Deck 1: The Scale of the Cosmos: Space and Time
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Scale of the Cosmos: Space and Time
1
Which statement best describes the study of astronomy in ancient times?
A) Only a few civilizations were interested in studying astronomy and they made most of the early discoveries.
B) Only people who could afford a telescope could participate in astronomy.
C) Astronomy was studied by many civilizations but didn't have much effect on people's daily lives.
D) Civilizations around the world used astronomy to help understand their place in the universe.
A) Only a few civilizations were interested in studying astronomy and they made most of the early discoveries.
B) Only people who could afford a telescope could participate in astronomy.
C) Astronomy was studied by many civilizations but didn't have much effect on people's daily lives.
D) Civilizations around the world used astronomy to help understand their place in the universe.
Civilizations around the world used astronomy to help understand their place in the universe.
2
Which one of the following statements best describes a planet?
A) a non-luminous body
B) an irregular shape
C) a body that generates energy by nuclear fusion
D) a body located at the centre of the Solar System
A) a non-luminous body
B) an irregular shape
C) a body that generates energy by nuclear fusion
D) a body located at the centre of the Solar System
a non-luminous body
3
If the distance from the Sun to the Earth is represented by roughly 15 metres, then what would the distance from the Earth to the Moon on the same scale be?
A) about 30 metres
B) about 10 metres
C) about 1 metre
D) smaller than the width of your hand
A) about 30 metres
B) about 10 metres
C) about 1 metre
D) smaller than the width of your hand
smaller than the width of your hand
4
Which one of the following statements best describes the Sun?
A) generates energy by nuclear fusion
B) located 10 AU from Earth
C) orbiting the Solar System
D) located in the centre of the Milky Way
A) generates energy by nuclear fusion
B) located 10 AU from Earth
C) orbiting the Solar System
D) located in the centre of the Milky Way

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement best describes the study of astronomy in modern times?
A) One country is responsible for almost all new discoveries.
B) A small number of scientists do research and report their results.
C) It has contributions from many cultures and countries.
D) It mainly involves studying the texts of ancient Greek astronomers.
A) One country is responsible for almost all new discoveries.
B) A small number of scientists do research and report their results.
C) It has contributions from many cultures and countries.
D) It mainly involves studying the texts of ancient Greek astronomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the average distance from Earth to the Sun?
A) 1 ly
B) 1 AU
C) 1 million km
D) 1 billion km
A) 1 ly
B) 1 AU
C) 1 million km
D) 1 billion km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the diagram, what is the diameter of Jupiter? 
A) about 7.0 × 104 km
B) about 7.0 × 105 km
C) about 1.4 × 104 km
D) about 1.4 × 105 km

A) about 7.0 × 104 km
B) about 7.0 × 105 km
C) about 1.4 × 104 km
D) about 1.4 × 105 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the approximate diameter of the Earth?
A) 1 AU
B) 13,000 light-years
C) 13,000 kilometres
D) 1,000,000 kilometres
A) 1 AU
B) 13,000 light-years
C) 13,000 kilometres
D) 1,000,000 kilometres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Earth has a radius of about 6400 km, the Sun has a radius of about 7.0×105 km, and a rubber ball has a radius of 6.4 cm. If you were to construct a scale model of the Solar System using the rubber ball to represent Earth, what is the radius of a ball needed to represent the Sun in your model?
A) 7.0 × 105 cm
B) 7.0 cm
C) 700 cm
D) 70 cm
A) 7.0 × 105 cm
B) 7.0 cm
C) 700 cm
D) 70 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How is a planet different from a star?
A) Planets are larger than stars.
B) Planets reflect light, while stars produce their own light.
C) Stars move faster in the sky than planets.
D) Planets are brighter than stars.
A) Planets are larger than stars.
B) Planets reflect light, while stars produce their own light.
C) Stars move faster in the sky than planets.
D) Planets are brighter than stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Assume the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball (diameter about 7 cm). At this scale, the Earth is about 15 metres (150 million km or 8 light-minutes) away. How far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? Pick the closest answer.
A) about the distance between Windsor and Toronto (about 400 km)
B) about 100 metres away
C) about the distance across Canada from Toronto to Vancouver (about 4300 km)
D) about the distance across 50 football fields (50 x 100 m, or 5 km)
A) about the distance between Windsor and Toronto (about 400 km)
B) about 100 metres away
C) about the distance across Canada from Toronto to Vancouver (about 4300 km)
D) about the distance across 50 football fields (50 x 100 m, or 5 km)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the diagram, what is the diameter of Mercury? 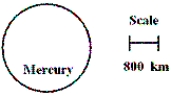
A) about 240 km
B) about 2400 km
C) about 24,000 km
D) about 240,000 km

A) about 240 km
B) about 2400 km
C) about 24,000 km
D) about 240,000 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Why is scientific notation used in science?
A) because it makes it easy to write very big or very small numbers
B) because all astronomical distances are expressed in metric units
C) because it makes conversions between units easy
D) because it makes conversions between distances easy
A) because it makes it easy to write very big or very small numbers
B) because all astronomical distances are expressed in metric units
C) because it makes conversions between units easy
D) because it makes conversions between distances easy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What does the Solar System contain?
A) the Sun, its planets, and some smaller bodies
B) the Sun, galaxies, planets, and stars
C) the Sun, planets, moons, and stars
D) the Sun, planets, asteroids, and galaxies
A) the Sun, its planets, and some smaller bodies
B) the Sun, galaxies, planets, and stars
C) the Sun, planets, moons, and stars
D) the Sun, planets, asteroids, and galaxies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is 5.7×107 the same as?
A) 5.7 million
B) 57 thousand
C) 570 thousand
D) 57 million
A) 5.7 million
B) 57 thousand
C) 570 thousand
D) 57 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the smallest?
A) size of a typical planet
B) 1 AU
C) 1 light-year
D) size of a typical galaxy
A) size of a typical planet
B) 1 AU
C) 1 light-year
D) size of a typical galaxy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is 1.95 billion the same as?
A) 1.95 × 1012
B) 1.95 × 109
C) 1.95 × 106
D) 1.95 × 105
A) 1.95 × 1012
B) 1.95 × 109
C) 1.95 × 106
D) 1.95 × 105

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is no longer considered a major planet?
A) Mercury
B) Uranus
C) Pluto
D) Saturn
A) Mercury
B) Uranus
C) Pluto
D) Saturn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How does the radius of the Moon's orbit compare to the radius of the Earth?
A) It is 0.6 times as large.
B) It is 6 times as large.
C) It is 60 times as large.
D) It is 600 times as large.
A) It is 0.6 times as large.
B) It is 6 times as large.
C) It is 60 times as large.
D) It is 600 times as large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Approximately how many times larger than the diameter of a typical planet (the Earth) is the diameter of a typical star (the Sun)?
A) 10 times
B) 100 times
C) 1000 times
D) 10,000 times
A) 10 times
B) 100 times
C) 1000 times
D) 10,000 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How long does it take for light to cross the Milky Way galaxy?
A) about 8 minutes
B) about 4 years
C) about 100,000 years
D) about 200 million years
A) about 8 minutes
B) about 4 years
C) about 100,000 years
D) about 200 million years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which sequence is correct when ordered by increasing size?
A) Earth, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy, clusters of galaxies
B) Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Galaxy
C) Earth, Milky Way Galaxy, Solar System, galaxy clusters
D) galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy, Earth
A) Earth, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy, clusters of galaxies
B) Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Galaxy
C) Earth, Milky Way Galaxy, Solar System, galaxy clusters
D) galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy, Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the name of the hazy band of light that circles our sky, produced by the glow of our galaxy?
A) the Milky Way
B) the Solar System
C) a spiral arm
D) Alpha Centauri
A) the Milky Way
B) the Solar System
C) a spiral arm
D) Alpha Centauri

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The speed of light is 3.0×105 km/s, and it takes 1.3 seconds for light to travel from the Moon to Earth. Based on this information, what is the distance from the Earth to the Moon?
A) 390,000 km
B) 230,000 km
C) 3.9 km
D) 2.3 km
A) 390,000 km
B) 230,000 km
C) 3.9 km
D) 2.3 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How long does it take for light to travel from the Sun to Neptune?
A) several seconds
B) several minutes
C) several hours
D) several weeks
A) several seconds
B) several minutes
C) several hours
D) several weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How does one light-year relate to Astronomical Units, roughly?
A) 63,000 AU
B) 10,000 AU
C) 380,000 AU
D) 1,400 AU
A) 63,000 AU
B) 10,000 AU
C) 380,000 AU
D) 1,400 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
It takes light 1.3 seconds to travel from the Moon to Earth and 8 minutes for light to travel from the Sun to Earth. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The Sun is 6.2 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
B) The Sun is 10 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
C) The Sun is 370 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
D) The Sun is 0.10 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
A) The Sun is 6.2 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
B) The Sun is 10 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
C) The Sun is 370 times farther from Earth than the Moon.
D) The Sun is 0.10 times farther from Earth than the Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following has the distances arranged in order from smallest to largest?
A) kilometre, light year, millimetre, Astronomical Unit
B) Astronomical Unit, millimetre, light year, kilometre
C) millimetre, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, light year
D) light year, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, millimetre
A) kilometre, light year, millimetre, Astronomical Unit
B) Astronomical Unit, millimetre, light year, kilometre
C) millimetre, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, light year
D) light year, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, millimetre

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What does a typical galaxy like our Milky Way galaxy contain?
A) primarily planets
B) gas only
C) stars (some with planets), gas, and dust
D) a single star and planets
A) primarily planets
B) gas only
C) stars (some with planets), gas, and dust
D) a single star and planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why can't we see any parts of the universe that are farther than 13.8 billion light-years away?
A) The farthest object in the universe is 13.8 billion light-years away and there is nothing beyond it.
B) We haven't built a telescope that is powerful enough to see any farther.
C) There is a giant cloud that obscures our view of anything farther away.
D) Light from farther distances hasn't had time to reach us.
A) The farthest object in the universe is 13.8 billion light-years away and there is nothing beyond it.
B) We haven't built a telescope that is powerful enough to see any farther.
C) There is a giant cloud that obscures our view of anything farther away.
D) Light from farther distances hasn't had time to reach us.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If light takes 8 minutes to travel from the Sun to Earth, and over 4 hours to travel from the Sun to the planet Neptune, what is the distance from the Sun to Neptune?
A) 5 AU
B) 30 AU
C) 30 ly
D) 5 ly
A) 5 AU
B) 30 AU
C) 30 ly
D) 5 ly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement best describes the Milky Way Galaxy?
A) It contains about 100 billion stars.
B) It is about 400 light-years in diameter.
C) It is the largest known object in the universe.
D) It contains numerous clusters and superclusters.
A) It contains about 100 billion stars.
B) It is about 400 light-years in diameter.
C) It is the largest known object in the universe.
D) It contains numerous clusters and superclusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away, how does that affect how we see it?
A) We see it as it looked 1,000 years ago.
B) We see it as it would appear to our ancestors 1,000 years ago.
C) We see it as it looked 1,000 light-years ago.
D) We see it as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer.
A) We see it as it looked 1,000 years ago.
B) We see it as it would appear to our ancestors 1,000 years ago.
C) We see it as it looked 1,000 light-years ago.
D) We see it as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many centimetres are there in one kilometre?
A) 100
B) 1,000
C) 10,000
D) 100,000
A) 100
B) 1,000
C) 10,000
D) 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is one thousandth of one metre?
A) one kilometre
B) one centimetre
C) one millimetre
D) one hectometre
A) one kilometre
B) one centimetre
C) one millimetre
D) one hectometre

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the implication if the distance to the nearest star is 4.2 light-years?
A) The star is 4.2 million AU away.
B) The light we see left the star 4.2 years ago.
C) The star must be very old.
D) The star must be very young.
A) The star is 4.2 million AU away.
B) The light we see left the star 4.2 years ago.
C) The star must be very old.
D) The star must be very young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the reason for compressing the history of the universe into a single year in the cosmic calendar?
A) to compare astronomical timescales with human experience
B) to emphasize how old the universe is
C) to simplify calculations of ages of objects in the universe
D) to express the distances of objects in light-years
A) to compare astronomical timescales with human experience
B) to emphasize how old the universe is
C) to simplify calculations of ages of objects in the universe
D) to express the distances of objects in light-years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the distance to a star is 450 light-years, what can we conclude about the star?
A) The star is 450 million AU away.
B) The star's light takes 450 years to reach us.
C) The star must have formed 450 billion years ago.
D) The star must be very young.
A) The star is 450 million AU away.
B) The star's light takes 450 years to reach us.
C) The star must have formed 450 billion years ago.
D) The star must be very young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement best describes the Milky Way Galaxy?
A) It is a spiral galaxy.
B) It is comprised of several smaller galaxies.
C) It is about 1,000 light-years in diameter.
D) It is type of supercluster.
A) It is a spiral galaxy.
B) It is comprised of several smaller galaxies.
C) It is about 1,000 light-years in diameter.
D) It is type of supercluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following has the distances arranged in order from largest to smallest?
A) light year, Astronomical Unit, kilometre, millimetre
B) Astronomical Unit, millimetre, light year, kilometre
C) kilometre, millimetre, Astronomical Unit, light year
D) light year, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, millimetre
A) light year, Astronomical Unit, kilometre, millimetre
B) Astronomical Unit, millimetre, light year, kilometre
C) kilometre, millimetre, Astronomical Unit, light year
D) light year, kilometre, Astronomical Unit, millimetre

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A(n) ____________________ is the distance that light would travel in one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Using a cosmic calendar where the entire history of the universe is spread over only one day starting at 12 A.m., at about what time did the era of dinosaurs end?
A) 10:35 p.m.
B) 10:55 p.m.
C) 11:53 p.m.
D) 11:59 p.m.
A) 10:35 p.m.
B) 10:55 p.m.
C) 11:53 p.m.
D) 11:59 p.m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The nearest star is 1 ly from the Solar System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The name of the average distance from Earth to the Sun is one ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The average distance from Earth to the Sun is 1 AU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The numbers 9.85 × 105 and 985,000 are equivalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A kilometre contains 1 million metres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Sun is a star in the Milky Way Galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Light takes about 8 minutes to travel from the Sun to Earth and about 40 minutes to travel from the Sun to Jupiter. Jupiter is about ____________________ AU from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Using a cosmic calendar where the big bang happened at midnight January 1, at what time did human civilization emerge?
A) 1 hour before midnight on December 31
B) 30 minutes before midnight on December 31
C) 30 seconds before midnight on December 31
D) 11 seconds before midnight on December 31
A) 1 hour before midnight on December 31
B) 30 minutes before midnight on December 31
C) 30 seconds before midnight on December 31
D) 11 seconds before midnight on December 31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A(n) ____________________ is the largest known structure in the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The metric system is a decimal system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Sun is located at the centre of the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
3.49 × 107 km is the same as 3.49 × 104 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A cluster of galaxy clusters is called a(n) ________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A supercluster refers to a large group of stars within the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Using the cosmic calendar, where the Big Bang happened January 1, in which of the following months did the Milky Way most likely form?
A) January
B) March
C) August
D) December
A) January
B) March
C) August
D) December

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An astronomical unit is larger than a light-year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



