Deck 5: Efficiency
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Efficiency
1
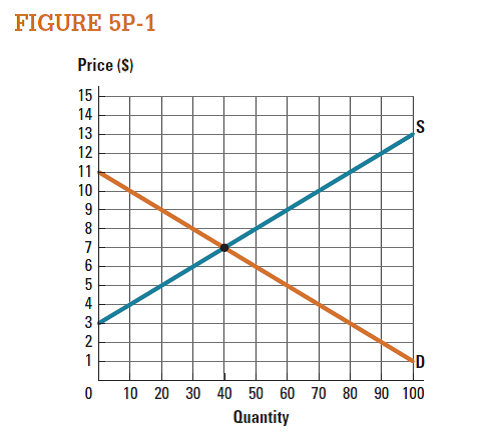
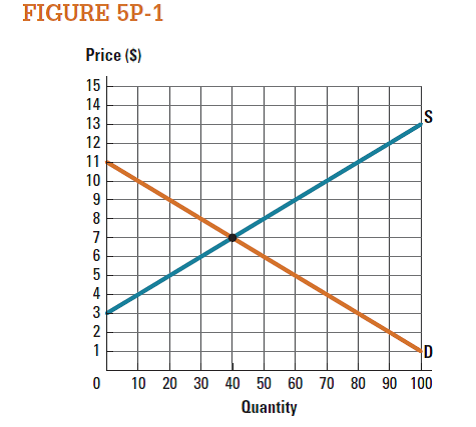
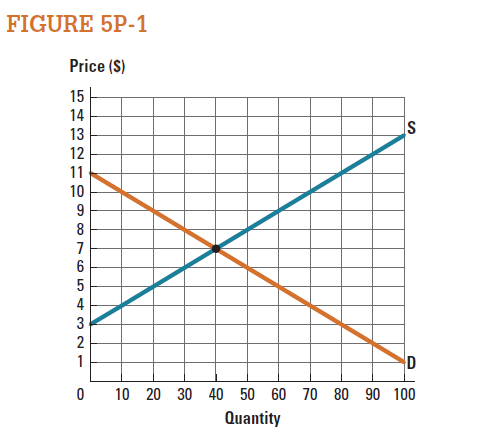
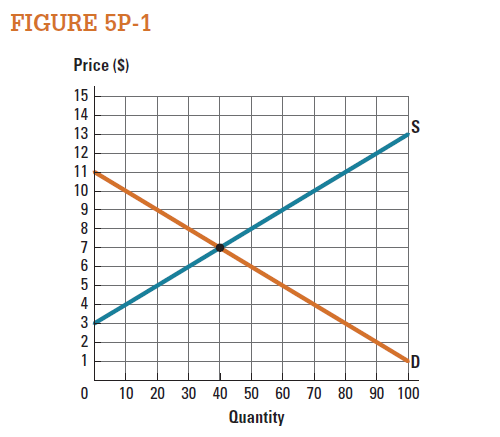
Use the market represented in Figure 5P-1 to draw the consumer surplus when the market price is $8. What is the value of consumer surplus at this price?
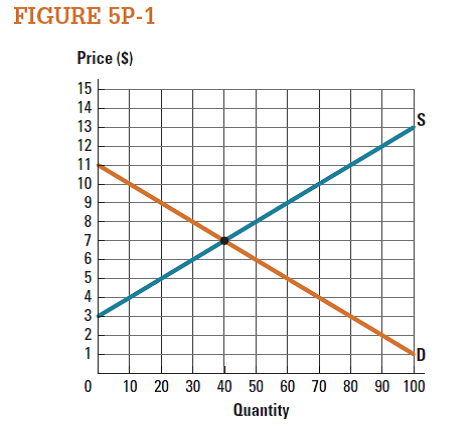

Graph:
Figure -1 illustrates the equilibrium in the market and shows the consumer surplus.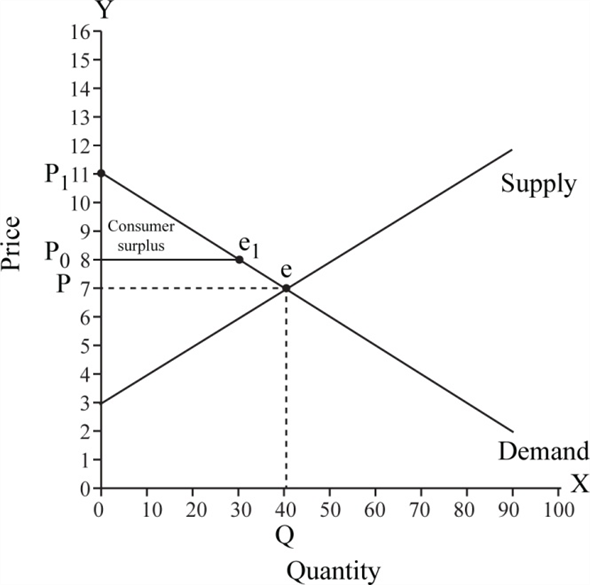 Figure -1
Figure -1
In figure -1, X axis measures quantity and Y axis measures price. Economy is in equilibrium at point 'e' where the demand curve intersects with supply curve. At this point equilibrium price is $7 and equilibrium quantity is 40 units.
If the price increases from $7 to $8, the quantity decreases to 30 units. Consumer surplus is the area of below the demand curve and above the price line. Thus, consumer surplus is the triangle area of 'P 0 , P 1 , e'.
Consumer surplus:
Figure -1 indicates that willingness price of the consumer is $11. Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows: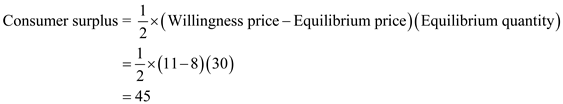 Thus, the value of consumer surplus is
Thus, the value of consumer surplus is 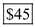 .
.
Figure -1 illustrates the equilibrium in the market and shows the consumer surplus.
 Figure -1
Figure -1In figure -1, X axis measures quantity and Y axis measures price. Economy is in equilibrium at point 'e' where the demand curve intersects with supply curve. At this point equilibrium price is $7 and equilibrium quantity is 40 units.
If the price increases from $7 to $8, the quantity decreases to 30 units. Consumer surplus is the area of below the demand curve and above the price line. Thus, consumer surplus is the triangle area of 'P 0 , P 1 , e'.
Consumer surplus:
Figure -1 indicates that willingness price of the consumer is $11. Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows:
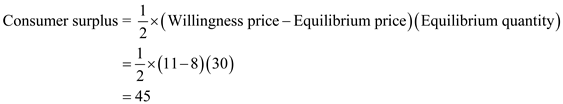 Thus, the value of consumer surplus is
Thus, the value of consumer surplus is 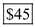 .
. 2
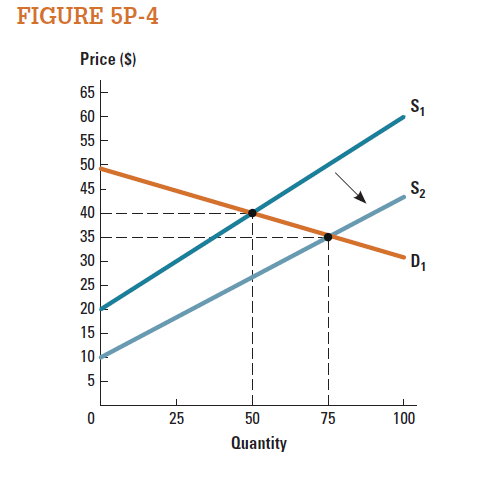
Consider the market represented in Figure 5P-4.
a. Calculate total surplus when supply is S 1.
b. Calculate total surplus when supply increases to S 2.
a. Calculate total surplus when supply is S 1.
b. Calculate total surplus when supply increases to S 2.

Give information:
Below information is obtained from the figure.• Willing to pay price is $50.
• Willing to sell price with supply 1 is $20.
• Willing to sell price with supply 2 is $10.
• Equilibrium quantity with supply 1 is 50.
• Equilibrium quantity with supply 2 is 70.
a.Total surplus with supply1:
Total surplus can be calculated as follows. Thus, the value of total surplus with supply 1 is
Thus, the value of total surplus with supply 1 is 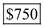 .
.
b.Total surplus with supply 2:
Total surplus can be calculated as follows. Thus, the value of total surplus with demand 2 is
Thus, the value of total surplus with demand 2 is 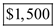 .
.
Below information is obtained from the figure.• Willing to pay price is $50.
• Willing to sell price with supply 1 is $20.
• Willing to sell price with supply 2 is $10.
• Equilibrium quantity with supply 1 is 50.
• Equilibrium quantity with supply 2 is 70.
a.Total surplus with supply1:
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
 Thus, the value of total surplus with supply 1 is
Thus, the value of total surplus with supply 1 is 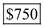 .
.b.Total surplus with supply 2:
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
 Thus, the value of total surplus with demand 2 is
Thus, the value of total surplus with demand 2 is 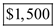 .
. 3
Consider a market in equilibrium. Suppose demand in this market decreases. How will this affect producer surplus? Explain.
Willingness to accept:
Willingness to accept refers to the lowest price that producer accepts to sell an additional unit of goods and services.
Producer surplus:
Producer surplus refers the difference between the potential price the producer intent to sell and actual price he sold.Impact of decreasing demand on producer surplus:
When other things remain the same decreasing demand leads to decreases the price of goods. Since the equilibrium price decreases, it leads to decrease the difference between the willingness to accept price and the equilibrium price. Thus, decreasing demand reduces the producer surplus.
Willingness to accept refers to the lowest price that producer accepts to sell an additional unit of goods and services.
Producer surplus:
Producer surplus refers the difference between the potential price the producer intent to sell and actual price he sold.Impact of decreasing demand on producer surplus:
When other things remain the same decreasing demand leads to decreases the price of goods. Since the equilibrium price decreases, it leads to decrease the difference between the willingness to accept price and the equilibrium price. Thus, decreasing demand reduces the producer surplus.
4
Suppose price is 5 percent above equilibrium in two markets: a market for a necessity and a market for a luxury good. All else equal (including supply conditions), in which market do you expect deadweight loss to be greater? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Based on Figure 5P-1 , consumer surplus is $0 when price is greater than or equal to what price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the market represented in Figure 5P-5.
a. Draw the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the market is functioning at the equilibrium price and quantity. Compute the total surplus if the market is functioning at the equilibrium price and quantity.
b. Compute the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the price is $30.
c. Compute the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the price is $10.
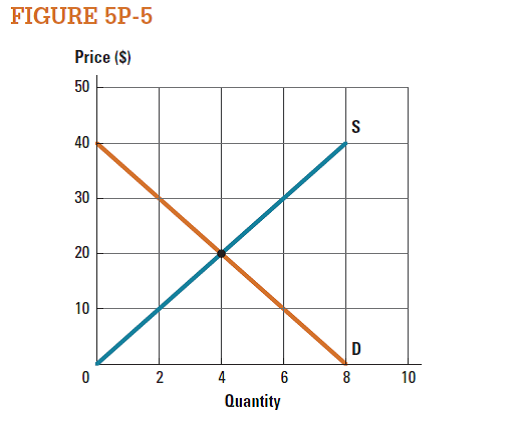
a. Draw the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the market is functioning at the equilibrium price and quantity. Compute the total surplus if the market is functioning at the equilibrium price and quantity.
b. Compute the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the price is $30.
c. Compute the consumer surplus and producer surplus if the price is $10.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the market for plane tickets to Hawaii. A bad winter in the mainland United States increases demand for tropical vacations, shifting the demand curve to the right. The supply curve stays constant. Does total surplus increase or decrease? ( Hint: Sketch out a generic supply and demand curve and look at what happens to the size of the triangle that represents total surplus when the demand curve shifts right.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Your grandmother likes old-fashioned yard sales and doesn't understand why everyone is so excited about eBay. Explain to her why the creation of a market that enables people who don't live in the same town to buy and sell used goods increases total surplus over the yard-sale market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Based on Table 5P-2 , calculate producer surplus for each producer when the price is $12. What is total producer surplus at this price?
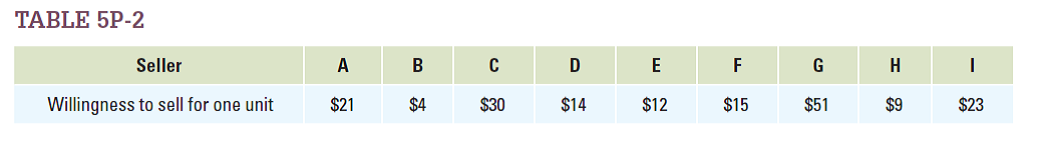
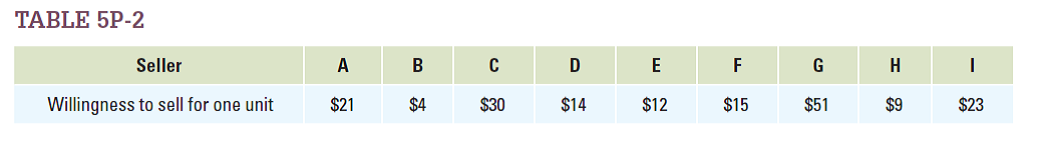

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Assume the market for wine is functioning at its equilibrium. For each of the following situations, say whether the new market outcome will be efficient or inefficient.
a. A new report shows that wine is good for heart health.
b. The government sets a minimum price for wine, which increases the current price.
c. An unexpected late frost ruins large crops of grapes.
d. Grape pickers demand higher wages, increasing the price of wine.
a. A new report shows that wine is good for heart health.
b. The government sets a minimum price for wine, which increases the current price.
c. An unexpected late frost ruins large crops of grapes.
d. Grape pickers demand higher wages, increasing the price of wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
You need to paint your fence but you really hate this task. You decide to hire the kid next door to do it for you. You would be willing to pay him up to $100, but you start by offering $50, expecting to negotiate. To your great surprise, he accepts your $50 offer. When you tell your friend about the great deal you got, she is shocked that you would take advantage of someone. What can you tell your friend to assure her that you did not cheat the kid next door?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At Zooey's elementary school, children are not allowed to trade lunches or components of their lunches with other students. Lunchroom monitors watch closely and strictly enforce this policy. Help Zooey make an argument about the inefficiency of this policy to her principal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Answer the following questions based on Tables 5P-1 and 5P-2.
a. What is the quantity demanded at $10? What is the quantity supplied at $10?
b. What is the quantity demanded at $25? What is the quantity supplied at $25?
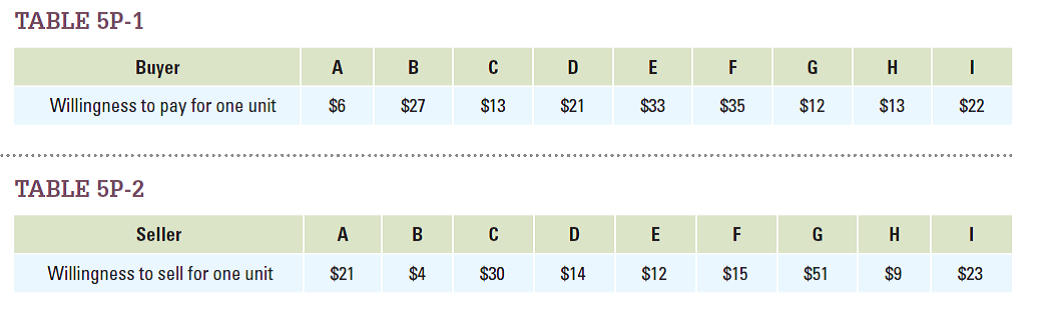
a. What is the quantity demanded at $10? What is the quantity supplied at $10?
b. What is the quantity demanded at $25? What is the quantity supplied at $25?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
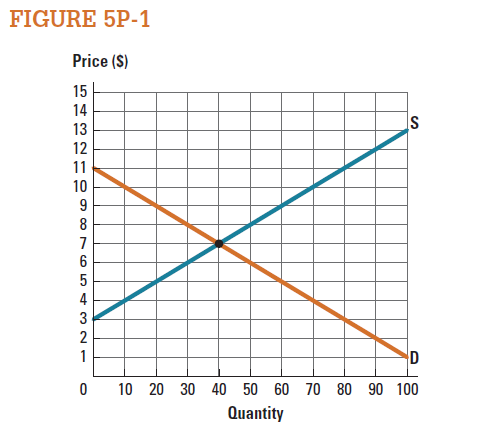
14
Use the market represented in Figure 5P-1 to draw the producer surplus when the market is in equilibrium. What is the value of producer surplus at the equilibrium price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
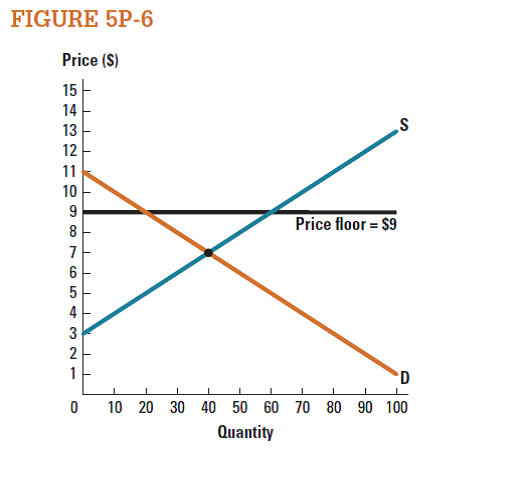
Based on Figure 5P-6 , choose all of the following options that are true.
a. The market is efficient.
b. Total surplus is higher than it would be at market equilibrium.
c. Total surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.
d. Producer surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.
e. Consumer surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.
a. The market is efficient.
b. Total surplus is higher than it would be at market equilibrium.
c. Total surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.
d. Producer surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.
e. Consumer surplus is lower than it would be at market equilibrium.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Bill is a professional photographer. His camera is broken, and he needs a new one within the next hour, or he will miss an important deadline. Lisa is a high school student who doesn't have a camera but wants to get one to take pictures at her prom next month. Who do you think would have a higher willingness to pay for a particular camera today? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
New York City has a long-standing policy of controlling rents in certain parts of the city-in essence, a price ceiling on rent. Is the market for apartments likely to be efficient or inefficient? What does this imply for the size of total surplus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which of the following situations can you say, without further information, that consumer surplus decreases relative to the market equilibrium level? a. Your state passes a law that pushes the interest rate (i.e., the price) for payday loans below the equilibrium rate.
B) The federal government enforces a law that raises the price of dairy goods above the equilibrium.
C) Your city passes a local property tax, under which buyers of new houses have to pay an additional 5 percent on top of the purchase price.
D) The government lowers the effective price of food purchases through a food-stamp program.
B) The federal government enforces a law that raises the price of dairy goods above the equilibrium.
C) Your city passes a local property tax, under which buyers of new houses have to pay an additional 5 percent on top of the purchase price.
D) The government lowers the effective price of food purchases through a food-stamp program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
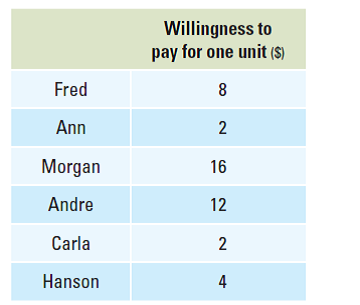
Use the information below to construct a stepgraph of the six consumers' willingness to pay.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the market represented in Figure 5P-1 to draw the producer surplus when the market price is $5. What is the value of producer surplus at this price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the areas labeled in the market represented in Figure 5P-7 to answer the following questions.
a. What area(s) are consumer surplus at the market equilibrium price?
b. What area(s) are producer surplus at the market equilibrium price?
c. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do consumers lose if price is P 2 ?
d. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do producers lose if the price is P 2 ?
e. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do producers gain if the price is P 2 ? f. Compared to the equilibrium, total surplus decreases by what area(s) if the price is P 2 ?
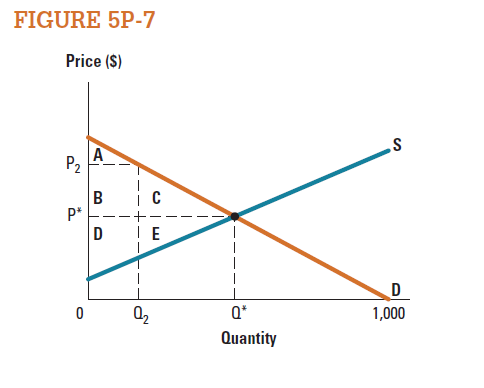
a. What area(s) are consumer surplus at the market equilibrium price?
b. What area(s) are producer surplus at the market equilibrium price?
c. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do consumers lose if price is P 2 ?
d. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do producers lose if the price is P 2 ?
e. Compared to the equilibrium, what area(s) do producers gain if the price is P 2 ? f. Compared to the equilibrium, total surplus decreases by what area(s) if the price is P 2 ?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You are in the market for a new couch and have found two advertisements for the kind of couch you want to buy. One seller notes in her ad that she is selling because she is moving to a smaller apartment, and the couch won't fit in the new space. The other seller says he is selling because the couch doesn't match his other furniture. Which seller do you expect to buy from? Why? ( Hint: Think who would be the more motivated seller.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Total surplus is maximized at the equilibrium price and quantity. When demand increases, price increases. Explain how total surplus is still maximized if price increases due to an increase in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
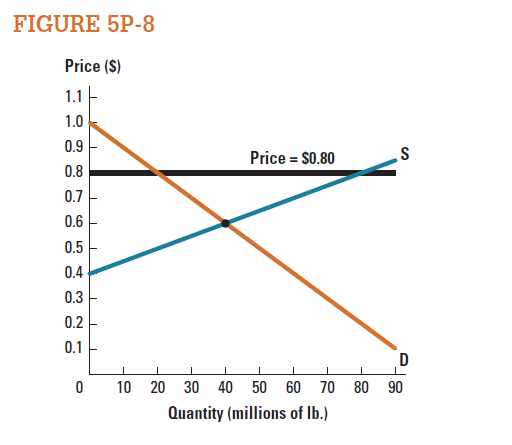
Figure 5P-8 shows a market for cotton, with the price held at $0.80 per pound. Calculate the deadweight loss caused by this policy.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
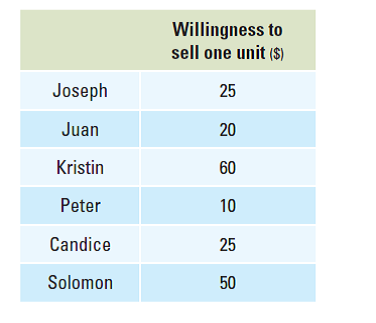
Use the information below to construct a stepgraph of the six sellers' willingness to sell.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Based on Figure 5P-1 , producer surplus is $0 when price is less than or equal to what price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the market represented in Figure 5P-9.
a. Suppose the government sets a minimum price of $25 in the market. Calculate the deadweight loss.
b. Suppose the government sets a maximum price of $25 in the market. Calculate the deadweight loss.
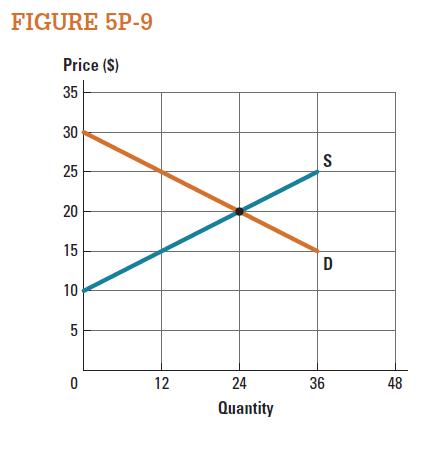
a. Suppose the government sets a minimum price of $25 in the market. Calculate the deadweight loss.
b. Suppose the government sets a maximum price of $25 in the market. Calculate the deadweight loss.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose you are at a flea market and are considering buying a box of vintage records. You are trying to bargain down the price, but the seller overhears you telling a friend that you are willing to pay up to $50. Why is your consumer surplus now likely to be lower than it would have been if the seller hadn't overheard you?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the price of gasoline was very high in the summer of 2008, several U.S. presidential candidates proposed implementing a national price ceiling to keep fuel affordable. How would this policy have affected producer and consumer surplus? How would it have affected total surplus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
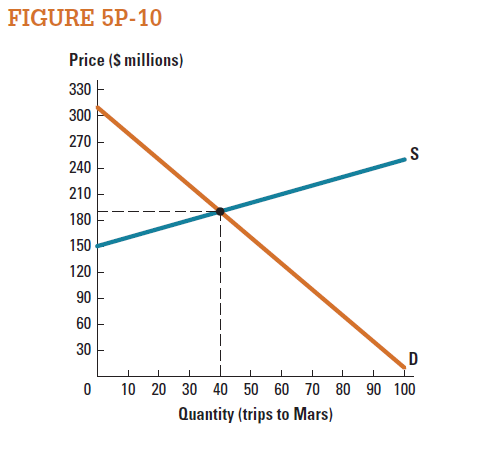
We can consider the market for traveling to Mars to be missing, because no technology exists that allows this service to be bought and sold. Suppose that someone has invented space-travel technology that will enable this service to be provided. Figure 5P-10 shows the estimated market for trips to Mars. Calculate the surplus that could be generated by filling in this missing market.
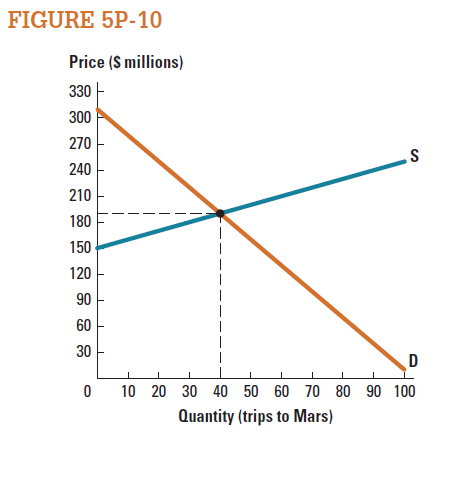


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Based on Table 5P-1 , calculate consumer surplus for each consumer when the price is $17. What is the total consumer surplus at this price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the value of the existence of the market represented in Figure 5P-2 ?
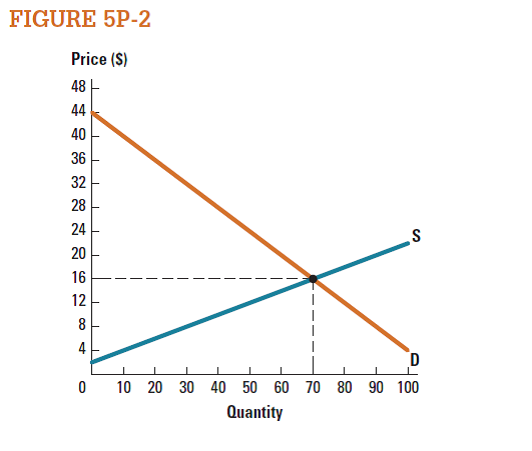


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the market for travelling to Mars represented in Figure 5P-10. Assuming consumers knew they would each eventually pay $190,000 for the trip itself, how much would they collectively be willing to invest to support the space program that would make this trip possible?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider a market in equilibrium. Suppose supply in this market increases. How will this affect consumer surplus? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider a policy to help struggling farmers by setting a minimum trade price for wheat. Will this be an effective way to increase their surplus? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the market represented in Figure 5P-1 to draw the consumer surplus when the market is in equilibrium. What is the value of consumer surplus at the equilibrium price?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the market represented in Figure 5P-3.
a. Calculate total surplus when demand is D 1.
b. Calculate total surplus when demand decreases to D 2.
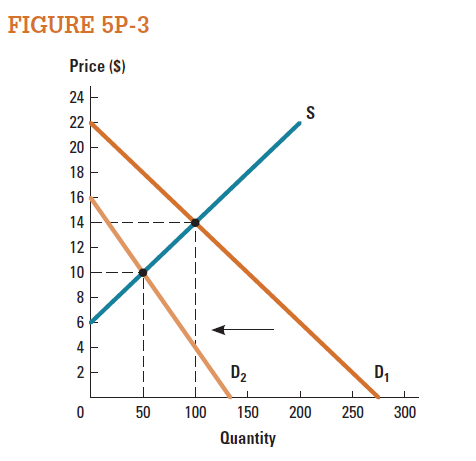
a. Calculate total surplus when demand is D 1.
b. Calculate total surplus when demand decreases to D 2.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
You currently have a television that you want to sell. You can either pick a price and try to sell it at a yard sale or auction it off on eBay. Which method do you think will yield a higher producer surplus? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If rent control creates deadweight loss for both consumers and suppliers of housing, why are consumers often in favor of this policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



