Deck 7: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
What is the general relationship between a country's price level and the quantity of its domestic output (real GDP) demanded Who are the buyers of U.S. real GDP
Output produced in domestic territory of an economy demanded is the aggregated demand of people of an economy.
Country's price level is the general price level of all goods and services being supplied or demanded in a country.
Similar to individual demand of a good and its price or similar to the market demand of a good and its price, there is negative relationship between an economy's price level and the quantity of its domestic output.
In other words with an increase in general price level of the country, the aggregate demand or real GDP will fall.
U.S households (private consumers), government and foreign buyers are the buyers of the U.S real GDP.
Country's price level is the general price level of all goods and services being supplied or demanded in a country.
Similar to individual demand of a good and its price or similar to the market demand of a good and its price, there is negative relationship between an economy's price level and the quantity of its domestic output.
In other words with an increase in general price level of the country, the aggregate demand or real GDP will fall.
U.S households (private consumers), government and foreign buyers are the buyers of the U.S real GDP.
2
What assumptions cause the immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve to be horizontal Why is the long-run aggregate supply curve vertical Explain the shape of the short-run aggregate supply curve. Why is the short-run curve relatively flat to the left of the full-employment output and relatively steep to the right
In the immediate short run, the aggregate supply curve is horizontal because price and wage are sticky.
In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping because only output price is flexible while input prices are fixed.
The short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively flat to the left of the full-employment output because the price reflects the per-unit cost which increases slower below the full-employment output. Below full-employment the per-unit cost increases slower because the productivity is increased by making full advantage of the idle machines; the short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively steep to the right because productivity is reduced with too many workers and constrained capital.
In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping because only output price is flexible while input prices are fixed.
The short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively flat to the left of the full-employment output because the price reflects the per-unit cost which increases slower below the full-employment output. Below full-employment the per-unit cost increases slower because the productivity is increased by making full advantage of the idle machines; the short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively steep to the right because productivity is reduced with too many workers and constrained capital.
3
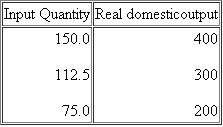
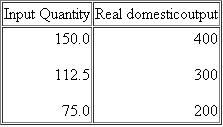
Suppose that the aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
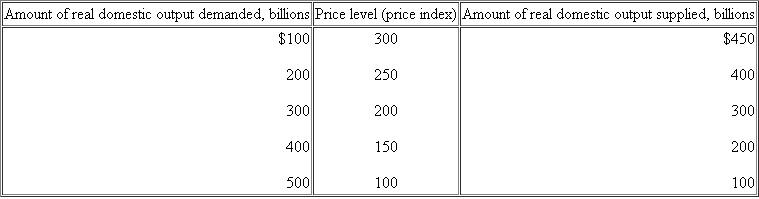 a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What are the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full employment real output Explain.
a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What are the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full employment real output Explain.
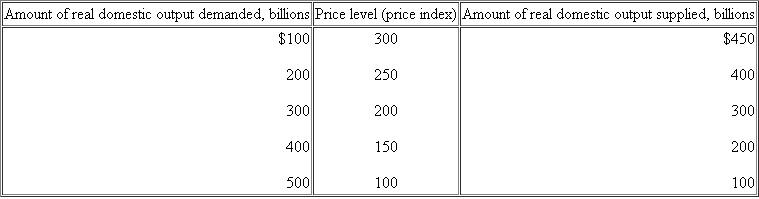 a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What are the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full employment real output Explain.
a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What are the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full employment real output Explain.See the graph. Equilibrium price level = 200. Equilibrium real output = $300 billion. No, the full-capacity level of GDP is more likely at $400 billion, where the AS curve starts to become steeper.
4
Suppose that the aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
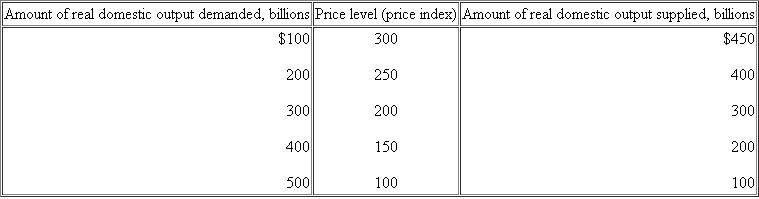 b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
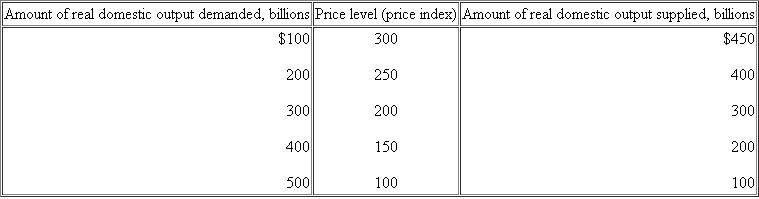 b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy Why not 250
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose that the aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
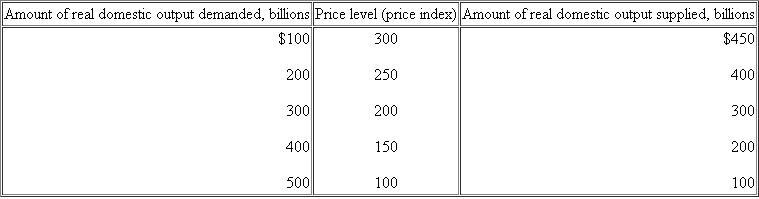 c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output
c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output
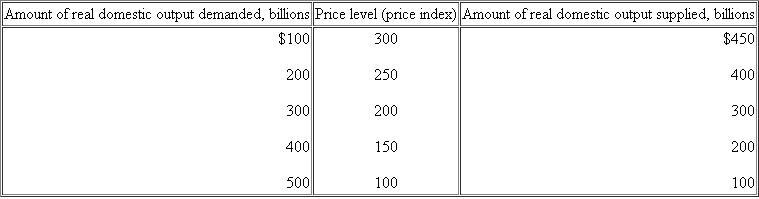 c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output
c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD 1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that output:
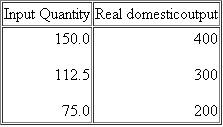 a. What is productivity in this economy
a. What is productivity in this economy
 a. What is productivity in this economy
a. What is productivity in this economy
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that output:
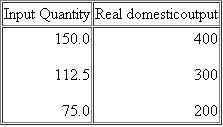 b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
 b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input is $2
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that output:
 c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction would the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction would the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
 c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction would the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production In what direction would the $1 increase in input price push the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that output:
 d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but, instead, that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per-unit production cost have on the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but, instead, that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per-unit production cost have on the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
 d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but, instead, that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per-unit production cost have on the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but, instead, that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production What effect would this change in per-unit production cost have on the economy's aggregate supply curve What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
a. A reduction in the economy's real interest rate.
a. A reduction in the economy's real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
b.A major increase in Federal spending for health care (with no increase in taxes).
b.A major increase in Federal spending for health care (with no increase in taxes).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
c.The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half.
c.The complete disintegration of OPEC, causing oil prices to fall by one-half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
d. A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates (with no change in government spending).
d. A 10 percent reduction in personal income tax rates (with no change in government spending).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
e.A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages).
e.A sizable increase in labor productivity (with no change in nominal wages).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
f. A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity).
f. A 12 percent increase in nominal wages (with no change in productivity).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Other things equal, what effects would each of the following have on aggregate demand oraggregate supply In each case use a diagram to show the expected effects on the equilibrium price level and the level of real output.
g. A sizable depreciation in the international value of the dollar.
g. A sizable depreciation in the international value of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following have on the equilibrium price level and level of real output
a. An increase in aggregate demand in the steep portion of the aggregate supply curve.
a. An increase in aggregate demand in the steep portion of the aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following have on the equilibrium price level and level of real output
b. An increase in aggregate supply, with no change in aggregate demand (assume that prices and wages are flexible upward and downward).
b. An increase in aggregate supply, with no change in aggregate demand (assume that prices and wages are flexible upward and downward).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following have on the equilibrium price level and level of real output
c. Equal increases in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
c. Equal increases in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following have on the equilibrium price level and level of real output
d. A reduction in aggregate demand in the relatively flat portion of the aggregate supply curve.
d. A reduction in aggregate demand in the relatively flat portion of the aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Other things equal, what effect will each of the following have on the equilibrium price level and level of real output
e. An increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in aggregate supply.
e. An increase in aggregate demand and a decrease in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why does a reduction in aggregate demand tend to reduce real output, rather than the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain: "Unemployment can be caused by a decrease of aggregate demand or a decrease of aggregate supply." In each case, specify price level outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In early 2001 investment spending sharply declined in the United States. In the 2 months following the September 11, 2001, attacks on the United States, consumption also declined. Use AD-AS analysis to show the two impacts on real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the concept of the multiplier, explain why mass layoffs by large companies such as Boeing or General Motors are a concern to the citizens and leaders where those firms are located.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



