Deck 6: The Family of Stars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Family of Stars
1
How can we tell that some stars are relatively close to us in the sky?
A) Some stars are occasionally eclipsed by the Moon, so they must be nearby.
B) Some stars vary in brightness caused by sunspots that we can see because they are so close.
C) Some stars appear to be extremely bright and must therefore be very close to us.
D) Some stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth's movement around the Sun.
A) Some stars are occasionally eclipsed by the Moon, so they must be nearby.
B) Some stars vary in brightness caused by sunspots that we can see because they are so close.
C) Some stars appear to be extremely bright and must therefore be very close to us.
D) Some stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth's movement around the Sun.
Some stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth's movement around the Sun.
2
Star A has twice the intrinsic visual luminosity as Star B, and Star A is twice as far from Earth as Star B. How will the flux received from each star compare as recorded by a certain telescope on Earth?
A) The flux from Star A will equal the flux from Star B.
B) The flux from Star A will be twice the flux from Star B.
C) The flux from Star A will be half the flux from Star B.
D) The flux from Star A will be one-quarter the flux from Star B.
A) The flux from Star A will equal the flux from Star B.
B) The flux from Star A will be twice the flux from Star B.
C) The flux from Star A will be half the flux from Star B.
D) The flux from Star A will be one-quarter the flux from Star B.
The flux from Star A will be half the flux from Star B.
3
If you compare two stars, which one will always have the greater luminosity?
A) The one with the larger radius will always have the greater luminosity.
B) The one with the higher surface temperature will always have the greater luminosity.
C) The one with the smaller absolute magnitude will always have the greater luminosity.
D) The one with the largest distance will always have the greater luminosity.
A) The one with the larger radius will always have the greater luminosity.
B) The one with the higher surface temperature will always have the greater luminosity.
C) The one with the smaller absolute magnitude will always have the greater luminosity.
D) The one with the largest distance will always have the greater luminosity.
The one with the smaller absolute magnitude will always have the greater luminosity.
4
What is the most accurate way to determine the surface temperature of a star?
A) Study the pattern of absorption lines from various atoms.
B) Study the relative intensities of light measured through different photometric filters.
C) Study the peak wavelength of the star's continuum blackbody spectrum.
D) Study the pattern of emission lines on the star's spectrum.
A) Study the pattern of absorption lines from various atoms.
B) Study the relative intensities of light measured through different photometric filters.
C) Study the peak wavelength of the star's continuum blackbody spectrum.
D) Study the pattern of emission lines on the star's spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What aspect of a star is a measure of the total energy radiated by the star in one second?
A) apparent visual magnitude
B) luminosity class
C) spectral type
D) luminosity
A) apparent visual magnitude
B) luminosity class
C) spectral type
D) luminosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is absolute visual magnitude?
A) the luminosity of a star observed from Earth
B) the luminosity of a star observed from a distance of 1000 parsecs
C) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from a distance of 10 parsecs
D) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from Earth
A) the luminosity of a star observed from Earth
B) the luminosity of a star observed from a distance of 1000 parsecs
C) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from a distance of 10 parsecs
D) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude that a star would have if observed at a distance of 33 light-years. Consider a star at a distance of 350 light-years that has an apparent magnitude of +5. What would its absolute magnitude be?
A) It would be less than +5.
B) It would be exactly +5.
C) It would be greater than +5.
D) More information on the star's luminosity would be required to answer this question.
A) It would be less than +5.
B) It would be exactly +5.
C) It would be greater than +5.
D) More information on the star's luminosity would be required to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the spectral sequence in order of decreasing temperature?
A) OBAFGKM
B) OBAGFKM
C) BAGFKMO
D) ABFGKMO
A) OBAFGKM
B) OBAGFKM
C) BAGFKMO
D) ABFGKMO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The parsec is defined so that a star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of one arcsecond. If a star has a parallax of 0.05 seconds of arc, what is its distance?
A) 2 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 20 parsecs
D) 50 parsecs
A) 2 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 20 parsecs
D) 50 parsecs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What would make parallax easier to measure?
A) the Earth's orbit being larger
B) the stars being farther away
C) the Earth moving faster along its orbit
D) stars moving faster in their orbits
A) the Earth's orbit being larger
B) the stars being farther away
C) the Earth moving faster along its orbit
D) stars moving faster in their orbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Imagine you tried to measure the parallax of distant stars from the surface of Mars. How would your results compare to what you would find from Earth?
A) Each star's parallax would be smaller because Mars has a smaller orbital speed.
B) Each star's parallax would be smaller because Mars is farther from the Sun.
C) Each star's parallax would be larger because Mars is closer to the stars.
D) Each star's parallax would be larger because Mars has a larger orbit.
A) Each star's parallax would be smaller because Mars has a smaller orbital speed.
B) Each star's parallax would be smaller because Mars is farther from the Sun.
C) Each star's parallax would be larger because Mars is closer to the stars.
D) Each star's parallax would be larger because Mars has a larger orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following can the strength of spectral lines tell you about a star?
A) the radius
B) the distance
C) the temperature
D) the visual magnitude
A) the radius
B) the distance
C) the temperature
D) the visual magnitude

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If two stars are emitting the same amount of light, how will the star that is farther away appear?
A) brighter
B) dimmer
C) redder
D) bluer
A) brighter
B) dimmer
C) redder
D) bluer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about four light-years away and has a luminosity about 0.001 times that of the Sun. If Proxima Centauri were at a distance of one light-year instead of four, how much brighter would it appear in the sky?
A) twice as bright
B) four times as bright
C) 16 times as bright
D) 4000 times as bright
A) twice as bright
B) four times as bright
C) 16 times as bright
D) 4000 times as bright

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You observe weak hydrogen Balmer lines in a star's spectrum. What can you conclude about the star's temperature?
A) The star has a low temperature, less than about 6000 K.
B) The star has an intermediate temperature, about 10 000 K.
C) The star has a high temperature, greater than about 20 000 K.
D) The star may have a low or high temperature.
A) The star has a low temperature, less than about 6000 K.
B) The star has an intermediate temperature, about 10 000 K.
C) The star has a high temperature, greater than about 20 000 K.
D) The star may have a low or high temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which stars have a large positive absolute magnitude?
A) stars of high luminosity
B) stars of low luminosity
C) nearby stars
D) distant stars
A) stars of high luminosity
B) stars of low luminosity
C) nearby stars
D) distant stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The parsec is defined so that a star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of one arcsecond. If a star is located at a distance of 40 parsecs, what is its parallax?
A) 0.25 arcseconds
B) 0.025 arcseconds
C) 0.04 arcseconds
D) 0.05 arcseconds
A) 0.25 arcseconds
B) 0.025 arcseconds
C) 0.04 arcseconds
D) 0.05 arcseconds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The parsec is defined so that a star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of one arcsecond. If a star has a parallax of 0.02 seconds of arc, what is its distance?
A) 2 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 20 parsecs
D) 50 parsecs
A) 2 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 20 parsecs
D) 50 parsecs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How does a star's surface temperature determine the appearance of its spectrum?
A) Surface temperature affects which elements are solid, liquid, or gaseous.
B) Surface temperature determines the luminosity of the star.
C) Surface temperature affects which elements can escape from the surface of the star.
D) Surface temperature determines the velocity of collision rates of atoms and ions.
A) Surface temperature affects which elements are solid, liquid, or gaseous.
B) Surface temperature determines the luminosity of the star.
C) Surface temperature affects which elements can escape from the surface of the star.
D) Surface temperature determines the velocity of collision rates of atoms and ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The parsec is defined so that a star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of one arcsecond. If a star is located at a distance of 10 parsecs, what is its parallax?
A) 0.1 arcseconds
B) 0.01 arcseconds
C) 1 arcsecond
D) 10 arcseconds
A) 0.1 arcseconds
B) 0.01 arcseconds
C) 1 arcsecond
D) 10 arcseconds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which star in the table has the highest surface temperature?
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following can we use to determine the surface temperature of a star?
A) determining if the star has a companion star
B) studying its line absorption spectrum
C) measuring the star's distance
D) measuring the star's parallax
A) determining if the star has a companion star
B) studying its line absorption spectrum
C) measuring the star's distance
D) measuring the star's parallax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
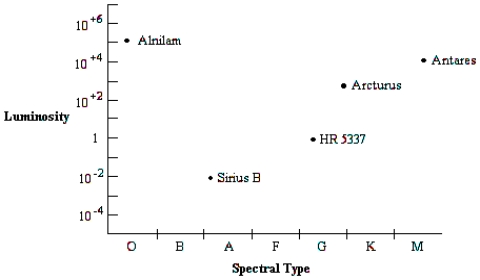
When compared to stars near the middle of the diagram, how are stars in the upper right part of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram different?
A) They are always cooler.
B) They are always larger.
C) They are always smaller.
D) They are always more massive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are 90 percent of all the stars found?
A) in the giant region
B) in the supergiant region
C) on the dwarf sequence
D) on the main sequence
A) in the giant region
B) in the supergiant region
C) on the dwarf sequence
D) on the main sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The table lists the spectral types for each of four stars. Which star in this table would have the highest surface temperature?
A) α For
B) ο Cet
C) γ Tri
D) ξ Per
A) α For
B) ο Cet
C) γ Tri
D) ξ Per

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to answer the following question: Which star in the diagram has the highest surface temperature?
A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which star in the table is the closest to Earth?
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Sirius A and B are two stars at the same distance from the Earth. In this binary system, Sirius A is much brighter but Sirius B is much hotter. From this information, what can you conclude about the two stars?
A) Sirius B must be much smaller than Sirius A.
B) Sirius B must be much larger than Sirius A.
C) Sirius B must be much more massive than Sirius A.
D) Sirius B must be much less massive than Sirius A.
A) Sirius B must be much smaller than Sirius A.
B) Sirius B must be much larger than Sirius A.
C) Sirius B must be much more massive than Sirius A.
D) Sirius B must be much less massive than Sirius A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The star named Circini has the spectral type and luminosity class of O 8.5 V. Based on this information, how does Circini compare to the Sun?
A) Circini is cooler and larger than the Sun.
B) Circini is cooler and smaller than the Sun.
C) Circini is hotter and more luminous than the Sun.
D) Circini is hotter and less luminous than the Sun.
A) Circini is cooler and larger than the Sun.
B) Circini is cooler and smaller than the Sun.
C) Circini is hotter and more luminous than the Sun.
D) Circini is hotter and less luminous than the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The star named Sheat is of spectral type M2 and luminosity class II. Based on this information, how does Sheat compare to the Sun?
A) Sheat is cooler and larger than the Sun.
B) Sheat is cooler and smaller than the Sun.
C) Sheat is hotter and more luminous than the Sun.
D) Sheat is hotter and larger than the Sun.
A) Sheat is cooler and larger than the Sun.
B) Sheat is cooler and smaller than the Sun.
C) Sheat is hotter and more luminous than the Sun.
D) Sheat is hotter and larger than the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the spectral sequence in order of increasing temperature?
A) MKFAGBO
B) BAFGKMO
C) MKGFABO
D) ABFMKGO
A) MKFAGBO
B) BAFGKMO
C) MKGFABO
D) ABFMKGO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which star in the table has the largest diameter?
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa
A) δ Cen
B) HR 4758
C) HD 39801
D) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why do white dwarfs have very low luminosities?
A) They are very small.
B) They have cooled down after leaving the main sequence.
C) They have very low mass.
D) White light is dimmer than blue or red light.
A) They are very small.
B) They have cooled down after leaving the main sequence.
C) They have very low mass.
D) White light is dimmer than blue or red light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How do we know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the Sun?
A) They are more luminous but have about the same temperature.
B) They are less luminous but have about the same temperature.
C) They are hotter but have about the same luminosity.
D) They are cooler but have about the same luminosity.
A) They are more luminous but have about the same temperature.
B) They are less luminous but have about the same temperature.
C) They are hotter but have about the same luminosity.
D) They are cooler but have about the same luminosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Where are red giant stars found in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
A) above the main sequence
B) below the main sequence
C) on the lower main sequence
D) on the upper main sequence
A) above the main sequence
B) below the main sequence
C) on the lower main sequence
D) on the upper main sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A certain star moves from the middle toward the top right of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. How is the star changing?
A) It is moving farther away from the Sun in space.
B) It is getting dimmer and hotter.
C) It is getting larger and cooler.
D) It is getting brighter and smaller.
A) It is moving farther away from the Sun in space.
B) It is getting dimmer and hotter.
C) It is getting larger and cooler.
D) It is getting brighter and smaller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to answer the following question: Which star in the diagram is most like the Sun?
A) Alnilam
B) Arcturus
C) HR 5337
D) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What properties of a star determine its luminosity?
A) distance and diameter
B) temperature and distance
C) temperature and diameter
D) apparent magnitude and temperature
A) distance and diameter
B) temperature and distance
C) temperature and diameter
D) apparent magnitude and temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are the stars with the smallest radius found?
A) in the upper left corner
B) in the upper right corner
C) in the lower left corner
D) in the lower right corner
A) in the upper left corner
B) in the upper right corner
C) in the lower left corner
D) in the lower right corner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The table lists the spectral types for each of four stars. Which star in this table would have the lowest surface temperature?
A) α For
B) ο Cet
C) γ Tri
D) ξ Per
A) α For
B) ο Cet
C) γ Tri
D) ξ Per

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
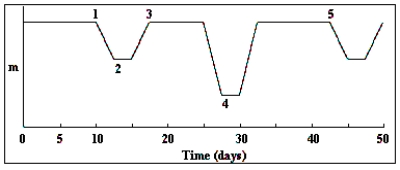
If the orbital velocity of the lower-mass star in an eclipsing binary is 97 km/sec and it is completely eclipsed by the more massive star for 2 hours, what is the approximate diameter of the more massive star?
A) 194 km
B) 4656 km
C) 350,000 km
D) 700,000 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compared with the spectral lines in the solar spectrum, how are lines in a supergiant star's spectrum different?
A) They are narrower.
B) They are broader.
C) They are weaker.
D) They are stronger.
A) They are narrower.
B) They are broader.
C) They are weaker.
D) They are stronger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider two binary star systems, A and B, in which the distance between the stars is the same. If the total mass of the stars in system A is greater than the total mass of the stars in system B, which of following can you conclude?
A) The primary in A is closer to the centre of mass than the primary in B.
B) The primary in A is farther from the centre of mass than the primary in B.
C) The orbital period of the stars in A is shorter than the orbital period of the stars in B.
D) The orbital period of the stars in A is longer than the orbital period of the stars in B.
A) The primary in A is closer to the centre of mass than the primary in B.
B) The primary in A is farther from the centre of mass than the primary in B.
C) The orbital period of the stars in A is shorter than the orbital period of the stars in B.
D) The orbital period of the stars in A is longer than the orbital period of the stars in B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following describes the method of spectroscopic parallax?
A) Estimate the distance to a star using its apparent brightness and luminosity class.
B) Estimate the distance to a star using the amount that it moves relative to more distant stars over a year.
C) Measure the spectrum of a star using the amount that it moves relative to more distant stars over a year.
D) Measure the spectrum of a star using its apparent brightness and luminosity class.
A) Estimate the distance to a star using its apparent brightness and luminosity class.
B) Estimate the distance to a star using the amount that it moves relative to more distant stars over a year.
C) Measure the spectrum of a star using the amount that it moves relative to more distant stars over a year.
D) Measure the spectrum of a star using its apparent brightness and luminosity class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An eclipsing binary has been analyzed and it has been determined that the ratio of the mass of star A to the mass of star B is about 6 : 1, and that the total mass of the two stars is 26 solar masses. What are the masses of star A and star B?
A) Star A has a mass of 6 solar mass and star B has a mass of 1 solar masses.
B) Star A has a mass of 20 solar masses and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
C) Star A has a mass of 22.3 solar masses and star B has a mass of 3.7 solar masses.
D) Star A has a mass of 31.2 solar masses and star B has a mass of 5.2 solar masses.
A) Star A has a mass of 6 solar mass and star B has a mass of 1 solar masses.
B) Star A has a mass of 20 solar masses and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
C) Star A has a mass of 22.3 solar masses and star B has a mass of 3.7 solar masses.
D) Star A has a mass of 31.2 solar masses and star B has a mass of 5.2 solar masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a binary system, where will the more massive star be found?
A) at the centre of mass
B) farthest from the centre of mass
C) nearest the centre of mass
D) following the largest orbit
A) at the centre of mass
B) farthest from the centre of mass
C) nearest the centre of mass
D) following the largest orbit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What would be the most reliable way to measure the mass of a star for which the distance is unknown?
A) apply the mass-temperature relation
B) measure its orbit around another star
C) measure its radius, then compute its volume and multiply by density to get the mass
D) compute its spectroscopic parallax, then apply the mass-luminosity relation
A) apply the mass-temperature relation
B) measure its orbit around another star
C) measure its radius, then compute its volume and multiply by density to get the mass
D) compute its spectroscopic parallax, then apply the mass-luminosity relation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What does a spectroscopic binary show periodic variations in?
A) brightness
B) motion perpendicular to the line of sight
C) motion along the line of sight
D) spectral type
A) brightness
B) motion perpendicular to the line of sight
C) motion along the line of sight
D) spectral type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Why are spectroscopic binaries difficult to analyze?
A) We can't see the shape or tilt of the orbit.
B) We can't find the diameters of the stars.
C) We can't determine the luminosities of the stars.
D) The Doppler shift is not measurable.
A) We can't see the shape or tilt of the orbit.
B) We can't find the diameters of the stars.
C) We can't determine the luminosities of the stars.
D) The Doppler shift is not measurable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If we can solve the orbital motion of a spectroscopic binary, what can we find?
A) the mass of each star
B) the diameter of each star
C) the orbital period
D) the sum of the stars' masses
A) the mass of each star
B) the diameter of each star
C) the orbital period
D) the sum of the stars' masses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
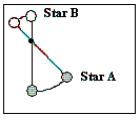
The diagram illustrates two stars in a visual binary system and the centre of mass of this system. Based on this diagram, what is the ratio of the mass of star A to the mass of star B?
A) 2 to 1
B) 1 to 2
C) 2 to 3
D) 3 to 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In what kind of star are the hydrogen lines narrowest?
A) supergiants
B) main-sequence stars
C) subgiants
D) dwarfs
A) supergiants
B) main-sequence stars
C) subgiants
D) dwarfs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
You observe a spectroscopic binary star system. If you measure Doppler shifts in the spectrum and determine that star A is blueshifted and star B is redshifted, what can you conclude about the stars?
A) Star B is receding and star A is approaching.
B) Star B is approaching and star A is receding.
C) The stars are perpendicular to the line of sight.
D) Star A is moving faster than star B.
A) Star B is receding and star A is approaching.
B) Star B is approaching and star A is receding.
C) The stars are perpendicular to the line of sight.
D) Star A is moving faster than star B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
To determine the orbital period of a visual binary, what must we measure?
A) position on the sky
B) brightness
C) luminosity
D) temperature
A) position on the sky
B) brightness
C) luminosity
D) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is a characteristic of an eclipsing binary?
A) It will be more luminous than a visual binary.
B) It will also be observed as a spectroscopic binary.
C) It will show a constant Doppler shift in its spectral lines.
D) It will show two stars with variable proper motion.
A) It will be more luminous than a visual binary.
B) It will also be observed as a spectroscopic binary.
C) It will show a constant Doppler shift in its spectral lines.
D) It will show two stars with variable proper motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

At what point in the eclipsing binary light curve shown in the diagram is the cooler star in front of the hotter star?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How is a luminosity class assigned to a star?
A) by combining the apparent magnitude with the star's parallax
B) by measuring the period of variability in the star's apparent magnitude
C) by studying the absorption line width in the spectrum of the star
D) by observing the angular size of the star's image in a photograph or digital image
A) by combining the apparent magnitude with the star's parallax
B) by measuring the period of variability in the star's apparent magnitude
C) by studying the absorption line width in the spectrum of the star
D) by observing the angular size of the star's image in a photograph or digital image

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
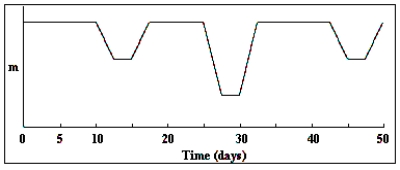
In the light curve shown in the diagram, what is the period of the eclipsing binary?
A) 5 days
B) 32.5 days
C) 42.5 days
D) 50 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the most reliable way to measure the mass of a star for which the distance is known?
A) Apply the mass-luminosity relation.
B) Measure its orbit around another star.
C) Measure its radius, then compute its volume and multiply by density to get the mass.
D) Apply the mass-temperature relation.
A) Apply the mass-luminosity relation.
B) Measure its orbit around another star.
C) Measure its radius, then compute its volume and multiply by density to get the mass.
D) Apply the mass-temperature relation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to answer the following question: Which star in the diagram has the largest absolute visual magnitude?
A) Antares
B) Arcturus
C) HR 5337
D) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Most stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram are on the _______ ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What property do most of the nearest stars in the sky share?
A) They have high temperatures.
B) They are very luminous.
C) They are main-sequence stars.
D) They are red dwarfs.
A) They have high temperatures.
B) They are very luminous.
C) They are main-sequence stars.
D) They are red dwarfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63

Define the range of a property as the maximum value divided by the minimum value. Which property of stars has the greatest range?
A) mass
B) radius
C) luminosity
D) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If you know the apparent brightness of a star and its intrinsic brightness you can easily find its ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
____________________ can be used to determine the distance to a star, when the spectrum of the star can be used to determine its spectral type and luminosity class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following pieces of information are needed to calculate the total mass of a binary system?
A) the ratio of the angular separation from the centre of mass of each of the stars
B) the size of the orbits and the orbital period
C) the radial velocities of the two stars
D) the time required for the small star to eclipse the larger star
A) the ratio of the angular separation from the centre of mass of each of the stars
B) the size of the orbits and the orbital period
C) the radial velocities of the two stars
D) the time required for the small star to eclipse the larger star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which star type in the Milky Way is likely to be most completely catalogued?
A) red main-sequence stars, because there are so many of them
B) luminous stars, because they are bright and easy to find
C) stars like the Sun, because the Sun is a typical star
D) white dwarf stars, because they are so old
A) red main-sequence stars, because there are so many of them
B) luminous stars, because they are bright and easy to find
C) stars like the Sun, because the Sun is a typical star
D) white dwarf stars, because they are so old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following kinds of stars best obey the mass-luminosity relation?
A) main-sequence stars
B) giant stars
C) supergiant stars
D) white dwarfs
A) main-sequence stars
B) giant stars
C) supergiant stars
D) white dwarfs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Luminosity class IV objects are known as ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
This diagram shows the velocity along the line of sight (labelled vr) for two stars in a spectroscopic binary. Which of the stars is most massive? ____________________ 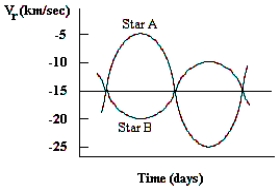


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What type of stars are the most common?
A) supergiants
B) giants
C) upper (more luminous) main-sequence stars
D) lower (less luminous) main-sequence stars
A) supergiants
B) giants
C) upper (more luminous) main-sequence stars
D) lower (less luminous) main-sequence stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Based on the mass-luminosity relation, approximately what luminosity would a 2 solar mass star on the main sequence have?
A) 0.5 solar luminosities
B) 2 solar luminosities
C) 4 solar luminosities
D) 11 solar luminosities
A) 0.5 solar luminosities
B) 2 solar luminosities
C) 4 solar luminosities
D) 11 solar luminosities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which one of the following kinds of stars is most dense?
A) a supergiant star
B) a main-sequence star
C) a giant star
D) a white dwarf
A) a supergiant star
B) a main-sequence star
C) a giant star
D) a white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The strength of a star's spectral lines can be used to determine its ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which stars on the main sequence have the greatest mass?
A) the spectral type M stars
B) the spectral type O stars
C) the stars in the lower right of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
D) the stars in the lower left of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
A) the spectral type M stars
B) the spectral type O stars
C) the stars in the lower right of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
D) the stars in the lower left of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If you took a random sample of 100 main-sequence stars in the Sun's neighbourhood, what would you expect their total mass to be?
A) Much less than 1 solar mass.
B) About 1 solar mass.
C) About 10 solar masses.
D) About 100 solar masses.
A) Much less than 1 solar mass.
B) About 1 solar mass.
C) About 10 solar masses.
D) About 100 solar masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A G2 I star is ____________________ in diameter and ____________________ luminous than the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The largest of the red stars are the ____________________ stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What property do most of the (apparently) bright stars in the sky share?
A) They are close to Earth.
B) They are very luminous.
C) They are main-sequence stars.
D) They are red dwarfs.
A) They are close to Earth.
B) They are very luminous.
C) They are main-sequence stars.
D) They are red dwarfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The apparent visual magnitude a star would have from 33 ly away is called the ________ _____________ ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



