loss on sale of investments is debited. Accrued interest is also sold, hence it is credited.
B. Bond investment transaction:
Journal Entries:
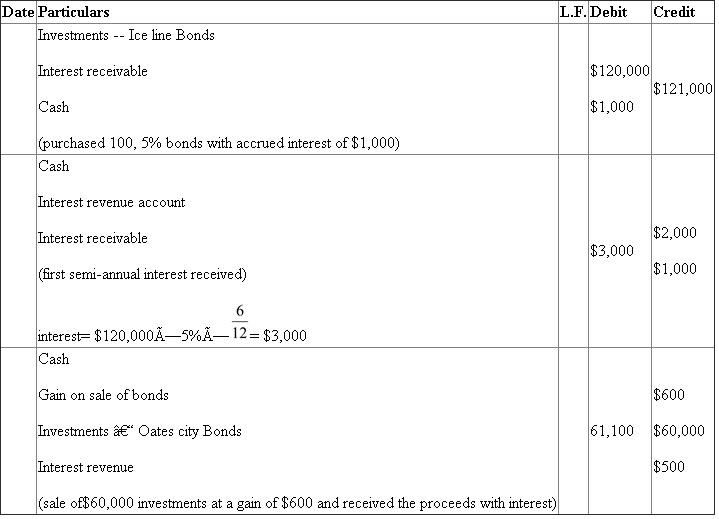
Journal Entries:
 a. investments and accrued interest are purchased, hence they are debited and cash is paid, hence it is credited.
a. investments and accrued interest are purchased, hence they are debited and cash is paid, hence it is credited.b. semi-annual interest is received in the form of cash, hence cash is debited. Interest revenue is an income, hence it is credited. Interest receivable is credited to cancel the debit in the previous entry.
Cash is received on sale of investments, hence it is debited and investments are surrendering, hence they are credited. Any loss is to be debited; hence loss on sale of investments is debited. Accrued interest is also sold, hence it is credited.
B. Bond investment transaction:
Journal Entries:

2
Selected transactions completed by Equinox Products Inc. during the fiscal year ended December 31, Year 1, were as follows:
a. Issued 15,000 shares of $20 par common stock at $30, receiving cash.
b. Issued 4,000 shares of $80 par preferred 5% stock at $100, receiving cash.
c. Issued $500,000 of 10-year, 5% bonds at 104, with interest payable semiannually.
d. Declared a quarterly dividend of $0.50 per share on common stock and $1.00 per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 100,000 shares of common stock were outstanding, no treasury shares were held and 20,000 shares of preferred stock were outstanding.
e. Paid the cash dividends declared in (d).
f. Purchased 7,500 shares of Solstice Corp. at $40 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. The investment is classified as an available-for-sale investment.
g. Purchased 8,000 shares of treasury common stock at $33 per share.
h. Purchased 40,000 shares of Pinkberry Co. stock directly from the founders for $24 per share. Pinkberry has 125,000 shares issued and outstanding. Equinox Products Inc. treated the investment as an equity method investment.
i. Declared a $1.00 quarterly cash dividend per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 20,000 shares of preferred stock had been issued.
j. Paid the cash dividends to the preferred stockholders.
k. Received $27,500 dividend from Pinkberry Co. investment in (h).
l. Purchased $90,000 of Dream Inc. 10-year, 5% bonds, directly from the issuing company, at their face amount plus accrued interest of $375. The bonds are classified as a heldto- maturity long-term investment.
m. Sold, at $38 per share, 2,600 shares of treasury common stock purchased in (g).
n. Received a dividend of $0.60 per share from the Solstice Corp. investment in (f).
o. Sold 1,000 shares of Solstice Corp. at $45, including commission.
p. Recorded the payment of semiannual interest on the bonds issued in (c) and the amortization of the premium for six months. The amortization is determined using the straight-line method.
q. Accrued interest for three months on the Dream Inc. bonds purchased in (l).
r. Pinkberry Co. recorded total earnings of $240,000. Equinox Products recorded equity earnings for its share of Pinkberry Co. net income.
s. The fair value for Solstice Corp. stock was $39.02 per share on December 31, Year 1. The investment is adjusted to fair value, using a valuation allowance account. Assume that Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a beginning balance of zero.
Instructions
1. Journalize the selected transactions.
2. After all of the transactions for the year ended December 31, Year 1, had been posted [including the transactions recorded in part (1) and all adjusting entries], the data that
follows were taken from the records of Equinox Products Inc.
a. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1, concluding with earnings per share. In computing earnings per share, assume that the average number of common shares outstanding was 100,000 and preferred dividends were $100,000. Round earnings per share to the nearest cent.
b. Prepare a retained earnings statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1.
c. Prepare a balance sheet in report form as of December 31, Year 1.
![Selected transactions completed by Equinox Products Inc. during the fiscal year ended December 31, Year 1, were as follows: a. Issued 15,000 shares of $20 par common stock at $30, receiving cash. b. Issued 4,000 shares of $80 par preferred 5% stock at $100, receiving cash. c. Issued $500,000 of 10-year, 5% bonds at 104, with interest payable semiannually. d. Declared a quarterly dividend of $0.50 per share on common stock and $1.00 per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 100,000 shares of common stock were outstanding, no treasury shares were held and 20,000 shares of preferred stock were outstanding. e. Paid the cash dividends declared in (d). f. Purchased 7,500 shares of Solstice Corp. at $40 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. The investment is classified as an available-for-sale investment. g. Purchased 8,000 shares of treasury common stock at $33 per share. h. Purchased 40,000 shares of Pinkberry Co. stock directly from the founders for $24 per share. Pinkberry has 125,000 shares issued and outstanding. Equinox Products Inc. treated the investment as an equity method investment. i. Declared a $1.00 quarterly cash dividend per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 20,000 shares of preferred stock had been issued. j. Paid the cash dividends to the preferred stockholders. k. Received $27,500 dividend from Pinkberry Co. investment in (h). l. Purchased $90,000 of Dream Inc. 10-year, 5% bonds, directly from the issuing company, at their face amount plus accrued interest of $375. The bonds are classified as a heldto- maturity long-term investment. m. Sold, at $38 per share, 2,600 shares of treasury common stock purchased in (g). n. Received a dividend of $0.60 per share from the Solstice Corp. investment in (f). o. Sold 1,000 shares of Solstice Corp. at $45, including commission. p. Recorded the payment of semiannual interest on the bonds issued in (c) and the amortization of the premium for six months. The amortization is determined using the straight-line method. q. Accrued interest for three months on the Dream Inc. bonds purchased in (l). r. Pinkberry Co. recorded total earnings of $240,000. Equinox Products recorded equity earnings for its share of Pinkberry Co. net income. s. The fair value for Solstice Corp. stock was $39.02 per share on December 31, Year 1. The investment is adjusted to fair value, using a valuation allowance account. Assume that Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a beginning balance of zero. Instructions 1. Journalize the selected transactions. 2. After all of the transactions for the year ended December 31, Year 1, had been posted [including the transactions recorded in part (1) and all adjusting entries], the data that follows were taken from the records of Equinox Products Inc. a. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1, concluding with earnings per share. In computing earnings per share, assume that the average number of common shares outstanding was 100,000 and preferred dividends were $100,000. Round earnings per share to the nearest cent. b. Prepare a retained earnings statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1. c. Prepare a balance sheet in report form as of December 31, Year 1.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/SM1486/11eb6eb8_2464_de63_9fd7_6fca5d6c40a5_SM1486_00.jpg)
a. Issued 15,000 shares of $20 par common stock at $30, receiving cash.
b. Issued 4,000 shares of $80 par preferred 5% stock at $100, receiving cash.
c. Issued $500,000 of 10-year, 5% bonds at 104, with interest payable semiannually.
d. Declared a quarterly dividend of $0.50 per share on common stock and $1.00 per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 100,000 shares of common stock were outstanding, no treasury shares were held and 20,000 shares of preferred stock were outstanding.
e. Paid the cash dividends declared in (d).
f. Purchased 7,500 shares of Solstice Corp. at $40 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. The investment is classified as an available-for-sale investment.
g. Purchased 8,000 shares of treasury common stock at $33 per share.
h. Purchased 40,000 shares of Pinkberry Co. stock directly from the founders for $24 per share. Pinkberry has 125,000 shares issued and outstanding. Equinox Products Inc. treated the investment as an equity method investment.
i. Declared a $1.00 quarterly cash dividend per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 20,000 shares of preferred stock had been issued.
j. Paid the cash dividends to the preferred stockholders.
k. Received $27,500 dividend from Pinkberry Co. investment in (h).
l. Purchased $90,000 of Dream Inc. 10-year, 5% bonds, directly from the issuing company, at their face amount plus accrued interest of $375. The bonds are classified as a heldto- maturity long-term investment.
m. Sold, at $38 per share, 2,600 shares of treasury common stock purchased in (g).
n. Received a dividend of $0.60 per share from the Solstice Corp. investment in (f).
o. Sold 1,000 shares of Solstice Corp. at $45, including commission.
p. Recorded the payment of semiannual interest on the bonds issued in (c) and the amortization of the premium for six months. The amortization is determined using the straight-line method.
q. Accrued interest for three months on the Dream Inc. bonds purchased in (l).
r. Pinkberry Co. recorded total earnings of $240,000. Equinox Products recorded equity earnings for its share of Pinkberry Co. net income.
s. The fair value for Solstice Corp. stock was $39.02 per share on December 31, Year 1. The investment is adjusted to fair value, using a valuation allowance account. Assume that Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a beginning balance of zero.
Instructions
1. Journalize the selected transactions.
2. After all of the transactions for the year ended December 31, Year 1, had been posted [including the transactions recorded in part (1) and all adjusting entries], the data that
follows were taken from the records of Equinox Products Inc.
a. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1, concluding with earnings per share. In computing earnings per share, assume that the average number of common shares outstanding was 100,000 and preferred dividends were $100,000. Round earnings per share to the nearest cent.
b. Prepare a retained earnings statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1.
c. Prepare a balance sheet in report form as of December 31, Year 1.
![Selected transactions completed by Equinox Products Inc. during the fiscal year ended December 31, Year 1, were as follows: a. Issued 15,000 shares of $20 par common stock at $30, receiving cash. b. Issued 4,000 shares of $80 par preferred 5% stock at $100, receiving cash. c. Issued $500,000 of 10-year, 5% bonds at 104, with interest payable semiannually. d. Declared a quarterly dividend of $0.50 per share on common stock and $1.00 per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 100,000 shares of common stock were outstanding, no treasury shares were held and 20,000 shares of preferred stock were outstanding. e. Paid the cash dividends declared in (d). f. Purchased 7,500 shares of Solstice Corp. at $40 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. The investment is classified as an available-for-sale investment. g. Purchased 8,000 shares of treasury common stock at $33 per share. h. Purchased 40,000 shares of Pinkberry Co. stock directly from the founders for $24 per share. Pinkberry has 125,000 shares issued and outstanding. Equinox Products Inc. treated the investment as an equity method investment. i. Declared a $1.00 quarterly cash dividend per share on preferred stock. On the date of record, 20,000 shares of preferred stock had been issued. j. Paid the cash dividends to the preferred stockholders. k. Received $27,500 dividend from Pinkberry Co. investment in (h). l. Purchased $90,000 of Dream Inc. 10-year, 5% bonds, directly from the issuing company, at their face amount plus accrued interest of $375. The bonds are classified as a heldto- maturity long-term investment. m. Sold, at $38 per share, 2,600 shares of treasury common stock purchased in (g). n. Received a dividend of $0.60 per share from the Solstice Corp. investment in (f). o. Sold 1,000 shares of Solstice Corp. at $45, including commission. p. Recorded the payment of semiannual interest on the bonds issued in (c) and the amortization of the premium for six months. The amortization is determined using the straight-line method. q. Accrued interest for three months on the Dream Inc. bonds purchased in (l). r. Pinkberry Co. recorded total earnings of $240,000. Equinox Products recorded equity earnings for its share of Pinkberry Co. net income. s. The fair value for Solstice Corp. stock was $39.02 per share on December 31, Year 1. The investment is adjusted to fair value, using a valuation allowance account. Assume that Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a beginning balance of zero. Instructions 1. Journalize the selected transactions. 2. After all of the transactions for the year ended December 31, Year 1, had been posted [including the transactions recorded in part (1) and all adjusting entries], the data that follows were taken from the records of Equinox Products Inc. a. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1, concluding with earnings per share. In computing earnings per share, assume that the average number of common shares outstanding was 100,000 and preferred dividends were $100,000. Round earnings per share to the nearest cent. b. Prepare a retained earnings statement for the year ended December 31, Year 1. c. Prepare a balance sheet in report form as of December 31, Year 1.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/SM1486/11eb6eb8_2464_de63_9fd7_6fca5d6c40a5_SM1486_00.jpg)
Financial Statement
Financial statement refers that recording of financial activities of the business. In other words, it includes Income statement, Balance sheet, Cash flow which shows the true picture of the business of the enterprises.
1.
a.
Pass Journal entries to the selected transaction of E P incorporation:
Journal entry related to the issue of common stock:
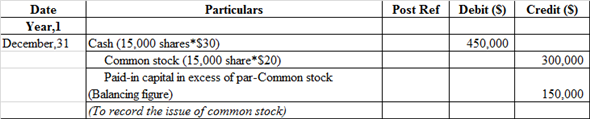 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
Common stock is credited because it is increased and it comes under liability and owners' equity whenever it increases, it is always credited and paid in capital in excess of par-common stock is balancing figure and it also comes under liability when it increases, it is always credited.
b.
Journal entry related to the issue of preferred stock:
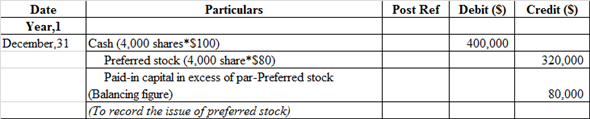 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
Preferred stock is credited because it is increased and it comes under liability and owners' equity whenever it increases, it is always credited and paid in capital in excess of par- preferred stock is balancing figure and it also comes under liability when it increases, it is always credited.
c.
Journal entry related to the issue of bonds payable:
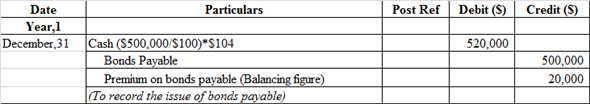 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
Bonds payable and premium on bonds payable are credited because it comes under liability whenever liabilities increases, they are always credited.
Note: The par value of Bonds is $100
d.
Journal entry to record the issue of dividends declare on common stock:
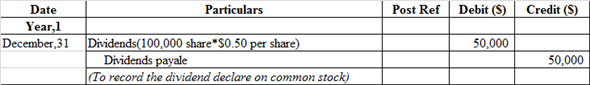 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Journal entry related to the issue of dividends declare on preferred stock:
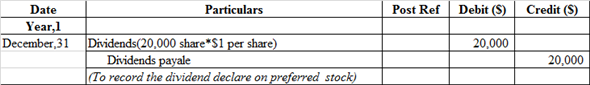 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
e.
Journal entry to record cash dividends paid:
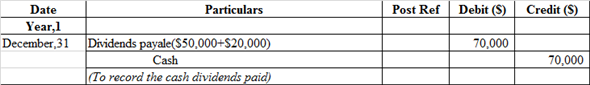 Cash dividends payable is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited.
Cash dividends payable is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited.
Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
f.
Journal entry to record purchased shares of S corporation:
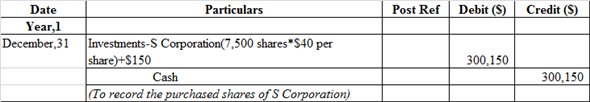 Investment- S Corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Investment- S Corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
g.
Journal entry to record purchased treasury common stock:
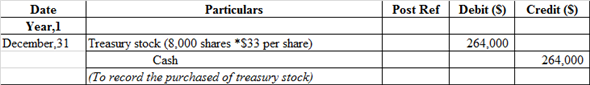 Treasury stock is debited as the company repurchases their share, and this decreases their liability and any decrease in liability is always debited. Cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company.
Treasury stock is debited as the company repurchases their share, and this decreases their liability and any decrease in liability is always debited. Cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company.
h.
Journal entry to record purchased share of P company stock:
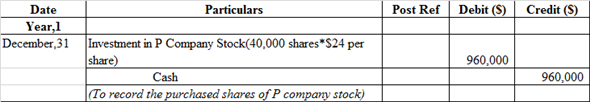 Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
i.
Journal entry to record declared dividends on preferred stock:
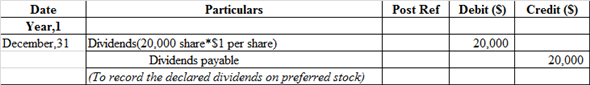 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
j.
Journal entry to record the cash dividends paid:
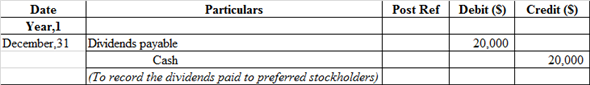 The dividend payable is debited as the payment of dividend has been made by the company. On the other hand, the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule.
The dividend payable is debited as the payment of dividend has been made by the company. On the other hand, the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule.
k.
Journal entry to record the dividends received from P company investment:
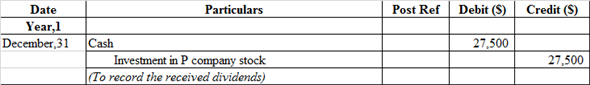 The cash account is debited because cash is received by the company and "what comes in" is always debited and other side Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited.
The cash account is debited because cash is received by the company and "what comes in" is always debited and other side Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited.
l.
Journal entry to record the purchase of bonds with accrued interest:
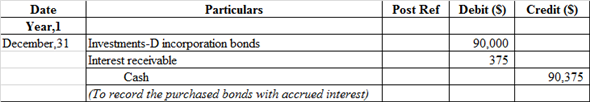 Investment in P corporation account and Interest receivable are debited because it is an asset whenever assets increase they are always debited and the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule of assets.
Investment in P corporation account and Interest receivable are debited because it is an asset whenever assets increase they are always debited and the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule of assets.
m.
Journal entry related to the Sale of treasury stock
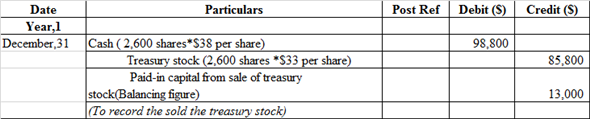 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The common stock is credited as it increases the liability of the company. On the other hand, paid-in capital is credited as the shares are issued at a price higher than the par value.
n.
Journal entry related to the cash dividends received:
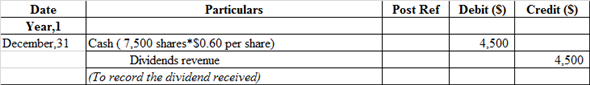 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited whereas dividends revenue account is credited because it is treated as an income whenever it increases it is always credited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited whereas dividends revenue account is credited because it is treated as an income whenever it increases it is always credited.
o.
Journal entry related to the investment sold S company:
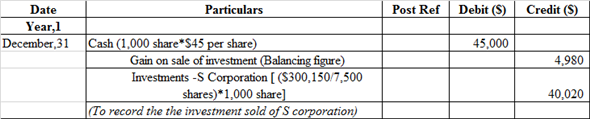 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited and gain on sale of investment account is credited because it is a counter account.
p.
Journal entry related to the payment of semiannually interest:
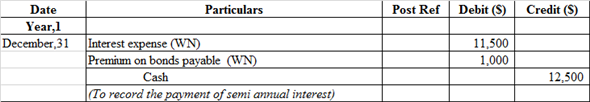 Interest expense account is debited because it comes under expense head whenever expense increases, it is always debited and premium on bonds payable account is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited
Interest expense account is debited because it comes under expense head whenever expense increases, it is always debited and premium on bonds payable account is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited
Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Working Note:
Compute the interest expense, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
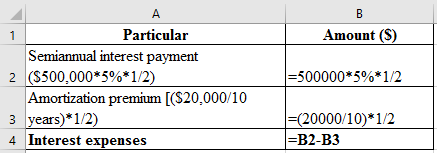 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:
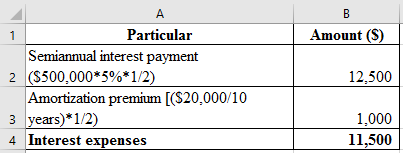 Thus, interest expense is $11,500.
Thus, interest expense is $11,500.
q.
Journal entry to record the accrued interest for three months:
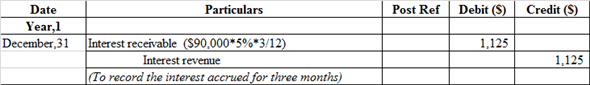 Interest earned by the company refers as income therefore, it is recorded at credit side. But yet it is not received by the company thus, it recognizes the asset as accounts receivable and recorded at debit side.
Interest earned by the company refers as income therefore, it is recorded at credit side. But yet it is not received by the company thus, it recognizes the asset as accounts receivable and recorded at debit side.
r.
Journal entry to record the earnings from P company:
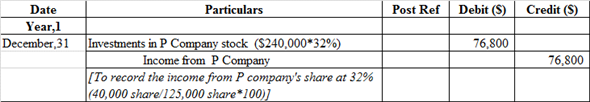 Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited whereas income from P company account is credited because it generates revenue.
Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited whereas income from P company account is credited because it generates revenue.
s.
Journal entry to record the valuation allowance for available for sale:
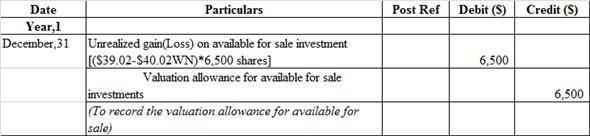 Unrealized loss on available for sale investment account is debited because it treated as expenses whenever it increases it is always debited whereas valuation allowance for available for sale account is credited because it is counter account.
Unrealized loss on available for sale investment account is debited because it treated as expenses whenever it increases it is always debited whereas valuation allowance for available for sale account is credited because it is counter account.
Working Note:
Compute the common stock per share in S company:
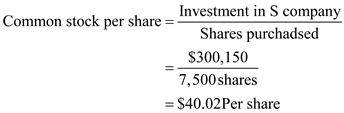 Thus, common stock per share in S company is $40.02.
Thus, common stock per share in S company is $40.02.
2.
a.
Prepare the income statement, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
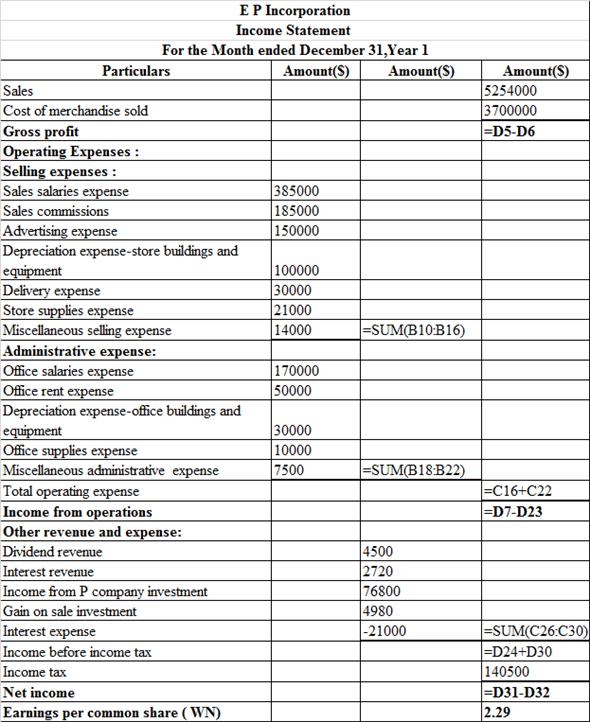 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:
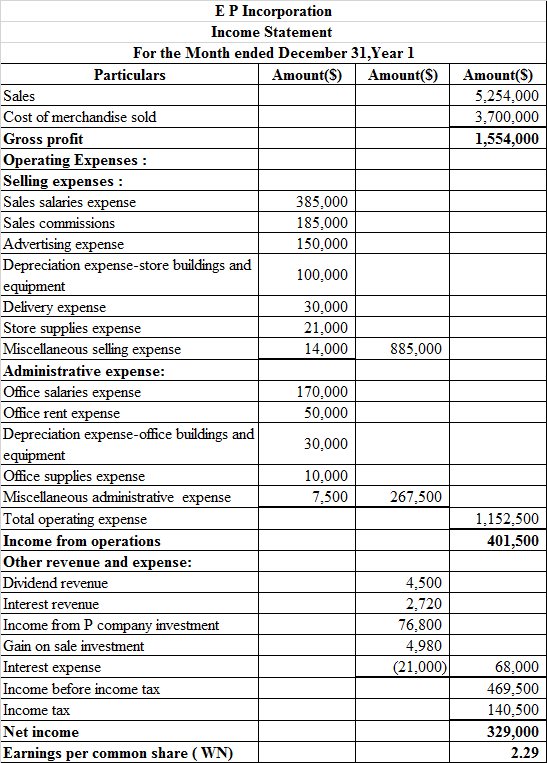 Hence, the aforementioned table shows the statement of income statement.
Hence, the aforementioned table shows the statement of income statement.
Working Note:
Compute the earning per common share, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
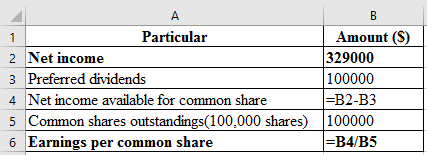 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:
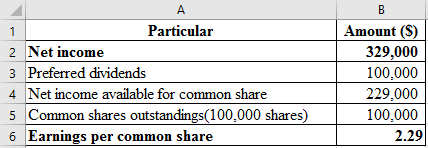 Hence, earning per common share is 2.9
Hence, earning per common share is 2.9
b.
Prepare the retained earnings statement, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
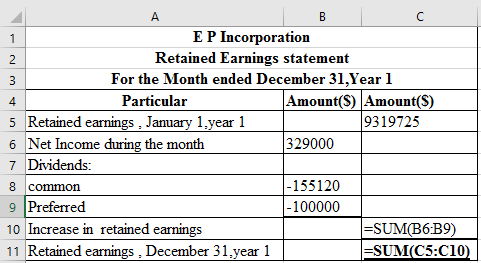 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:
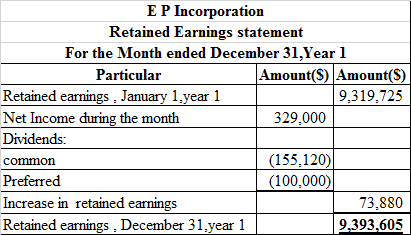 Thus, the aforementioned table shows the statement of retained earnings.
Thus, the aforementioned table shows the statement of retained earnings.
c.
Prepare the statement of balance sheet, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
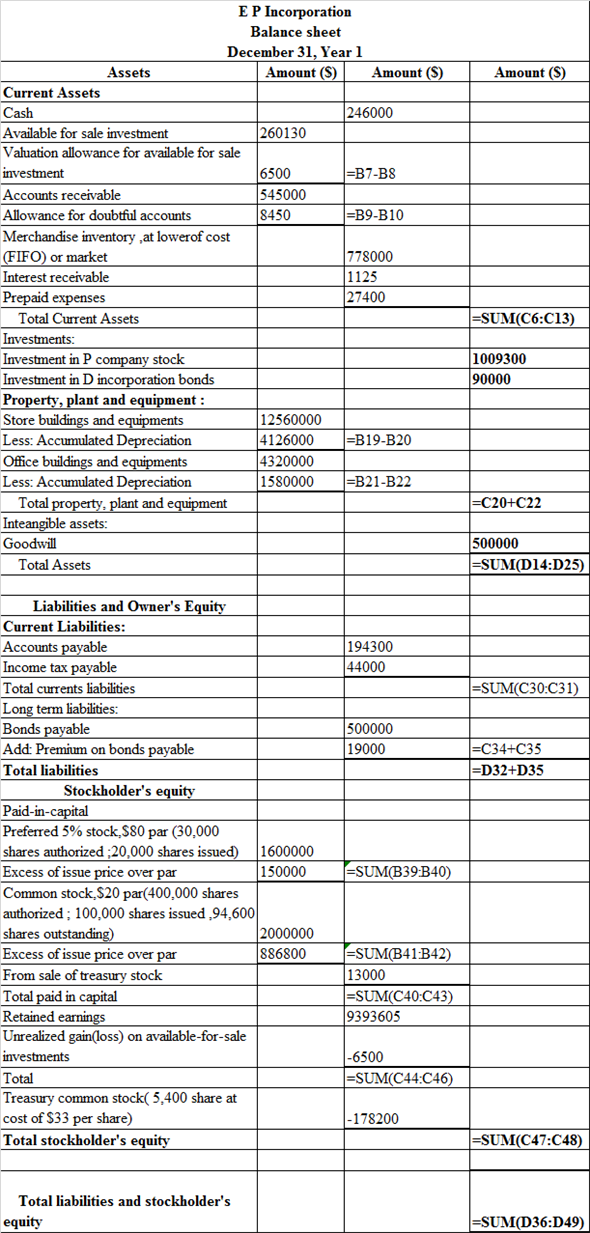 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:
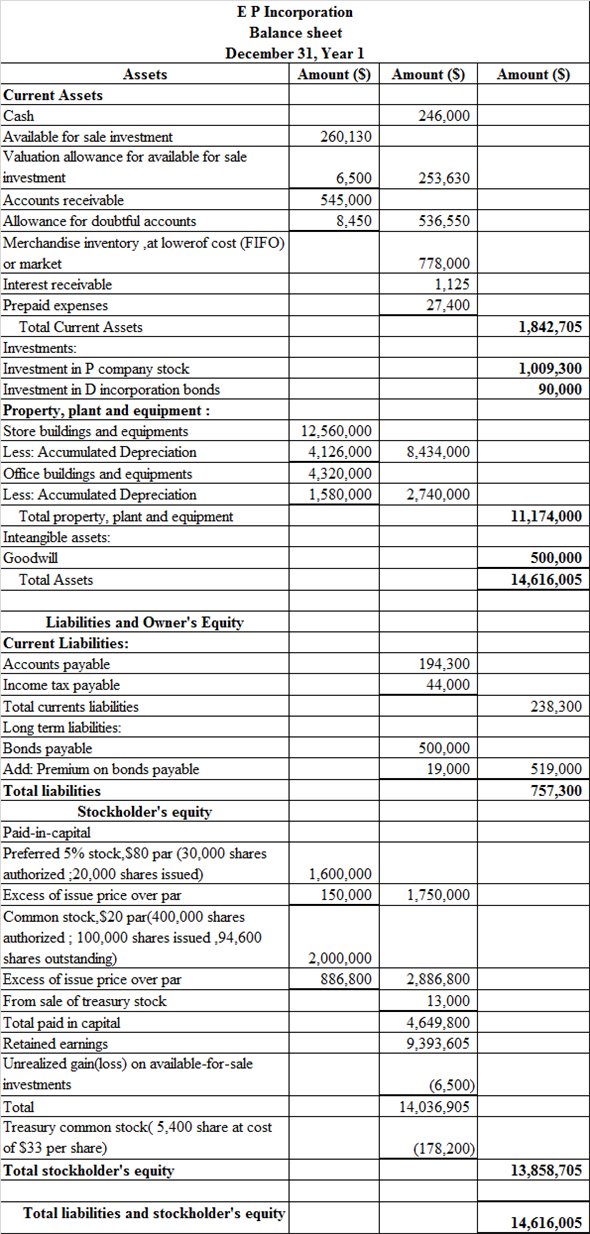 Hence, the aforementioned table shows the balance sheet.
Hence, the aforementioned table shows the balance sheet.
Financial statement refers that recording of financial activities of the business. In other words, it includes Income statement, Balance sheet, Cash flow which shows the true picture of the business of the enterprises.
1.
a.
Pass Journal entries to the selected transaction of E P incorporation:
Journal entry related to the issue of common stock:
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.Common stock is credited because it is increased and it comes under liability and owners' equity whenever it increases, it is always credited and paid in capital in excess of par-common stock is balancing figure and it also comes under liability when it increases, it is always credited.
b.
Journal entry related to the issue of preferred stock:
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.Preferred stock is credited because it is increased and it comes under liability and owners' equity whenever it increases, it is always credited and paid in capital in excess of par- preferred stock is balancing figure and it also comes under liability when it increases, it is always credited.
c.
Journal entry related to the issue of bonds payable:
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.Bonds payable and premium on bonds payable are credited because it comes under liability whenever liabilities increases, they are always credited.
Note: The par value of Bonds is $100
d.
Journal entry to record the issue of dividends declare on common stock:
 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.Journal entry related to the issue of dividends declare on preferred stock:
 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.e.
Journal entry to record cash dividends paid:
 Cash dividends payable is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited.
Cash dividends payable is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited.Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
f.
Journal entry to record purchased shares of S corporation:
 Investment- S Corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Investment- S Corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.g.
Journal entry to record purchased treasury common stock:
 Treasury stock is debited as the company repurchases their share, and this decreases their liability and any decrease in liability is always debited. Cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company.
Treasury stock is debited as the company repurchases their share, and this decreases their liability and any decrease in liability is always debited. Cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company.h.
Journal entry to record purchased share of P company stock:
 Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited, whereas Cash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.i.
Journal entry to record declared dividends on preferred stock:
 Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.
Dividends account is debited because it is treated as an expense. So, whenever it increases it is always debited and in order to recognize liability dividend payable would be recorded at credit side.j.
Journal entry to record the cash dividends paid:
 The dividend payable is debited as the payment of dividend has been made by the company. On the other hand, the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule.
The dividend payable is debited as the payment of dividend has been made by the company. On the other hand, the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule.k.
Journal entry to record the dividends received from P company investment:
 The cash account is debited because cash is received by the company and "what comes in" is always debited and other side Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited.
The cash account is debited because cash is received by the company and "what comes in" is always debited and other side Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited.l.
Journal entry to record the purchase of bonds with accrued interest:
 Investment in P corporation account and Interest receivable are debited because it is an asset whenever assets increase they are always debited and the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule of assets.
Investment in P corporation account and Interest receivable are debited because it is an asset whenever assets increase they are always debited and the cash account is credited because cash is paid by the company and "what goes out" is always credited as per rule of assets.m.
Journal entry related to the Sale of treasury stock
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.The common stock is credited as it increases the liability of the company. On the other hand, paid-in capital is credited as the shares are issued at a price higher than the par value.
n.
Journal entry related to the cash dividends received:
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited whereas dividends revenue account is credited because it is treated as an income whenever it increases it is always credited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited whereas dividends revenue account is credited because it is treated as an income whenever it increases it is always credited.o.
Journal entry related to the investment sold S company:
 The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.
The cash account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases, it always debited.Investment-P company stock account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases it is always credited and gain on sale of investment account is credited because it is a counter account.
p.
Journal entry related to the payment of semiannually interest:
 Interest expense account is debited because it comes under expense head whenever expense increases, it is always debited and premium on bonds payable account is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debited
Interest expense account is debited because it comes under expense head whenever expense increases, it is always debited and premium on bonds payable account is debited because it comes under liability whenever liability decreases, it is always debitedCash account is credited because it is an asset whenever asset decreases, it is always credit.
Working Note:
Compute the interest expense, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula: Thus, interest expense is $11,500.
Thus, interest expense is $11,500. q.
Journal entry to record the accrued interest for three months:
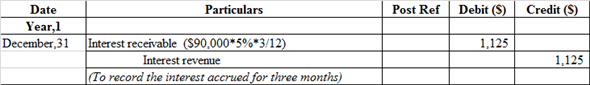 Interest earned by the company refers as income therefore, it is recorded at credit side. But yet it is not received by the company thus, it recognizes the asset as accounts receivable and recorded at debit side.
Interest earned by the company refers as income therefore, it is recorded at credit side. But yet it is not received by the company thus, it recognizes the asset as accounts receivable and recorded at debit side.r.
Journal entry to record the earnings from P company:
 Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited whereas income from P company account is credited because it generates revenue.
Investment in P corporation account is debited because it is an asset whenever asset increases it is always debited whereas income from P company account is credited because it generates revenue.s.
Journal entry to record the valuation allowance for available for sale:
 Unrealized loss on available for sale investment account is debited because it treated as expenses whenever it increases it is always debited whereas valuation allowance for available for sale account is credited because it is counter account.
Unrealized loss on available for sale investment account is debited because it treated as expenses whenever it increases it is always debited whereas valuation allowance for available for sale account is credited because it is counter account.Working Note:
Compute the common stock per share in S company:
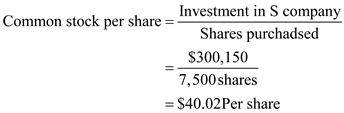 Thus, common stock per share in S company is $40.02.
Thus, common stock per share in S company is $40.02. 2.
a.
Prepare the income statement, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula: Hence, the aforementioned table shows the statement of income statement.
Hence, the aforementioned table shows the statement of income statement.Working Note:
Compute the earning per common share, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:  Hence, earning per common share is 2.9
Hence, earning per common share is 2.9 b.
Prepare the retained earnings statement, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula: Thus, the aforementioned table shows the statement of retained earnings.
Thus, the aforementioned table shows the statement of retained earnings.c.
Prepare the statement of balance sheet, which is presented in spreadsheet formula:
 Following is the result of the formula:
Following is the result of the formula:  Hence, the aforementioned table shows the balance sheet.
Hence, the aforementioned table shows the balance sheet. 3
Entries for stock investments, dividends, and sale of stock
Yerbury Corp. manufactures construction equipment. Journalize the entries to record the following selected equity investment transactions completed by Yerbury during a recent year:
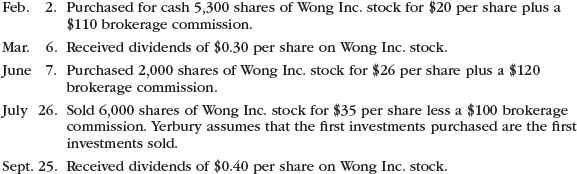
Yerbury Corp. manufactures construction equipment. Journalize the entries to record the following selected equity investment transactions completed by Yerbury during a recent year:

Entries for Investment in stock, receipt of dividends, and sale of stock:
Entry for purchase of stock:
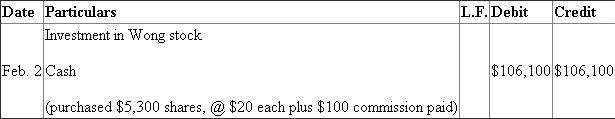 Shares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited, cash is going out, and hence it is to be credited.
Shares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited, cash is going out, and hence it is to be credited.
Entry for dividend revenue:
 Dividend is an income, hence, it is to be credited, and cash is coming into the business, hence it is to be debited.
Dividend is an income, hence, it is to be credited, and cash is coming into the business, hence it is to be debited.
Entry for purchase of stock:
 hares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited and cash is to be credited.
hares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited and cash is to be credited.
Entry for sale of shares:
 Working note:
Working note:
Company sold 6,000 shares
It includes 5,300 from shares purchased on Feb.2 and 700 share purchased on June 7
Total cost of 5,300 shares=$106,100
Cost of 700 shares=$52,120×
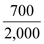 =$18,242
=$18,242
Total cost=$106,100+$18,242=$124,342
Calculation of sale proceeds:
Sale proceeds of 6,000 shares=6,000×$35=$210,000 $100 (commission)
Net Sale proceeds=$209,900
Gain on sale of shares=$209,900 $124,342=$85,558
Entry for dividend revenue:

Entry for purchase of stock:
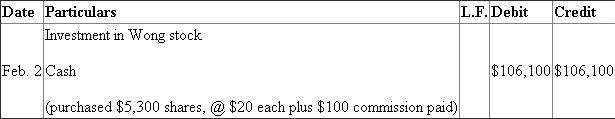 Shares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited, cash is going out, and hence it is to be credited.
Shares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited, cash is going out, and hence it is to be credited.Entry for dividend revenue:
 Dividend is an income, hence, it is to be credited, and cash is coming into the business, hence it is to be debited.
Dividend is an income, hence, it is to be credited, and cash is coming into the business, hence it is to be debited.Entry for purchase of stock:
 hares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited and cash is to be credited.
hares are coming into the business, hence, they are to be debited and cash is to be credited.Entry for sale of shares:
 Working note:
Working note:Company sold 6,000 shares
It includes 5,300 from shares purchased on Feb.2 and 700 share purchased on June 7
Total cost of 5,300 shares=$106,100
Cost of 700 shares=$52,120×
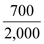 =$18,242
=$18,242Total cost=$106,100+$18,242=$124,342
Calculation of sale proceeds:
Sale proceeds of 6,000 shares=6,000×$35=$210,000 $100 (commission)
Net Sale proceeds=$209,900
Gain on sale of shares=$209,900 $124,342=$85,558
Entry for dividend revenue:

4
Fair value journal entries, available-for-sale investments
Storm, Inc. purchased the following available-for-sale securities during Year 1, its first year of operations:
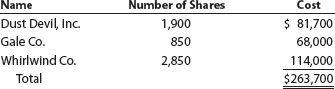
The market price per share for the available-for-sale security portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:
a. Provide the journal entry to adjust the available-for-sale security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. Describe the income statement impact from the December 31, Year 1, journal entry.
Storm, Inc. purchased the following available-for-sale securities during Year 1, its first year of operations:

The market price per share for the available-for-sale security portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:
a. Provide the journal entry to adjust the available-for-sale security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. Describe the income statement impact from the December 31, Year 1, journal entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is a "biological asset"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Debt investment transactions, available-for-sale valuation
Gaelic Industries Inc. is an athletic footware company that began operations on January 1 2016. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Gaelic Industries Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure
Gaelic Industries Inc. is an athletic footware company that began operations on January 1 2016. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Gaelic Industries Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How does the accounting for a dividend received differ between the cost method and the equity method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What are the factors contributing to the trend toward fair value accounting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Balance sheet presentation of available-for-sale investments
During Year 1, its first year of operations, Galileo Company purchased two available-forsale investments as follows:
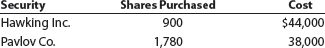
Assume that as of December 31, Year 1, the Hawking Inc. stock had a market value of $50 per share and the Pavlov Co. stock had a market value of $24 per share. Galileo Company had net income of $300,000 and paid no dividends for the year ended December 31, Year 1. All of the available-for-sale investments are classified as current assets.
a. Prepare the Current Assets section of the balance sheet presentation for the availablefor- sale investments.
b. Prepare the Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet to reflect the earnings and unrealized gain (loss) for the available-for-sale investments.
During Year 1, its first year of operations, Galileo Company purchased two available-forsale investments as follows:
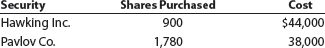
Assume that as of December 31, Year 1, the Hawking Inc. stock had a market value of $50 per share and the Pavlov Co. stock had a market value of $24 per share. Galileo Company had net income of $300,000 and paid no dividends for the year ended December 31, Year 1. All of the available-for-sale investments are classified as current assets.
a. Prepare the Current Assets section of the balance sheet presentation for the availablefor- sale investments.
b. Prepare the Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet to reflect the earnings and unrealized gain (loss) for the available-for-sale investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the most significant IFRS departure from U.S. GAAP for valuing property, plant, and equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Debt investment transactions, available-for-sale valuation
Rekya Mart Inc. is a general merchandise retail company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Rekya Mart Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure
Rekya Mart Inc. is a general merchandise retail company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to debt investments acquired by Rekya Mart Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. If the bond portfolio is classified as available for sale, what impact would this have on financial statement disclosure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Entries for investment in bonds, interest, and sale of bonds
The following bond investment transactions were completed during 2016 by Starks Company:

a. Journalize the entries for these transactions.
b. Provide the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry for semiannual interest earned on the bonds.
The following bond investment transactions were completed during 2016 by Starks Company:

a. Journalize the entries for these transactions.
b. Provide the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry for semiannual interest earned on the bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Entries for stock investments, dividends, and sale of stock
Seamus Industries Inc. buys and sells investments as part of its ongoing cash management. The following investment transactions were completed during the year:

Journalize the entries for these transactions.
Seamus Industries Inc. buys and sells investments as part of its ongoing cash management. The following investment transactions were completed during the year:

Journalize the entries for these transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Balance sheet presentation of available-for-sale investments
During Year 2, Copernicus Corporation held a portfolio of available-for-sale securities having a cost of $185,000. There were no purchases or sales of investments during the year. The market values at the beginning and end of the year were $225,000 and $160,000, respectively. The net income for Year 2 was $180,000, and no dividends were paid during the year. The Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet was as follows on December 31, Year 1:

Prepare the Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet for December 31, Year 2.
During Year 2, Copernicus Corporation held a portfolio of available-for-sale securities having a cost of $185,000. There were no purchases or sales of investments during the year. The market values at the beginning and end of the year were $225,000 and $160,000, respectively. The net income for Year 2 was $180,000, and no dividends were paid during the year. The Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet was as follows on December 31, Year 1:

Prepare the Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet for December 31, Year 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is a "share premium"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
International fair value accounting
International Financial Reporting Standard No. 16 provides companies the option of valuing property, plant, and equipment at either historical cost or fair value. If fair value is selected, then the property, plant, and equipment must be revalued periodically to fair value. Under fair value, if there is an increase in the value of the property, plant, and equipment during the reporting period, then the increase is credited to stockholders' equity. However, if there is a decrease in fair value, then the decrease is reported as an expense for the period.
How is the international accounting treatment for changes in fair value for property, plant, and equipment similar to investments
International Financial Reporting Standard No. 16 provides companies the option of valuing property, plant, and equipment at either historical cost or fair value. If fair value is selected, then the property, plant, and equipment must be revalued periodically to fair value. Under fair value, if there is an increase in the value of the property, plant, and equipment during the reporting period, then the increase is credited to stockholders' equity. However, if there is a decrease in fair value, then the decrease is reported as an expense for the period.
How is the international accounting treatment for changes in fair value for property, plant, and equipment similar to investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A Valuing trading securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the trading securities portfolio was $385,000, and the fair value was $357,400. Prepare the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on trading investments.
B Valuing trading securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the trading securities portfolio was $41,500, and the fair value was $46,300. Prepare the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on trading investments.
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the trading securities portfolio was $385,000, and the fair value was $357,400. Prepare the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on trading investments.
B Valuing trading securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Trading Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the trading securities portfolio was $41,500, and the fair value was $46,300. Prepare the December 31, 2016, adjusting journal entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on trading investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How are the balance sheet and income statement affected by fair value accounting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Dividend yield
At the market close on March 28 of a recent year, McDonald's Corporation had a closing stock price of $99.69. In addition, McDonald's Corporation had a dividend per share of $2.87 during the previous year.
Determine McDonald's Corporation's dividend yield. (Round to one decimal place.)
At the market close on March 28 of a recent year, McDonald's Corporation had a closing stock price of $99.69. In addition, McDonald's Corporation had a dividend per share of $2.87 during the previous year.
Determine McDonald's Corporation's dividend yield. (Round to one decimal place.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How is the term reserve used under IFRS, and how does it differ from its meaning under U.S. GAAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What causes a gain or loss on the sale of a bond investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Investment reporting
O'Brien Industries Inc. is a book publisher. The comparative unclassified balance sheets for December 31, Year 2 and Year 1 follow. Selected missing balances are shown by letters.
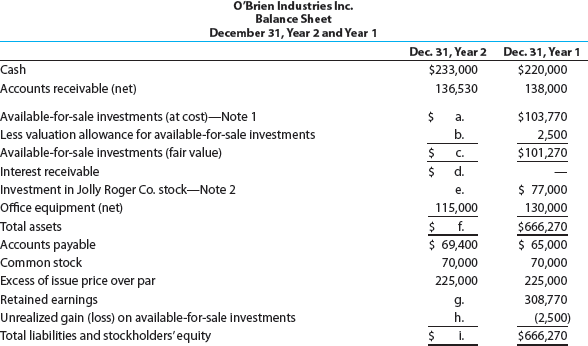
Note 1. Investments are classified as available for sale. The investments at cost and fair value on December 31, Year 1, are as follows:
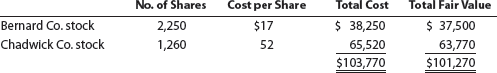
Note 2. The investment in Jolly Roger Co. stock is an equity method investment representing 30% of the outstanding shares of Jolly Roger Co.
The following selected investment transactions occurred during Year 2:
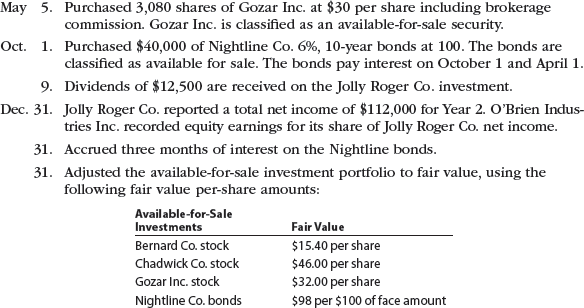
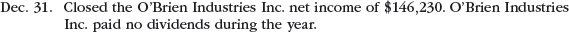
Instructions
Determine the missing letters in the unclassified balance sheet. Provide appropriate supporting calculations.
O'Brien Industries Inc. is a book publisher. The comparative unclassified balance sheets for December 31, Year 2 and Year 1 follow. Selected missing balances are shown by letters.

Note 1. Investments are classified as available for sale. The investments at cost and fair value on December 31, Year 1, are as follows:
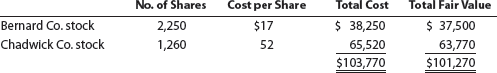
Note 2. The investment in Jolly Roger Co. stock is an equity method investment representing 30% of the outstanding shares of Jolly Roger Co.
The following selected investment transactions occurred during Year 2:

Instructions
Determine the missing letters in the unclassified balance sheet. Provide appropriate supporting calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Equity method for stock investment
At a total cost of $6,300,000, Veravo Corporation acquired 210,000 shares of Strado Corp. common stock as a long-term investment. Veravo Corporation uses the equity method of accounting for this investment. Strado Corp. has 700,000 shares of common stock outstanding, including the shares acquired by Veravo Corporation.
a. Journalize the entries by Veravo Corporation to record the following information:
1. Strado Corp. reports net income of $860,000 for the current period.
2. A cash dividend of $0.32 per common share is paid by Strado Corp. during the current period.
b. Why is the equity method appropriate for the Strado Corp. investment
At a total cost of $6,300,000, Veravo Corporation acquired 210,000 shares of Strado Corp. common stock as a long-term investment. Veravo Corporation uses the equity method of accounting for this investment. Strado Corp. has 700,000 shares of common stock outstanding, including the shares acquired by Veravo Corporation.
a. Journalize the entries by Veravo Corporation to record the following information:
1. Strado Corp. reports net income of $860,000 for the current period.
2. A cash dividend of $0.32 per common share is paid by Strado Corp. during the current period.
b. Why is the equity method appropriate for the Strado Corp. investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Dividend yield
The market price for Microsoft Corporation closed at $26.71 and $25.96 on December 31, current year, and previous year, respectively. The dividends per share were $0.80 for current year and $0.64 for previous year.
a. Determine the dividend yield for Microsoft on December 31, current year, and previous year. (Round percentages to two decimal places.)
b. Interpret these measures.
The market price for Microsoft Corporation closed at $26.71 and $25.96 on December 31, current year, and previous year, respectively. The dividends per share were $0.80 for current year and $0.64 for previous year.
a. Determine the dividend yield for Microsoft on December 31, current year, and previous year. (Round percentages to two decimal places.)
b. Interpret these measures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How is treasury stock reported under IFRS How does this differ from its treatment under U.S. GAAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Entries for investments in bonds, interest, and sale of bonds
Kalyagin Investments acquired $220,000 of Jerris Corp., 7% bonds at their face amount on October 1, 2016. The bonds pay interest on October 1 and April 1. On April 1, 2017, Kalyagin sold $80,000 of Jerris Corp. bonds at 103.
Journalize the entries to record the following:
a. The initial acquisition of the Jerris Corp. bonds on October 1, 2016.
b. The adjusting entry for three months of accrued interest earned on the Jerris Corp. bonds on December 31, 2016.
c. The receipt of semiannual interest on April 1, 2017.
d. The sale of $80,000 of Jerris Corp. bonds on April 1, 2017, at 103.
Kalyagin Investments acquired $220,000 of Jerris Corp., 7% bonds at their face amount on October 1, 2016. The bonds pay interest on October 1 and April 1. On April 1, 2017, Kalyagin sold $80,000 of Jerris Corp. bonds at 103.
Journalize the entries to record the following:
a. The initial acquisition of the Jerris Corp. bonds on October 1, 2016.
b. The adjusting entry for three months of accrued interest earned on the Jerris Corp. bonds on December 31, 2016.
c. The receipt of semiannual interest on April 1, 2017.
d. The sale of $80,000 of Jerris Corp. bonds on April 1, 2017, at 103.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Investment reporting
Teasdale Inc. manufactures and sells commercial and residential security equipment. The comparative unclassified balance sheets for December 31, Year 2 and Year 1 are provided below. Selected missing balances are shown by letters.
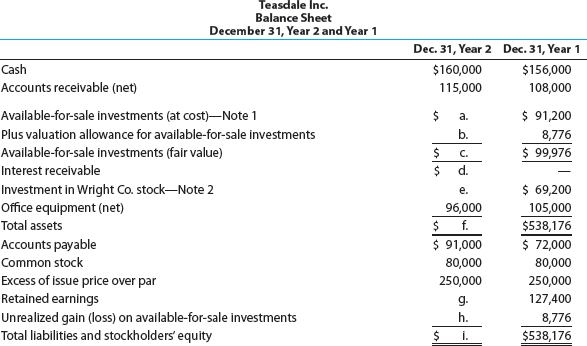
Note 1. Investments are classified as available for sale. The investments at cost and fair value on December 31, Year 1, are as follows:
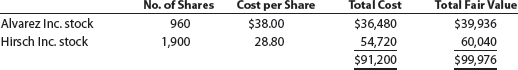
Note 2. The Investment in Wright Co. stock is an equity method investment representing 30% of the outstanding shares of Wright Co.
The following selected investment transactions occurred during Year 2:
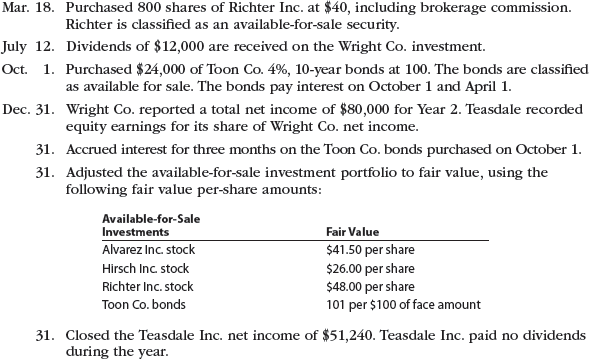
Instructions
Determine the missing letters in the unclassified balance sheet. Provide appropriate supporting calculations.
Teasdale Inc. manufactures and sells commercial and residential security equipment. The comparative unclassified balance sheets for December 31, Year 2 and Year 1 are provided below. Selected missing balances are shown by letters.

Note 1. Investments are classified as available for sale. The investments at cost and fair value on December 31, Year 1, are as follows:
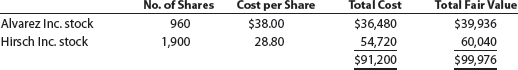
Note 2. The Investment in Wright Co. stock is an equity method investment representing 30% of the outstanding shares of Wright Co.
The following selected investment transactions occurred during Year 2:

Instructions
Determine the missing letters in the unclassified balance sheet. Provide appropriate supporting calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Equity method for stock investment
On January 4, 2016, Spandella Company purchased 175,000 shares of Filington Company directly from one of the founders for a price of $30 per share. Filington has 500,000 shares outstanding, including the Penman shares. On July 2, 2016, Filington paid $620,000 in total dividends to its shareholders. On December 31, 2016, Filington reported a net income of $1,050,000 for the year. Spandella uses the equity method in accounting for its investment in Filington.
a. Provide the Spandella Inc. journal entries for the transactions involving its investment in Filington Inc. during 2016.
b. Determine the December 31, 2016, balance of the Investment in Filington Company. Stock account.
On January 4, 2016, Spandella Company purchased 175,000 shares of Filington Company directly from one of the founders for a price of $30 per share. Filington has 500,000 shares outstanding, including the Penman shares. On July 2, 2016, Filington paid $620,000 in total dividends to its shareholders. On December 31, 2016, Filington reported a net income of $1,050,000 for the year. Spandella uses the equity method in accounting for its investment in Filington.
a. Provide the Spandella Inc. journal entries for the transactions involving its investment in Filington Inc. during 2016.
b. Determine the December 31, 2016, balance of the Investment in Filington Company. Stock account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Dividend yield
eBay Inc. developed a web-based marketplace at www.ebay.com, in which individuals can buy and sell a variety of items. eBay also acquired PayPal, an online payments system that allows businesses and individuals to send and receive online payments securely. In a recent annual report, eBay published the following dividend policy:
We have never paid cash dividends on our stock and currently anticipate that we will continue to retain any future earnings for the foreseeable future.
Given eBay's dividend policy, why would investors be attracted to its stock
eBay Inc. developed a web-based marketplace at www.ebay.com, in which individuals can buy and sell a variety of items. eBay also acquired PayPal, an online payments system that allows businesses and individuals to send and receive online payments securely. In a recent annual report, eBay published the following dividend policy:
We have never paid cash dividends on our stock and currently anticipate that we will continue to retain any future earnings for the foreseeable future.
Given eBay's dividend policy, why would investors be attracted to its stock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A Stock investment transactions
On February 10, 15,000 shares of Sting Company are acquired at a price of $25 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. On April 12, a $0.40-per-share dividend was received on the Sting Company stock. On May 29, 6,000 shares of the Sting Company stock were sold for $32 per share less a $120 brokerage commission. Prepare the journal entries for the original purchase, the dividend, and the sale under the cost method.
B Stock investment transactions
On September 12, 2,000 shares of Aspen Company are acquired at a price of $50 per share plus a $200 brokerage commission. On October 15, a $0.50-per-share dividend was received on the Aspen Company stock. On November 10, 1,200 shares of the Aspen Company stock were sold for $42 per share less a $150 brokerage commission. Prepare the journal entries for the original purchase, the dividend, and the sale under the cost method.
On February 10, 15,000 shares of Sting Company are acquired at a price of $25 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission. On April 12, a $0.40-per-share dividend was received on the Sting Company stock. On May 29, 6,000 shares of the Sting Company stock were sold for $32 per share less a $120 brokerage commission. Prepare the journal entries for the original purchase, the dividend, and the sale under the cost method.
B Stock investment transactions
On September 12, 2,000 shares of Aspen Company are acquired at a price of $50 per share plus a $200 brokerage commission. On October 15, a $0.50-per-share dividend was received on the Aspen Company stock. On November 10, 1,200 shares of the Aspen Company stock were sold for $42 per share less a $150 brokerage commission. Prepare the journal entries for the original purchase, the dividend, and the sale under the cost method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Reporting investments
Group Project
In groups of three or four, find the latest annual report for Microsoft Corporation. The annual report can be found on the company's website at www.microsoft.com/msft/default.mspx.
The notes to the financial statements include details of Microsoft's investments. Find the notes that provide details of its investments (Note 4) and the income from its investments (Note 3).
From these disclosures, answer the following questions:
1. What is the total cost of investments
2. What is the fair value (recorded value) of investments
3. What is the total unrealized gain from investments
4. What is the total unrealized loss from investments
5. What percent of total investments (at fair value) are:
a. Cash and equivalents
b. Short-term investments
c. Equity and other investments (long term)
6. What was the total combined dividend and interest revenue
7. What was the recognized net gain or loss from sale of investments
Group Project
In groups of three or four, find the latest annual report for Microsoft Corporation. The annual report can be found on the company's website at www.microsoft.com/msft/default.mspx.
The notes to the financial statements include details of Microsoft's investments. Find the notes that provide details of its investments (Note 4) and the income from its investments (Note 3).
From these disclosures, answer the following questions:
1. What is the total cost of investments
2. What is the fair value (recorded value) of investments
3. What is the total unrealized gain from investments
4. What is the total unrealized loss from investments
5. What percent of total investments (at fair value) are:
a. Cash and equivalents
b. Short-term investments
c. Equity and other investments (long term)
6. What was the total combined dividend and interest revenue
7. What was the recognized net gain or loss from sale of investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Equity method for stock investment with loss
On January 6, Year 1, Bulldog Co. purchased 34% of the outstanding stock of Gator Co. for $212,000. Gator Co. paid total dividends of $24,000 to all shareholders on June 30. Gator had a net loss of $56,000 for Year 1.
a. Journalize Bulldog's purchase of the stock, receipt of the dividends, and the adjusting entry for the equity loss in Gator Co. stock.
b. Compute the balance of Investment in Gator Co. Stock on December 31, Year 1.
c. How does valuing an investment under the equity method differ from valuing an investment at fair value
On January 6, Year 1, Bulldog Co. purchased 34% of the outstanding stock of Gator Co. for $212,000. Gator Co. paid total dividends of $24,000 to all shareholders on June 30. Gator had a net loss of $56,000 for Year 1.
a. Journalize Bulldog's purchase of the stock, receipt of the dividends, and the adjusting entry for the equity loss in Gator Co. stock.
b. Compute the balance of Investment in Gator Co. Stock on December 31, Year 1.
c. How does valuing an investment under the equity method differ from valuing an investment at fair value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Comprehensive income
On May 12, Year 1, Chewco Co. purchased 2,000 shares of Jedi Inc. for $112 per share, including the brokerage commission. The Jedi investment was classified as an available-for-sale security. On December 31, Year 1, the fair value of Jedi Inc. was $124 per share. The net income of Chewco Co. was $50,000 for Year 1.
Compute the comprehensive income for Chewco Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 1.
On May 12, Year 1, Chewco Co. purchased 2,000 shares of Jedi Inc. for $112 per share, including the brokerage commission. The Jedi investment was classified as an available-for-sale security. On December 31, Year 1, the fair value of Jedi Inc. was $124 per share. The net income of Chewco Co. was $50,000 for Year 1.
Compute the comprehensive income for Chewco Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Stock investment transactions, trading securities
Scofield Financial Co. is a regional insurance company that began operations on January 1, 2016. The following transactions relate to trading securities acquired by Scofield Financial Co., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related current asset balance sheet presentation for Scofield Financial Co. on December 31, 2017.
3. How are unrealized gains or losses on trading investments presented in the financial statements of Scofield Financial Co.
Scofield Financial Co. is a regional insurance company that began operations on January 1, 2016. The following transactions relate to trading securities acquired by Scofield Financial Co., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related current asset balance sheet presentation for Scofield Financial Co. on December 31, 2017.
3. How are unrealized gains or losses on trading investments presented in the financial statements of Scofield Financial Co.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If an investor owns more than 50% of an investee, how is the investment treated on the investor's financial statements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Equity method for stock investment
Hawkeye Company's balance sheet reported, under the equity method, its long-term investment in Raven Company for comparative years as follows:
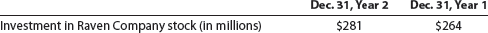
In addition, the Year 2 Hawkeye Company income statement disclosed equity earnings in the Raven Company investment as $25 million. Hawkeye Company neither purchased nor sold Raven Company stock during Year 2. The fair value of the Raven Company stock investment on December 31, Year 2, was $310 million.
Explain the change in Investment in Raven Company Stock from December 31, Year 1, to December 31, Year 2.
Hawkeye Company's balance sheet reported, under the equity method, its long-term investment in Raven Company for comparative years as follows:
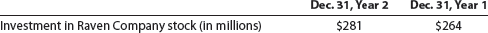
In addition, the Year 2 Hawkeye Company income statement disclosed equity earnings in the Raven Company investment as $25 million. Hawkeye Company neither purchased nor sold Raven Company stock during Year 2. The fair value of the Raven Company stock investment on December 31, Year 2, was $310 million.
Explain the change in Investment in Raven Company Stock from December 31, Year 1, to December 31, Year 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Comprehensive income
On December 31, Year 1, Valur Co. had the following available-for-sale investment disclosure within the Current Assets section of the balance sheet:

There were no purchases or sales of available-for-sale investments during Year 2. On December 31, Year 2, the fair value of the available-for-sale investment portfolio was $200,000. The net income of Valur Co. was $210,000 for Year 2.
Compute the comprehensive income for Valur Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 2.
On December 31, Year 1, Valur Co. had the following available-for-sale investment disclosure within the Current Assets section of the balance sheet:

There were no purchases or sales of available-for-sale investments during Year 2. On December 31, Year 2, the fair value of the available-for-sale investment portfolio was $200,000. The net income of Valur Co. was $210,000 for Year 2.
Compute the comprehensive income for Valur Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Stock investment transactions, trading securities
Zeus Investments Inc. is a regional investment company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to trading securities acquired by Zeus Investments Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:


Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related current asset balance sheet presentation for Zeus Investments Inc. on December 31, Year 2.
3. How are unrealized gains or losses on trading investments presented in the financial statements of Zeus Investments Inc.
Zeus Investments Inc. is a regional investment company that began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to trading securities acquired by Zeus Investments Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:


Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related current asset balance sheet presentation for Zeus Investments Inc. on December 31, Year 2.
3. How are unrealized gains or losses on trading investments presented in the financial statements of Zeus Investments Inc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Interest on bond investments
On April 1, 2016, Rizzo Company purchased $80,000 of 4.5%, 20-year Energizer Company bonds at their face amount plus one month's accrued interest. The bonds pay interest on March 1 and September 1. On November 1, 2016, Rizzo Company sold $30,000 of the Energizer Company bonds acquired on April 1, plus two months' accrued interest. On December 31, 2016, four months' interest was accrued for the remaining bonds.
Determine the interest earned by Rizzo Company on Energizer Company bonds for 2016.
On April 1, 2016, Rizzo Company purchased $80,000 of 4.5%, 20-year Energizer Company bonds at their face amount plus one month's accrued interest. The bonds pay interest on March 1 and September 1. On November 1, 2016, Rizzo Company sold $30,000 of the Energizer Company bonds acquired on April 1, plus two months' accrued interest. On December 31, 2016, four months' interest was accrued for the remaining bonds.
Determine the interest earned by Rizzo Company on Energizer Company bonds for 2016.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Missing statement items, trading investments
JED Capital Inc. makes investments in trading securities. Selected income statement items for the years ended December 31, Year 2 and Year 3, plus selected items from comparative balance sheets, are as follows:

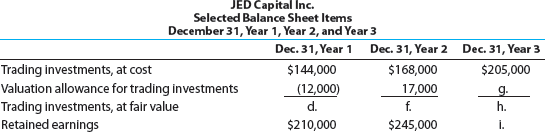
There were no dividends.
Determine the missing lettered items.
JED Capital Inc. makes investments in trading securities. Selected income statement items for the years ended December 31, Year 2 and Year 3, plus selected items from comparative balance sheets, are as follows:


There were no dividends.
Determine the missing lettered items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Contrast U.S. GAAP financial statement terms with their different IFRS terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Ethics in Action
Financial assets include stocks and bonds. These are fairly simple securities that can often be valued using quoted market prices. However, there are more complex financial instruments that do not have quoted market prices. These complex securities must still be valued on the balance sheet at fair value. Generally accepted accounting principles require that the reporting entity use assumptions in valuing investments when market prices or critical valuation inputs are unobservable.
What are the ethical considerations in making subjective valuations of these complex financial instruments
Financial assets include stocks and bonds. These are fairly simple securities that can often be valued using quoted market prices. However, there are more complex financial instruments that do not have quoted market prices. These complex securities must still be valued on the balance sheet at fair value. Generally accepted accounting principles require that the reporting entity use assumptions in valuing investments when market prices or critical valuation inputs are unobservable.
What are the ethical considerations in making subjective valuations of these complex financial instruments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A Valuing available-for-sale securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the available-for-sale securities was $78,400, and the fair value was $72,600. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on available-for-sale investments on December 31, 2016.
B Valuing available-for-sale securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the available-for-sale securities was $24,260, and the fair value was $26,350. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on available-for-sale investments on December 31, 2016.
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the available-for-sale securities was $78,400, and the fair value was $72,600. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on available-for-sale investments on December 31, 2016.
B Valuing available-for-sale securities at fair value
On January 1, 2016, Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments had a zero balance. On December 31, 2016, the cost of the available-for-sale securities was $24,260, and the fair value was $26,350. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the unrealized gain or loss on available-for-sale investments on December 31, 2016.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Fair value journal entries, trading investments
The investments of Charger Inc. include a single investment: 14,500 shares of Raiders Inc. common stock purchased on February 24, Year 1, for $38 per share including brokerage commission. These shares were classified as trading securities. As of the December 31, Year 1, balance sheet date, the share price had increased to $42 per share.
a. Journalize the entries to acquire the investment on February 24 and record the adjustment to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. How is the unrealized gain or loss for trading investments reported on the financial statements
The investments of Charger Inc. include a single investment: 14,500 shares of Raiders Inc. common stock purchased on February 24, Year 1, for $38 per share including brokerage commission. These shares were classified as trading securities. As of the December 31, Year 1, balance sheet date, the share price had increased to $42 per share.
a. Journalize the entries to acquire the investment on February 24 and record the adjustment to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. How is the unrealized gain or loss for trading investments reported on the financial statements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Unilever Group is a global company that markets a wide variety of products, including Lever ® soap, Breyer's ® ice cream, and Hellman's ® mayonnaise. A recent income statement and statement of comprehensive income for the Dutch company, Unilever Group, follow:
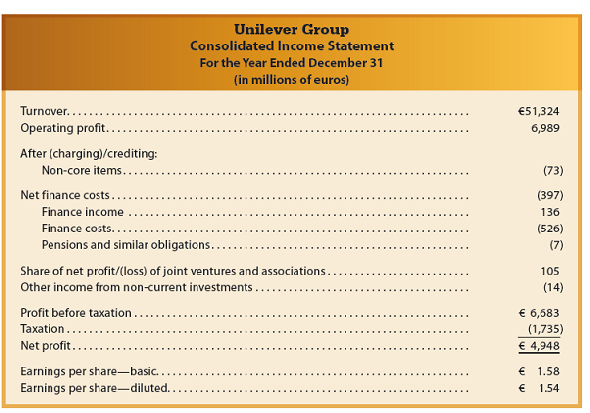

a. What do you think is meant by "turnover"
b. How does Unilever's income statement presentation differ significantly from that of Mornin' Joe
c. How is the total for net finance costs presented differently from what typically would be found under U.S. GAAP


a. What do you think is meant by "turnover"
b. How does Unilever's income statement presentation differ significantly from that of Mornin' Joe
c. How is the total for net finance costs presented differently from what typically would be found under U.S. GAAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When is the equity method the appropriate accounting for equity investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the major difference in the accounting for a portfolio of trading securities and a portfolio of available-for-sale securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Fair value journal entries, trading investments
Jets Bancorp Inc. purchased a portfolio of trading securities during 2016. The cost and fair value of this portfolio on December 31, 2016, was as follows:
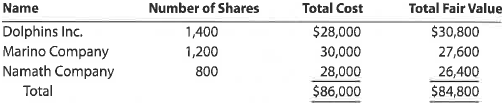
On May 10, 2017, Jets Bancorp Inc. purchased 1,000 shares of Giants Inc. at $24 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission.
Provide the journal entries to record the following:
a. The adjustment of the trading security portfolio to fair value on December 31, 2016.
b. The May 10, 2017, purchase of Giants Inc. stock.
Jets Bancorp Inc. purchased a portfolio of trading securities during 2016. The cost and fair value of this portfolio on December 31, 2016, was as follows:

On May 10, 2017, Jets Bancorp Inc. purchased 1,000 shares of Giants Inc. at $24 per share plus a $150 brokerage commission.
Provide the journal entries to record the following:
a. The adjustment of the trading security portfolio to fair value on December 31, 2016.
b. The May 10, 2017, purchase of Giants Inc. stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the difference between classifying an expense by nature or function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Entries for investment in bonds, interest, and sale of bonds
Bocelli Co. purchased $120,000 of 6%, 20-year Sanz County bonds on May 11, Year 1, directly from the county, at their face amount plus accrued interest. The bonds pay semiannual interest on April 1 and October 1. On October 31, Year 1, Bocelli Co. sold $30,000 of the Sanz County bonds at 99 plus $150 accrued interest less a $100 brokerage commission.
Provide journal entries for the following:
a. The purchase of the bonds on May 11 plus 40 days of accrued interest.
b. Semiannual interest on October 1.
c. Sale of the bonds on October 31.
d. Adjusting entry for accrued interest of $1,365 on December 31, Year 1.
Bocelli Co. purchased $120,000 of 6%, 20-year Sanz County bonds on May 11, Year 1, directly from the county, at their face amount plus accrued interest. The bonds pay semiannual interest on April 1 and October 1. On October 31, Year 1, Bocelli Co. sold $30,000 of the Sanz County bonds at 99 plus $150 accrued interest less a $100 brokerage commission.
Provide journal entries for the following:
a. The purchase of the bonds on May 11 plus 40 days of accrued interest.
b. Semiannual interest on October 1.
c. Sale of the bonds on October 31.
d. Adjusting entry for accrued interest of $1,365 on December 31, Year 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Entries for investment in stock, receipt of dividends, and sale of shares
On March 4, Breen Corporation acquired 7,500 shares of the 200,000 outstanding shares of Melton Co. common stock at $40 plus commission charges of $175. On June 15, a cash dividend of $2.10 per share was received. On October 12, 3,000 shares were sold at $46, less commission charges of $175.
Using the cost method, journalize the entries for (a) the purchase of stock, (b) the receipt of dividends, and (c) the sale of 3,000 shares.
On March 4, Breen Corporation acquired 7,500 shares of the 200,000 outstanding shares of Melton Co. common stock at $40 plus commission charges of $175. On June 15, a cash dividend of $2.10 per share was received. On October 12, 3,000 shares were sold at $46, less commission charges of $175.
Using the cost method, journalize the entries for (a) the purchase of stock, (b) the receipt of dividends, and (c) the sale of 3,000 shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Fair value journal entries, trading investments
Last Unguaranteed Financial Inc. purchased the following trading securities during Year 1, its first year of operations:
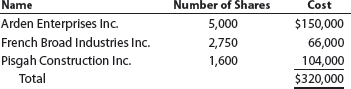
The market price per share for the trading security portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:

a. Provide the journal entry to adjust the trading security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. Assume that the market prices of the portfolio were the same on December 31, Year 2, as they were on December 31, Year 1. What would be the journal entry to adjust the portfolio to fair value
Last Unguaranteed Financial Inc. purchased the following trading securities during Year 1, its first year of operations:

The market price per share for the trading security portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:

a. Provide the journal entry to adjust the trading security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. Assume that the market prices of the portfolio were the same on December 31, Year 2, as they were on December 31, Year 1. What would be the journal entry to adjust the portfolio to fair value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following is a recent consolidated statement of financial position on December 31 of a recent year for LVMH , a French company that markets the Louis Vuitton ® and Moët Hennessy ® brands:
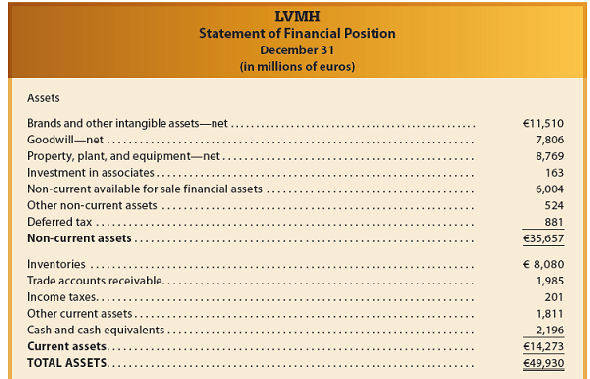


a. Identify presentation differences between the balance sheet of LVMH and a balance sheet prepared under U.S. GAAP. Use the Mornin' Joe balance sheet (Exhibit 2) as an example of a U.S. GAAP balance sheet. (Ignore minority interests and cumulative translation adjustment.)
b. Compare the terms used in this balance sheet with the terms used by Mornin' Joe (Exhibit 2), using the table that follows:

c. What does the "Revaluation reserves" in the Equity section of the balance sheet represent



a. Identify presentation differences between the balance sheet of LVMH and a balance sheet prepared under U.S. GAAP. Use the Mornin' Joe balance sheet (Exhibit 2) as an example of a U.S. GAAP balance sheet. (Ignore minority interests and cumulative translation adjustment.)
b. Compare the terms used in this balance sheet with the terms used by Mornin' Joe (Exhibit 2), using the table that follows:

c. What does the "Revaluation reserves" in the Equity section of the balance sheet represent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A Equity method
On January 2, Peyroux Company acquired 35% of the outstanding stock of Gruden Company for $625,000. For the year ended December 31, Gruden Company earned income of $110,000 and paid dividends of $26,000. Prepare the entries for Peyroux Company for the purchase of the stock, the share of Gruden income, and the dividends received from Gruden Company.
B Equity method
On January 2, Yorkshire Company acquired 40% of the outstanding stock of Fain Company for $500,000. For the year ended December 31, Fain Company earned income of $140,000 and paid dividends of $50,000. Prepare the entries for Yorkshire Company for the purchase of the stock, the share of Fain income, and the dividends received from Fain Company.
On January 2, Peyroux Company acquired 35% of the outstanding stock of Gruden Company for $625,000. For the year ended December 31, Gruden Company earned income of $110,000 and paid dividends of $26,000. Prepare the entries for Peyroux Company for the purchase of the stock, the share of Gruden income, and the dividends received from Gruden Company.
B Equity method
On January 2, Yorkshire Company acquired 40% of the outstanding stock of Fain Company for $500,000. For the year ended December 31, Fain Company earned income of $140,000 and paid dividends of $50,000. Prepare the entries for Yorkshire Company for the purchase of the stock, the share of Fain income, and the dividends received from Fain Company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Dividend yield
On June 30, Setzer Corporation had a market price of $100 per share of common stock. For the previous year, Setzer paid an annual dividend of $4.00. Compute the dividend yield for Setzer Corporation.
On June 30, Setzer Corporation had a market price of $100 per share of common stock. For the previous year, Setzer paid an annual dividend of $4.00. Compute the dividend yield for Setzer Corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Balance sheet presentation, trading investments
The income statement for Delta-tec Inc. for the year ended December 31, Year 2, was as follows:

The balance sheet dated December 31, Year 1, showed a Retained Earnings balance of $825,000. During Year 2, the company purchased trading investments for the first time at a cost of $346,000. In addition, trading investments with a cost of $66,000 were sold at a gain during Year 2. The company paid $65,000 in dividends during Year 2.
a. Determine the December 31, Year 2, Retained Earnings balance.
b. Provide the December 31, Year 2, balance sheet presentation for Trading Investments.
The income statement for Delta-tec Inc. for the year ended December 31, Year 2, was as follows:

The balance sheet dated December 31, Year 1, showed a Retained Earnings balance of $825,000. During Year 2, the company purchased trading investments for the first time at a cost of $346,000. In addition, trading investments with a cost of $66,000 were sold at a gain during Year 2. The company paid $65,000 in dividends during Year 2.
a. Determine the December 31, Year 2, Retained Earnings balance.
b. Provide the December 31, Year 2, balance sheet presentation for Trading Investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a functional expense classification is used for the statement of comprehensive income, what must also be disclosed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Benefits of fair value
On July 16, 1998, Wyatt Corp. purchased 40 acres of land for $350,000. The land has been held for a future plant site until the current date, December 31, 2016. On December 18, 2016, TexoPete Inc. purchased 40 acres of land for $2,000,000 to be used for a distribution center. The TexoPete land is located next to the Wyatt Corp. land. Thus, both Wyatt Corp. and TexoPete Inc. own nearly identical pieces of land.
1. What are the valuations of land on the balance sheets of Wyatt Corp. and TexoPete Inc. using generally accepted accounting principles
2. How might fair value accounting aid comparability when evaluating these two companies
On July 16, 1998, Wyatt Corp. purchased 40 acres of land for $350,000. The land has been held for a future plant site until the current date, December 31, 2016. On December 18, 2016, TexoPete Inc. purchased 40 acres of land for $2,000,000 to be used for a distribution center. The TexoPete land is located next to the Wyatt Corp. land. Thus, both Wyatt Corp. and TexoPete Inc. own nearly identical pieces of land.
1. What are the valuations of land on the balance sheets of Wyatt Corp. and TexoPete Inc. using generally accepted accounting principles
2. How might fair value accounting aid comparability when evaluating these two companies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Stock investment transactions, equity method and available-for-sale securities
Forte Inc. produces and sells theater set designs and costumes. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Forte Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders' equity balance sheet presentation for Forte Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $389,000.
Forte Inc. produces and sells theater set designs and costumes. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Forte Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record these transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders' equity balance sheet presentation for Forte Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $389,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If Valuation Allowance for Available-for-Sale Investments has a credit balance, how is it treated on the balance sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Missing statement items, available-for-sale securities
Highland Industries Inc. makes investments in available-for-sale securities. Selected income statement items for the years ended December 31, Year 2 and Year 3, plus selected items from comparative balance sheets, are as follows:
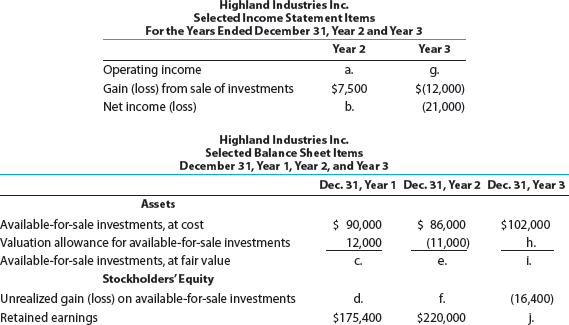
There were no dividends.
Determine the missing lettered items.
Highland Industries Inc. makes investments in available-for-sale securities. Selected income statement items for the years ended December 31, Year 2 and Year 3, plus selected items from comparative balance sheets, are as follows:

There were no dividends.
Determine the missing lettered items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Under U.S. GAAP, LIFO is an acceptable inventory method. Financial statement information for three companies that use LIFO follows. All table numbers are in millions of dollars.
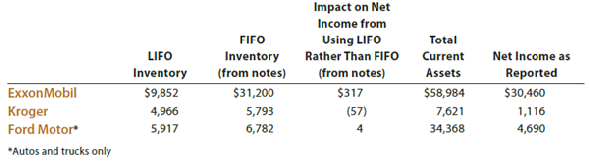
Assume that these companies adopted IFRS and thus were required to use FIFO rather than LIFO.
a. Prepare a table with the following columns:
(1) Difference between FIFO and LIFO inventory valuation
(2) Revised IFRS net income using FIFO
(3) Difference between FIFO and LIFO inventory valuation as a percent of total current assets (rounded to the nearest whole percent)
(4) Revised IFRS net income as a percent of the reported net income (rounded to the nearest whole percent)
b. Complete the table for the three companies.
c. For which company would a change to IFRS for inventory valuation have the largest percentage impact on total current assets (Col. 3)
d. For which company would a change to IFRS for inventory valuation have the largest percentage impact on net income (Col. 4)
e. Why might Kroger have a negative impact on net income from using LIFO, while the other two companies have a positive impact on net income from using LIFO

Assume that these companies adopted IFRS and thus were required to use FIFO rather than LIFO.
a. Prepare a table with the following columns:
(1) Difference between FIFO and LIFO inventory valuation
(2) Revised IFRS net income using FIFO
(3) Difference between FIFO and LIFO inventory valuation as a percent of total current assets (rounded to the nearest whole percent)
(4) Revised IFRS net income as a percent of the reported net income (rounded to the nearest whole percent)
b. Complete the table for the three companies.
c. For which company would a change to IFRS for inventory valuation have the largest percentage impact on total current assets (Col. 3)
d. For which company would a change to IFRS for inventory valuation have the largest percentage impact on net income (Col. 4)
e. Why might Kroger have a negative impact on net income from using LIFO, while the other two companies have a positive impact on net income from using LIFO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why might a business invest cash in temporary investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Stock investment transactions, equity method and available-for-sale securities
Glacier Products Inc. is a wholesaler of rock climbing gear. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Glacier Products Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record the preceding transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders' equity balance sheet presentation for Glacier Products Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $700,000.
Glacier Products Inc. is a wholesaler of rock climbing gear. The company began operations on January 1, Year 1. The following transactions relate to securities acquired by Glacier Products Inc., which has a fiscal year ending on December 31:

Instructions
1. Journalize the entries to record the preceding transactions.
2. Prepare the investment-related asset and stockholders' equity balance sheet presentation for Glacier Products Inc. on December 31, Year 2, assuming that the Retained Earnings balance on December 31, Year 2, is $700,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Entries for investment in stock, receipt of dividends, and sale of shares
The following equity investment transactions were completed by Chung Company in 2016:
Journalize the entries for these transactions.
The following equity investment transactions were completed by Chung Company in 2016:
Journalize the entries for these transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Fair value journal entries, available-for-sale investments
The investments of Steelers Inc. include a single investment: 33,100 shares of Bengals Inc. common stock purchased on September 12, Year 1, for $13 per share including brokerage commission. These shares were classified as available-for-sale securities. As of the December 31, Year 1, balance sheet date, the share price declined to $11 per share.
a. Journalize the entries to acquire the investment on September 12 and record the adjustment to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. How is the unrealized gain or loss for available-for-sale investments disclosed on the financial statements
The investments of Steelers Inc. include a single investment: 33,100 shares of Bengals Inc. common stock purchased on September 12, Year 1, for $13 per share including brokerage commission. These shares were classified as available-for-sale securities. As of the December 31, Year 1, balance sheet date, the share price declined to $11 per share.
a. Journalize the entries to acquire the investment on September 12 and record the adjustment to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
b. How is the unrealized gain or loss for available-for-sale investments disclosed on the financial statements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How is the term provision used differently under IFRS than under U.S. GAAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Entries for investment in bonds, interest, and sale of bonds
Parilo Company acquired $170,000 of Makofske Co., 5% bonds on May 1, 2016, at their face amount. Interest is paid semiannually on May 1 and November 1. On November 1, 2016, Parilo Company sold $50,000 of the bonds for 96.
Journalize entries to record the following:
a. The initial acquisition of the bonds on May 1.
b. The semiannual interest received on November 1.
c. The sale of the bonds on November 1.
d. The accrual of $1,000 interest on December 31, 2016.
Parilo Company acquired $170,000 of Makofske Co., 5% bonds on May 1, 2016, at their face amount. Interest is paid semiannually on May 1 and November 1. On November 1, 2016, Parilo Company sold $50,000 of the bonds for 96.
Journalize entries to record the following:
a. The initial acquisition of the bonds on May 1.
b. The semiannual interest received on November 1.
c. The sale of the bonds on November 1.
d. The accrual of $1,000 interest on December 31, 2016.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Warren Buffett and "look-through" earnings
Berkshire Hathaway , the investment holding company of Warren Buffett, reports its "less than 20% ownership" investments according to generally accepted accounting principles. However, it also provides additional disclosures that it terms "look-through" earnings.
Warren Buffett states,
Many of these companies (in the less than 20%-owned category) pay out relatively small proportions of their earnings in dividends. This means that only a small proportion of their earning power is recorded in our own current operating earnings, But, while our reported operating earnings reflect only the dividends received from such companies, our economic well-being is determined by their earnings, not their dividends.
The value to Berkshire Hathaway of retained earnings (of our investees) is not determined by whether we own 100%, 50%, 20%, or 1% of the businesses in which they reside.… Our perspective on such "forgotten-but-not-gone" earnings is simple: the way they are accounted for is of no importance, but their ownership and subsequent utilization is all-important. We care not whether the auditors hear a tree fall in the forest; we do care who owns the tree and what's next done with it.
I believe the best way to think about our earnings is in terms of "look-through" results, calculated as follows: Take $250 million, which is roughly our share of the operating earnings retained by our investees ( 20% ownership holdings); subtract… incremental taxes we would have owed had that $250 million been paid to us in dividends; then add the remainder, $220 million, to our reported earnings of $371 million. Thus, our "look-through" earnings were about $590 million.
Source: Warren Buffett, The Essays of Warren Buffett: Lessons for Corporate America , edited by Lawrence A, Cunningham, pp, 180-183 (excerpted).
1. What are look-through earnings
2. Why does Warren Buffett favor look-through earnings
Berkshire Hathaway , the investment holding company of Warren Buffett, reports its "less than 20% ownership" investments according to generally accepted accounting principles. However, it also provides additional disclosures that it terms "look-through" earnings.
Warren Buffett states,
Many of these companies (in the less than 20%-owned category) pay out relatively small proportions of their earnings in dividends. This means that only a small proportion of their earning power is recorded in our own current operating earnings, But, while our reported operating earnings reflect only the dividends received from such companies, our economic well-being is determined by their earnings, not their dividends.
The value to Berkshire Hathaway of retained earnings (of our investees) is not determined by whether we own 100%, 50%, 20%, or 1% of the businesses in which they reside.… Our perspective on such "forgotten-but-not-gone" earnings is simple: the way they are accounted for is of no importance, but their ownership and subsequent utilization is all-important. We care not whether the auditors hear a tree fall in the forest; we do care who owns the tree and what's next done with it.
I believe the best way to think about our earnings is in terms of "look-through" results, calculated as follows: Take $250 million, which is roughly our share of the operating earnings retained by our investees ( 20% ownership holdings); subtract… incremental taxes we would have owed had that $250 million been paid to us in dividends; then add the remainder, $220 million, to our reported earnings of $371 million. Thus, our "look-through" earnings were about $590 million.
Source: Warren Buffett, The Essays of Warren Buffett: Lessons for Corporate America , edited by Lawrence A, Cunningham, pp, 180-183 (excerpted).
1. What are look-through earnings
2. Why does Warren Buffett favor look-through earnings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How would a debit balance in Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for-Sale Investments be reported in the financial statements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Fair value journal entries, available-for-sale investments
Hurricane Inc. purchased a portfolio of available-for-sale securities in Year 1, its first year of operations. The cost and fair value of this portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:
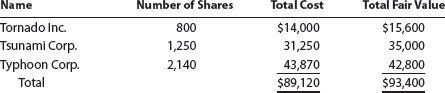
On June 12, Year 2, Hurricane purchased 1,450 shares of Rogue Wave Inc. at $45 per share plus a $100 brokerage commission.
a. Provide the journal entries to record the following:
1. The adjustment of the available-for-sale security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
2. The June 12, Year 2, purchase of Rogue Wave Inc. stock.
b. How are unrealized gains and losses treated differently for available-for-sale securities than for trading securities
Hurricane Inc. purchased a portfolio of available-for-sale securities in Year 1, its first year of operations. The cost and fair value of this portfolio on December 31, Year 1, was as follows:

On June 12, Year 2, Hurricane purchased 1,450 shares of Rogue Wave Inc. at $45 per share plus a $100 brokerage commission.
a. Provide the journal entries to record the following:
1. The adjustment of the available-for-sale security portfolio to fair value on December 31, Year 1.
2. The June 12, Year 2, purchase of Rogue Wave Inc. stock.
b. How are unrealized gains and losses treated differently for available-for-sale securities than for trading securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What are two main differences in inventory valuation under IFRS compared to U.S. GAAP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



