Deck 3: The Origin of Modern Astronomy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Origin of Modern Astronomy
1
Which of the following astronomers described the universe in a way that matches the diagram? 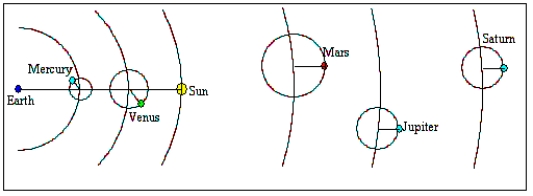
A) Kepler
B) Ptolemy
C) Copernicus
D) Galileo

A) Kepler
B) Ptolemy
C) Copernicus
D) Galileo
Ptolemy
2
In Ptolemy's view of the universe, what is at the centre of a planet's epicycle?
A) the Sun
B) the Earth
C) the deferent
D) the equant
A) the Sun
B) the Earth
C) the deferent
D) the equant
the deferent
3
In 1054 CE, the Chinese recorded a very interesting and powerful cosmic event. What was this event?
A) a star merger
B) a supernova
C) a galactic collapse
D) simultaneous solar and lunar eclipses
A) a star merger
B) a supernova
C) a galactic collapse
D) simultaneous solar and lunar eclipses
a supernova
4
You are observing the night sky from Mars. Which objects would you be able to see undergo retrograde motion in your night sky?
A) Only the planets that are more distant from the Sun than Mars
B) Only the planets located between Mars and the Sun
C) Only Earth and Venus
D) All planets
A) Only the planets that are more distant from the Sun than Mars
B) Only the planets located between Mars and the Sun
C) Only Earth and Venus
D) All planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When did the first recorded female astronomer make her detailed observations of the motion of planets?
A) more than 4000 years ago
B) about 2000 years ago
C) about 200 years ago
D) about 40 years ago
A) more than 4000 years ago
B) about 2000 years ago
C) about 200 years ago
D) about 40 years ago

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What feature of Ptolemy's model of the universe made it possible to explain retrograde motion?
A) heliocentrism
B) elliptical orbits
C) epicycles
D) geocentrism
A) heliocentrism
B) elliptical orbits
C) epicycles
D) geocentrism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following best explains why most astronomers accepted a geocentric model of the universe for 2000 years?
A) The geocentric model allowed astronomers to make accurate predictions about the positions of the planets.
B) The geocentric model was required to explain retrograde motion.
C) Astronomers were unlikely to question the authority of Aristotle.
D) Telescopes were required to show that Earth's orbit is not a perfect circle.
A) The geocentric model allowed astronomers to make accurate predictions about the positions of the planets.
B) The geocentric model was required to explain retrograde motion.
C) Astronomers were unlikely to question the authority of Aristotle.
D) Telescopes were required to show that Earth's orbit is not a perfect circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why were Mercury and Venus treated differently from the other known planets in Ptolemy's geocentric model of the universe?
A) They always appear close to the Sun.
B) They are the closest planets to Earth.
C) They do not exhibit retrograde motion.
D) They have the highest surface temperatures.
A) They always appear close to the Sun.
B) They are the closest planets to Earth.
C) They do not exhibit retrograde motion.
D) They have the highest surface temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What was a common feature of astronomy as practiced worldwide prior to the Greeks?
A) recognizing patterns
B) making hypotheses
C) defining the 24-hour clock
D) observing supernovae
A) recognizing patterns
B) making hypotheses
C) defining the 24-hour clock
D) observing supernovae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements reflects beliefs that were almost universally held in pre-Copernican astronomy?
A) The planets travelled in elliptical orbits around the Earth.
B) The planets travelled in elliptical orbits around the Sun.
C) The Sun was at the centre of the universe.
D) The Earth was at the centre of the universe.
A) The planets travelled in elliptical orbits around the Earth.
B) The planets travelled in elliptical orbits around the Sun.
C) The Sun was at the centre of the universe.
D) The Earth was at the centre of the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why did ancient astronomers believe that the Earth did not move?
A) because they could not detect parallax
B) because they believed in circular motion
C) because all observable planets follow retrograde motion
D) because parallax is only detectable during the day
A) because they could not detect parallax
B) because they believed in circular motion
C) because all observable planets follow retrograde motion
D) because parallax is only detectable during the day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When viewing from Earth, which objects can be seen to undergo retrograde motion in the night sky?
A) Only the planets located between Earth and the Sun
B) Only the planets that are more distant from the Sun than Earth
C) Only the Moon
D) All planets
A) Only the planets located between Earth and the Sun
B) Only the planets that are more distant from the Sun than Earth
C) Only the Moon
D) All planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Whose writings became so famous that he was known throughout the Middle East simply as "The Philosopher"?
A) Ptolemy
B) Eratosthenes
C) Aristotle
D) Hipparchus
A) Ptolemy
B) Eratosthenes
C) Aristotle
D) Hipparchus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is another name for the star the Inuit call Nuuttuittuq, meaning "the one that never moves"?
A) Sirius
B) Betelgeuse
C) Altair
D) Polaris
A) Sirius
B) Betelgeuse
C) Altair
D) Polaris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the term for the apparent westward motion of a planet in the sky compared to the background stars (as viewed from the Earth) when observed on successive nights?
A) epicycle
B) retrograde motion
C) prograde motion
D) heliocentric motion
A) epicycle
B) retrograde motion
C) prograde motion
D) heliocentric motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What did Eratosthenes measure very accurately?
A) the size of the Earth
B) the length of the year
C) the distance to the Moon
D) the length of the month
A) the size of the Earth
B) the length of the year
C) the distance to the Moon
D) the length of the month

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What was the reason for using epicycles and deferents to explain the motion of the planets in the night sky?
A) prograde motion
B) Mercury and Venus's limited angular distance from the Sun
C) retrograde motion
D) non-uniform speed of the planets in their orbits
A) prograde motion
B) Mercury and Venus's limited angular distance from the Sun
C) retrograde motion
D) non-uniform speed of the planets in their orbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the term for a small circle that has its centre located on the circumference of another larger circle?
A) equant
B) deferent
C) retrograde loop
D) epicycle
A) equant
B) deferent
C) retrograde loop
D) epicycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Who were the two great authorities of Greek astronomy?
A) Aristotle and Ptolemy
B) Julius Caesar and Aristotle
C) Columbus and Ptolemy
D) Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar
A) Aristotle and Ptolemy
B) Julius Caesar and Aristotle
C) Columbus and Ptolemy
D) Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is parallax?
A) the apparent motion of an object due to the motion of the observer
B) the distance between two straight lines
C) the small circle that the planets slid along in Ptolemy's geocentric universe
D) the distance between two foci of an ellipse
A) the apparent motion of an object due to the motion of the observer
B) the distance between two straight lines
C) the small circle that the planets slid along in Ptolemy's geocentric universe
D) the distance between two foci of an ellipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What was the greatest inaccuracy in Copernicus's model of the solar system?
A) that the planets travelled in circular orbits with uniform motion
B) that the planets travelled on epicycles, the centres of which followed orbits around the Sun
C) that the planets travelled in elliptical orbits
D) that the planets were allowed to travel backwards in their orbits
A) that the planets travelled in circular orbits with uniform motion
B) that the planets travelled on epicycles, the centres of which followed orbits around the Sun
C) that the planets travelled in elliptical orbits
D) that the planets were allowed to travel backwards in their orbits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose that a distant planet orbiting its sun has an orbital period of 8 years. What is the approximate distance from the sun to the planet?
A) 1 AU
B) 4 AU
C) 10 AU
D) 32 AU
A) 1 AU
B) 4 AU
C) 10 AU
D) 32 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The orbit of the planet Mars is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. What is located at the other focus?
A) nothing
B) the asteroid belt
C) Saturn
D) Venus
A) nothing
B) the asteroid belt
C) Saturn
D) Venus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An object has been located orbiting the Sun at a distance of 65 AU. What is the approximate orbital period of this object?
A) 8.1 years
B) 65 years
C) 524 years
D) 4225 years
A) 8.1 years
B) 65 years
C) 524 years
D) 4225 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The orbit of planet A has an eccentricity of 0.5 and the orbit of planet B has an eccentricity of 0.01. What can be said about the shape of the orbits of these two planets?
A) Planet A has a nearly circular orbit.
B) The orbit of planet A is more elongated than the orbit of planet B.
C) The orbit of planet B is more elongated than the orbit of planet A.
D) There is not enough information to say anything meaningful about the shape of either orbit.
A) Planet A has a nearly circular orbit.
B) The orbit of planet A is more elongated than the orbit of planet B.
C) The orbit of planet B is more elongated than the orbit of planet A.
D) There is not enough information to say anything meaningful about the shape of either orbit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The orbit of the planet Jupiter is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. What is located at the other focus?
A) the Earth
B) the asteroid belt
C) Saturn
D) nothing
A) the Earth
B) the asteroid belt
C) Saturn
D) nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is implied by Kepler's first law of planetary motion?
A) The planets move at a constant speed at all points in their orbits.
B) The planets all move around the Earth in elliptical orbits.
C) Uniform circular motion is adequate to describe the motion of all planets.
D) The planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun.
A) The planets move at a constant speed at all points in their orbits.
B) The planets all move around the Earth in elliptical orbits.
C) Uniform circular motion is adequate to describe the motion of all planets.
D) The planets move in elliptical orbits around the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium about?
A) It describes how Galileo's observations and Kepler's calculations proved the Copernican theory.
B) It describes the construction of Galileo's telescope and his observations.
C) It is a dialogue written to convince the general public of the merits of the Copernican theory.
D) It lays out the Copernican theory for the first time.
A) It describes how Galileo's observations and Kepler's calculations proved the Copernican theory.
B) It describes the construction of Galileo's telescope and his observations.
C) It is a dialogue written to convince the general public of the merits of the Copernican theory.
D) It lays out the Copernican theory for the first time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What did Kepler base his three laws of planetary motion on?
A) the idea that an ellipse is the perfect shape
B) precise observations of the apparent motions of planets
C) Newton's three laws of motion
D) the observation of the phases of Venus
A) the idea that an ellipse is the perfect shape
B) precise observations of the apparent motions of planets
C) Newton's three laws of motion
D) the observation of the phases of Venus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When Mars is located directly behind the Earth with respect to the Sun in its orbit, we see it at its highest in the sky. At what time of day or night does this happen?
A) at sunset
B) at midnight
C) at sunrise
D) at noon
A) at sunset
B) at midnight
C) at sunrise
D) at noon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Given its orbital period of 76 years, what is the average distance of Comet Halley from the Sun?
A) 18 AU
B) 38 AU
C) 51 AU
D) 114 AU
A) 18 AU
B) 38 AU
C) 51 AU
D) 114 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why does Mars appear to brighten during its retrograde motion?
A) Mars is closest to the Sun during this time.
B) Mars is closest to Earth during this time.
C) Mars is observed in a nearly full phase during this time.
D) Mars receives more direct sunlight during this time.
A) Mars is closest to the Sun during this time.
B) Mars is closest to Earth during this time.
C) Mars is observed in a nearly full phase during this time.
D) Mars receives more direct sunlight during this time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What two numbers tell us the size and shape of an ellipse?
A) radius, eccentricity
B) radius, deferent
C) semi-major axis, deferent
D) semi-major axis, eccentricity
A) radius, eccentricity
B) radius, deferent
C) semi-major axis, deferent
D) semi-major axis, eccentricity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following objects cannot transit (i.e. pass in front of) the Sun, as seen from Jupiter?
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Mars
D) Saturn
A) Mercury
B) Venus
C) Mars
D) Saturn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the term for a commonly accepted set of scientific ideas and assumptions?
A) theory
B) paradigm
C) hypothesis
D) natural law
A) theory
B) paradigm
C) hypothesis
D) natural law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Copernican system was no more accurate than the Ptolemaic system in predicting the positions of the planets because of a key factor that was unchanged from the Ptolemaic system. What was that factor?
A) The Copernican system assumed the Earth was at rest at the centre.
B) The Copernican system used elliptical planetary orbits.
C) The Copernican system used uniform circular motion.
D) The Copernican system assumed all planets orbited the Sun.
A) The Copernican system assumed the Earth was at rest at the centre.
B) The Copernican system used elliptical planetary orbits.
C) The Copernican system used uniform circular motion.
D) The Copernican system assumed all planets orbited the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What was Tycho Brahe's greatest contribution to astronomy?
A) his model of the universe
B) his telescopic observations
C) his discovery of three laws of motion
D) his 20 years of careful observations of the planets
A) his model of the universe
B) his telescopic observations
C) his discovery of three laws of motion
D) his 20 years of careful observations of the planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following describes the semi-major axis of an ellipse?
A) the ratio of the longest diameter of the ellipse to the shortest diameter of the ellipse
B) half the length of the shortest diameter of the ellipse
C) half the length of the longest diameter of the ellipse
D) the distance between the two foci of the ellipse
A) the ratio of the longest diameter of the ellipse to the shortest diameter of the ellipse
B) half the length of the shortest diameter of the ellipse
C) half the length of the longest diameter of the ellipse
D) the distance between the two foci of the ellipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The period of Jupiter's orbit around the Sun is approximately 12 years. What is the approximate distance from the Sun to Jupiter?
A) 5.2 AU
B) 42 AU
C) 144 AU
D) 1728 AU
A) 5.2 AU
B) 42 AU
C) 144 AU
D) 1728 AU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
On average, Saturn is 10 AU from the Sun. What is the approximate orbital period of Saturn?
A) 10 years
B) 32 years
C) 1000 years
D) 3200 years
A) 10 years
B) 32 years
C) 1000 years
D) 3200 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the term for a single conjecture that can be tested?
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) model
D) theory
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) model
D) theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Imagine a satellite in orbit around the Earth, always at a constant distance from the centre of the Earth. Which of its properties changes?
A) velocity
B) speed
C) acceleration
D) mass
A) velocity
B) speed
C) acceleration
D) mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following planets can be seen in a crescent phase when observed from the Earth?
A) Mercury and Venus
B) Venus and Mars
C) only Venus
D) Jupiter and Saturn
A) Mercury and Venus
B) Venus and Mars
C) only Venus
D) Jupiter and Saturn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What was the basis for Isaac Newton's conclusion that a force from the Earth must be acting on the Moon?
A) A force is needed to keep the Moon in motion in its orbit.
B) A force is needed to pull the Moon outward.
C) A force is needed to accelerate the Moon toward the Earth, away from straight-line motion.
D) The Moon moved at a constant velocity in a straight line.
A) A force is needed to keep the Moon in motion in its orbit.
B) A force is needed to pull the Moon outward.
C) A force is needed to accelerate the Moon toward the Earth, away from straight-line motion.
D) The Moon moved at a constant velocity in a straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements best describes Kepler's third law of planetary motion?
A) The smaller the diameter of a planet, the faster its rotational period.
B) The orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the diameter of the planet.
C) The smaller the orbit, the longer its orbital period.
D) The larger the orbit, the longer its orbital period.
A) The smaller the diameter of a planet, the faster its rotational period.
B) The orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the diameter of the planet.
C) The smaller the orbit, the longer its orbital period.
D) The larger the orbit, the longer its orbital period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Imagine you are travelling though the asteroid belt. Which of the following would you expect to observe?
A) All asteroids in the asteroid belt have shorter orbital period than Earth.
B) Asteroids closer to Mars have longer orbital period than those closer to Jupiter.
C) All asteroids within the asteroid belt have the same orbital period.
D) Asteroids closer to Mars have shorter orbital periods than those closer to Jupiter.
A) All asteroids in the asteroid belt have shorter orbital period than Earth.
B) Asteroids closer to Mars have longer orbital period than those closer to Jupiter.
C) All asteroids within the asteroid belt have the same orbital period.
D) Asteroids closer to Mars have shorter orbital periods than those closer to Jupiter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the term for a description of some natural phenomenon that can't be right or wrong, but is merely a convenient way to think about a natural phenomenon?
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) model
D) theory
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) model
D) theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When we say that gravitation is universal, what do we mean?
A) The Earth exerts gravitational force on objects on its surface.
B) The Earth exerts a gravitational force on its Moon and vice versa.
C) The Earth, the Moon, and the Sun exert gravitational force on each other.
D) All objects exert gravitational force on one another.
A) The Earth exerts gravitational force on objects on its surface.
B) The Earth exerts a gravitational force on its Moon and vice versa.
C) The Earth, the Moon, and the Sun exert gravitational force on each other.
D) All objects exert gravitational force on one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What does the eccentricity of a planet's orbit describe?
A) westward motion in the night sky when observed on successive nights
B) deviation in shape when compared to a circle
C) tilt with respect to the ecliptic plane
D) the tilt of the planet's rotational axis with respect to the ecliptic
A) westward motion in the night sky when observed on successive nights
B) deviation in shape when compared to a circle
C) tilt with respect to the ecliptic plane
D) the tilt of the planet's rotational axis with respect to the ecliptic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A comet is found in a highly elliptical orbit with a semi-major axis equal to one astronomical unit (AU). According to Kepler's third law of planetary motion, what would the sidereal period of this comet be?
A) It would be more than one year.
B) It would be one year.
C) It would be less than one year.
D) It would be 76 years; the same for every comet.
A) It would be more than one year.
B) It would be one year.
C) It would be less than one year.
D) It would be 76 years; the same for every comet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The orbit of the Moon is an ellipse with the Earth at one focus. What is located at the other focus?
A) nothing
B) the asteroid belt
C) comets
D) the Sun
A) nothing
B) the asteroid belt
C) comets
D) the Sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements is implied by Kepler's second law of planetary motion?
A) A planet should move at its greatest speed when it is closest to the Sun.
B) The most massive planets will have the greatest speed in their orbits.
C) The speed of a planet in its orbit depends on the size of the epicycle.
D) The mass of the planet determines how far the planet is from the Sun.
A) A planet should move at its greatest speed when it is closest to the Sun.
B) The most massive planets will have the greatest speed in their orbits.
C) The speed of a planet in its orbit depends on the size of the epicycle.
D) The mass of the planet determines how far the planet is from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the mass of the Earth increased by a factor of 3, with no change in the radius, what would happen to your weight?
A) It would increase by a factor of 3.
B) It would increase by a factor of 6.
C) It would decrease by a factor of 3.
D) It would decrease by a factor of 6.
A) It would increase by a factor of 3.
B) It would increase by a factor of 6.
C) It would decrease by a factor of 3.
D) It would decrease by a factor of 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Would your mass and weight change if you went to the Moon?
A) Weight would change but mass would not.
B) Mass would change but weight would not.
C) Both would change.
D) Neither would change.
A) Weight would change but mass would not.
B) Mass would change but weight would not.
C) Both would change.
D) Neither would change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Galileo's telescopic discovery of mountains on the Moon were controversial because it suggested something about the Moon. What was it?
A) that it is older than the Earth
B) that it is not a perfect sphere
C) that it was inhabited
D) that it orbits the Earth
A) that it is older than the Earth
B) that it is not a perfect sphere
C) that it was inhabited
D) that it orbits the Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What did Galileo's observations of a complete set of phases of Venus prove?
A) that Venus orbited the Sun
B) that the Earth orbited the Sun
C) that all of the planets orbited the Sun
D) that Venus had an atmosphere
A) that Venus orbited the Sun
B) that the Earth orbited the Sun
C) that all of the planets orbited the Sun
D) that Venus had an atmosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the mass of the Earth decreased by a factor of 2, with no change in the radius, what would happen to your weight?
A) It would increase by a factor of 2.
B) It would increase by a factor of 4.
C) It would decrease by a factor of 2.
D) It would decrease by a factor of 4.
A) It would increase by a factor of 2.
B) It would increase by a factor of 4.
C) It would decrease by a factor of 2.
D) It would decrease by a factor of 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If your mass is 65 kg on the earth, what would your mass be on Jupiter?
A) 650 lbs
B) 65 lbs
C) 650 kg
D) 65 kg
A) 650 lbs
B) 65 lbs
C) 650 kg
D) 65 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How did Galileo's observations of moons orbiting Jupiter conflict with the geocentric model of the universe of his time?
A) The moons moved in non-circular orbits about Jupiter.
B) The moons did not appear to orbit the Sun.
C) The moons did not appear to orbit the Earth.
D) The moons appeared to be too small, and therefore too far away, to be considered part of the solar system.
A) The moons moved in non-circular orbits about Jupiter.
B) The moons did not appear to orbit the Sun.
C) The moons did not appear to orbit the Earth.
D) The moons appeared to be too small, and therefore too far away, to be considered part of the solar system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the term for a well supported (observationally and/or experimentally) system of rules and principles that can be applied to a wide variety of circumstances but that is not universally accepted?
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) theory
D) model
A) hypothesis
B) paradigm
C) theory
D) model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How does the force of gravity that Earth exerts on you compare to the force of gravity that you exert on Earth?
A) They are equal.
B) Earth exerts a greater force on you than you do on Earth.
C) You exert a greater force on Earth than it does on you.
D) It depends on the velocities of you and Earth.
A) They are equal.
B) Earth exerts a greater force on you than you do on Earth.
C) You exert a greater force on Earth than it does on you.
D) It depends on the velocities of you and Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What does the force due to gravity between two objects depend on?
A) the objects' masses and velocities
B) the objects' masses and the distance between them
C) the objects' velocities and the distance between them
D) the objects' distance from the Earth
A) the objects' masses and velocities
B) the objects' masses and the distance between them
C) the objects' velocities and the distance between them
D) the objects' distance from the Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Ptolemy formulated a(n) ____________________ model of the solar system to predict positions of the Sun, Moon, and planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The apparent backward motion of a planet relative to distant stars is called _________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following orbits are referred to as open orbits?
A) circle and spiral
B) hyperbola and parabola
C) ellipse and circle
D) ellipse and parabola
A) circle and spiral
B) hyperbola and parabola
C) ellipse and circle
D) ellipse and parabola

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A ___________ is a system of rules and principles that can be applied to a wide variety of circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following occur only when the Moon is in the first or third quarter?
A) neap tides
B) spring tides
C) total solar eclipses
D) annular eclipses
A) neap tides
B) spring tides
C) total solar eclipses
D) annular eclipses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A(n) ____________________ is a circle, the centre of which moves in a circular orbit around the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An ellipse with an eccentricity of zero is also called a ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
At which lunar phase(s) are tides at their lowest?
A) both new Moon and first quarter Moon
B) both first quarter Moon and third quarter Moon
C) new Moon
D) full Moon
A) both new Moon and first quarter Moon
B) both first quarter Moon and third quarter Moon
C) new Moon
D) full Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The first observations of objects in the solar system that orbited neither the Sun nor the Earth were made by ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What do we call an orbit that has the same period as the rotation period of the Earth?
A) a daily orbit
B) a lunar orbit
C) an epicycle orbit
D) a geosynchronous orbit
A) a daily orbit
B) a lunar orbit
C) an epicycle orbit
D) a geosynchronous orbit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Gravity obeys an inverse square relation. What does this statement imply about the force due to gravity between two masses?
A) It will increase as the distance between the two masses increases.
B) It will decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases.
C) It will cause the two masses to move in a straight line.
D) It will cause the two masses to orbit each other.
A) It will increase as the distance between the two masses increases.
B) It will decrease as the square of the distance between the two masses increases.
C) It will cause the two masses to move in a straight line.
D) It will cause the two masses to orbit each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When do spring tides occur?
A) at new Moon and first quarter Moon
B) at first quarter Moon and third quarter Moon
C) at new Moon and full Moon
D) at third quarter Moon and full Moon
A) at new Moon and first quarter Moon
B) at first quarter Moon and third quarter Moon
C) at new Moon and full Moon
D) at third quarter Moon and full Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to Kepler's third law, a planet's orbital period ____________________ is equal to its average distance from the Sun ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The first modern astronomer to propose a heliocentric model for the solar system was ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Around 2500 bce, Egyptians used the first visibility at dawn of the star ____________________ to mark the beginning of their calendar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why do astronauts feel weightless when in orbit around Earth?
A) There is no gravity at the location of their orbit.
B) Gravity is very weak at the location of their orbit.
C) They are falling around Earth at the same rate as the spaceship.
D) There is no air pressure in space.
A) There is no gravity at the location of their orbit.
B) Gravity is very weak at the location of their orbit.
C) They are falling around Earth at the same rate as the spaceship.
D) There is no air pressure in space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the relationship between Kepler's laws of planetary motion and Newton's laws of motion and universal gravitation?
A) Newton's laws are more accurate than Kepler's laws.
B) Newton's laws apply to objects on Earth and Kepler's laws apply for orbiting objects.
C) Newton's laws can explain Kepler's laws.
D) Newton's laws are identical to Kepler's laws.
A) Newton's laws are more accurate than Kepler's laws.
B) Newton's laws apply to objects on Earth and Kepler's laws apply for orbiting objects.
C) Newton's laws can explain Kepler's laws.
D) Newton's laws are identical to Kepler's laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the mass of the Earth increased by a factor of 4, with no change in the radius, what would happen to your mass?
A) It would increase.
B) It would decrease.
C) It would stay the same.
D) It would exponentially decrease to zero.
A) It would increase.
B) It would decrease.
C) It would stay the same.
D) It would exponentially decrease to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



