Deck 8: Genome Structure, Chromatin and the Nucleosome
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Genome Structure, Chromatin and the Nucleosome
1
Explain why stored negative superhelicity from packaging DNA into nucleosomes is advantageous for cellular functions.
Topoisomerases are the enzymes that relax the DNA from superhelicity. DNA is packed into nucleosomes would exist as negatively super coiled because any nucleosome removed from the DNA would allow to wrap in the DNA opposite manner. Therefore nucleosomes are viewed as storing or stabilizing the negative superhelicity.
Unwinding of DNA is required for processes like DNA replication, transcription and recombination. The unwinding of DNA in these processes is readily accomplished by negatively super coiled DNA. Therefore, the removal of nucleosome allows more access to the DNA facilitating the unwinding of nearby DNA sequences thus a cell maintains negative superhelicity for its cellular functions.
Unwinding of DNA is required for processes like DNA replication, transcription and recombination. The unwinding of DNA in these processes is readily accomplished by negatively super coiled DNA. Therefore, the removal of nucleosome allows more access to the DNA facilitating the unwinding of nearby DNA sequences thus a cell maintains negative superhelicity for its cellular functions.
2
Which protein domain(s) recognize the acetylation of histone amino-terminal tails? Which protein domain(s) recognize methylated histone amino-terminal tails?
Specific proteins to the chromatin are recruited by the modified histone tails. Modified histone tails are recognized by protein domains called bromodomains, chromodomains, TUDOR domains and PHD (plant homeodomain) fingers. Bromodomains contain the proteins that interact with acetylated histone tails.
Chromodomain, TUDOR domain and PHD finger consists of proteins that are capable of interacting with methylated histone tails. A protein domain called SANT domain contains the proteins that interact with unmodified histone tails.
Chromodomain, TUDOR domain and PHD finger consists of proteins that are capable of interacting with methylated histone tails. A protein domain called SANT domain contains the proteins that interact with unmodified histone tails.
3
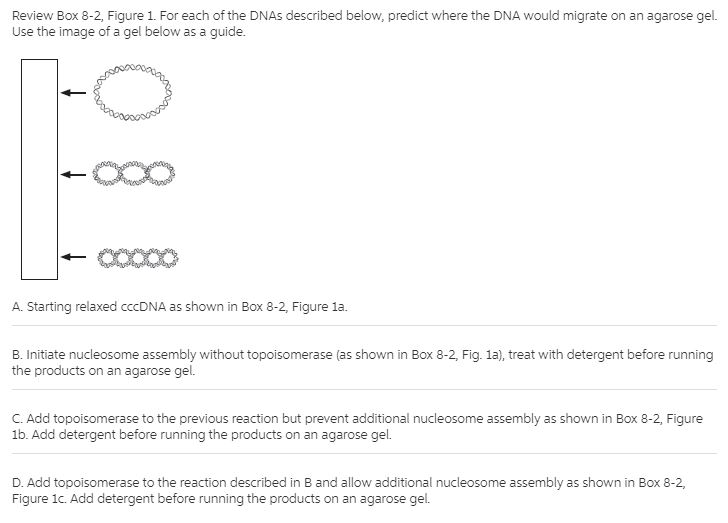
not answer
4
You want to study the potential interaction between nucleosome-bound DNA and a specific histone deacetylase. You decide to perform an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). For a review of this technique, see Chapter 7. You use a 32 P end-labeled, linear template DNA that contains two nucle-osome positioning sites. You assemble two nucleosomes on the DNA template before incubation with and without the histone deacetylase. For some reactions, you use unmodified nucleo-somes. For other reactions, you use nucleosomes that are methylated at lysine 36 of the histone protein H3.
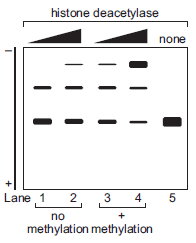
A. Based on the data, propose a model for the interaction between the histone deacetylase and nucleosome-bound DNA.
B. What type of protein domain do you predict allows the his-tone deacetylase to interact with the nucleosomes?
Adapted from Huh et al. (2012. EMBO J. 31: 3564?3574).

A. Based on the data, propose a model for the interaction between the histone deacetylase and nucleosome-bound DNA.
B. What type of protein domain do you predict allows the his-tone deacetylase to interact with the nucleosomes?
Adapted from Huh et al. (2012. EMBO J. 31: 3564?3574).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
List at least three properties that differ between the chromosome makeup in E. coli compared to human cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Explain where the chromosomal DNA is located in prokaryotic versus eukaryotic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Does genome size correlate directly with organism complexity? Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Intergenic sequences make up 60% of the human genome. Where do these intergenic sequences come from and what are some of their functions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explain why each chromosome in a eukaryotic cell contains multiple origins of replication but includes one and only one centromere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How does the sister chromatid cohesion ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of each chromosome?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For a diploid human cell, state how many copies of each chromosome are present in each cell (or soon to be daughter cell).
Start of mitosis
End of mitosis
Start of meiosis
End of meiosis I
End of meiosis II
Start of mitosis
End of mitosis
Start of meiosis
End of meiosis I
End of meiosis II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For humans, what cells undergo mitosis? What cells undergo meiosis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Describe the components of a nucleosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Name the types of bonds that occur between histone proteins and DNA and the region of DNA where these bonds form. Are these interactions sequence-specific? Explain why or why not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



