Deck 13: Membrane Channels and Pumps
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/51
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Membrane Channels and Pumps
1
What are passages that exist between adjacent cells that allow movement of ions and small molecules?
A) gap interchanges
B) gap exchanges
C) gap crossings
D) gap inter
E) gap junctions
A) gap interchanges
B) gap exchanges
C) gap crossings
D) gap inter
E) gap junctions
E
2
In a cell-to-cell junction, 12 molecules of what protein form the gap junction?
A) actin
B) keratin
C) connexin
D) tubulin
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) actin
B) keratin
C) connexin
D) tubulin
E) None of the answers is correct.
C
3
What membrane proteins allow specifically charged species to flow freely across a membrane?
A) aquaporins
B) sodium potassium ATPase
C) glucose transporter
D) ion channels
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) aquaporins
B) sodium potassium ATPase
C) glucose transporter
D) ion channels
E) None of the answers is correct.
D
4
Which of the following is a plant extract of steroids used to treat heart failure?
A) digitalis
B) nitroglycerin
C) St. John's wort
D) salicylic acid
E) warfarin
A) digitalis
B) nitroglycerin
C) St. John's wort
D) salicylic acid
E) warfarin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What technique is used to measure conductance across a membrane?
A) osmotic flow analysis
B) electron crystallography
C) stop-flow
D) patch-clamp
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) osmotic flow analysis
B) electron crystallography
C) stop-flow
D) patch-clamp
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The lactose permease transports lactose into the cell along with a(n) ______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
ABC transporters utilize ____________ to accomplish active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Cardiotonic steroids such as digitoxigenin inhibit the _______________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What amino acid residue receives a phosphoryl group from P-type ATPases?
A) serine
B) tyrosine
C) cysteine
D) lysine
E) aspartate
A) serine
B) tyrosine
C) cysteine
D) lysine
E) aspartate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
___________________ are an important class of channels that increase the rate at which water flows through membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The acetylcholine receptor is an example of a ____________-gated channel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Inorganic ions and most metabolites can flow between the interiors of cells joined by _______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the general term for membrane transporters that couple uphill transport of one species to the downhill flow of another species?
A) cotransporters
B) antiporters
C) symporters
D) uniporters
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) cotransporters
B) antiporters
C) symporters
D) uniporters
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Tetrodotoxin, isolated from puffer fish, binds tightly and specifically to ___________ channels in nerve cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A P-glycoprotein transporter is also referred to as MDR protein, which is an acronym for _________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What family of transport proteins possesses a separate domain or cassette that specifically binds ATP?
A) glucose transporters
B) Na+-K+ ATPase
C) ABC proteins
D) bicarbonate transporters
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) glucose transporters
B) Na+-K+ ATPase
C) ABC proteins
D) bicarbonate transporters
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What type of membrane transporter moves two species in opposite directions across a membrane?
A) symporter
B) antiporter
C) uniporter
D) cotransporter
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) symporter
B) antiporter
C) uniporter
D) cotransporter
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The specific transport of a species down its concentration gradient is referred to as _______________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Membrane pumps ____________________(consume, produce, or transduce) energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is another name for a nerve impulse?
A) action impulse
B) action potential
C) ion potential
D) ion impulse
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) action impulse
B) action potential
C) ion potential
D) ion impulse
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When an uncharged molecule moves from a concentration of 10 - 4 M to 10 - 2 M, is the process spontaneous, at equilibrium, or does it require an input of energy?
A) spontaneous
B) at equilibrium
C) input of energy required
D) It depends on the membrane potential.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) spontaneous
B) at equilibrium
C) input of energy required
D) It depends on the membrane potential.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ion channels
A) can be selective.
B) exist in open and closed states.
C) in the open state often spontaneously convert into an inactivated state.
D) can be selective and exist in open and closed states.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) can be selective.
B) exist in open and closed states.
C) in the open state often spontaneously convert into an inactivated state.
D) can be selective and exist in open and closed states.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How does the potassium channel maintain selectivity for potassium versus sodium ions?
A) The ion size is the determining factor.
B) The size of the ion and associated waters relative to the pore size are the determining factors in channel selectivity.
C) Dehydration of the potassium ion is compensated energetically by interactions with oxygen atoms in the selectivity filter, which is not possible with sodium ions.
D) Potassium ions associate with six molecules of water while sodium associates with four, thus allowing selectivity.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) The ion size is the determining factor.
B) The size of the ion and associated waters relative to the pore size are the determining factors in channel selectivity.
C) Dehydration of the potassium ion is compensated energetically by interactions with oxygen atoms in the selectivity filter, which is not possible with sodium ions.
D) Potassium ions associate with six molecules of water while sodium associates with four, thus allowing selectivity.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Membrane transporters that couple the downhill flow of one species to the uphill flow of another species in the opposite direction are called
A) antiporters.
B) symporters.
C) exchangers.
D) P-type transporters.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) antiporters.
B) symporters.
C) exchangers.
D) P-type transporters.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is simple diffusion? Provide an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Where are gap junctions found?
A) between nerve cells
B) in plasma membranes of apposed cells
C) in the synaptic cleft
D) between the ER and Golgi apparatus
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) between nerve cells
B) in plasma membranes of apposed cells
C) in the synaptic cleft
D) between the ER and Golgi apparatus
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following are true about gap junctions?
A) They are important for intercellular communication.
B) Polar molecules smaller than 1 kDa can pass through them.
C) The channels stay open seconds to minutes.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) They are important for intercellular communication.
B) Polar molecules smaller than 1 kDa can pass through them.
C) The channels stay open seconds to minutes.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the potassium ion channel, which of the following is critical in the function of the selectivity filter?
A) The K+ binds to a critical Glu residue.
B) The K+ binds to the amide groups of three residues in the selectivity filter.
C) The K+ binds to the carbonyl groups of the backbone of a conserved pentapeptide sequence.
D) An ATP molecule must be bound for the selectivity filter to operate.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) The K+ binds to a critical Glu residue.
B) The K+ binds to the amide groups of three residues in the selectivity filter.
C) The K+ binds to the carbonyl groups of the backbone of a conserved pentapeptide sequence.
D) An ATP molecule must be bound for the selectivity filter to operate.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
As potassium moves through the ion channel, the associated water molecules
A) are shed.
B) remain bound.
C) are rearranged around the ion.
D) react with CO2.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) are shed.
B) remain bound.
C) are rearranged around the ion.
D) react with CO2.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What clues provided evidence of the mechanism of channel inactivation?
A) Trypsin digestion of the cytoplasmic side caused the channel to stay open.
B) Protein mutants have different inactivation kinetics.
C) Inactivation could be restored by the addition of part of a missing peptide.
D) A and B
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) Trypsin digestion of the cytoplasmic side caused the channel to stay open.
B) Protein mutants have different inactivation kinetics.
C) Inactivation could be restored by the addition of part of a missing peptide.
D) A and B
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the function of selectivity filter amino acids in an ion channel?
A) They close the channel pore after ion passage.
B) They determine the preference for a particular ion.
C) They limit the number of ions passing through the channel.
D) They make sure that only positively charged ions move through the channel
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) They close the channel pore after ion passage.
B) They determine the preference for a particular ion.
C) They limit the number of ions passing through the channel.
D) They make sure that only positively charged ions move through the channel
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Channels that open in response to membrane depolarization are called __________ channels.
A) voltage-gated
B) symport
C) ligand-gated
D) ion-gated
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) voltage-gated
B) symport
C) ligand-gated
D) ion-gated
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How does active transport differ from passive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is NOT correct concerning the ABC proteins?
A) They undergo conformational changes upon ATP binding.
B) All are also members of the P-loop NTPase superfamily.
C) The ATP-binding domains are referred to as ATP-binding cassettes.
D) They transfer a phosphate to a conserved Asp residue.
E) They are all true statements.
A) They undergo conformational changes upon ATP binding.
B) All are also members of the P-loop NTPase superfamily.
C) The ATP-binding domains are referred to as ATP-binding cassettes.
D) They transfer a phosphate to a conserved Asp residue.
E) They are all true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What are the similarities between sodium, potassium, and calcium ion channels?
A) All allow passage of multiple different ions.
B) They contain homologous domains in the membrane spanning regions.
C) They all contain voltage-sensing segments that close the channel in response to a particular membrane potential.
D) They are capable of moving ions in both directions across a membrane.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) All allow passage of multiple different ions.
B) They contain homologous domains in the membrane spanning regions.
C) They all contain voltage-sensing segments that close the channel in response to a particular membrane potential.
D) They are capable of moving ions in both directions across a membrane.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Multidrug resistance in tumor cells is
A) due to the action of a membrane pump that transports small molecules out of the cells.
B) the development of resistance to several drugs following an initial resistance to a single drug.
C) caused by a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene.
D) due to the action of a membrane pump that transports small molecules out of the cells and the development of resistance to several drugs following an initial resistance to a single drug.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) due to the action of a membrane pump that transports small molecules out of the cells.
B) the development of resistance to several drugs following an initial resistance to a single drug.
C) caused by a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene.
D) due to the action of a membrane pump that transports small molecules out of the cells and the development of resistance to several drugs following an initial resistance to a single drug.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A channel that opens in response to binding a particular molecule is called a ________ channel.
A) passive diffusion
B) symport
C) ligand-gated
D) ABC-protein
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) passive diffusion
B) symport
C) ligand-gated
D) ABC-protein
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Aquaporins are found in high levels in all of the following tissues except
A) the kidneys.
B) salivary glands.
C) the cornea.
D) red blood cells.
E) the liver.
A) the kidneys.
B) salivary glands.
C) the cornea.
D) red blood cells.
E) the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is correct concerning the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase?
A) It is an example of an ABC transporter that interconverts between closed and open forms.
B) It transports Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm.
C) This P-type ATPase maintains a calcium ion concentration of approximately 0.1 M in the cytosol and 1.5 mM in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) One Ca2+ is transported for each ATP hydrolyzed.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) It is an example of an ABC transporter that interconverts between closed and open forms.
B) It transports Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm.
C) This P-type ATPase maintains a calcium ion concentration of approximately 0.1 M in the cytosol and 1.5 mM in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) One Ca2+ is transported for each ATP hydrolyzed.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Give the structure of the modified residue that is involved as an intermediate of P-type ATPases. 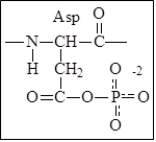


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain how a voltage-gated channel opens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the selectivity filter binds the potassium ion tightly, how are ions released to pass through the membrane?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How does energy affect the functioning of the Na+-K+ ATPase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Many pumps are members of the P-type ATPases. If you discovered a new enzyme with similar function, what reaction intermediate would help convince you that your enzyme was a member of this family?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is in the structure of aquaporin that prevents the transport of ions as well as water?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Describe the functional domains of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the acetylcholine receptor shape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why are gap junctions sealed when high concentrations of calcium ions and protons are present?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Since we know that certain amino acids are likely to be found in membranes, why is it so difficult to predict the structure of a channel protein?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the "ball-and-chain" model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why is it dangerous to eat puffer fish that are not properly prepared?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 51 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



